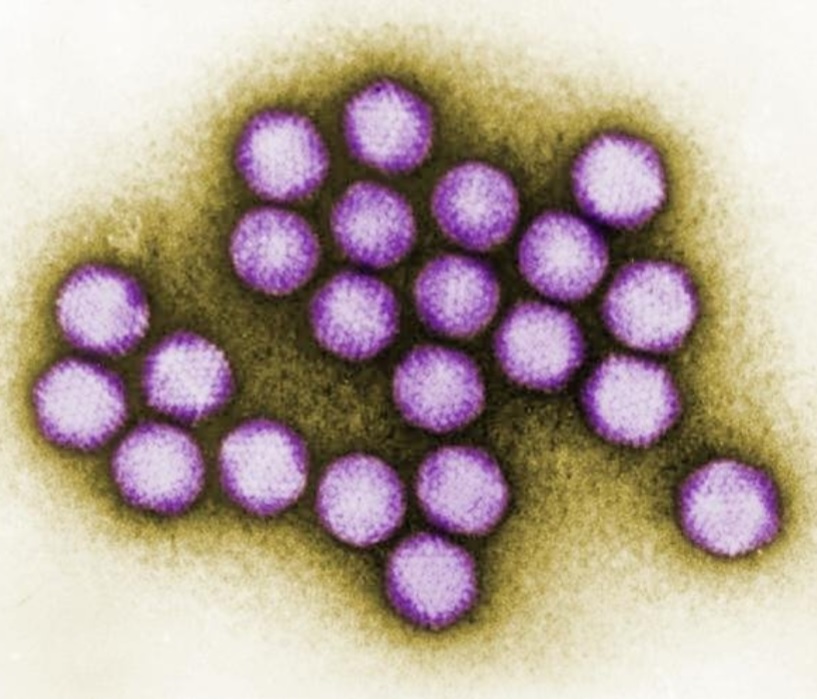
Adenovirus
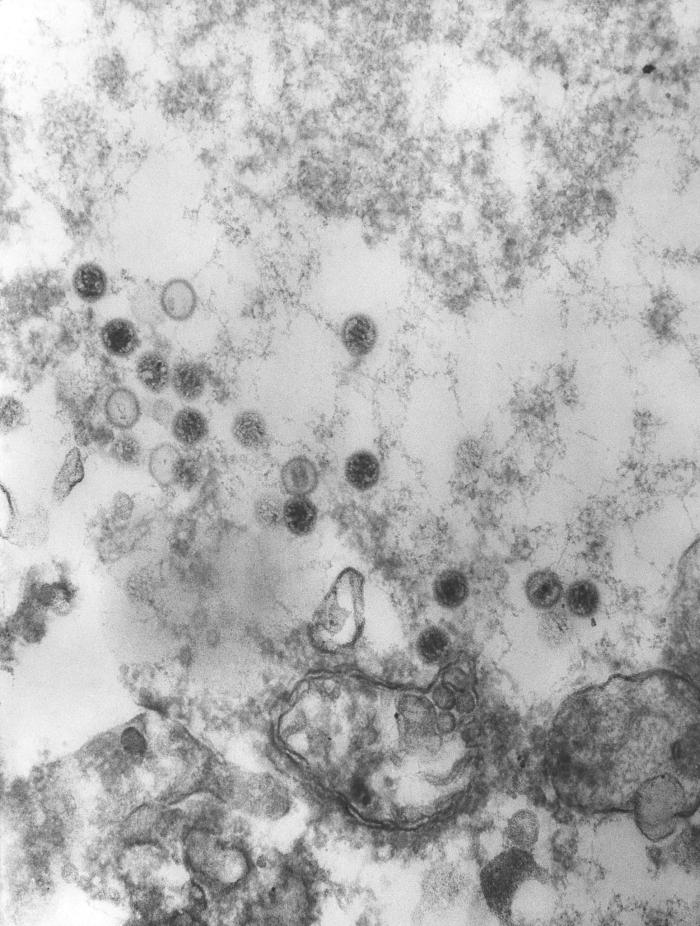
Epstein-Barr Virus
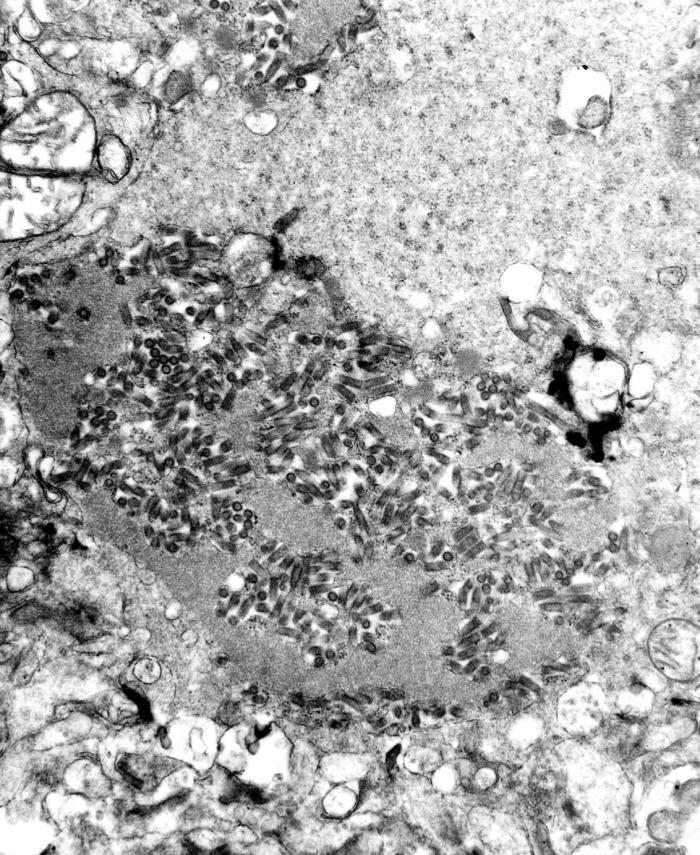
Rabies Virus
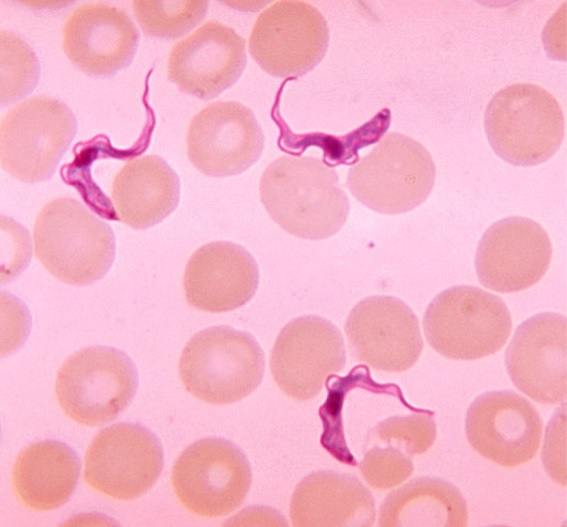
Trypanosoma cruzi/Chagas disease
Chikungunya Virus
Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus
Dengue Virus
Enterococcus
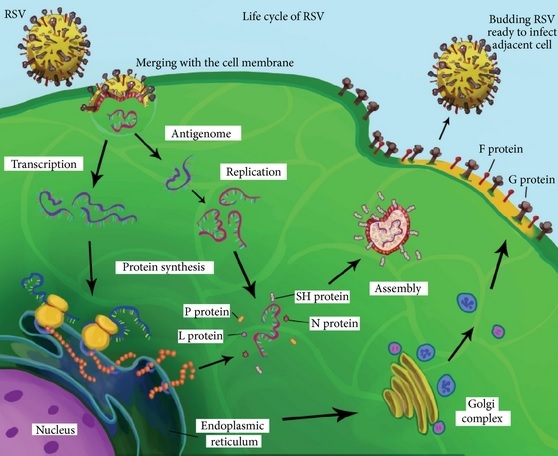
Respiratory Syncytial Virus
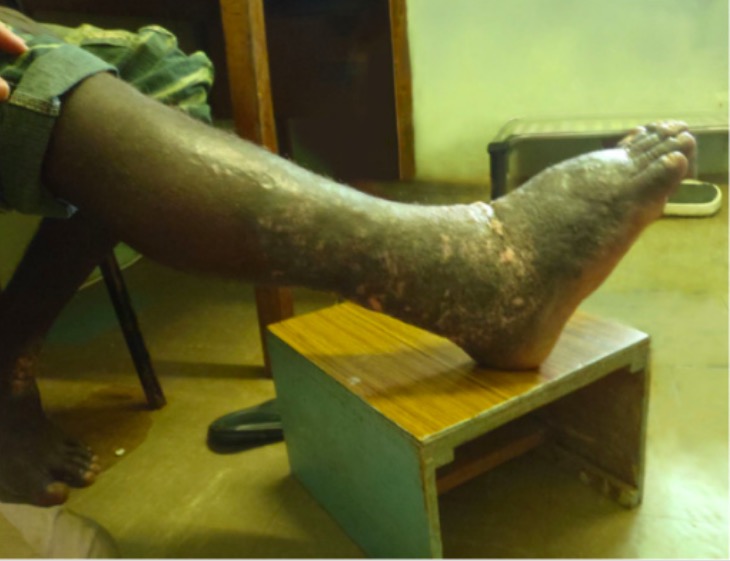
Lymphatic Filariasis (Elephantiasis)
