JC Virus and BK Virus
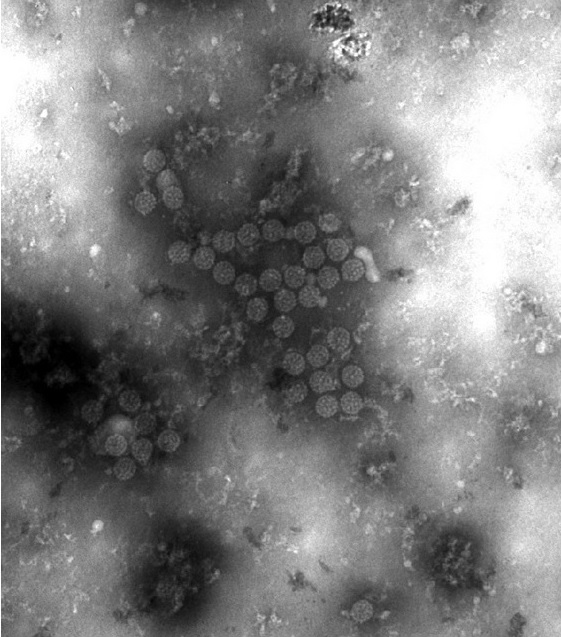
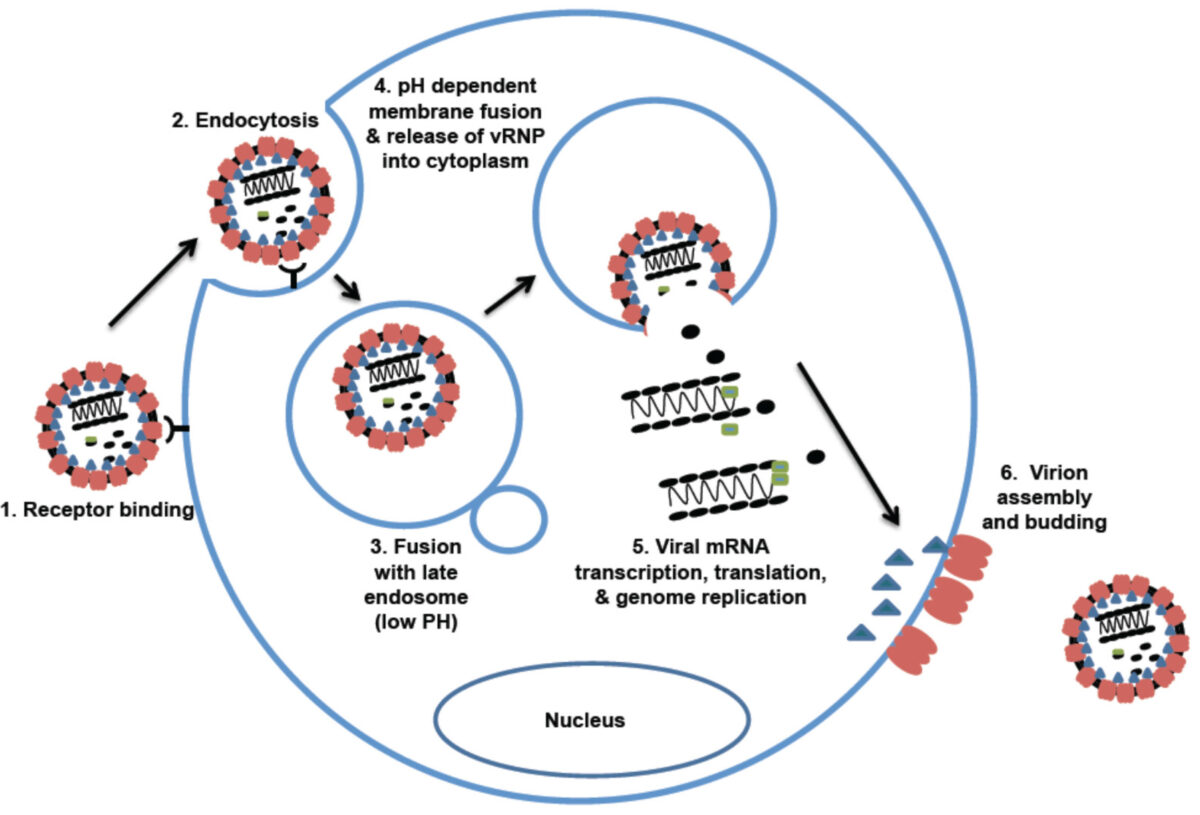
Classification General Characteristics and Epidemiology Taxonomy General features BKV and JCV share similar characteristics: Associated diseases Epidemiology Pathogenesis Reservoir Humans are the natural host for JCV and BKV (no animal reservoir). Transmission Host risk factors The clinical disease most often arises from reactivation of the virus in immunocompromised patients: Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation BKV Primary infection: […]
Lassa Virus
Classification General Characteristics Basic features Epidemiology Pathogenesis Reservoir and transmission Host risk factors Viral entry and disease process Clinical Presentation Lassa fever Complications and mortality Diagnosis and Management Tests Management Prevention Comparison of Arenaviruses Arenaviruses can cause hemorrhagic fevers (Lassa virus) and/or neurologic disease (lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV)). Table: Comparison of Arenaviruses Organism LCMV Lassa […]
Ebolavirus and Marburgvirus
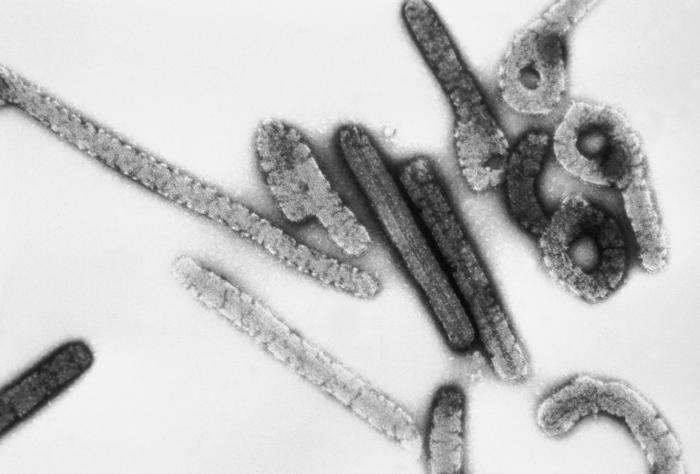
Classification General Characteristics Taxonomy Family: Filoviridae Genus Ebolavirus: Zaire ebolavirus Tai Forest ebolavirus Sudan ebolavirus Bundibugyo ebolavirus Bombali ebolavirus Reston ebolavirus (does not cause disease in humans) Genus Marburgvirus: Marburg marburgvirus Basic features of Ebola and Marburg viruses RNA virus: Nonsegmented Negative sense Single stranded Structure and morphology: Helical nucleocapsid Lipid membrane Filamentous Pleomorphic shape: […]
Trypanosoma brucei/African trypanosomiasis
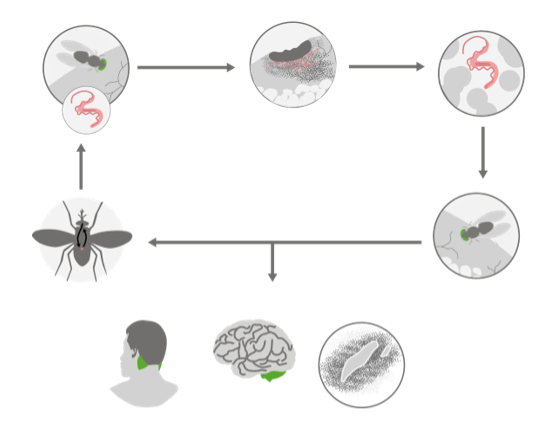
General Characteristics and Epidemiology General features of Trypanosoma brucei Parasitic protozoan Taxonomy: Family: Trypanosomatidae Genus: Trypanosoma Subspecies: T. brucei gambiense T. brucei rhodesiense General characteristics: Single flagellum Undulating membrane Variable surface glycoproteins allow for antigenic variation. Morphologic forms: Epimastigote (noninfectious form) Trypomastigotes (infectious form) Associated diseases T. brucei causes African trypanosomiasis, also known as African […]
Coccidioides/Coccidioidomycosis
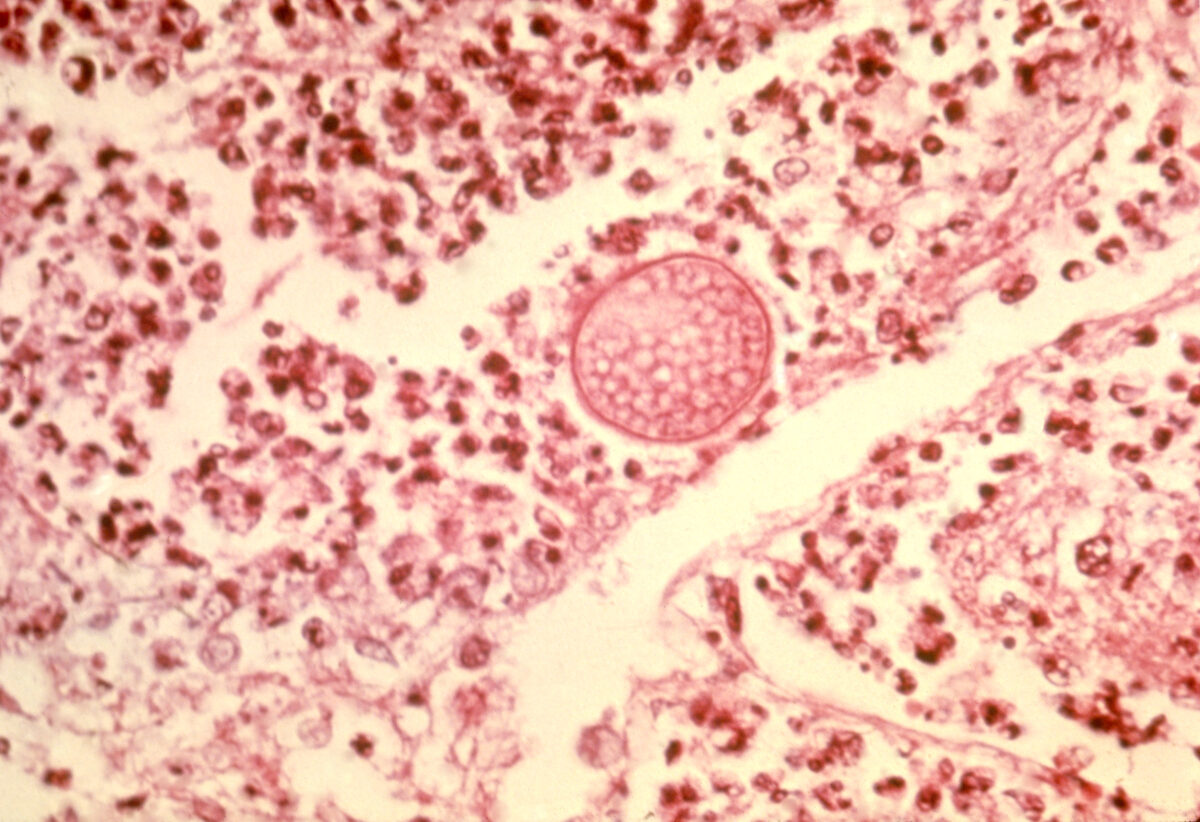
General Characteristics and Epidemiology Basic features of coccidioides Taxonomy: Order: Onygenales Family: Onygenaceae Genus: Coccidioides Forms: Dimorphic fungus Exists as both mycelia or as spherules (asexual forms) Reproduction: No sexual form has been found. Mycelia and spherules undergo binary fission. Arthroconidia are the infectious particles of the Coccidioides species. Transform into spherules in the lungs […]
Cryptococcus/Cryptococcosis
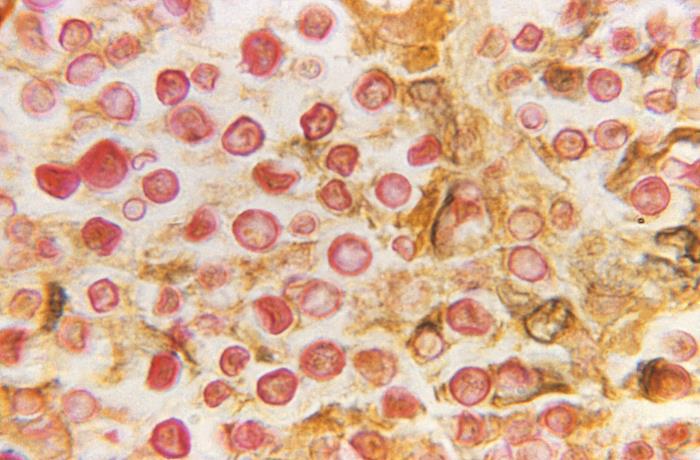
General Characteristics of Cryptococcus Features Clinically relevant species Forms of disease Epidemiology Incidence Morbidity and mortality Pathogenesis Infectious process Host risk factors The most significant risk factor for infection is an immunocompromised state. In decreasing frequency, the following conditions are most frequently associated with infection: Clinical Presentation General findings Clinical presentation varies depending on the […]
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2
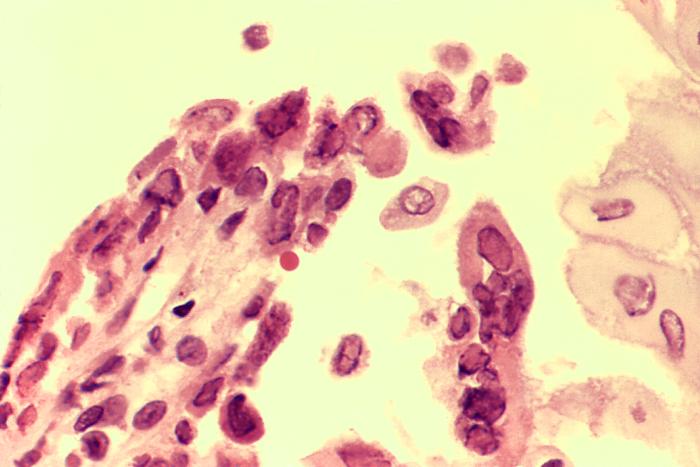
Classification General Characteristics and Epidemiology Basic features of herpes simplex virus Clinically relevant species Two types have been recognized to cause infections: Epidemiology HSV-1: HSV-2: Neonatal herpes infection: Pathogenesis Reservoir Humans are the main reservoir. Transmission HSV-1: HSV-2: Pathophysiology Primary infection: Lifetime latency: Reactivation: Pathology Herpes simplex viruses cause cytolytic infections that form the basis […]
Blastomyces/Blastomycosis
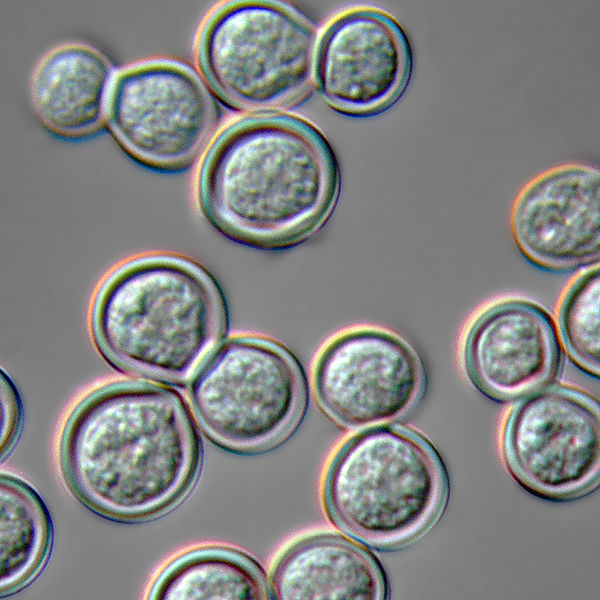
General Characteristics and Epidemiology Basic features of Blastomyces Clinically relevant species Blastomycosis is caused by Blastomyces dermatitidis. Epidemiology Pathogenesis Reservoir Transmission The conidia form of B. dermatitidis can be aerosolized by disturbing the fungal colony followed by inhalation. Host risk factors Blastomycosis is more common in individuals who are immunocompromised, but can occur in immunocompetent […]
Mucorales/Mucormycosis
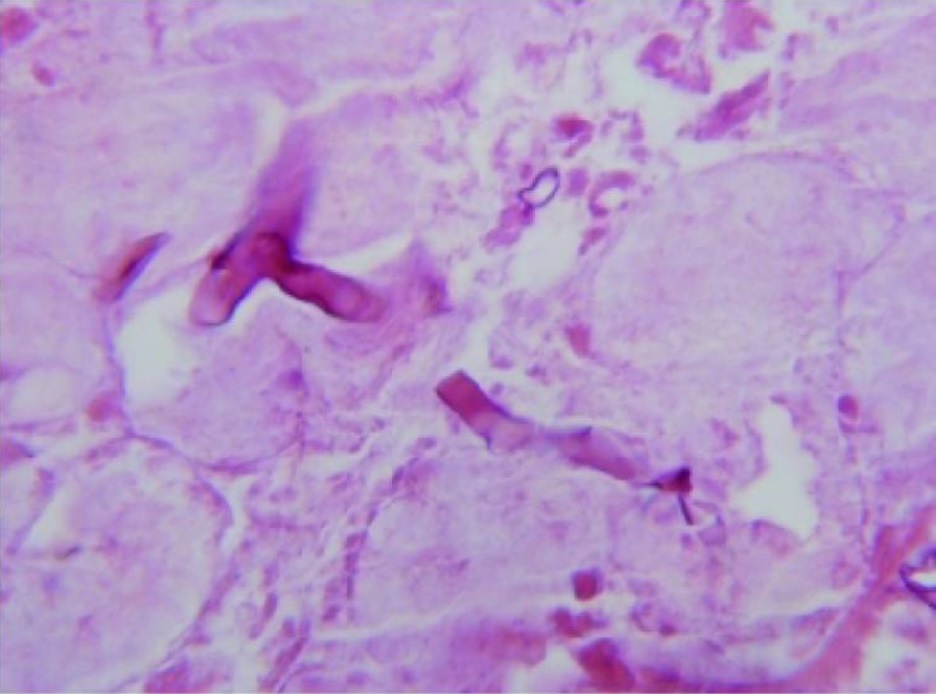
General Characteristics Basic features of Mucorales Taxonomy: Order: Mucorales Genera most commonly associated with human infection: Rhizopus Rhizomucor Mucor Cunninghamella Lichtheimia (formerly Absidia) Apophysomyces Saksenaea Morphology: Colonies: Fast growing Cottony White-to-yellow color → becomes gray Microscopic features: Wide hyphae Lack of or rare septations Branching at right angles Sporangiophores: Upright hyphae Support sac-like sporangia filled […]
Bunyavirales
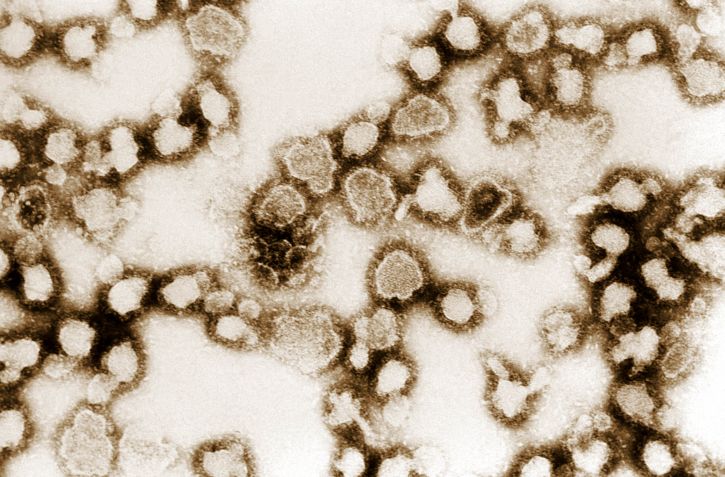
Classification Characteristics Basic features Hantavirus Etiology and epidemiology Pathophysiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis and management Table: Diagnosis and management Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome Hantavirus hemorrhagic fever Incubation 1–3 weeks 1–3 weeks (up to 6 weeks) Diagnosis Serology RT-PCR Serology RT-PCR Clinical manifestations Prodrome: flu-like symptoms, sudden onset of shortness of breath with rapidly evolving pulmonary edema Fever, […]