Laryngitis
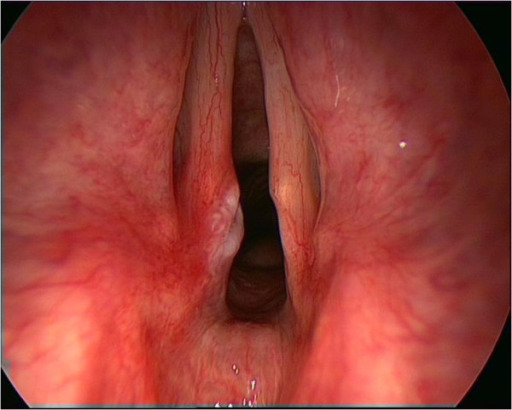
Etiology Laryngitis may be secondary to infection, allergies, trauma, benign or malignant lesions, neurologic dysfunction, functional issues, or systemic causes (see table). Causes of acute laryngitis Causes of chronic laryngitis Viral (most common): Rhinovirus Influenza virus Parainfluenza virus Adenovirus Coronavirus Respiratory syncytial virus Compromised immune systems may suffer from herpes, HIV, or coxsackievirus infections Bacterial: […]
Hemolytic Anemia
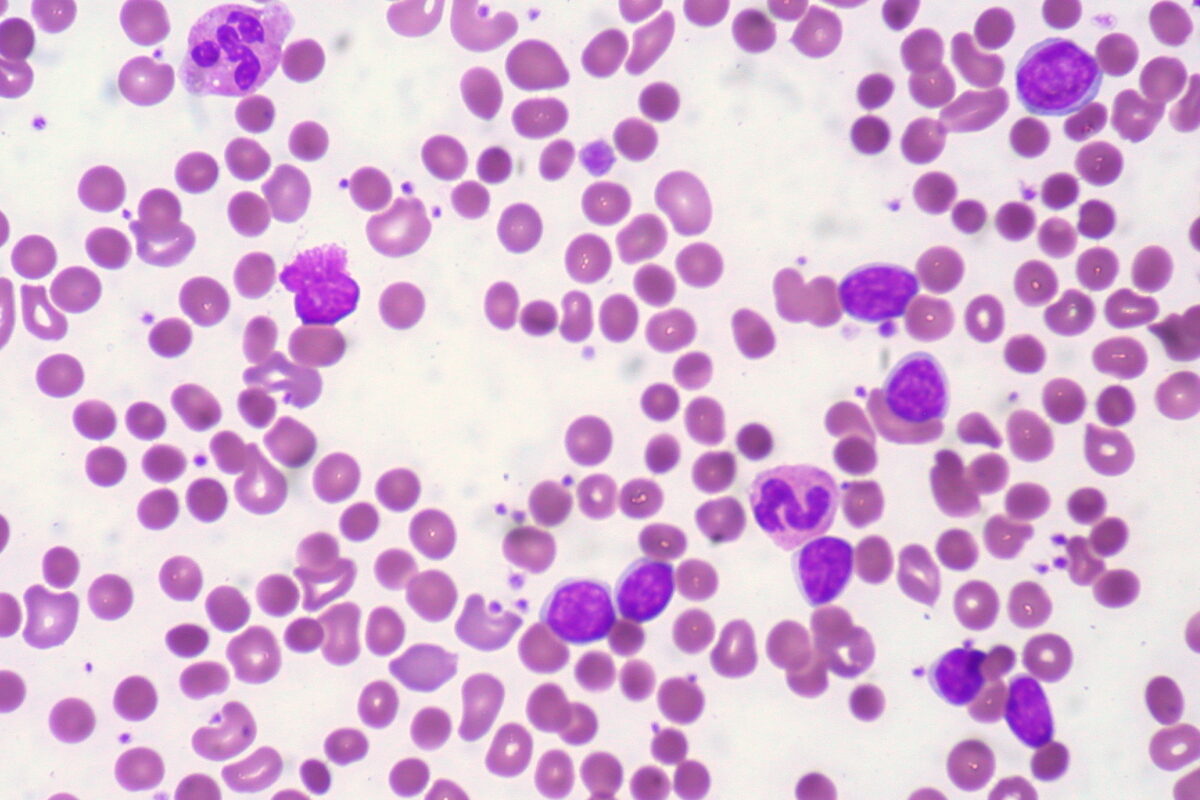
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Causes Intravascular hemolysis Extravascular hemolysis Pathophysiology Hemolytic anemia is a normocytic anemia. Clinical Manifestations Diagnostics General Intravascular hemolysis Extravascular hemolysis Treatment Differential Diagnoses
Pertussis (Whooping Cough)
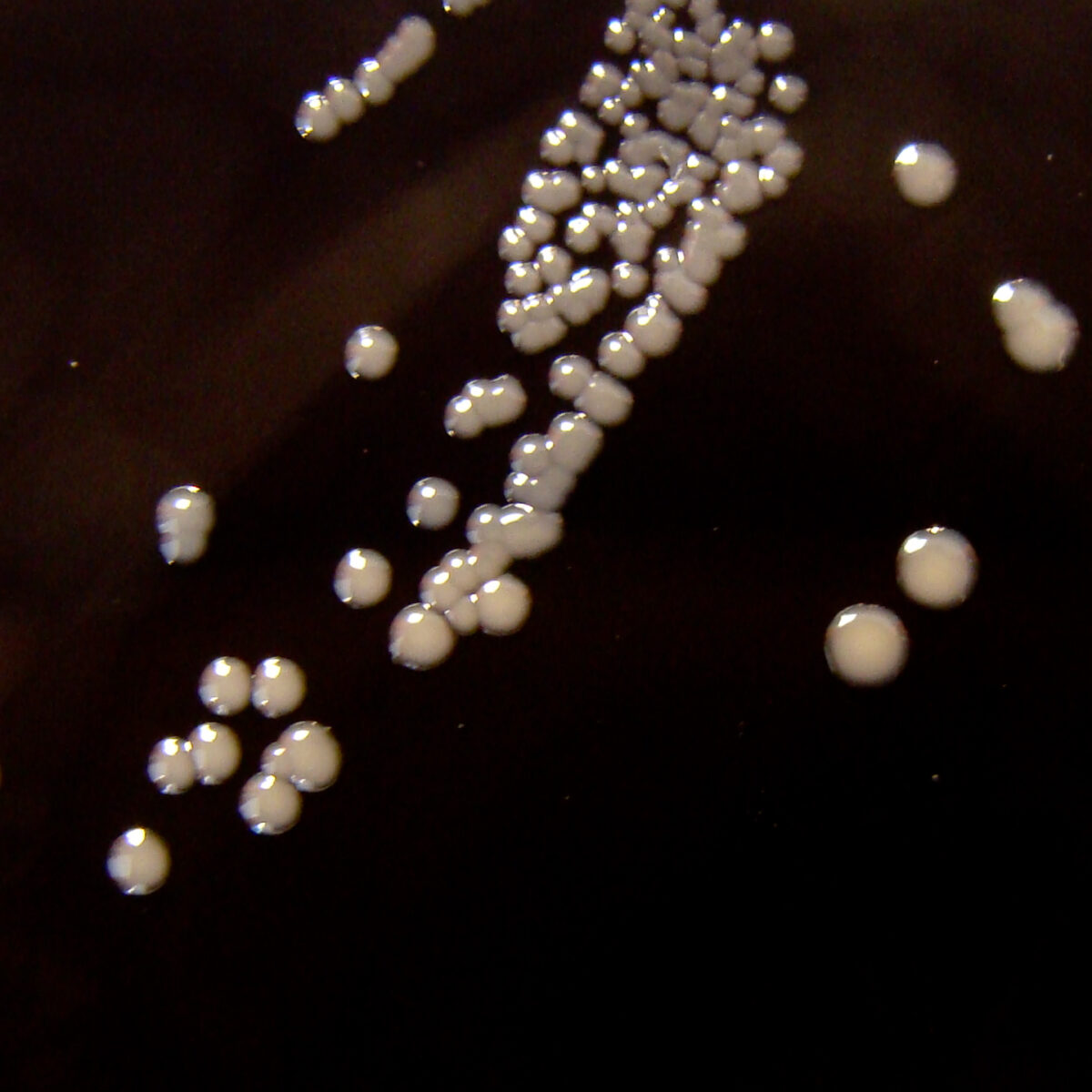

Overview Epidemiology Etiology Risk factors Individuals at risk for contracting pertussis and/or severe disease include: Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation First stage: catarrhal Second stage: paroxysmal Third stage: convalescent Diagnosis Management and Prevention Supportive care Medical therapy If the clinical history strongly supports the diagnosis of pertussis, it is highly suggested to initiate antibiotic therapy while awaiting […]
Mononucleosis
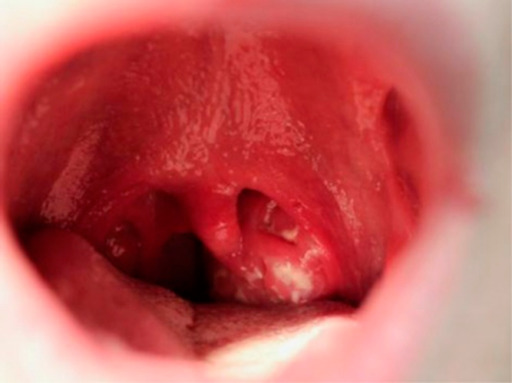
Overview Definition Infectious mononucleosis (IM) is a viral infectious disease most commonly caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and is characterized by a triad of fever, tonsillar pharyngitis, and lymphadenopathy. Synonyms Epidemiology Etiology EBV belongs to the group of human herpesviruses (HHV-4). Pathophysiology Pathogenicity EBV has an exceptionally high species specificity: Transmission The disease is […]
Haemophilus
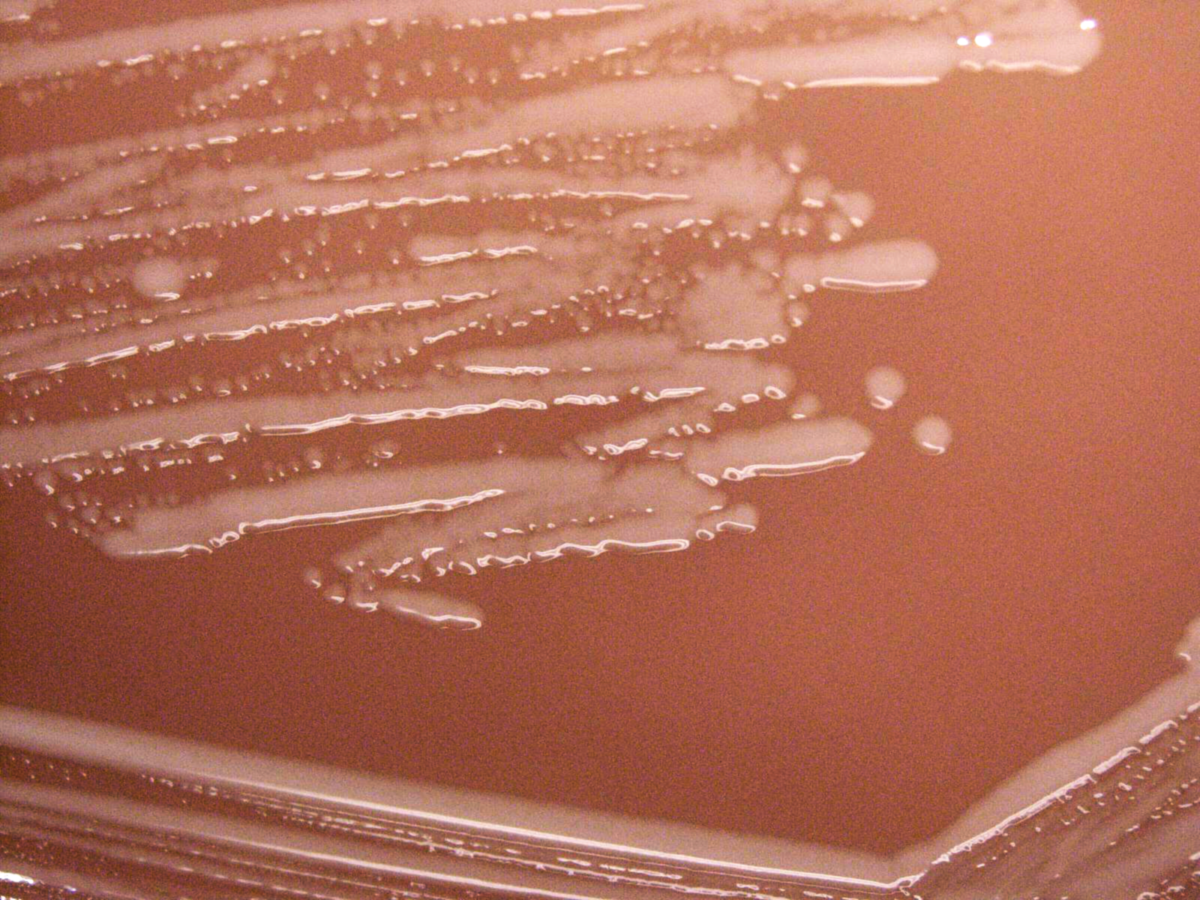

Classification General Characteristics General characteristics of Haemophilus species: Virulence factors of Haemophilus species: Haemophilus influenzae The table below summarizes the major clinical manifestations as well as symptoms and at-risk populations for H. influenzae infection. Pathogen Population at risk Symptoms H. influenzae Meningitis Infants 3–18 months of age Rare due to vaccine Predominantly caused by strains […]
Sinusitis
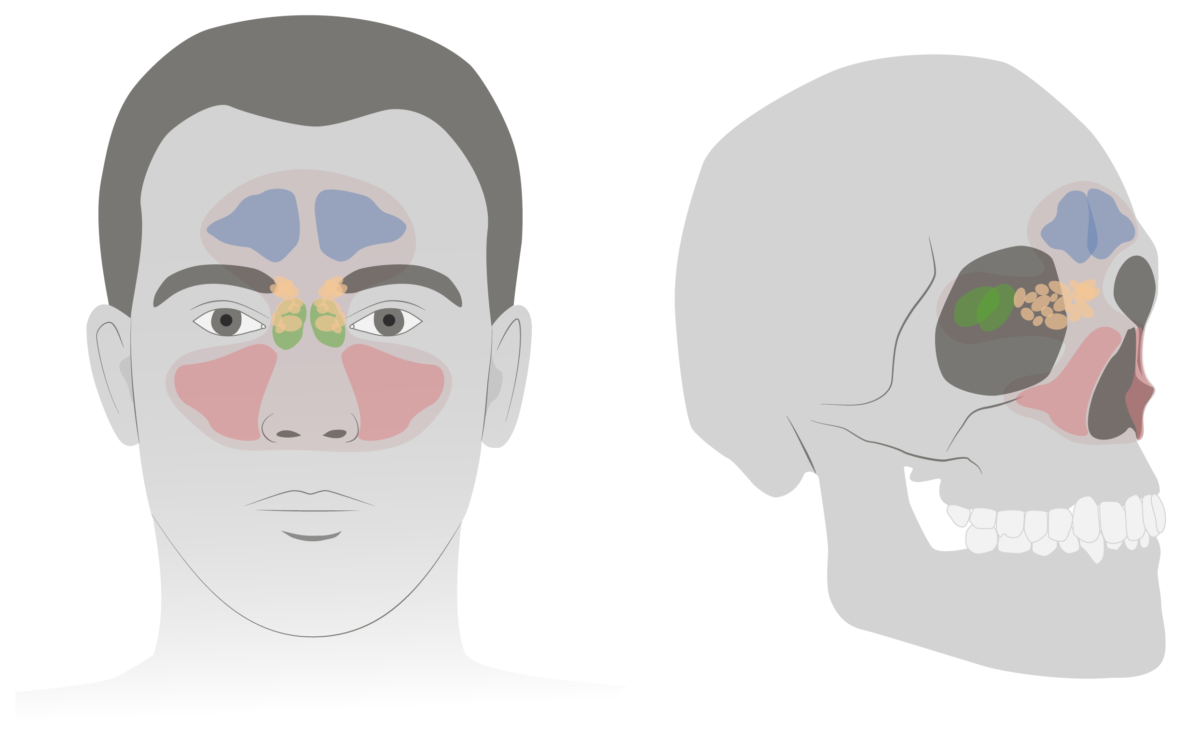
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Viral Bacterial Clinical Presentation General manifestations Viral sinusitis Viral sinusitis usually presents in a milder form and lasts 7–10 days. Bacterial sinusitis Fungal sinusitis Fungal sinusitis usually presents chronically, with atypical symptoms (epistaxis, dyspnea, and black/brown nasal secretions). Complications and/or associated conditions Diagnosis Diagnosis is usually based on clinical […]
Pleuritis
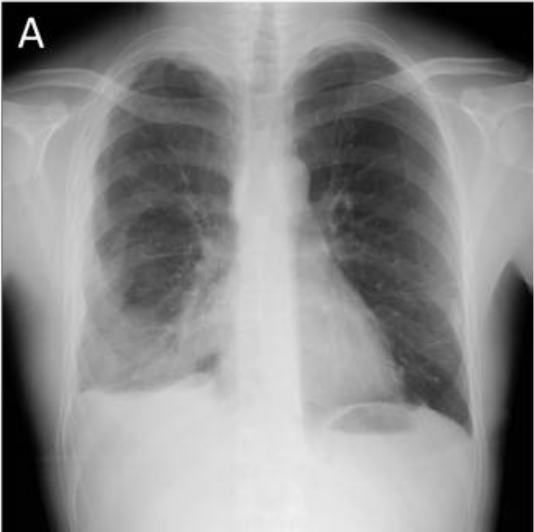
Etiology Pathogenesis Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Light’s criteria for pleural effusions Transudate Exudate Protein (pleural/serum) ≤ 0.5 > 0.5 LDH (pleural/serum) ≤ 0.6 > 0.6 Pleural LDH ≤ two-thirds upper limit of normal serum LDH Pleural LDH > two-thirds upper limit of normal serum LDH Common causes Hypoalbuminemia (cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome) Heart failure Constrictive pericarditis Autoimmune […]
Diphtheria
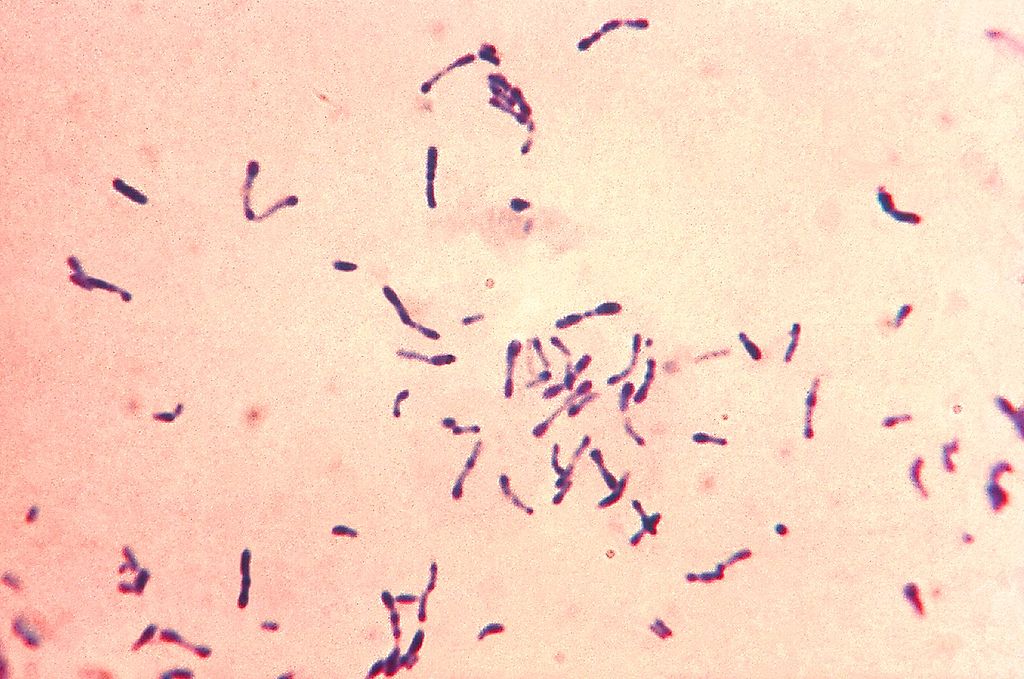
Etiology and Epidemiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Key points to remember about diphtheria: ABCDEFG: ADP-ribosylation, Beta-prophage, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Elongation factor 2, Granules Management and Prevention Complications Possible complications associated with diphtheria include: Differential Diagnosis The differential diagnosis of respiratory diphtheria includes: References
Rhinitis
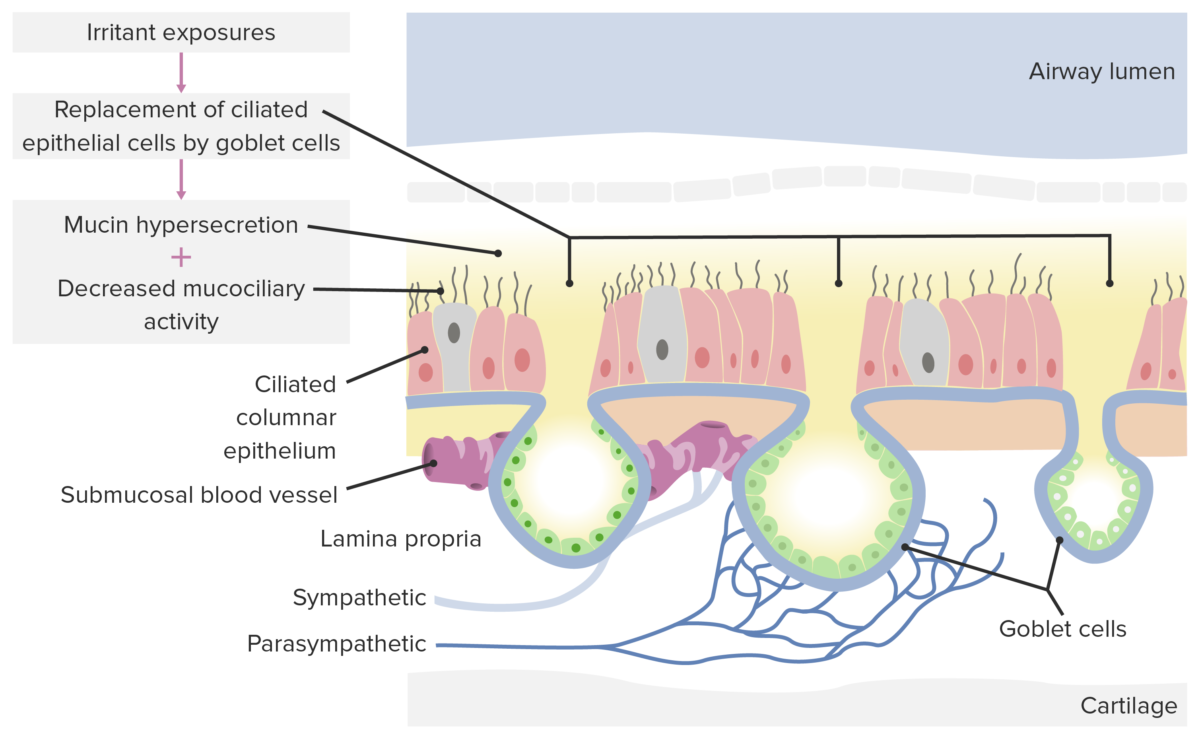
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Infectious Allergic Non-allergic Usually caused by a viral or bacterial infection Type I hypersensitivity reaction An increase in blood flow to the nasal mucosa due to irritants, but not allergens Acute: Viral: rhinovirus (most common), coronavirus, influenza virus, adenovirus, parainfluenza virus Bacterial: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Staphylococcus aureus, […]
Orbit and Extraocular Muscles: Anatomy
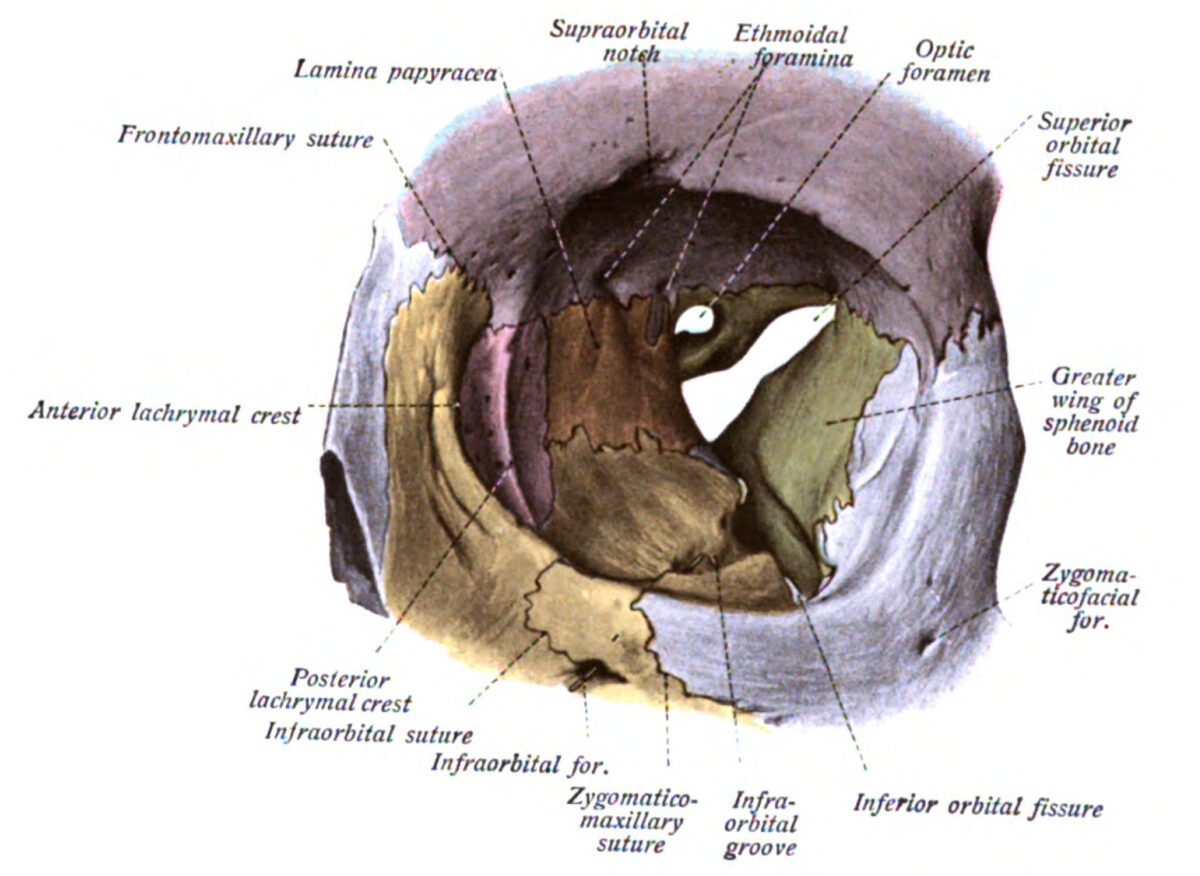
Bones and Structure of the Orbit Location Contents Optic foramen or canal Apex, bordered by the body and lesser wing of the sphenoid Optic nerve (CN II) Ophthalmic artery Ethmoidal foramina Junction between the superior and medial orbital walls In the ethmoid bone, lateral to olfactory groove Anterior and posterior ethmoidal veins, arteries, and nerves […]