Pneumoconiosis
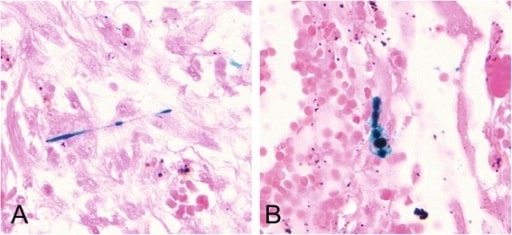
Epidemiology and Etiology Definition and types Pneumoconiosis is the classic term used to describe the non-neoplastic lung reaction to chronic inhalation of mineral dusts encountered at the workplace. Some lung experts believe that the term “pneumoconiosis” should also include diseases induced by chemical fumes and vapors but this is not a widespread practice and will […]
Autoimmune Hepatitis
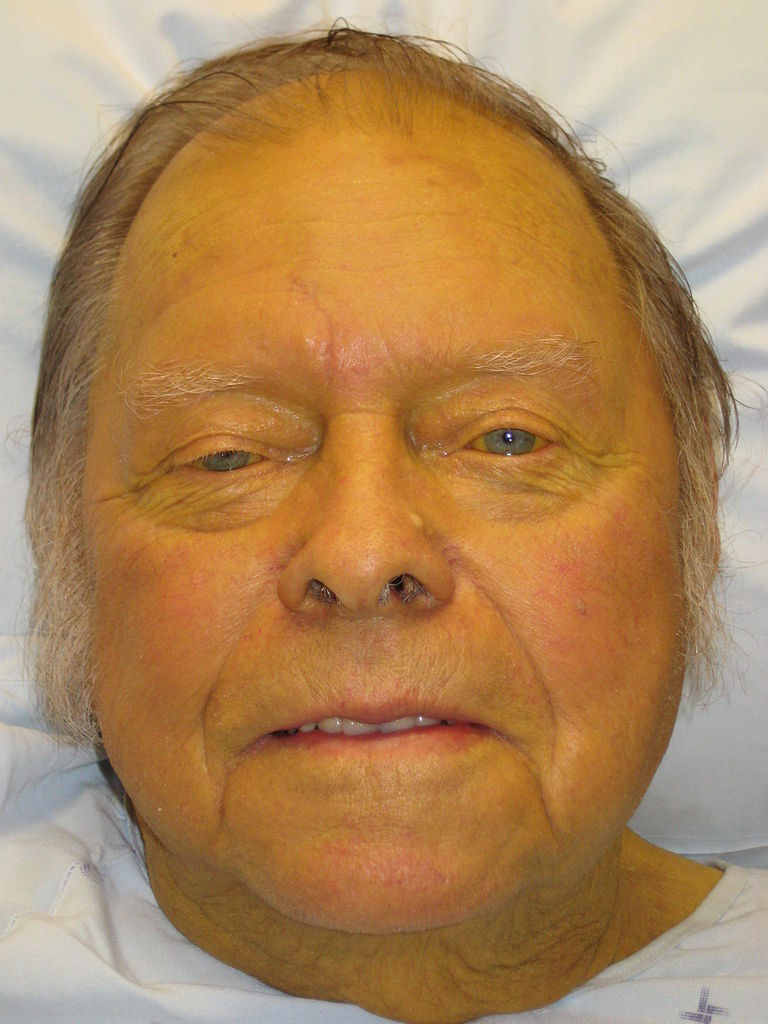
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Associated with other autoimmune conditions (e.g., Hashimoto thyroiditis, Graves disease, diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, celiac disease, Sjogren syndrome) Clinical Presentation Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a differential diagnosis for any patient presenting with at least one of the following: Autoimmune hepatitis is a diagnosis of exclusion, so […]
Atrial Fibrillation
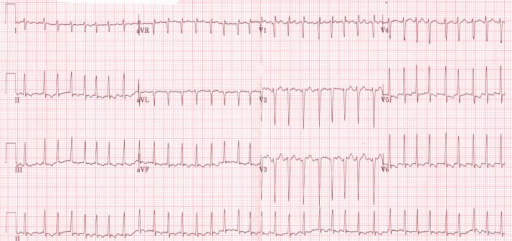
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology General risk factors for cardiovascular disease Risk factors for AF Cardiac risk factors Non-cardiac risk factors Myocardial infarction Coronary artery disease Heart failure Cardiomyopathy (specifically hypertrophic) Other arrhythmias Valvular heart disease Congenital heart disease Myocarditis Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) Electrolyte disturbances (e.g., hypokalemia) Diabetes Drugs (e.g., theophylline, adenosine, digoxin) Surgery (e.g., coronary […]
Wound Healing
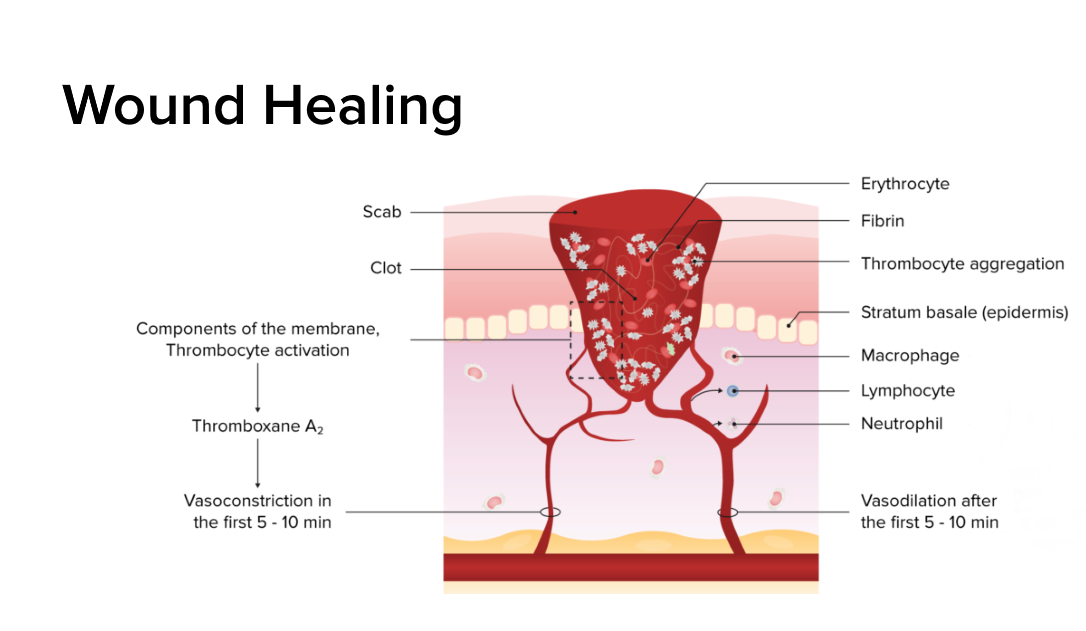
Stages of Wound Repair There are 3 main stages of wound healing: Timeline and steps of wound healing Day 1 Fibrin clot (hematoma) Neutrophils infiltrate Day 2 Squamous cells seal off the wound Macrophages migrate into the wound Day 3 Granulation tissue begins to form Initial deposition of type III collagen Macrophages replace neutrophils Days […]
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis
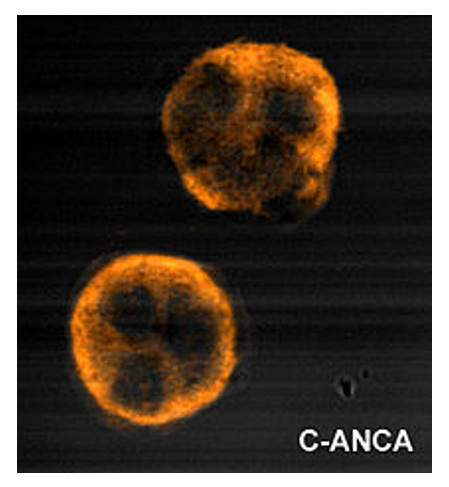
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Classification criteria 1. Nasal or oral inflammation Painful or painless oral ulcers or purulent or bloody nasal discharge 2. Abnormal chest radiograph Pulmonary nodules, fixed pulmonary infiltrates, or pulmonary cavities 3. Abnormal urinary sediment Microscopic haematuria with or without red cell casts (glomerulonephritis) 4. Granulomatous inflammation […]
Ventricular Fibrillation (V-fib)
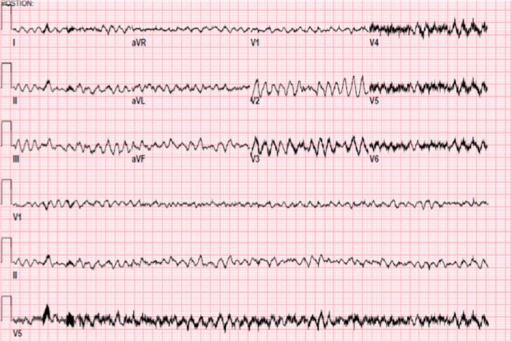
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Ventricular fibrillation (VF) secondary to myocardial infarction (MI) is the most common cause of sudden cardiac death (leading cause of death in developed countries). Etiology Pathophysiology Ventricular tachyarrhythmias are caused by abnormal ectopic contractions in the ventricle. Detailed process Mnemonic Sustained VF after an MI results from: Myocardial ischemia → Necrosis […]
Heart Failure
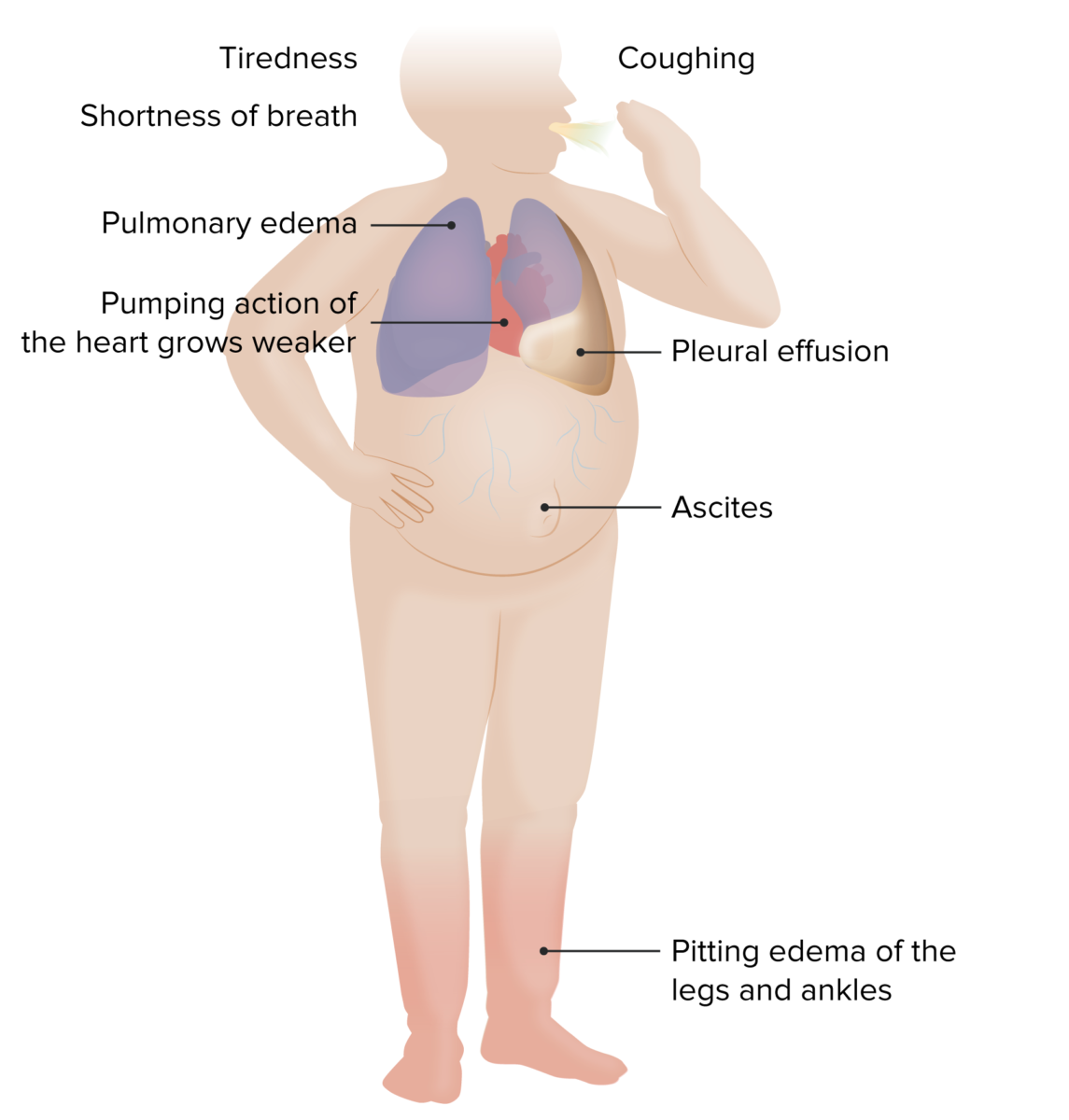
Epidemiology Etiology Underlying conditions include: Risk factors include: Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Symptoms of HF Signs of HF Mnemonic Advanced heart failure symptoms can be identified by the I NEED HELP mnemonic: New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional classification American Heart Association classification Diagnosis Initial approach Table: Common diagnostic findings in HF Test Findings BNP/pro-BNP Diagnosis […]
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
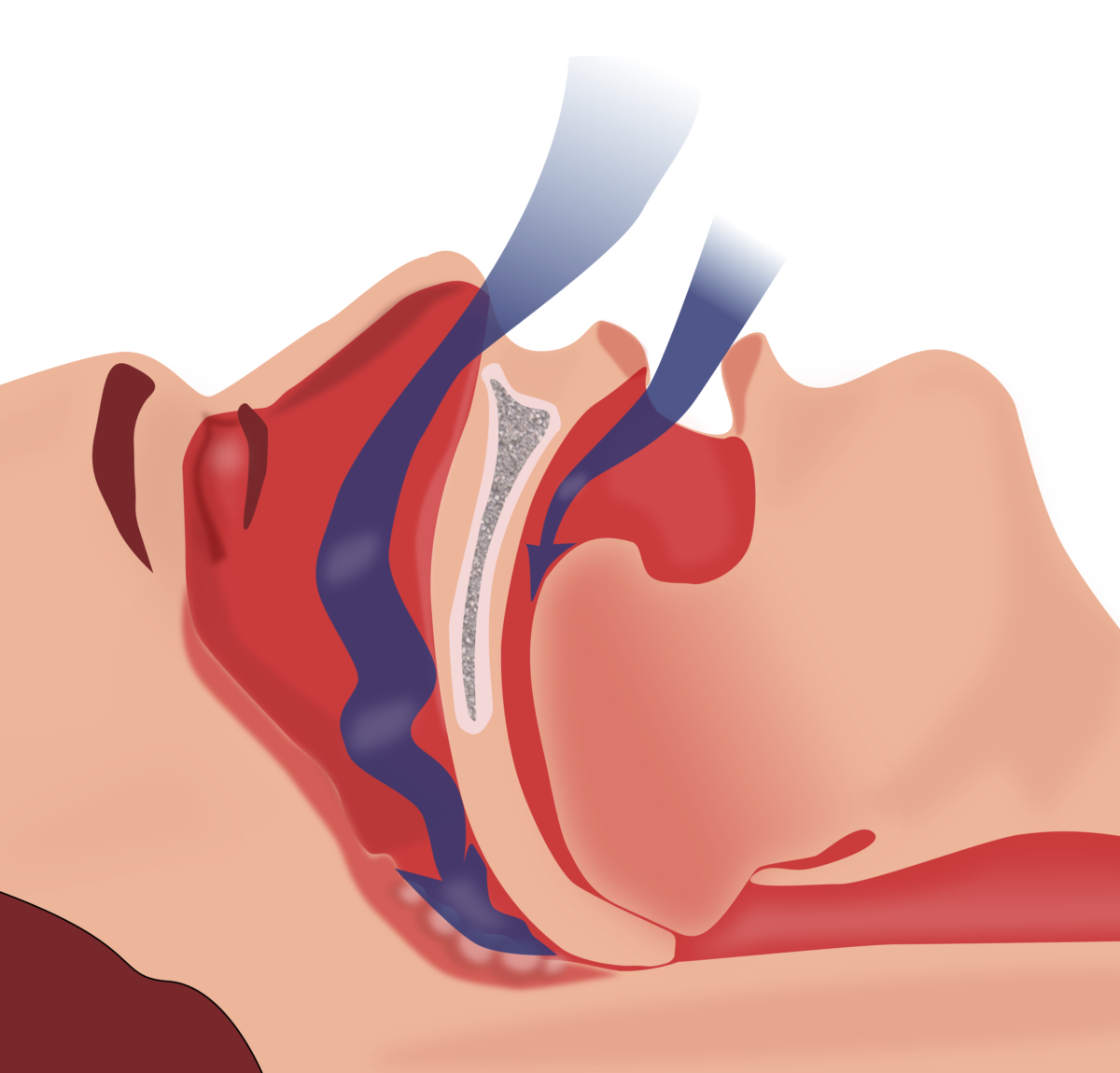
Epidemiology and Classification Epidemiology Classification Risk Factors and Pathophysiology Risk factors Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Management Conservative management Improving modifiable risk factors: Positive airway pressure devices Surgery Clinical Relevance Possible complications of obstructive sleep apnea:
Cystic Fibrosis
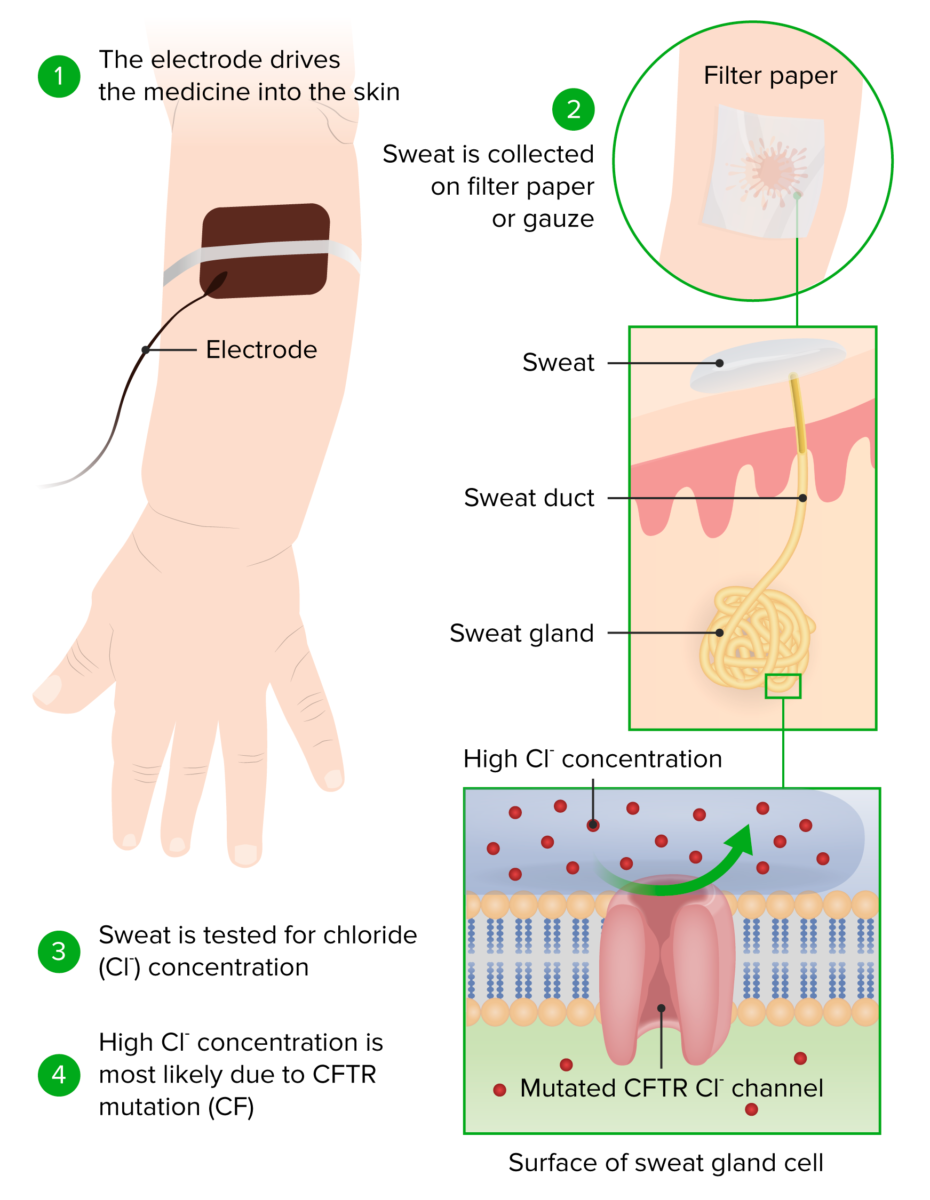
Epidemiology Etiology and Pathophysiology Etiology Pathophysiology Impact on organ systems Clinical Presentation Respiratory system Gastrointestinal system Small intestine Thick secretions impair absorption, increasing the risk of obstruction. Fails to pass meconium within 48 hrs of life in newborn Constipation, abdominal pain Bowel obstruction, unable to pass gas, abdominal distention, nausea, vomiting Large intestine Incompletely digested […]
Pharyngitis
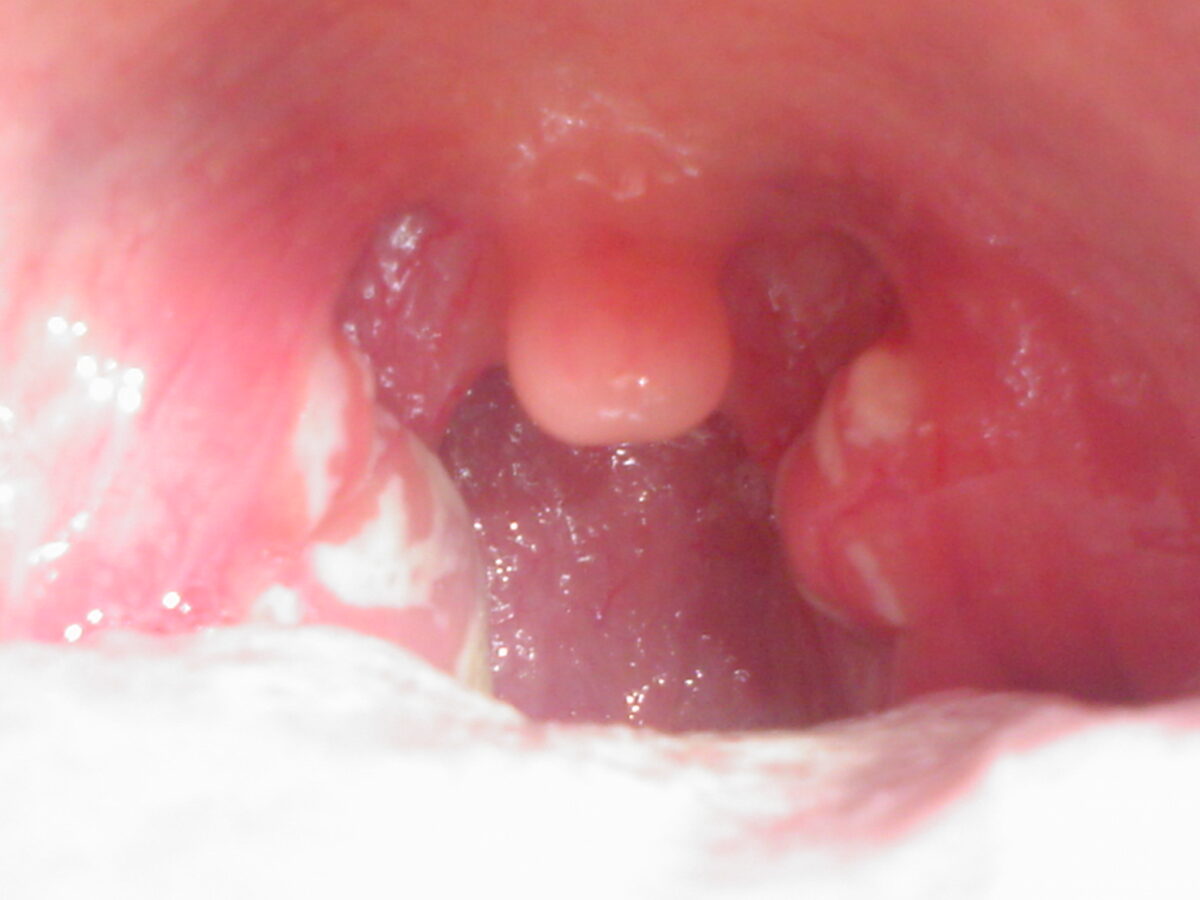
Etiology Pharyngitis is defined as inflammation of the pharynx and surrounding structures. Most cases are due to an infectious organism acquired from close contact with an infected individual. Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Centor score: estimates the probability that pharyngitis is streptococcal and suggests management course for adults Laboratory diagnosis: Identification of beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection is of […]