Deep Vein Thrombosis
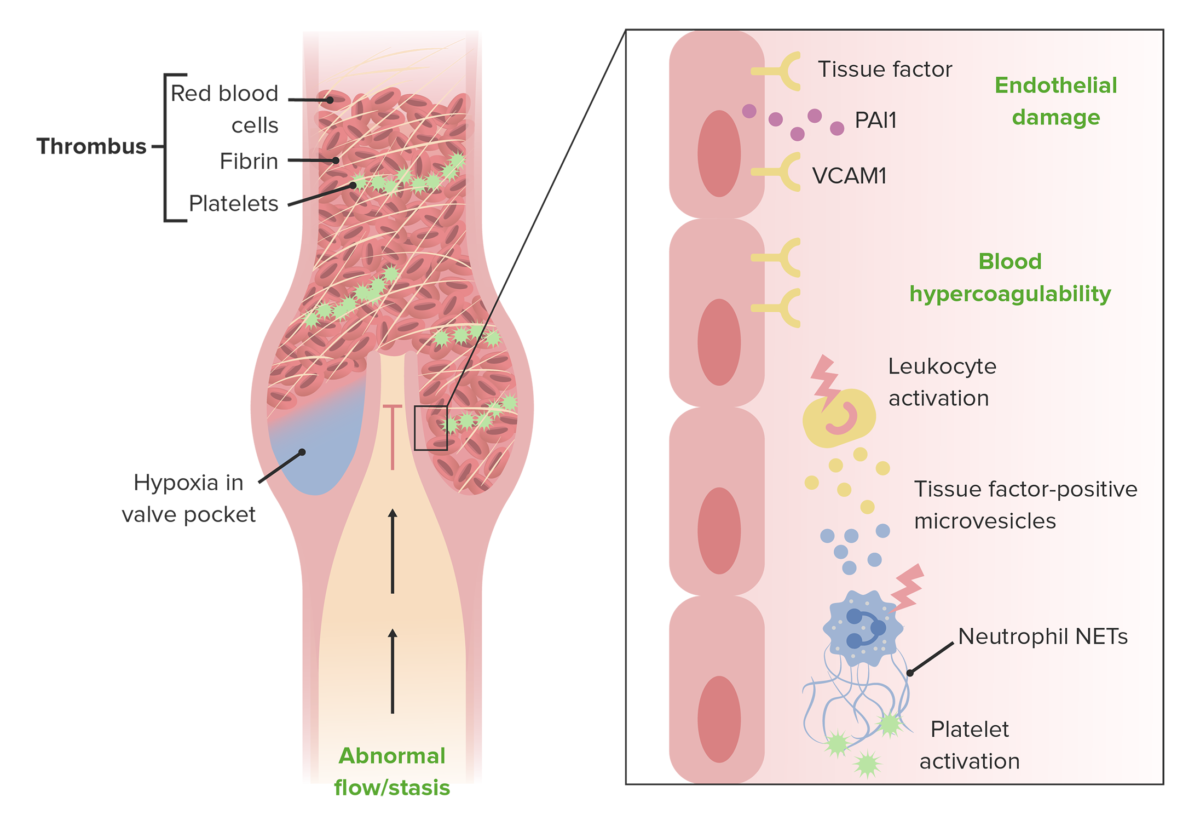
Epidemiology and Risk Factors Epidemiology Risk Factors The 3 primary factors (known as the Virchow triad) that contribute to DVT formation include: venous stasis, hypercoagulability, and vascular endothelial damage. Any condition which worsens one (or more) of these three factors increases the risk of DVT formation. Factors resulting in endothelial damage: Factors resulting in venous […]
Crohn’s Disease
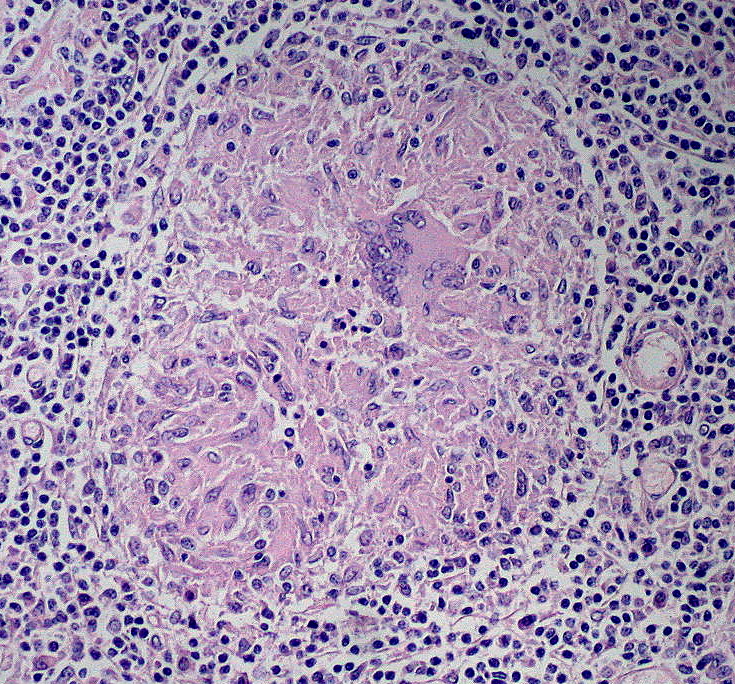
Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Epidemiology Risk factors Pathophysiology The exact pathophysiology is unknown but likely associated with a combination of dysregulation of the intestinal epithelium and the immune system. Location and pattern of inflammation: Clinical Presentation The typical presentation of Crohn’s disease is a relapsing disorder that includes: Reactivation of CD in an asymptomatic period can […]
Enteric Fever (Typhoid Fever)
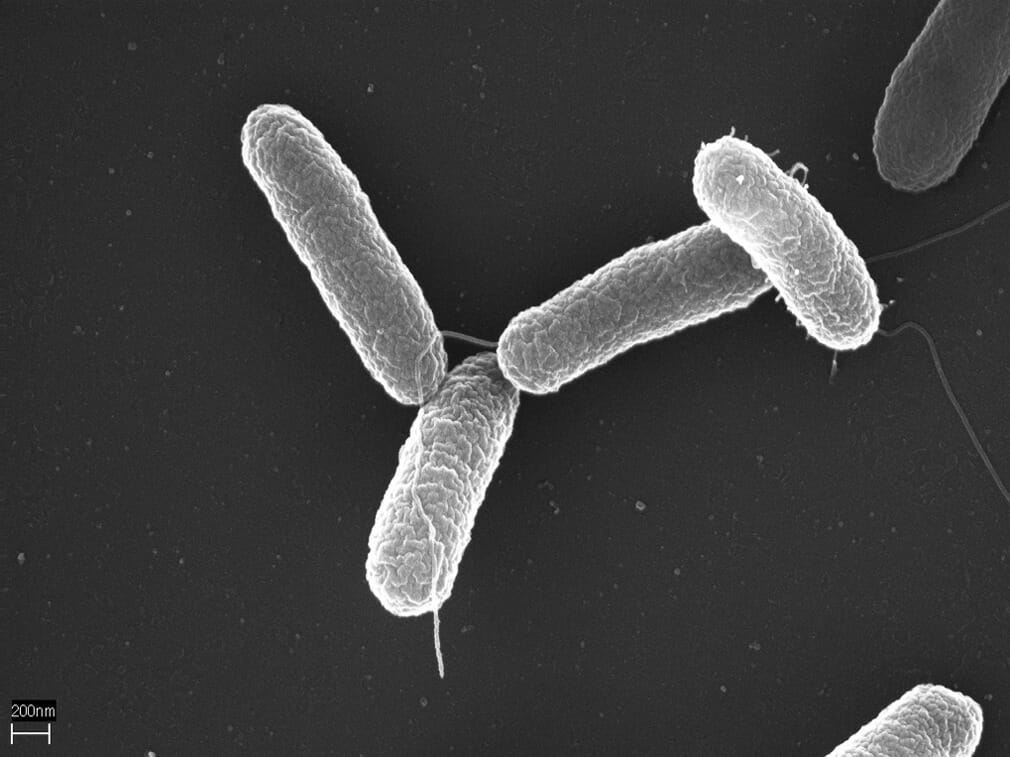
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Transmission Pathogenesis After ingestion of Salmonella Typhi: Clinical Presentation Infection with S. Typhi results in typhoid (or enteric ) fever. Typhoid fever is a severe systemic illness associated with fever and abdominal pain. The incubation period is 5–21 days. Three-phase or -week progression (if untreated) Clinical course Findings Week 1 Bacteremia Gradually rising fever […]
Pneumonia
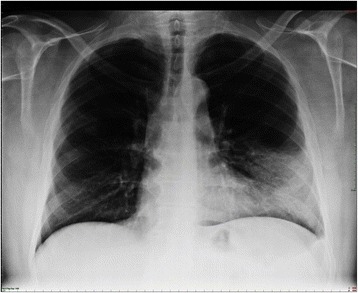
Definition and Epidemiology Types of pneumonia Epidemiology Risk Factors and Pathophysiology Risk factors for multidrug-resistant (MDR) pathogens Table 1: Risk factors for infection with pathogens that are resistant to antibiotics for CAP MDR gram-negative bacteria and MRSA Nosocomial (HAP and VAP) MRSA Community-acquired MRSA Hospitalization ≥ 2 days in recent 90 days Antibiotic use in […]
Ulcerative Colitis
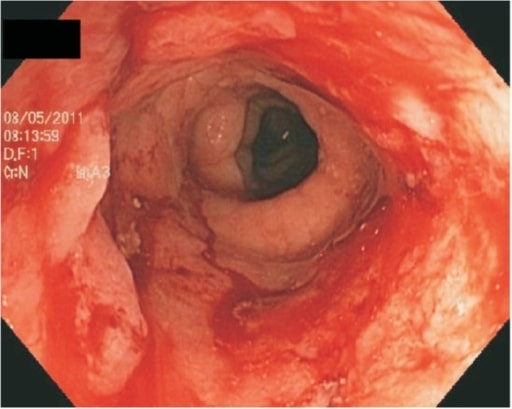
Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Epidemiology Risk factors An increased risk of developing ulcerative colitis (UC) may be associated with the following: Pathophysiology The exact pathophysiology is unknown, but is likely associated with a combination of dysregulation of the intestinal epithelium and the immune system. The inflammation invariably involves the rectum and may extend proximally through the […]
Long QT Syndrome
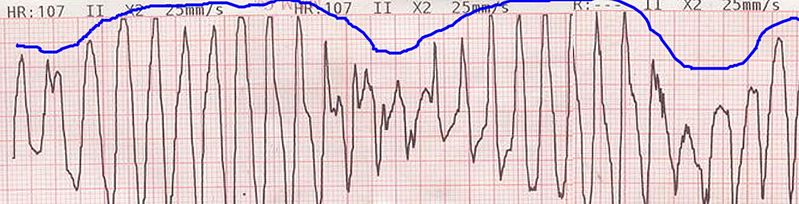
Definitions Etiology Congenital long QT syndrome Pathophysiology: Types of congenital LQTS: Variety of associated conditions: Acquired long QT syndrome Clinical Manifestations Congenital long QT syndrome Acquired long QT syndrome Diagnosis The diagnosis of long QT syndrome can be made via an ECG of the patient and/or 1st-degree relatives. A careful medication review is indicated for […]
Jaundice
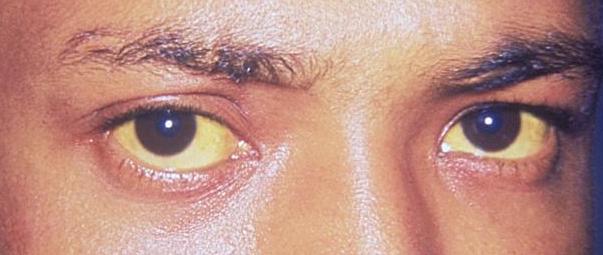
Definition Jaundice Discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes Begins at serum bilirubin > 4–5 mg/dL Scleral icterus Discoloration of the sclera (eyes) Begins at serum bilirubin > 2–3 mg/dL Pathophysiology Jaundice is caused by an elevation of serum bilirubin (hyperbilirubinemia), which can be caused by: Prehepatic pathologies Often occur due to increased hemolysis Causes […]
Impetigo
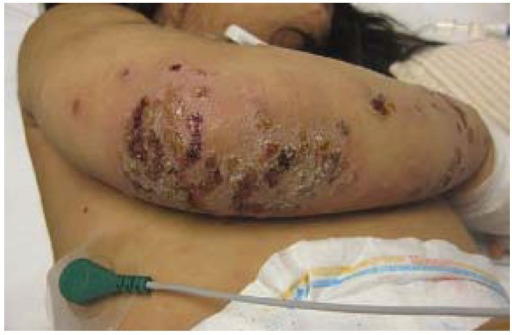
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Clinical Presentation There are 3 variants of impetigo: Non-bullous impetigo Bullous impetigo Ecthyma Diagnosis Diagnosis is usually clinical, based on the natural sequence of the lesions and the presence of honey-colored crusts on pediatric patients aged 2–5 years. Management and Complications Management Management depends on the type and severity of […]
Malignant Mesothelioma
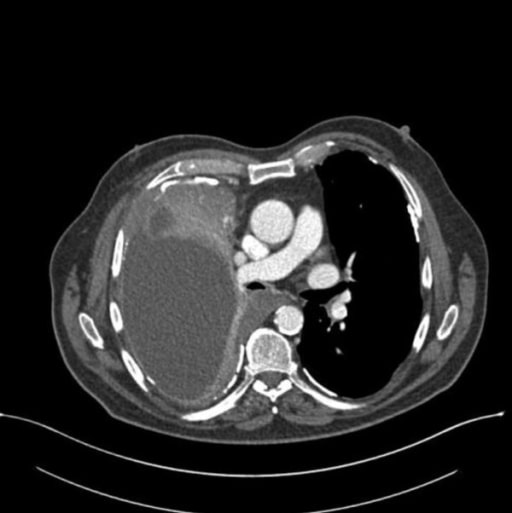
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Malignant mesothelioma (MM): usually referred to as simply “mesothelioma,” as it is much more common than its benign counterpart. Malignant mesothelioma is a primary malignant growth of mesothelial cells, strongly associated with prior exposure to asbestos. Mesothelial cells line the body cavities, including the pleura, peritoneum, pericardium, and testis. Most common […]
Infectious Folliculitis
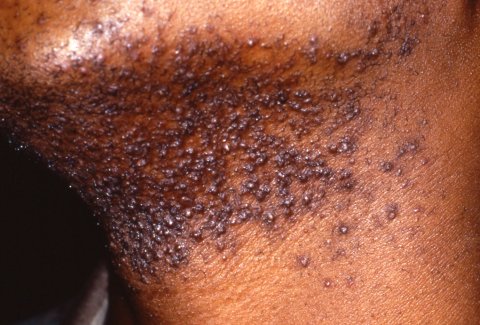
Etiology and Risk Factors Infectious folliculitis occurs due to inflammation of the superficial or deep portion of the hair follicle caused by an infectious agent (see table below). Table: Common etiologies, associated risk factors, and examples of pathogens of folliculitis Etiology Risk factors Pathogens Bacterial S. aureus nasal carriers Hyperhidrosis Pruritic skin diseases (e.g., eczema, […]