Neonatal Polycythemia
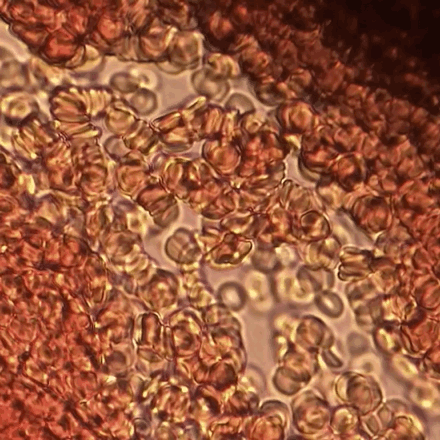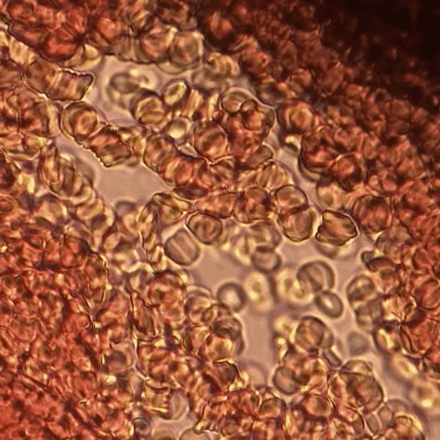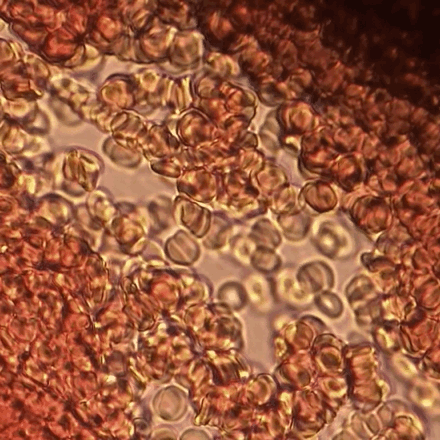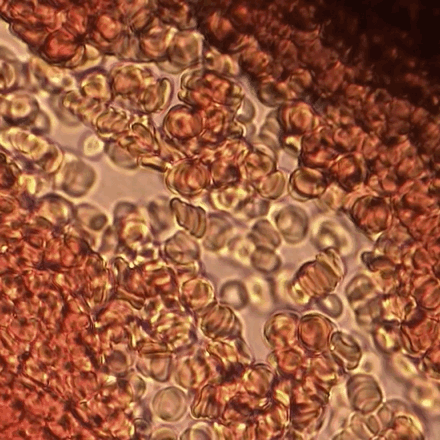
Overview Definitions Neonatal polycythemia (absolute polycythemia): increased erythrocyte mass defined as hematocrit (HCT) > 65% or hemoglobin (Hb) > 22 g/dL Hemoconcentration (relative polycythemia): a decrease in plasma volume resulting in an increased concentration of erythrocytes Epidemiology 1%–2% of children born at sea level 5% of children born at high altitudes Etiology Increased fetal erythropoiesis Placental […]
Interstitial Lung Diseases
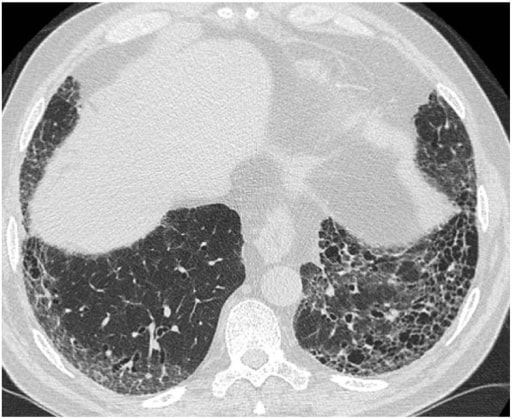
Overview Definition Epidemiology Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, and ILD associated with connective tissue diseases are the most common types of ILD. Classification It is useful to categorize ILDs into those with and without a known cause. Table: Types of interstitial lung disease Cause unknown Cause known Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP): Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) Nonspecific […]
Refractive Errors
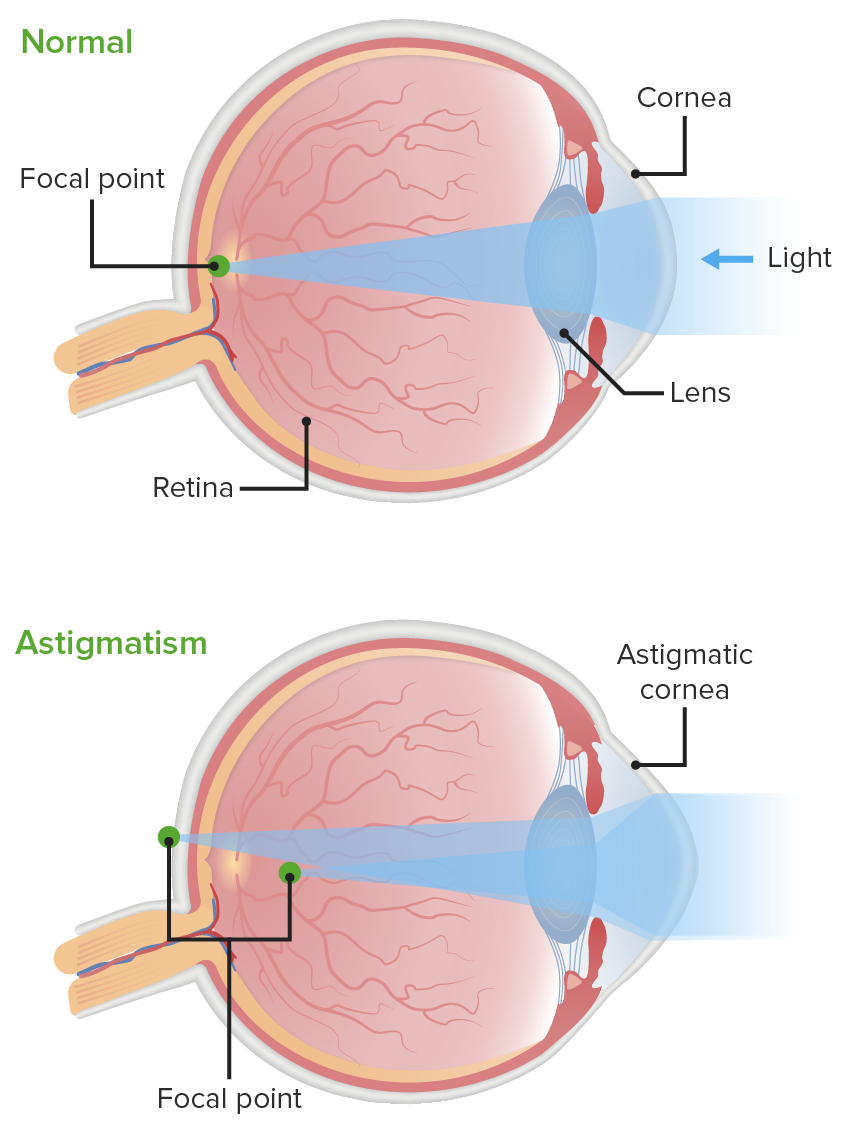
Definitions and Epidemiology Refraction Ametropia or refractive error Epidemiology Further definitions Clinical Presentation Myopia Hyperopia Astigmatism Focal point In front of retina Behind retina Multiple sites Causes Eye too long, cornea with too much curvature Eye too short, cornea with too little curvature Uneven curvature of the cornea Result Cannot focus distant objects Cannot focus […]
Gout
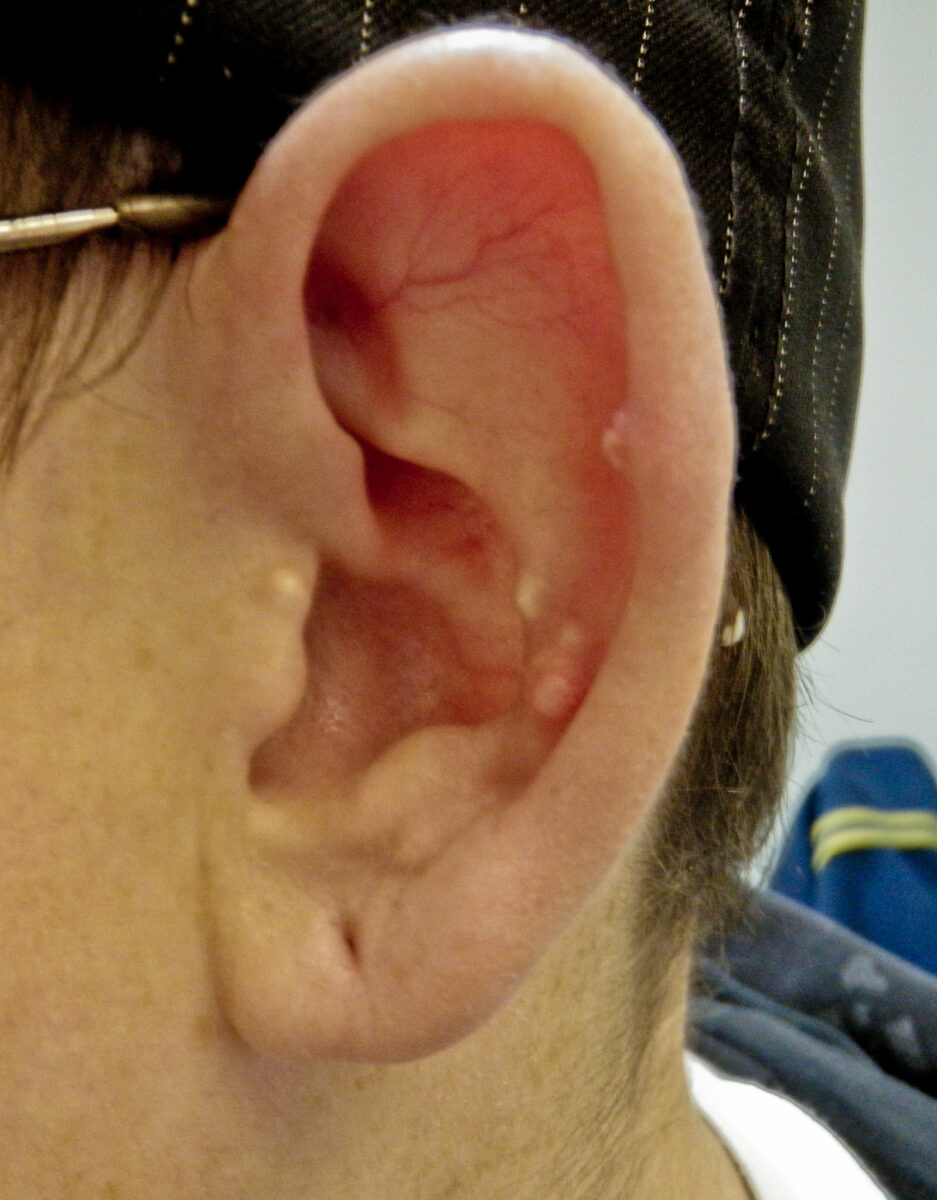
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Risk factors that increase UA levels Mnemonic Drugs causing acute precipitation of gout: FACT F: Furosemide diuretics A: Aspirin/Alcohol C: Anti-Cancer drugs (e.g., cyclosporine) T: Thiazide diuretics Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Gout flares Intercritical gout Upon resolution of an acute gout flare, patients enter an intercritical (between-flares) period. Tophaceous gout Associated […]
Supraventricular Tachycardias
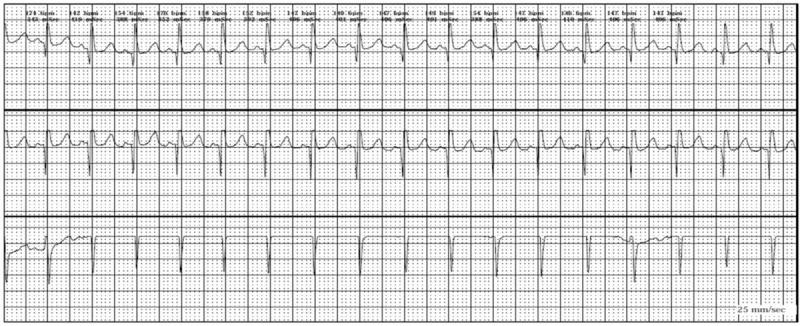
Sinus Tachycardia Etiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Treatment Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardias (PSVTs) Etiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Treatment Treat hemodynamic instability via urgent direct current (DC) cardioversion if present. AVNRT and AVRT: Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome Etiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Treatment Treatment is indicated in patients with symptomatic tachyarrhythmias to prevent RVR. Atrial Flutter and Atrial Fibrillation Atrial flutter […]
Seborrheic Dermatitis
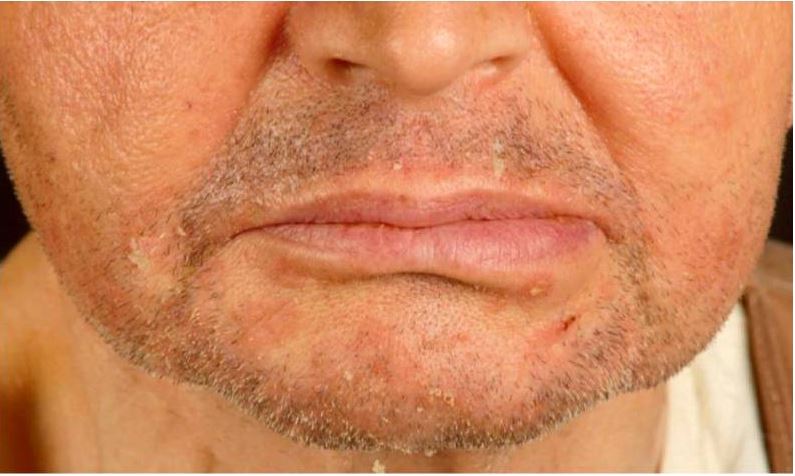
Epidemiology and Etiology Seborrheic dermatitis is a common chronic skin disorder that is characterized by erythematous patches with greasy, yellowish scales that most often appear in areas with prominent sebaceous glands (scalp, face, upper trunk, and anogenital area). Epidemiology Etiology Unclear, but may be affected by the following: Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation General features Seborrheic dermatitis […]
Glucose-6-phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) Deficiency
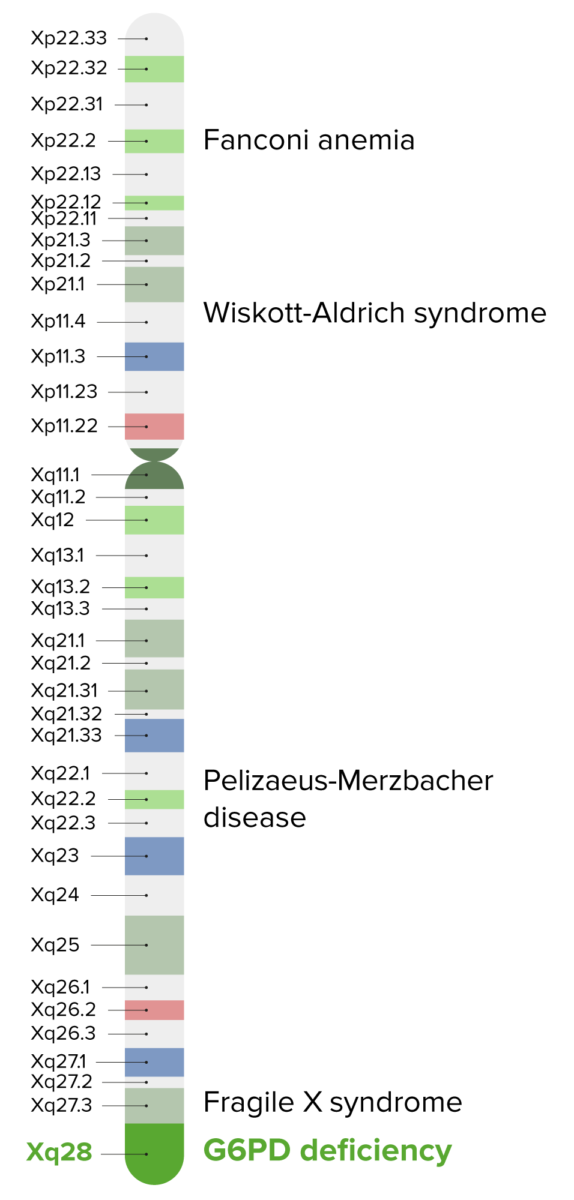
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Table: Common oxidative stressors Drugs Foods Other Sulfas (trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole [TMP/SMX]) Quinolones Nitrofurantoin Aspirin/nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Methylene blue Fava beans Blue food coloring Any infection (most common) Naphthalene (mothballs) Diabetic ketoacidosis Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency is suspected in cases of episodic hemolytic symptoms. Diagnostic testing should include […]
Labial and Genital Herpes
Definition Genital herpes is a mucocutaneous ulcerative disease caused by either herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1 or 2. HSV-1: HSV-2: Epidemiology Etiology Causative agent: herpes simplex virus Transmission Risk factors Pathophysiology Primary infection Primary infection occurs when the virus travels through tiny breaks or even microscopic abrasions in the skin or mucous membranes in […]
Gynecomastia
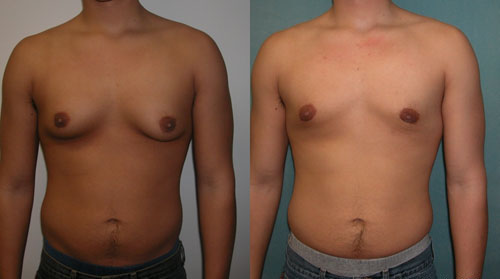
Overview Asymptomatic gynecomastia is common enough that it could almost be considered a normal condition, with a trimodal age distribution. Gynecomastia is classified into 3 major groups: physiological, pathological, and idiopathic. Physiological gynecomastia Pathological gynecomastia Idiopathic gynecomastia Mnemonic To recall the causes of gynecomastia, remember CODES: Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Management Differential Diagnosis The following conditions […]
Kawasaki Disease
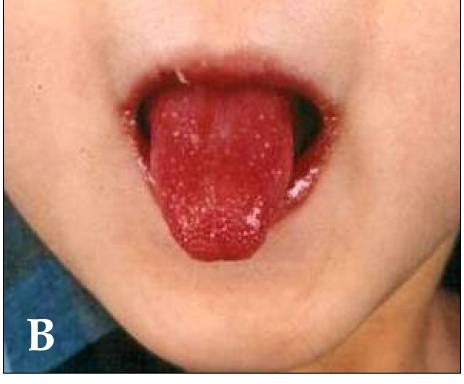
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology The etiology of Kawasaki disease (KD) is unknown. There are several theories: Immunologic response theory: Infection theory: Genetic predisposition theory: Environmental factors theory: Pathophysiology Kawasaki disease is a systemic, inflammatory illness that affects medium-sized arteries, especially the coronary arteries. Clinical Presentation Commonly presenting symptoms Less common manifestations Table: Other manifestations […]