Chronic Pancreatitis
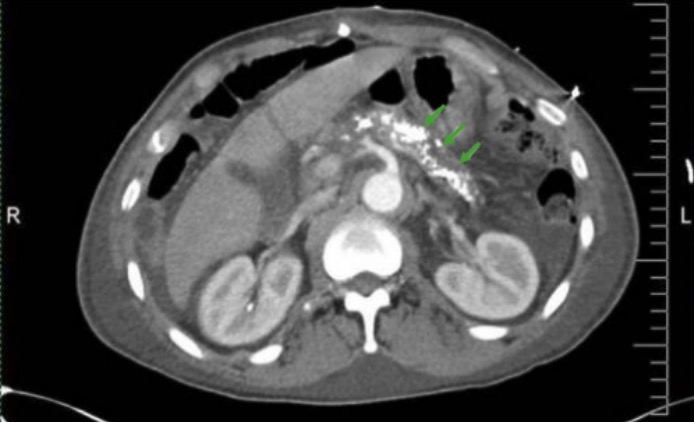
Overview Epidemiology Etiology Common etiologies of chronic pancreatitis are summarized with the “TIGAR-O” mnemonic: Table: TIGAR-O: Common etiologies of pancreatitis T Toxic/metabolic Alcohol (most common) Tobacco smoking Hypertriglyceridemia Hypercalcemia I Idiopathic May be early- or late-onset G Genetic mutations Autosomal dominant: PRSS1 Autosomal recessive: CFTR SPINK1 A Autoimmune Autoimmune pancreatitis type 1: immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)–related […]
Psoriasis
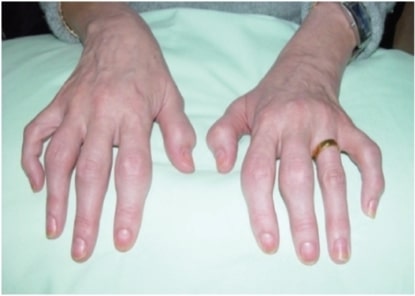
Overview Epidemiology Relatively common in children and adults 0.5%–11% of people worldwide 1%–3% of people in the United States Can be seen at any age, but incidence peaks at the ages of 20–30 and 50–60 (median age is 28 years) ⅓ of patients have a first-degree relative with the disease. Seasonal variation: worse in winter than […]
Hepatic Encephalopathy
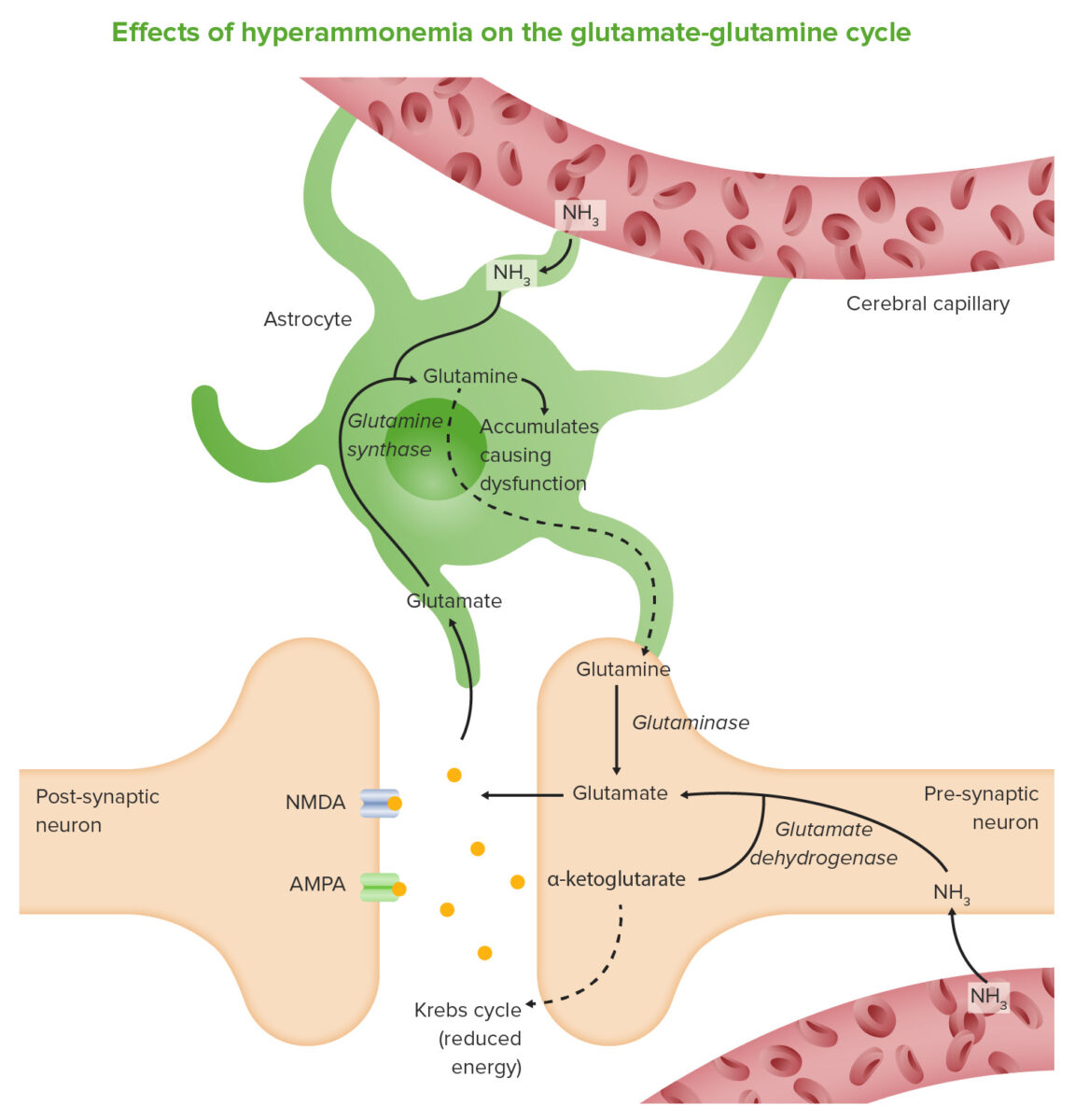
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Hepatic encephalopathy is seen in patients with severe liver disease or liver failure, and can be exacerbated by: Mnemonic Precipitating factors for hepatic encephalopathy can be remembered by the mnemonic “HEPATICS”: Pathophysiology Normal physiology: Liver disease allows disruption of normal ammonia regulation through: Impaired brain function results from a buildup of ammonia, […]
Ascites
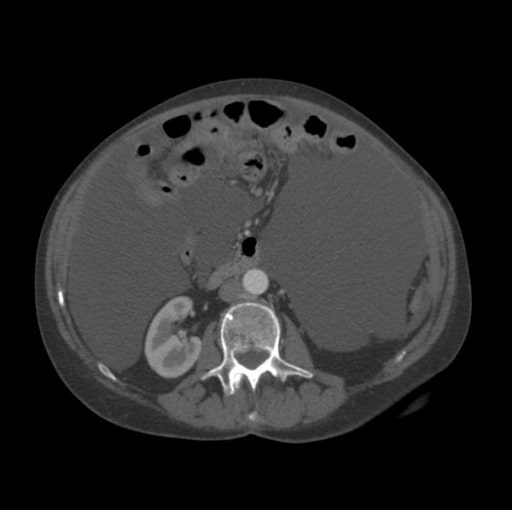
Overview Definition and epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Ascites is caused by an osmotic and/or hydrostatic pressure imbalance often secondary to: Portal hypertension-related ascites: Non-portal hypertension–related ascites: Clinical Presentation Symptoms Physical exam Diagnosis Initial steps Analysis of the ascitic fluid The next step requires analysis of the ascitic fluid. Other helpful laboratory investigations for a potential etiology […]
Barrett Esophagus
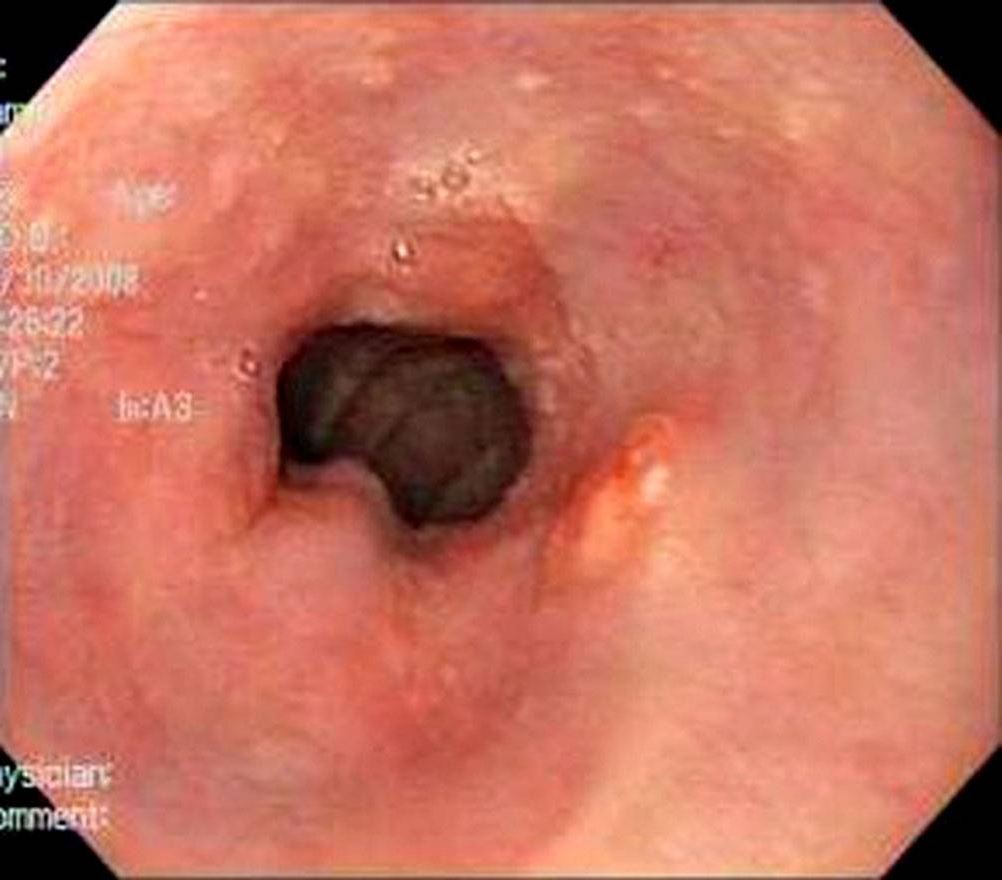
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Mucosal injury Metaplasia Dysplasia Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Screening: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD): Management and Complications Management The goal is to treat underlying acid reflux to decrease the risk of cancer development. Surveillance and dysplasia management Endoscopy biopsy findings Management Barrett esophagus (metaplasia only) PPIs and EGD every […]
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
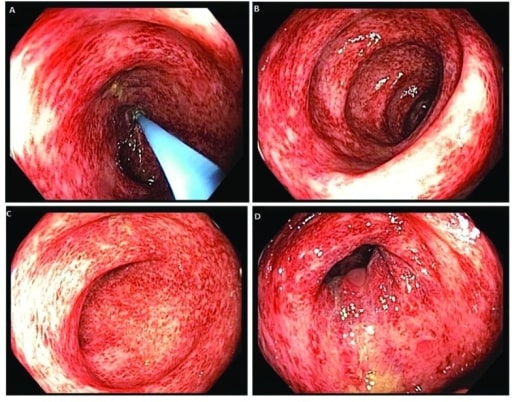
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Upper gastrointestinal bleed (proximal to the ligament of Treitz): Lower GIB (distal to the ligament of Treitz): Clinical Presentation Clinical manifestations Physical exam Diagnosis Diagnosis and management of GIB tend to go hand-in-hand and will vary depending on the hemodynamic stability of the patient. Laboratory evaluation Imaging Procedures Management Initial […]
Hordeolum (Stye)
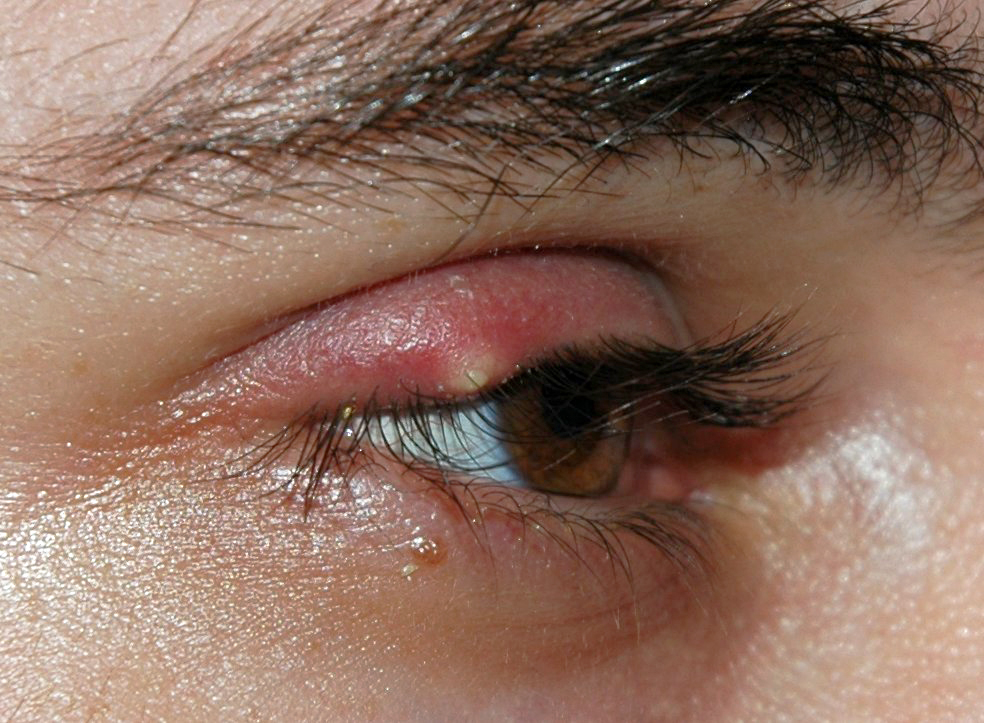
Overview Anatomy Hordeolum Table: Eyelid glands Name Type Opening location Infection Gland of Zeis Sebaceous gland Directly into the eyelash follicle External hordeolum Gland of Moll Modified sweat glands Between adjacent lashes External hordeolum Meibomian gland Modified sebaceous gland Behind eyelashes Internal hordeolum Etiology Clinical Presentation Complications Management Most hordeola resolve spontaneously, lasting up to […]
Hepatorenal Syndrome
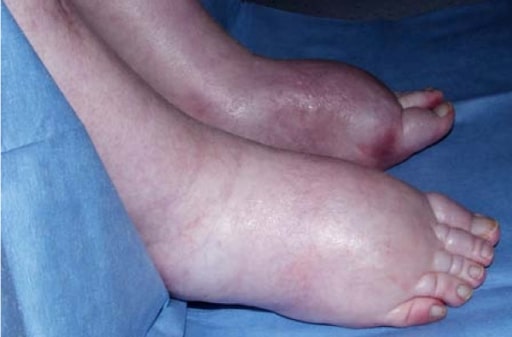
Overview Etiology Hepatorenal syndrome is associated with portal hypertension due to: Classification The classification system of hepatorenal syndrome was recently updated: Pathophysiology Trigger factors are any interventions or conditions that cause arterial hypovolemia: Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Management The goal of therapy is improvement in liver function. Differential Diagnosis Pre-renal disease: presents […]
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
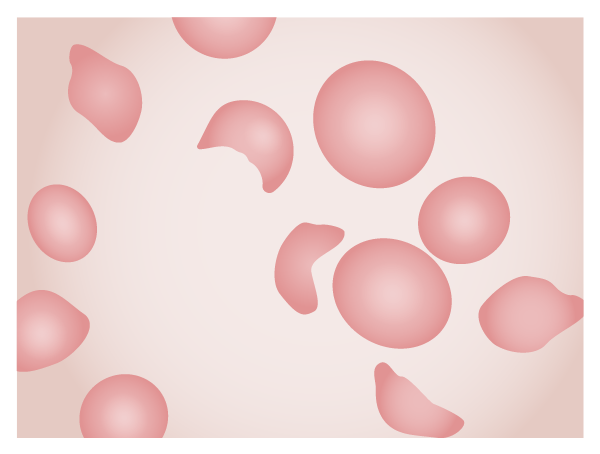
Overview Definition Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is a disease of the capillaries (microangiopathy) that causes the formation of blood clots, anemia caused by the destruction of RBC in these clotted capillaries (hemolytic anemia), acute kidney injury, and low platelets (thrombocytopenia). Epidemiology Etiology Etiology is classified as acquired (infectious versus noninfectious) or hereditary. Pathophysiology The pathophysiology […]
Cellular Accumulations
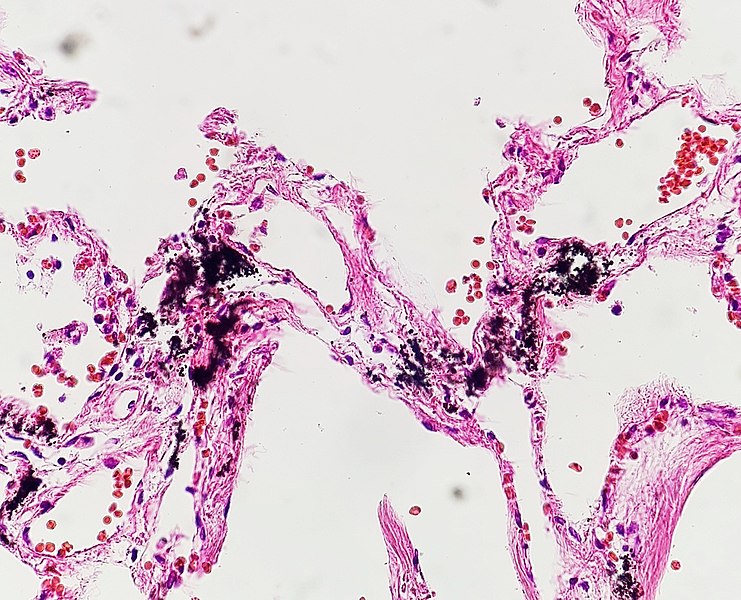
Overview Intracellular accumulations Mechanisms Pigments Exogenous pigments Pigments coming from outside the body: Endogenous pigments Endogenous pigments are synthesized within the body. Lipofuscin or lipochrome: Hemosiderosis (iron): Hemochromatosis (iron): Bilirubin: Melanin: Calcium Accumulation Metastatic calcification Dystrophic calcification Protein Accumulation Microscopic morphology Causes Lipid Accumulation Triglycerides Cholesterol Phospholipids Glycogen Accumulation Hyaline Change Description Cellular findings References