Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
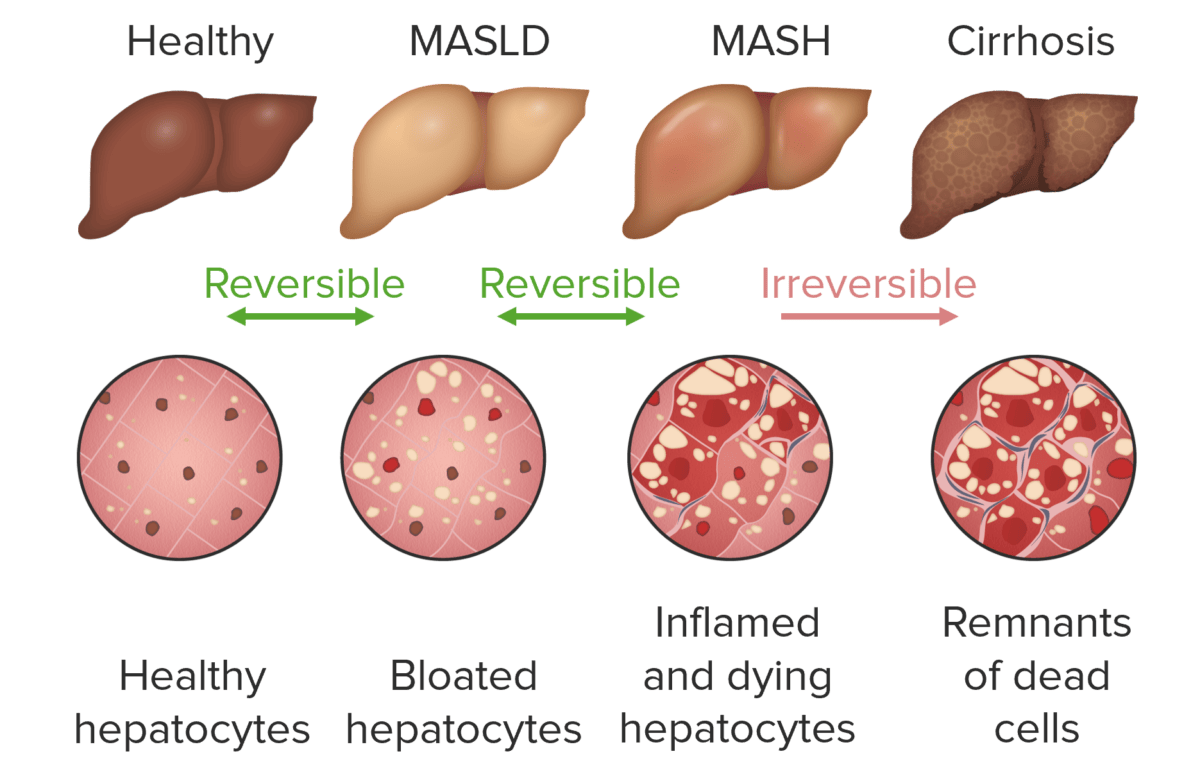
Definition Fatty liver (steatotic liver disease) has alcoholic (alcohol-associated liver disease) or nonalcoholic (metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease) subtypes. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): previously named nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Pathophysiology of MASLD MASLD MASH Potential outcomes If progression is not reversed, MASLD leads to MASH. With […]
Esophagitis
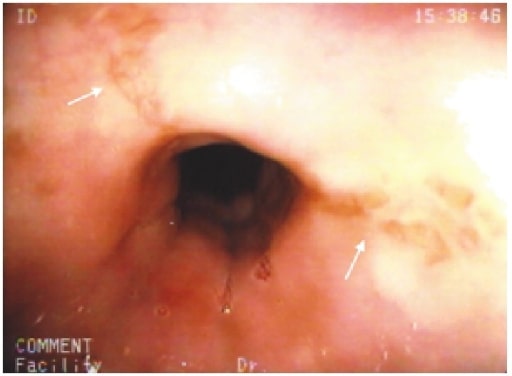
Overview Mnemonic To remember the common causes of esophagitis: “PIECE” Medication-induced Esophagitis Etiology Pathophysiology Risk factors Clinical presentation Diagnosis Prevention and management Infectious Esophagitis: Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Etiology Risk factors Clinical presentation Diagnosis Diagnosis is done by upper endoscopy. Management Infectious Esophagitis: Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) Etiology Risk factors Clinical presentation Diagnosis Diagnosis is done by […]
Tricuspid Stenosis
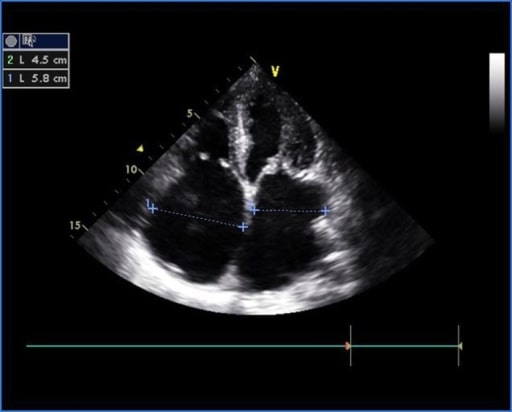
Overview Definition and epidemiology Tricuspid stenosis (TS) is the narrowing of the tricuspid valve, which obstructs the flow of blood from the right atrium to the right ventricle, resulting in a transvalvular gradient. Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Symptoms Physical exam Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Management Differential Diagnosis References
Bradyarrhythmias
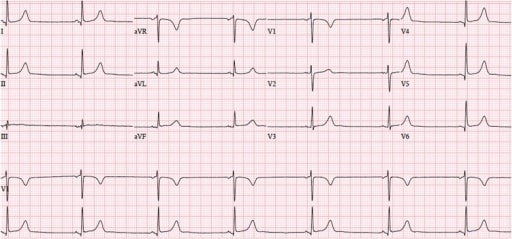
Overview Definition Bradyarrhythmia: Anatomy Physiology Sequential events of a cardiac cycle: Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Intrinsic causes: Extrinsic causes: Bradyarrhythmia Due to Sinus Node Dysfunction Sinus (sinoatrial) node dysfunction (SND) Pathophysiology Types Bradyarrhythmia Due to Atrioventricular Block Atrioventricular block Pathophysiology Types Clinical Presentation Symptoms are related to bradyarrhythmia, causing low cardiac output: Diagnosis Diagnostic […]
Tricuspid Regurgitation
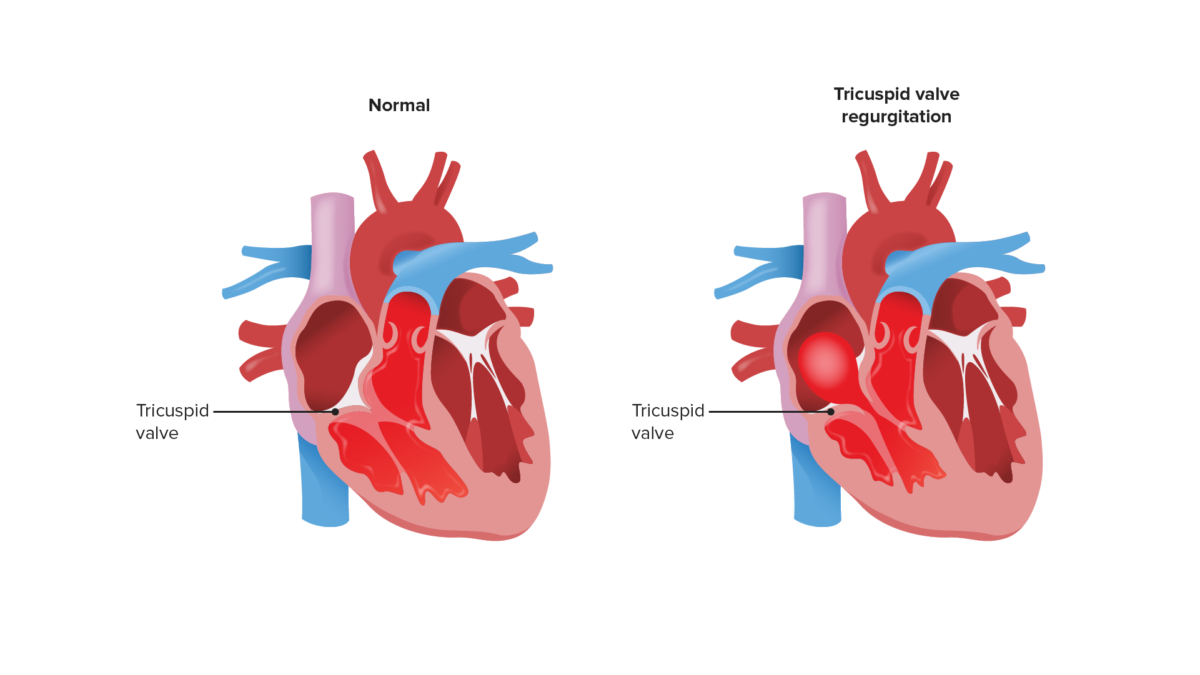
Overview Definition and epidemiology Tricuspid regurgitation (TR) is the backflow of blood through the tricuspid valve into the right atrium during ventricular systole. Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Symptoms Physical exam Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Management Differential Diagnosis References
Pupil: Physiology and Abnormalities
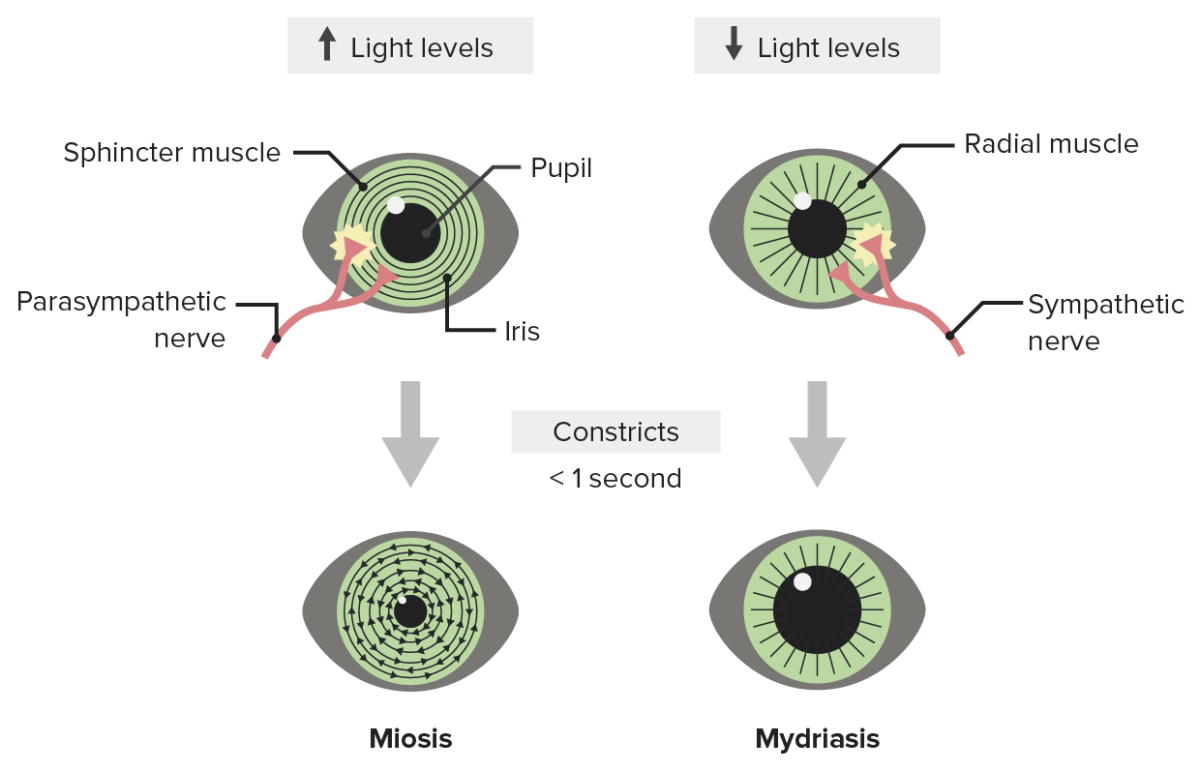
Overview Pupil Adjacent structures Physiology of the Pupil Visual pathway Afferent pathway From stimuli to the primary visual cortex: Parasympathetic innervation pathway (pupillary light reflex) Sympathetic innervation pathway Near response Consists of 3 responses: Examination of the Pupil Light and near response Pupil size Swinging-flashlight test Slit-lamp examination Pharmacologic tests Disorders of the Afferent Pathway […]
Aortic Stenosis
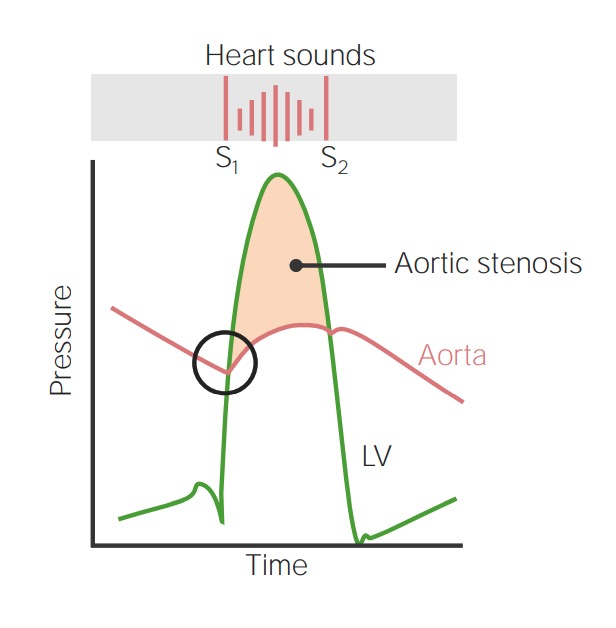
Overview Definition Aortic stenosis (AS) is the narrowing of the aortic valve aperture. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Mechanisms of valvular damage Mechanism of heart failure Clinical Presentation Symptoms Signs Audio: This audio clip is an example of severe aortic stenosis. This is a harsh, crescendo-decrescendo murmur occurring between S1 and S2. Due to the severity of […]
Actinic Keratosis

Overview Definition Epidemiology Risk factors Clinical Presentation Description of lesions Clinical course Variants Diagnosis Diagnosis is usually made clinically by inspection and palpation. Management Prevention Prevention consists of the use of sunscreen and sun protection. Treatment of head and neck lesions Treatment of other body sites Other field-ablation treatments Differential Diagnosis References
Hypertensive Retinopathy
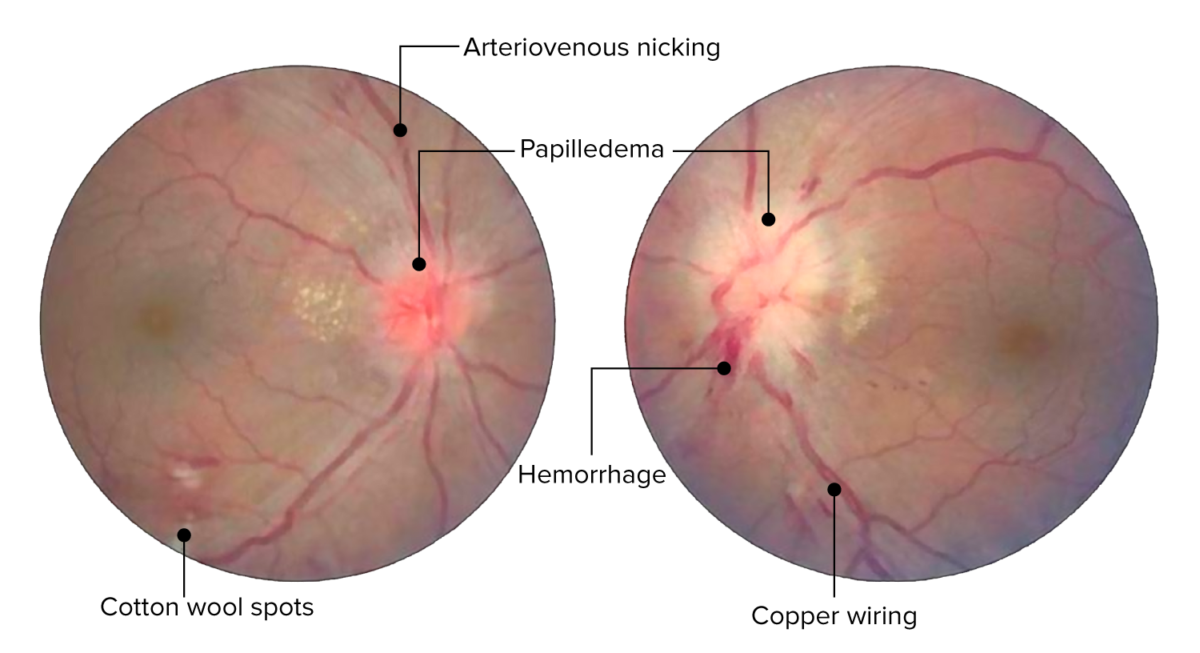
Overview Definition Hypertensive retinopathy: Characterized by microvascular retinal changes and damage from hypertension Arises from an acute increase in blood pressure and/or chronic hypertension Hypertension: Blood pressure category Systolic blood pressure Diastolic blood pressure Elevated blood pressure 120–129 mm Hg AND < 80 mm Hg Hypertension stage 1 130–139 mm Hg OR 80–89 mm Hg […]
Atrial Flutter
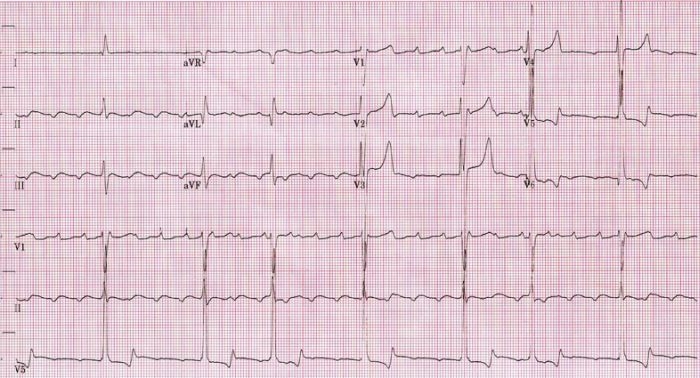
Overview Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Atrial flutter is caused by a macroreentrant electrical loop (reentrant circuit covers a large area of the atrium): Typical atrial flutter: Atypical atrial flutter: Clinical Presentation Symptoms Physical exam Complications Complication Possible symptoms Exam findings Cardiac: Long-term tachycardia can cause cardiac structural changes. Increased oxygen demand of the myocardium Heart failure […]