Asthma Drugs
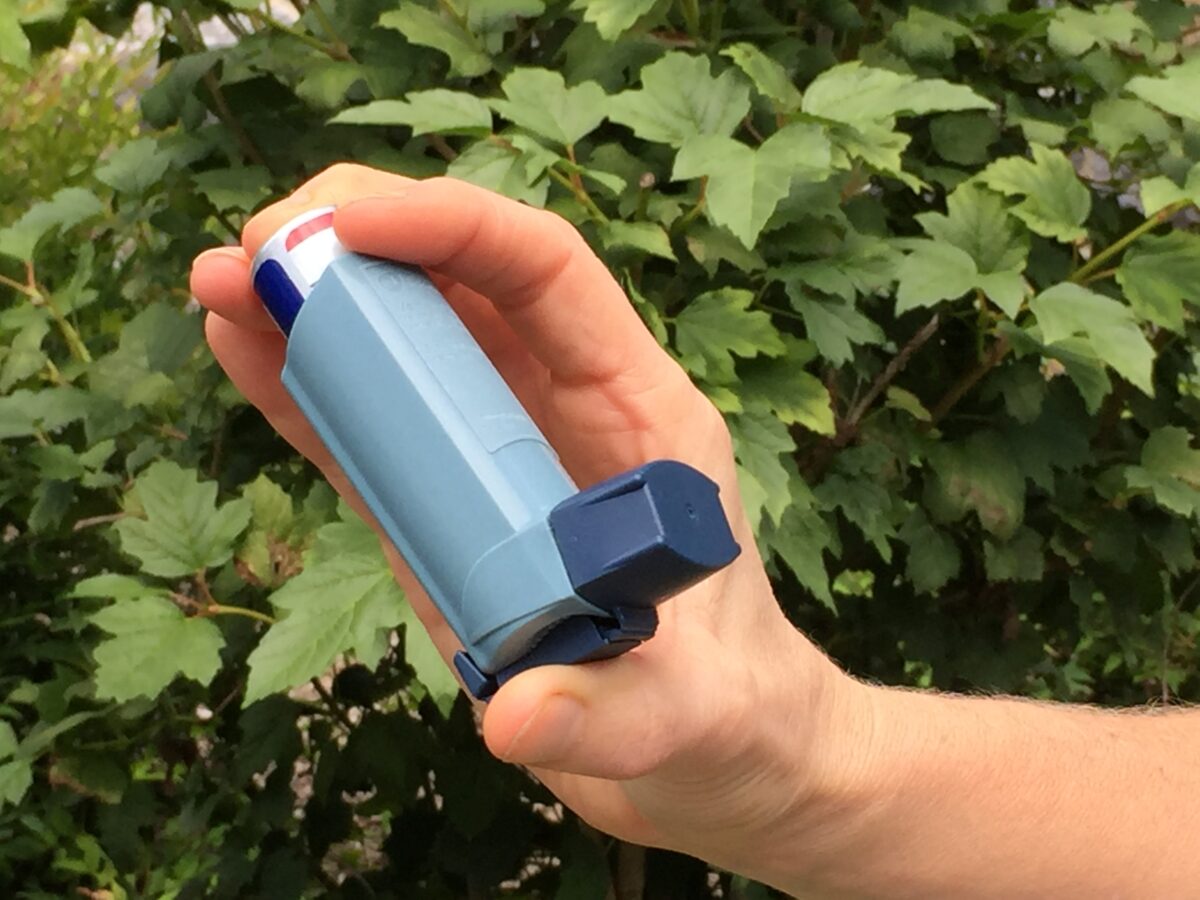

Overview Table: Classification of drugs used in asthma Function Class Examples Bronchodilators β-agonists Short-acting β-agonists (SABAs): albuterol, terbutaline, levalbuterol Long-acting β-agonists (LABAs): salmeterol, formoterol Methylxanthines Theophylline Muscarinic antagonists Short-acting muscarinic antagonist (SAMA): ipratropium Long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA): tiotropium Anti-inflammatory agents Mast cell degranulation inhibitors (chromones) Cromolyn, nedocromil Antibodies Against IgE: omalizumab Against interleukin (IL)-5: mepolizumab […]
Acute Cholangitis
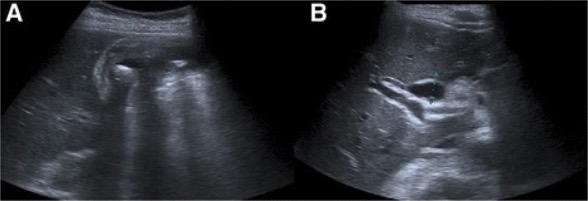
Overview Epidemiology Etiology Mnemonic: Bacteria responsible for cholangitis—KEEPS: Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Laboratory tests Imaging Note: If the patient is hemodynamically unstable and has clinical evidence of acute cholangitis, this imaging workup will be skipped. The patient should proceed directly to biliary decompression. Management Complications and Prognosis Complications Prognosis Differential Diagnosis The following table outlines […]
Primary Biliary Cholangitis
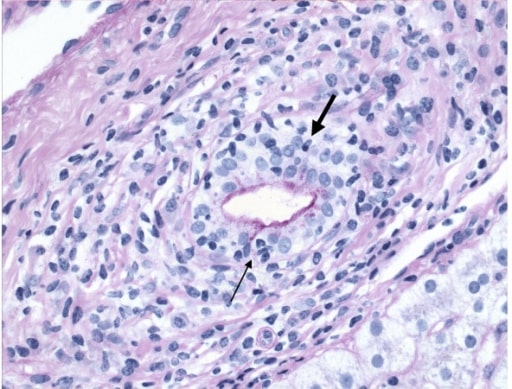
Overview Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Primary biliary cholangitis has a wide range of symptoms. The condition is often asymptomatic in the early phase and features symptoms of decompensated cirrhosis in the late phase. Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Management Differential Diagnosis References
Anal Cancer
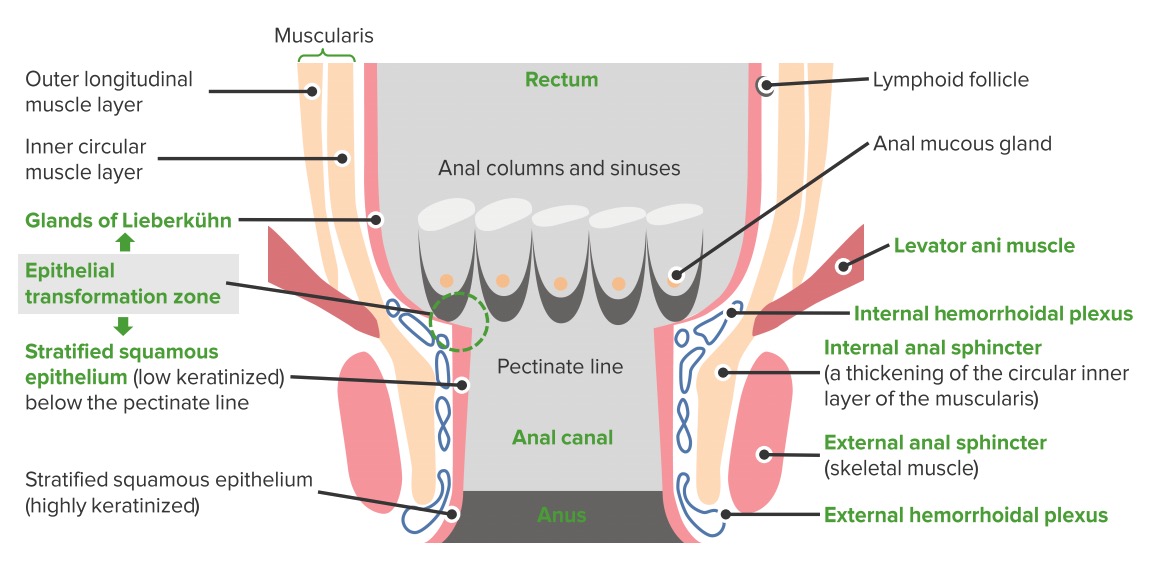
Overview Definition Anal cancers are cancers arising in the anal canal or anal margin. Anatomy: Histology: Epidemiology Etiology Risk factors for anal cancer: Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathophysiology Histologic types Lymphatic drainage of anal cancers Clinical presentation Diagnosis and Staging Clinical findings Diagnostic tests Staging Table: Anal cancer TNM staging Primary tumor (T) Regional lymph […]
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
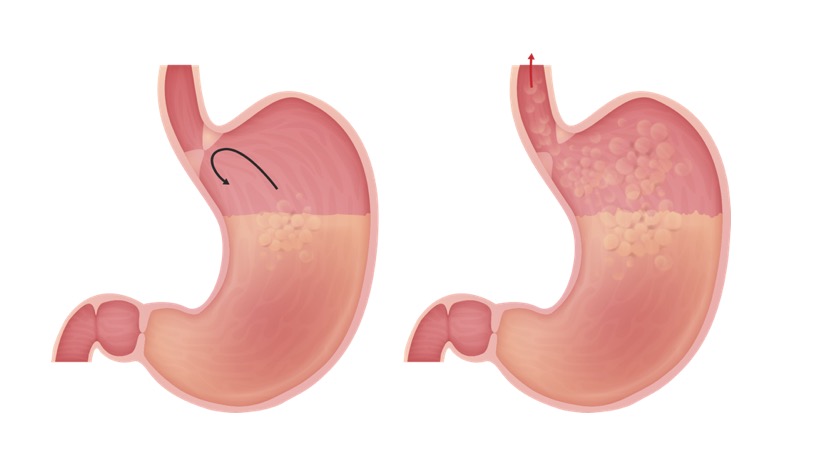
Epidemiology and Etiology Definition Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus that leads to symptoms or complications. Epidemiology Etiology Hiatal hernia Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Physiology Pathophysiology Factors leading to increased exposure of esophageal mucosa to gastric acid/contents: Clinical presentation Diagnosis Clinical diagnosis Ambulatory pH monitoring Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) Upper […]
Cholelithiasis
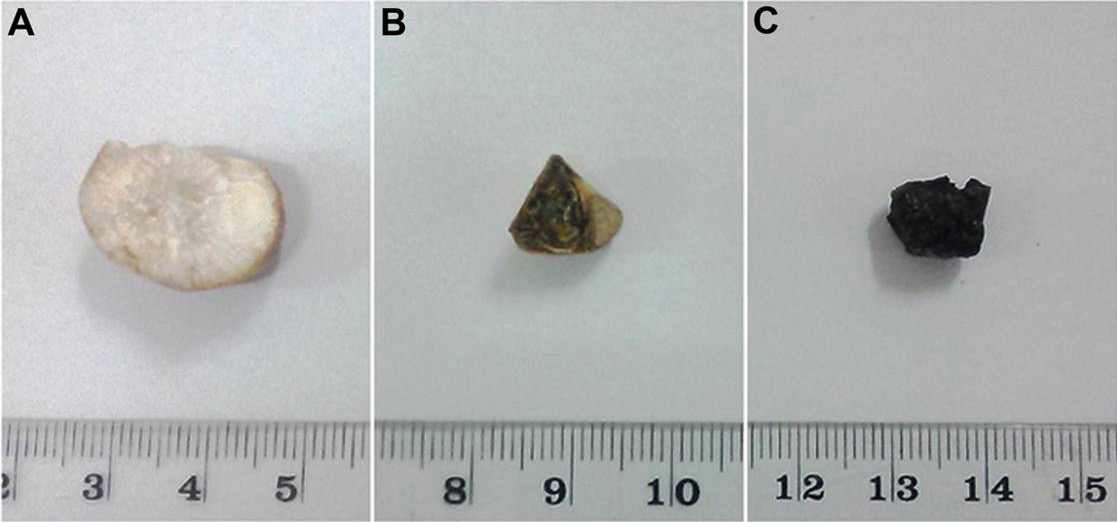
Overview Definition Cholelithiasis is the presence of gallstones in the gallbladder. Epidemiology Etiology Cholesterol stones (80%) Pigment stones (10%) Brown stones (“mixed”; 10%) Mnemonic Risk factors for cholesterol stones: 4 Fs Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathophysiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Management Medical management Surgical management Complications Condition Pathology Clinical presentation Laboratory studies Diagnostic imaging Management Cholecystitis […]
Giant Cell Arteritis
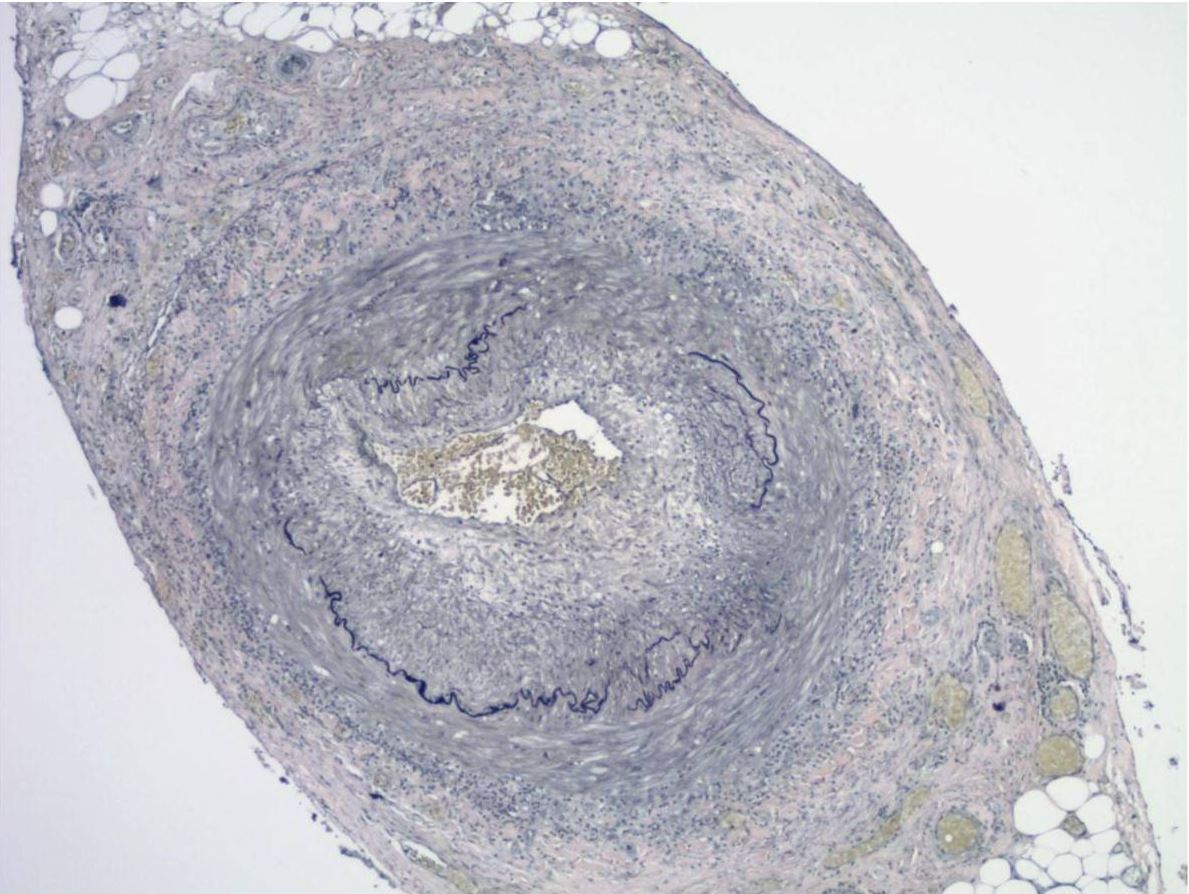
Overview Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is caused by a complicated cascade of vascular inflammation, damage, and dysfunctional repair: Clinical Presentation Clinical manifestations Physical exam Diagnosis Diagnostic algorithm Diagnostic modalities Management Treatment options General measures Differential Diagnosis References
Peritonsillar Abscess
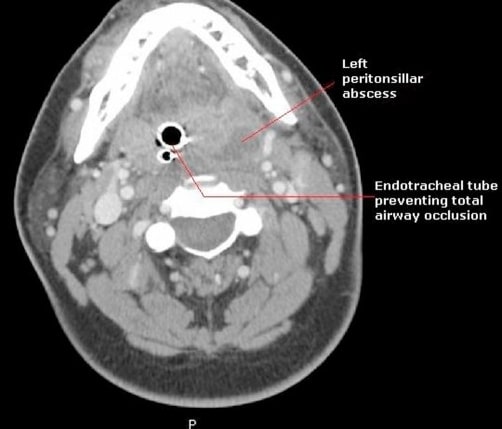
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Clinical Presentation Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Management Complications The spread of the infection into other parts of the body can lead to serious complications. These include the following: Differential Diagnosis References
Celiac Disease
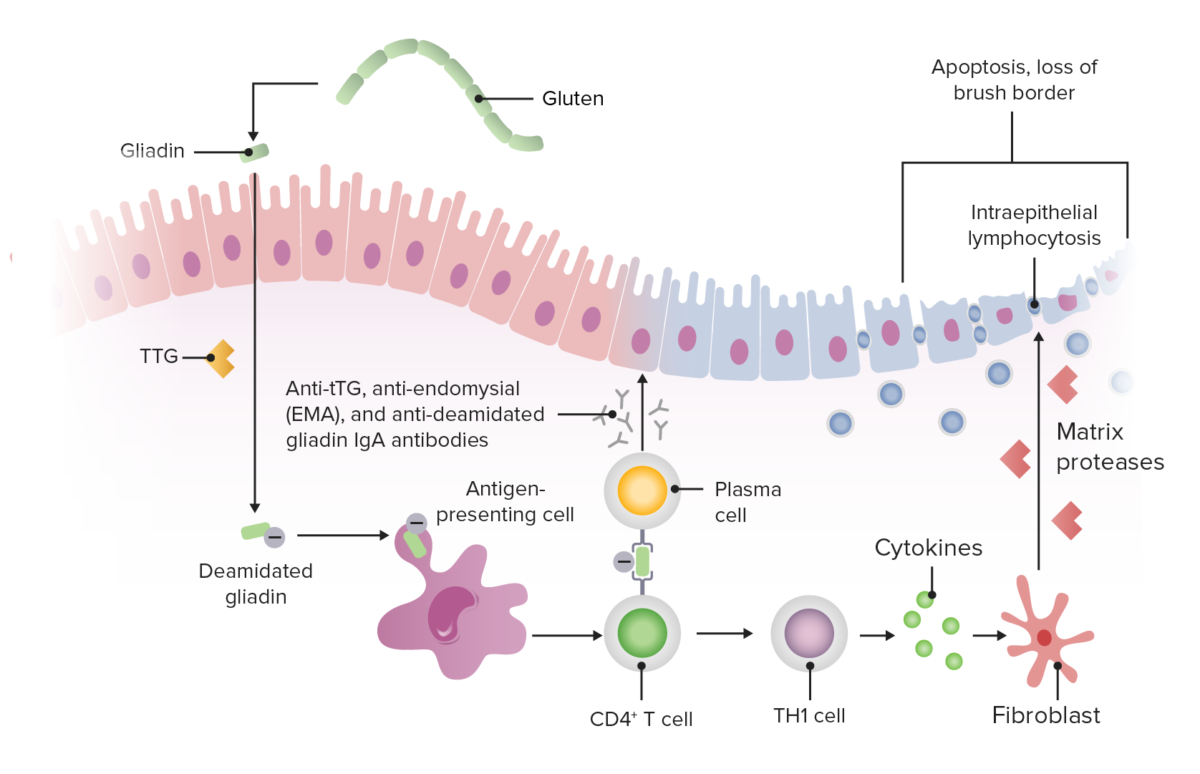
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Environmental, immunologic, and genetic factors contribute to the disease process: Pathophysiology Gluten peptides trigger the innate immune response in intestinal epithelial cells, leading to T cell–mediated mucosal damage of the proximal small intestine (distal duodenum and proximal jejunum). Clinical Presentation Clinical manifestations Celiac disease may present in infancy or in […]
Cell Injury and Death
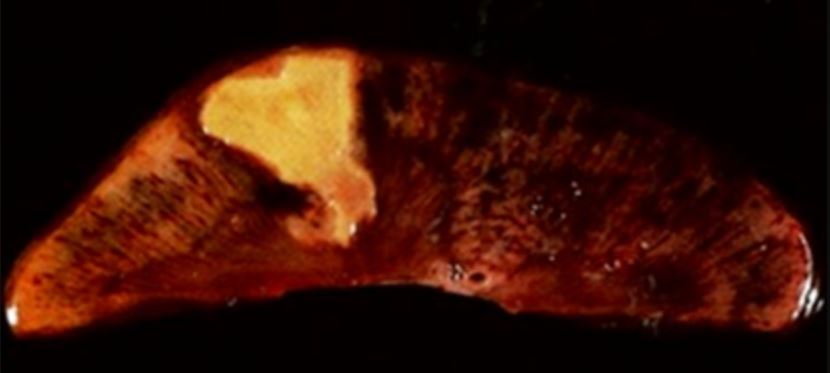
Overview Definitions Cell injury Cell death Etiology and Types of Cell Injury Injurious stimuli Types of cell injury Cell Injury by Mitochondrial Damage Mitochondria Consequences of mitochondrial damage Cell Injury by Abnormal Calcium Homeostasis Calcium homeostasis Consequences of impaired calcium homeostasis Cell Injury by DNA and Membrane Damage DNA damage Consequences of damaged DNA Membrane […]