Approach to Genital Ulcers (Clinical)
Etiologies, Epidemiology, and Pathophysiology Genital ulcers are most commonly due to sexually transmitted infections (STIs); however, there are numerous non–sexually transmitted etiologies, as well. STIs causing genital ulcers[1–4] Genital ulcers due to other causes[2–4] Table: Characteristics of genital ulcers[1–4] Disease Etiology Incubation period Ulcers painful? Other disease characteristics Genital herpes[14–19] HSV 2‒7 days Yes Recurrent […]
Celiac Disease (Clinical)
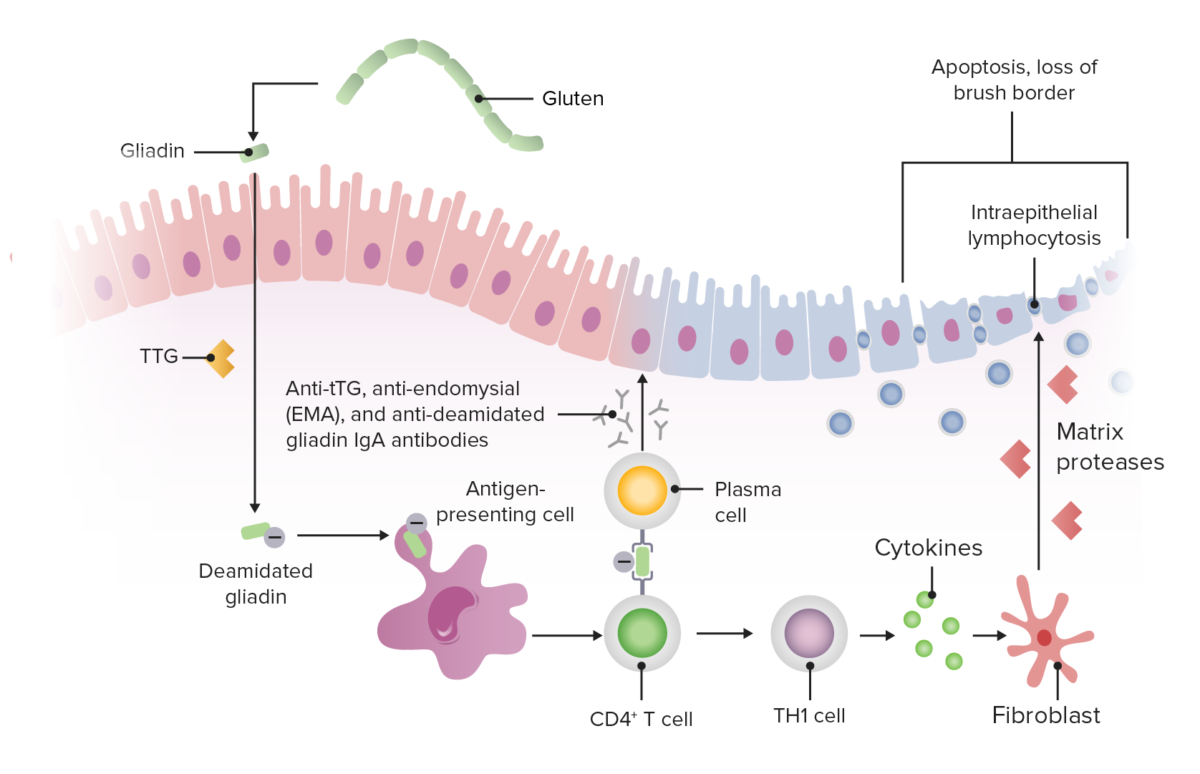
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[1,2,6,8,12] Etiology[1,2,6,8] Environmental, immunologic, and genetic factors contribute to the disease process: Pathophysiology Gluten peptides trigger the innate immune response in intestinal epithelial cells, leading to T cell–mediated mucosal damage of the proximal small intestine (distal duodenum and proximal jejunum).[2,8] Clinical Presentation Clinical manifestations[1,2,6–8] Gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms: Extraintestinal manifestations: Table: Manifestations and […]
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) (Clinical)

Overview Definition Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a pathogenic process that develops when a microorganism (usually bacteria) enters the body through the urethra and travels to the bladder and/or kidneys. Epidemiology[8,9,26] Prevalence: Risk factors[3,7–9,26] Etiology and Pathophysiology UTIs are caused by bacteria, and occasionally other organisms, that ascend into the urinary tract. Escherichia coli[7,8,26] Other […]
Acute Bronchitis (Clinical)
Overview Definition Acute bronchitis is an acute inflammation of the large airways of the lower respiratory tract wherein the pulmonary parenchyma is not affected. Epidemiology[15,16] Acute bronchitis is a very common disease. Etiology[15,16] Pathophysiology Acute bronchitis is characterized by infection and inflammation of the tissue lining the bronchi.[16] Clinical Presentation Acute bronchitis is typically a […]
Peptic Ulcer Disease (Clinical)
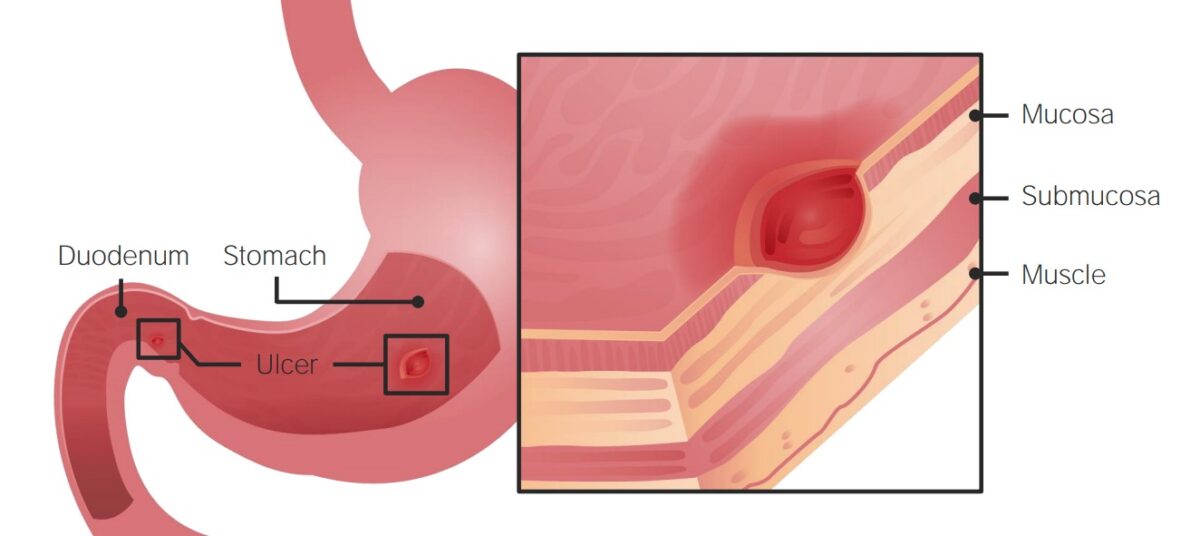
Overview Definition Peptic ulcers are mucosal defects > 5 mm in diameter that penetrate the muscularis mucosae in the wall of the stomach or duodenum. Epidemiology[2,3] Etiology[1-3,13] Risk factors[5–7,13] Pathophysiology Classification[2,3,13] Pathophysiology[3,8,13] PUD results from an imbalance in offending agents (acid, pepsin) and defense mechanisms, which leads to mucosal erosion. Clinical Presentation PUD may be […]
Labial and Genital Herpes (Clinical)
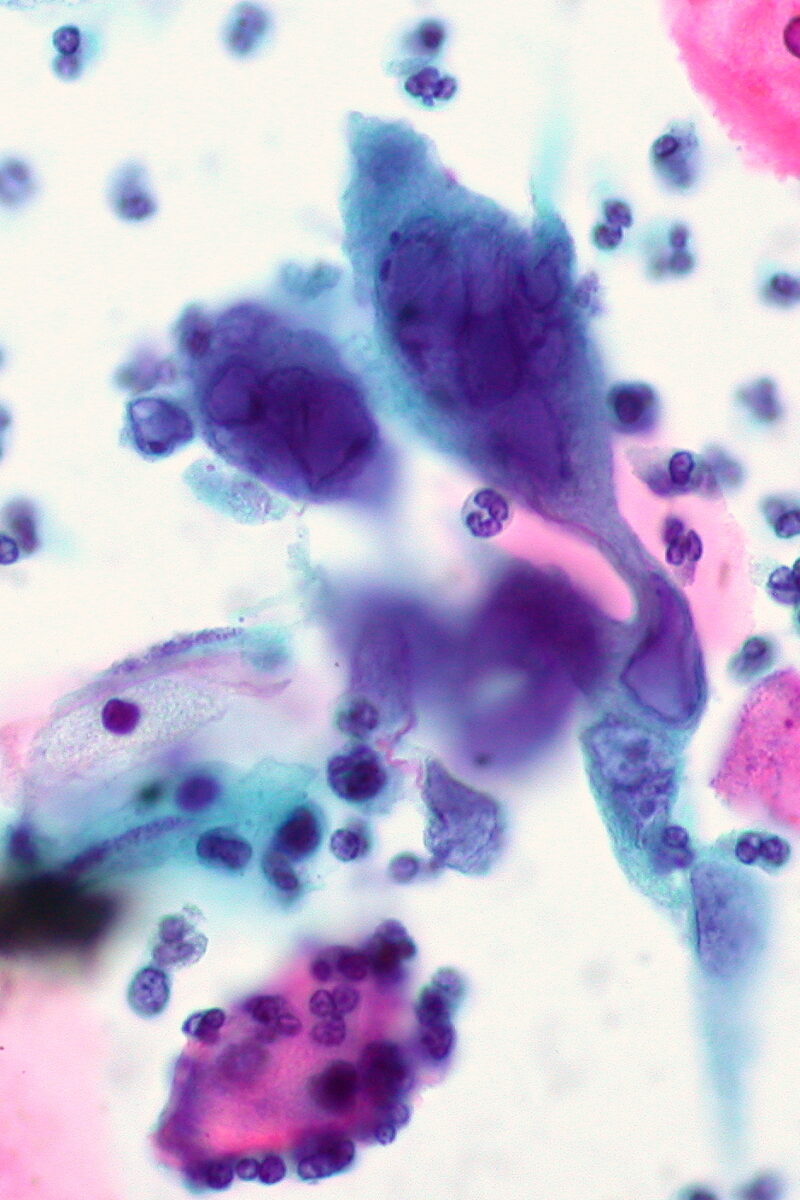
Definition Genital herpes is a mucocutaneous ulcerative disease caused by either herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1 or 2.[1,2,10] HSV-1: HSV-2: Types of infections: Epidemiology Etiology Causative agent: herpes simplex virus[1] Transmission[1,2,10] Risk factors[1,2,10] Pathophysiology First infection[1] Primary infection and non-primary infections occur when the virus travels through tiny breaks or even microscopic abrasions in […]
Myocarditis (Clinical)
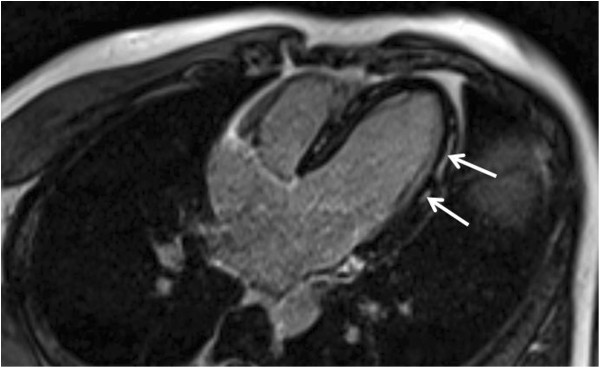
Overview Definition Myocarditis is an inflammatory disease of the myocardium. Epidemiology[5,11] Etiology[2,10,11] The most frequent causes of myocarditis are presumed viral infections, cardiotoxins such as those found in chemotherapy regimens and recreational drugs, and immune system activation. Infectious causes of infectious myocarditis[2,10,11] The following table summarizes the infectious causes of myocarditis. Keep in mind that […]
Vitiligo (Clinical)
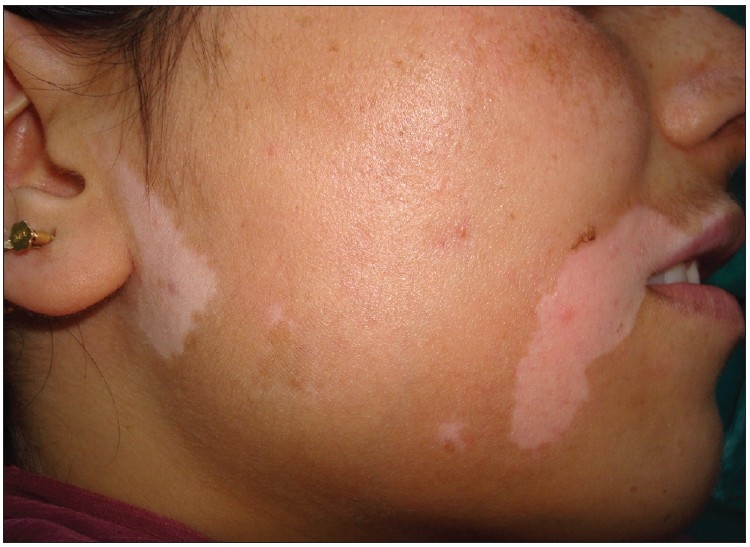
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Vitiligo is a progressive skin condition in which there is destruction of melanocytes resulting in the loss of skin pigmentation. Epidemiology[1] Etiology and Pathophysiology Etiology[1,3,8] The cause of vitiligo is unknown but is postulated to be a result of multiple factors. Pathophysiology[1,8] Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis Clinical presentation Vitiligo results in […]
Atrioventricular block (AV block) (Clinical)
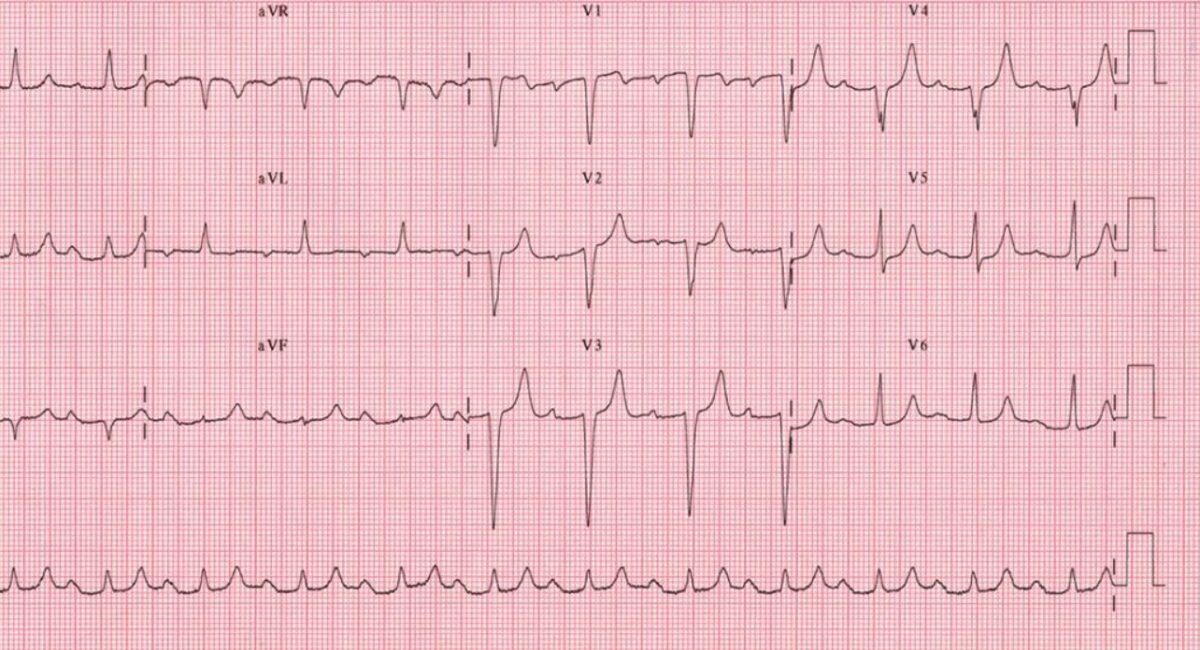
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[1] Etiology[1,2,7,10] Pathophysiology and Classification Atrioventricular (AV) block is a delay, or interruption, in the electrical impulse as it passes from the atria to the ventricles through the AV node or the His-Purkinje system. Atrioventricular block is classified based on the severity of the disruption. 1st-degree AV block[1,7,10] 2nd-degree AV block[1,4,5,7,10] 2nd-degree […]
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (Clinical)
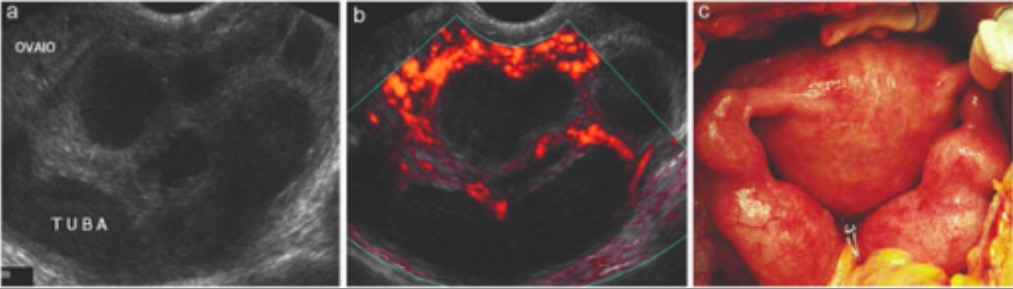
Overview Definition Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an acute upper genital tract infection in women that affects the uterus, fallopian tubes/oviducts, ovaries, and possibly the adjacent pelvic organs. Epidemiology[4,5] Etiology[1,4,5,7] Pathophysiology Normal pelvic protection[2,4] Pelvic infection[2‒4] Clinical Presentation Symptoms typically occur rather acutely over several days, though subclinical or chronic PID may develop more slowly, […]