Nephrolithiasis (Clinical)
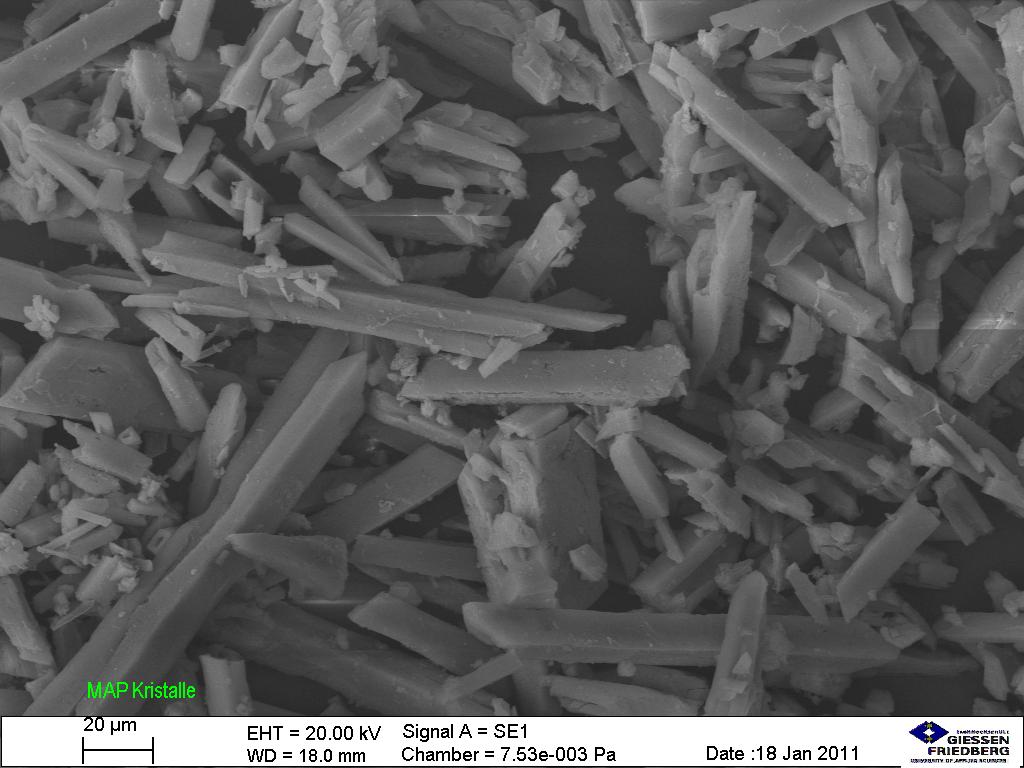

Overview Definition[15,18] Nephrolithiasis (also known as kidney stones, urolithiasis, or urinary calculi) is the formation of stones anywhere along the urinary tract. Classification[1,2,15,18] There are 5 main types of kidney stones: Epidemiology[18] Etiology[2,3,18] Nephrolithiasis occurs when normally soluble material supersaturates the urine and crystal formation begins. Risk factors[2,3,18] Pathophysiology Underlying medical (including genetic) and environmental […]
Carotid Artery Stenosis (Clinical)
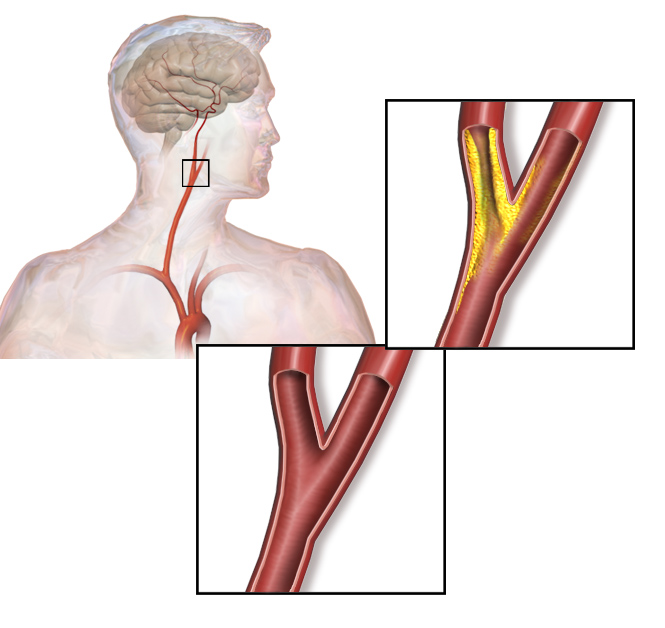
Overview Definition Carotid artery stenosis is a narrowing of the common and internal carotid arteries (ICAs) secondary to atherosclerosis. Epidemiology[1–3,5] Etiology[5] Pathophysiology Carotid stenosis can cause symptoms from a state of low flow or embolization. Low flow results from progressive narrowing of the carotid artery: Embolization: Clinical Presentation Asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis: carotid atherosclerosis without […]
Septic arthritis (Clinical)
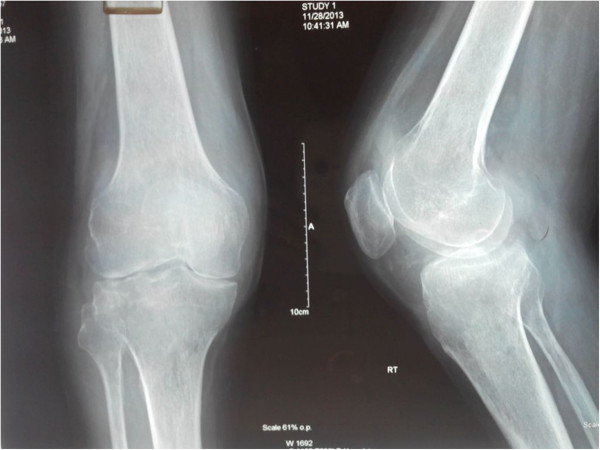
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[1,9] Etiology[1,7] The majority of septic arthritis infections are monomicrobial. Common organisms include: Risk factors[1,3,5,7,11] Table: Most common organisms in septic arthritis, based on some notable underlying risk factors Risk factors Infectious agents No specific risk factor S. aureus Prosthetic joint replacement S. aureus (particularly MRSA) S. epidermidis (creates biofilms on prosthetics) […]
Gonorrhea (Clinical)
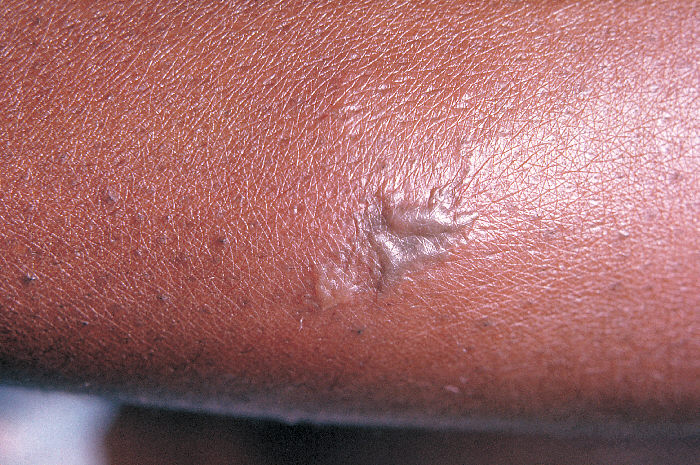
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[2,3,5,8] Etiology[1,2,8] Gonorrhea is caused by the pathogen Neisseria gonorrhoeae (N. gonorrhoeae): Risk factors: Pathophysiology Transmission[1,2] Virulence factors[1,6,8] Pathogenesis[1,6,8,12] Antimicrobial resistance[2,13] Clinical Presentation Urogenital infection in men[2,3,9,17,18] Urogenital infection in women[2,3,9,17,18] Infections in individuals following genital reconstructive surgery (GRS)[17] Extragenital infections[2,3,9] Disseminated gonococcal infection[3,10,17] Clinical presentation in children[2,21] Newborn infections: After the […]
Graves’ Disease (Clinical)
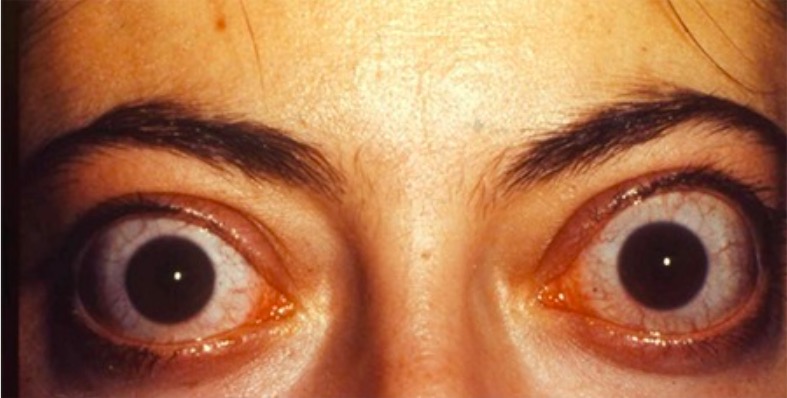
Overview Definition Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder in which antibodies against the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) receptors cause the thyroid gland to hyperfunction. The syndrome may have the following features: Epidemiology[4,6,8,9] Risk factors[4-6,8,9] Susceptibility to Graves’ disease is considered to be a combination of multiple factors. Pathophysiology Hyperthyroidism and goiter[4,6] Orbitopathy and myxedema[3,4,6] Clinical Presentation […]
Acute Pancreatitis (Clinical)
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[3,14,15] Etiology[1,3,7,11,14,15] Classification Acute pancreatitis is classified according to the Revised Atlanta Classification system, which describes: Table: Acute pancreatitis classification Type Interstitial edematous pancreatitis Necrotizing pancreatitis CT findings Edema is hypodense Heterogeneous contrast enhancement Necrotic areas show reduced contrast enhancement or lack thereof Fluid collection ≤ 4 weeks (no definable wall) Acute […]
Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis (Clinical)
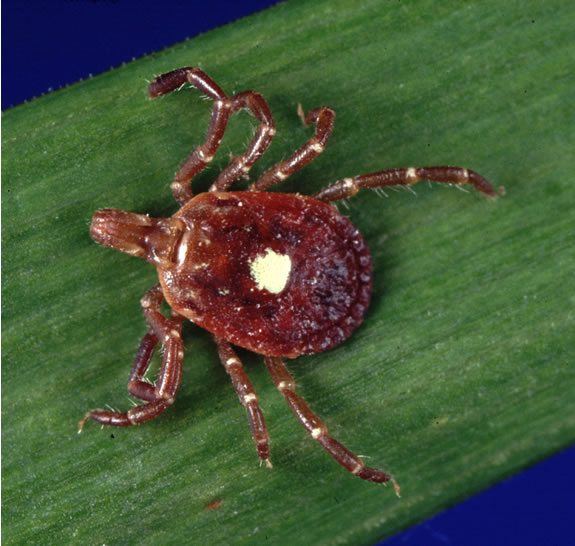

General Characteristics Basic features of Ehrlichia and Anaplasma[4,8,9,12] Clinically relevant species[1,11] The most notable species are: Rare causes of ehrlichiosis in humans: Epidemiology and Risk Factors Epidemiology[8,9,11,13] Risk factors[11,13,14] For ehrlichiosis/anaplasmosis: For severe disease: Pathogenesis Transmission[11,13,14] Reservoirs[5,9,14] A wide range of wild and domestic animals can serve as reservoirs. The most notable are: Virulence factors[10,15] […]
Anal Fissure (Clinical)
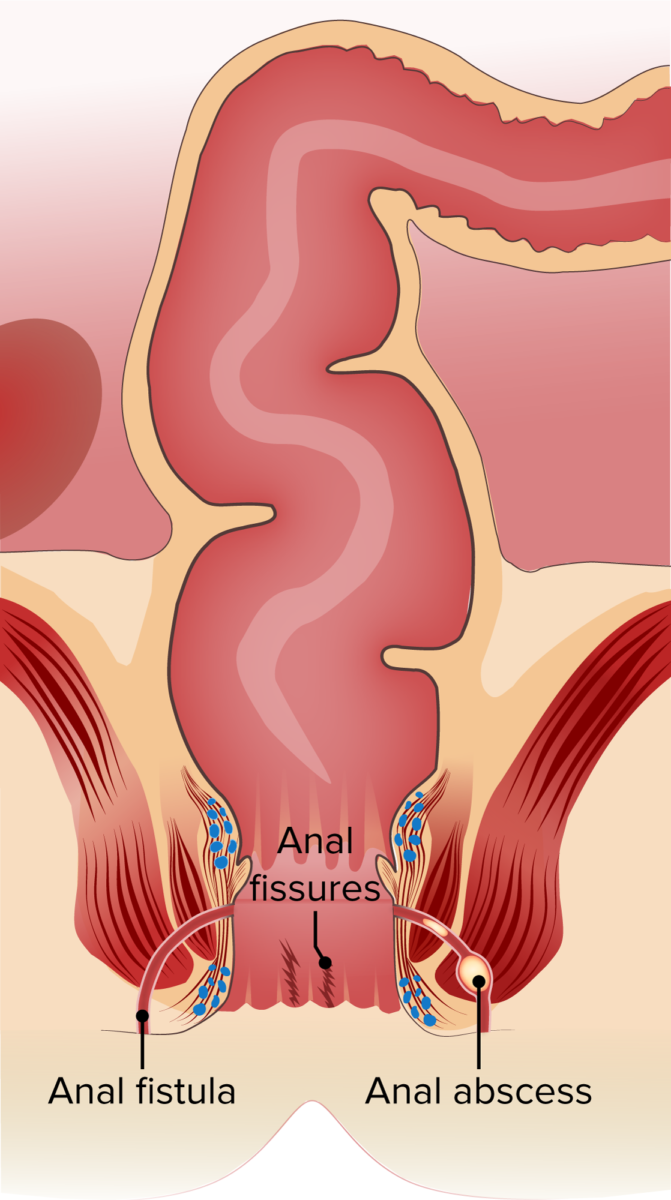
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Epidemiology[1,2,5] Etiology and Pathophysiology Etiology[1–3,7] Pathophysiology[1–3,5] Clinical Presentation Acute fissure[1–3,5,8] Chronic fissure[1–3,5,6,8] Diagnosis Mnemonic: The D’s of anal fissures: Management The following information is based on the practice guidelines from the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons and the American College of Gastroenterology. Management may be area-dependent; UK guidance on […]
Hemorrhoids (Clinical)
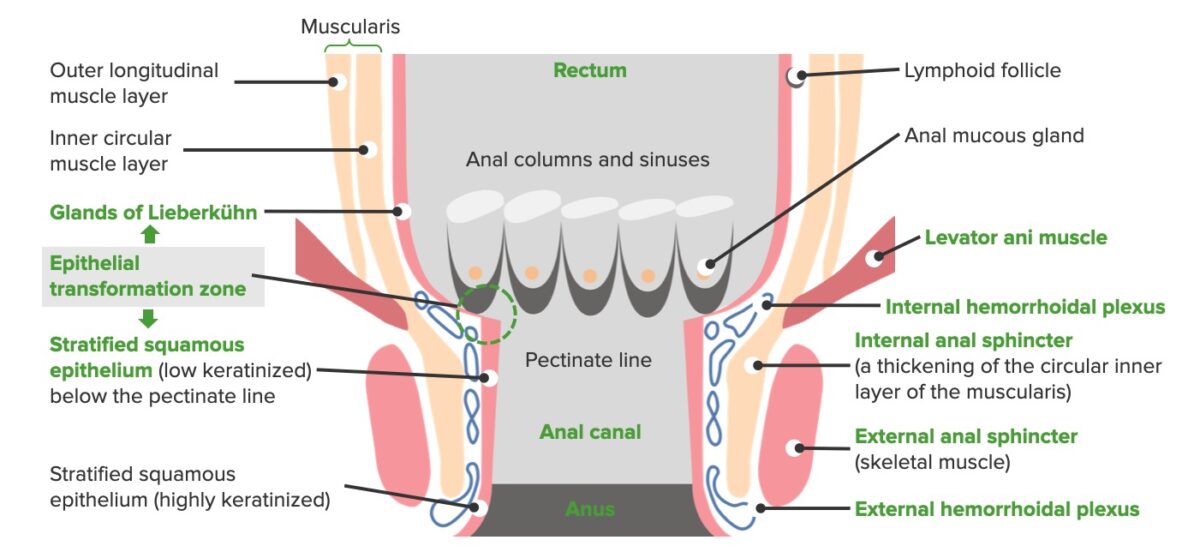
Overview Definition[2,3] Hemorrhoids are normal swollen vascular structures in the anorectal canal. Epidemiology[2,3,9] Etiology[2,9,10] Pathophysiology Pathogenesis[2–4,9] External hemorrhoids[2–4,9] Internal hemorrhoids[2–4,9] Clinical Presentation External hemorrhoids[2,3,9] Internal hemorrhoids[2,3,9] Diagnosis Physical examination[4–6,9,12] Laboratory studies and procedures Management Management may vary based on location. The following recommendations are based on US and international guidelines. Initial treatment approach Table: Hemorrhoid […]
Appendicitis (Clinical)

Overview Definition Appendicitis is the inflammation of the vermiform appendix. Epidemiology[1,4,5] Etiology[1,4,18] Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathophysiology[1,4,18] Time course[1,4] Early: Late: Perforation: Clinical presentation[1,4,8,9] Classic: Atypical: Anatomic factors: Diagnosis History[5–9] Physical exam[5–9] General: Abdominal exam: Rectal exam: Pelvic exam: Laboratory studies[2,5,6,9] Alvarado score[2,5,9] Table: Alvarado score Symptoms Migratory pain in the right iliac fossa 1 […]