Pericardial Effusion and Cardiac Tamponade
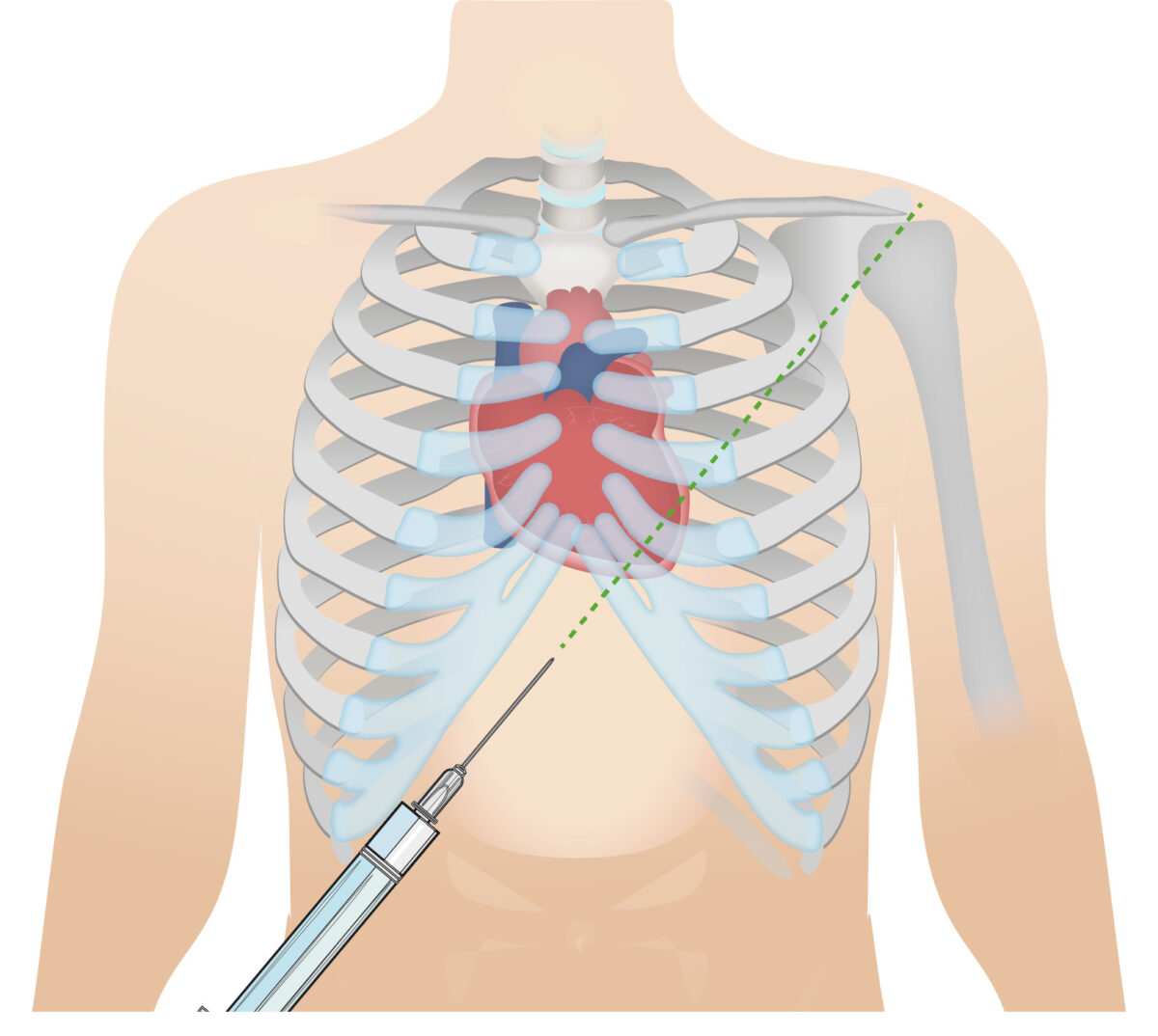
Epidemiology and Etiology Definition Pericardial effusion is the accumulation of fluid in the pericardial space. Cardiac tamponade is the accumulation of pericardial fluid sufficient to impair cardiac filling and cause hemodynamic compromise. The rate of fluid accumulation, and not necessarily the amount, is most important. Epidemiology Pericardial effusion: Cardiac tamponade: Etiology Many conditions are associated […]
Tumor Lysis Syndrome
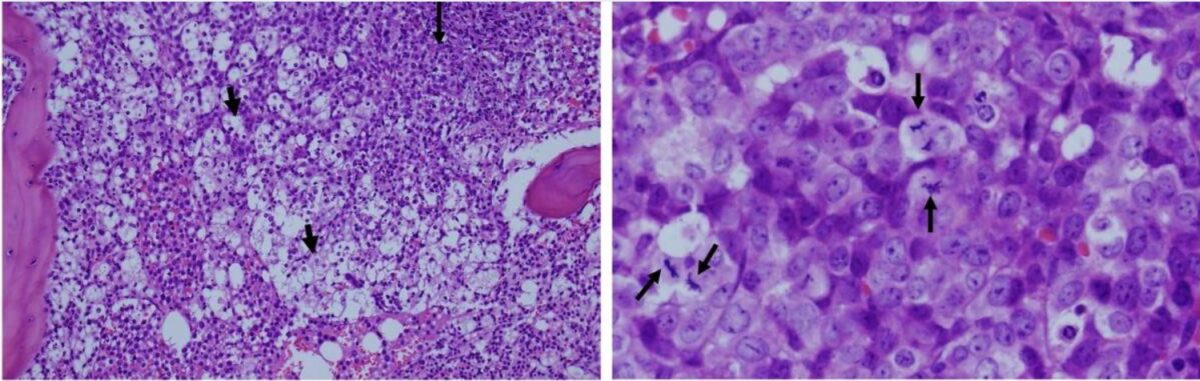
Overview Epidemiology National incidence reports are hampered by a lack of standard criteria for diagnosis. Etiology Tumor lysis syndrome results from massive tumor death and is primarily associated with the following hematologic malignancies: Risk factors Malignancy characteristics: Concurrent conditions: Pathophysiology Tumor lysis syndrome occurs secondary to the chemotherapeutic treatment of malignancies, resulting in massive cell […]
Acute Abdomen
Overview Definition Acute abdomen is the constellation of signs and symptoms associated with severe abdominal pain and peritonitis that frequently requires emergency surgical intervention. Epidemiology Etiology Nonsurgical causes of acute abdomen: Surgical causes of acute abdomen: Anatomy Boundaries of the abdominal cavity External anatomy For descriptive purposes, the abdomen can be divided into 4 quadrants […]
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
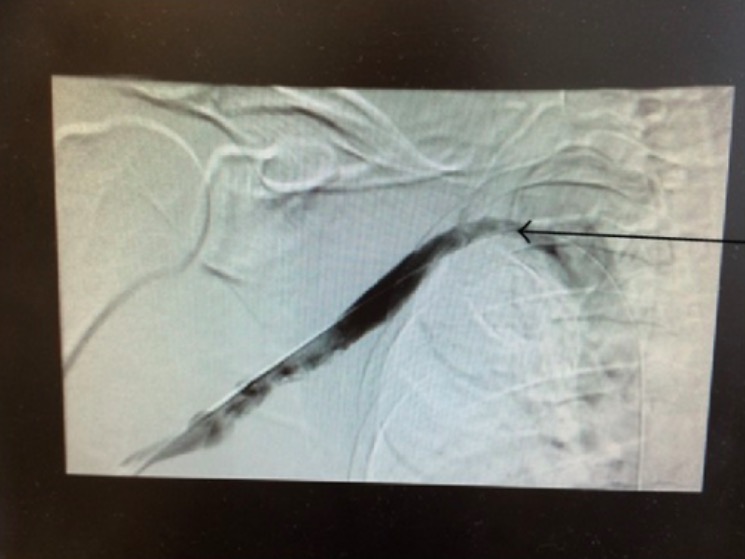
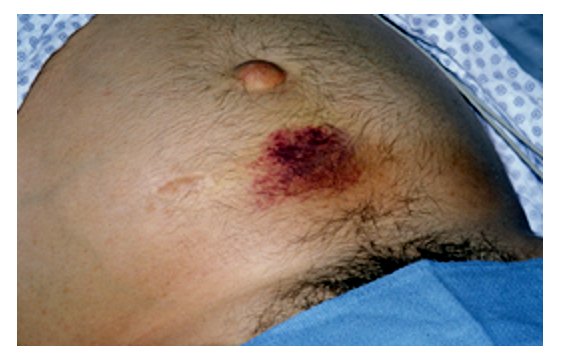
Overview Definition Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) refers to a spectrum of signs and symptoms that arise from the compression of the neurovascular bundle by any of the various structures within the confined space of the thoracic outlet, usually within the scalene triangle. Types Epidemiology Etiology Structural causes: Other causes: Anatomy and Pathophysiology Anatomy Thoracic outlet: […]
Perianal and Perirectal Abscess
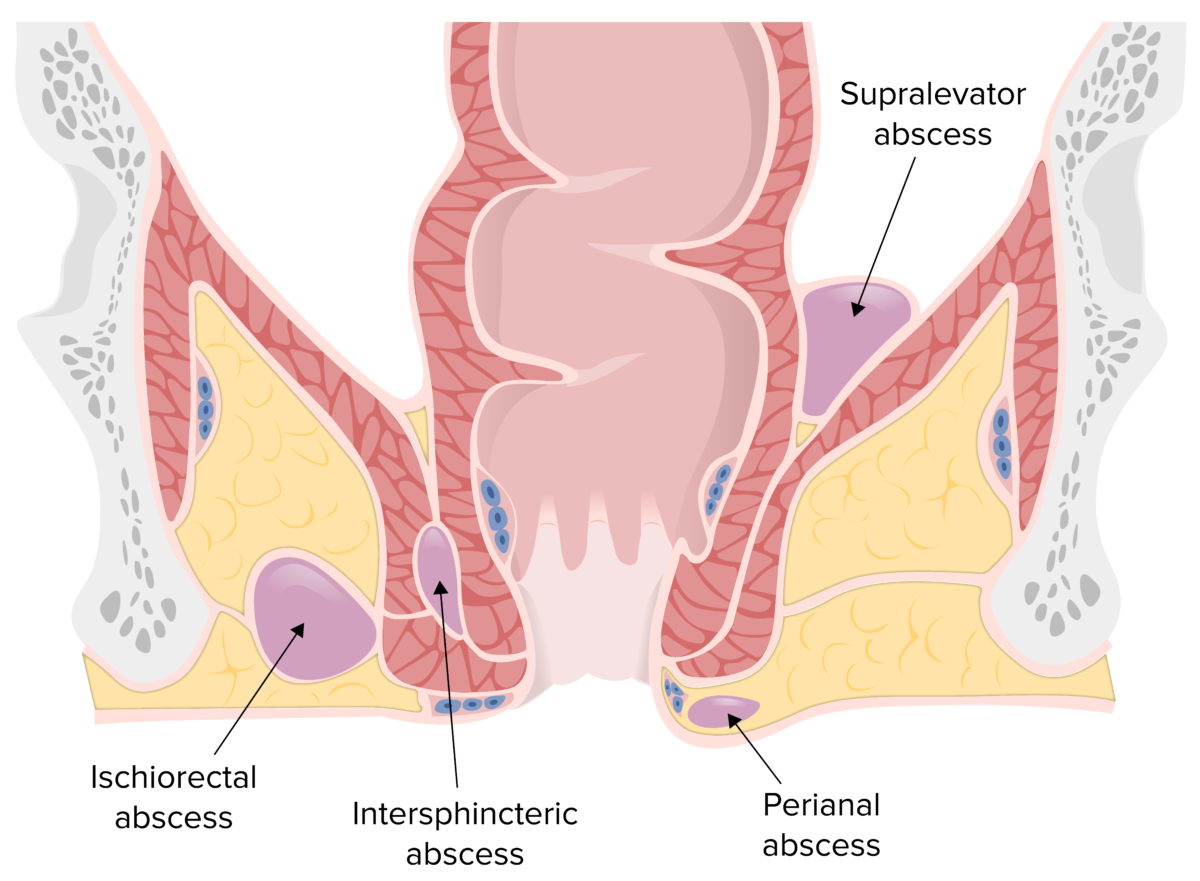
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Anal glands, found in the intersphincteric plane, drain into crypts found along the circumference of the dentate/pectinate line. Infection of an obstructed glandular crypt may occur due to: Common bacteria: Risk factors Classification and Pathophysiology Classification The classification of anorectal abscesses is based on their location. Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation and […]
Nephrolithiasis
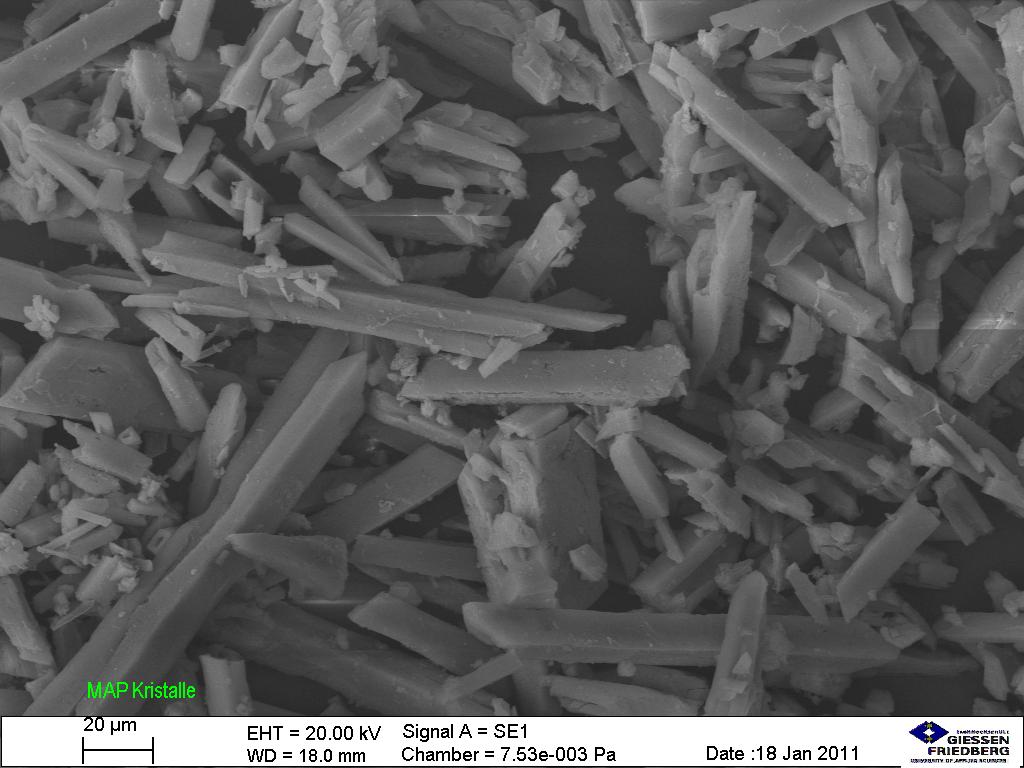

Overview Definition Nephrolithiasis (also known as kidney stones, urolithiasis, or urinary calculi) is the formation of stones anywhere along the urinary tract. Classification There are 5 main types of kidney stones: Epidemiology Etiology Normally soluble material supersaturates the urine and crystal formation begins. Risk factors: Pathophysiology Calcium oxalate stones Uric acid stones Struvite stones Calcium […]
Bronchiectasis
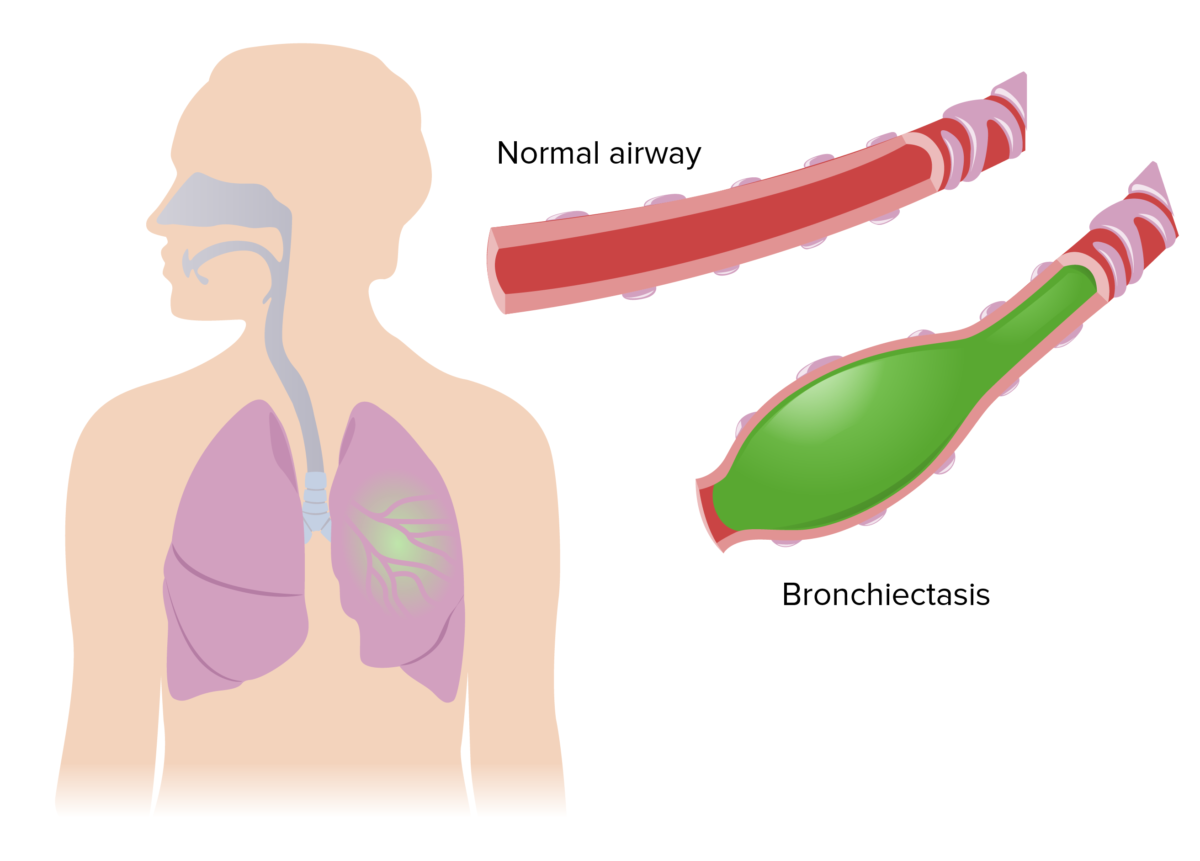
Epidemiology and Etiology Definition Bronchiectasis is a chronic disease in which there is permanent damage to the airways, causing abnormal bronchial dilation and mucosal inflammation. Epidemiology Prevalence is estimated to be approximately 350,000–500,000 cases in the United States. Age: Occurs at any age Increased incidence with older age More common in women Etiology Idiopathic (most […]
Myocarditis
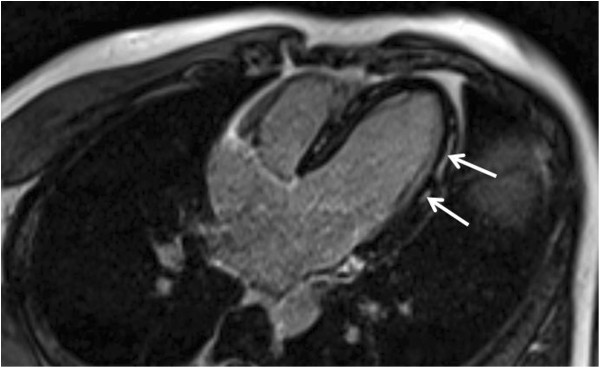
Overview Definition Myocarditis is an inflammatory disease of the myocardium. Epidemiology Etiology Causes of infectious myocarditis The following table summarizes the infectious causes of myocarditis. Keep in mind that this list is not exhaustive. Table: Causes of infectious myocarditis Viral Bacterial Parasitic Fungal Coxsackie B virus Adenovirus Parvovirus B19 Human herpesvirus 6 Epstein-Barr virus Cytomegalovirus […]
Hypocoagulable Conditions
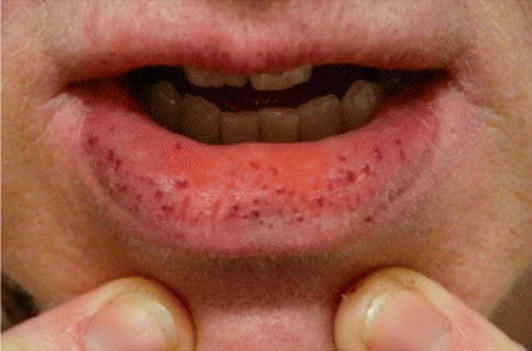
Overview Definition Hypocoagulable conditions, also known as bleeding disorders or bleeding diatheses, are a diverse group of diseases that result in abnormal hemostasis and increased bleeding risk. Physiologic hemostasis is dependent on normal structure and function of: Review of hemostasis The following is a summary of the process: Etiology The following conditions can lead to […]
Hemostasis
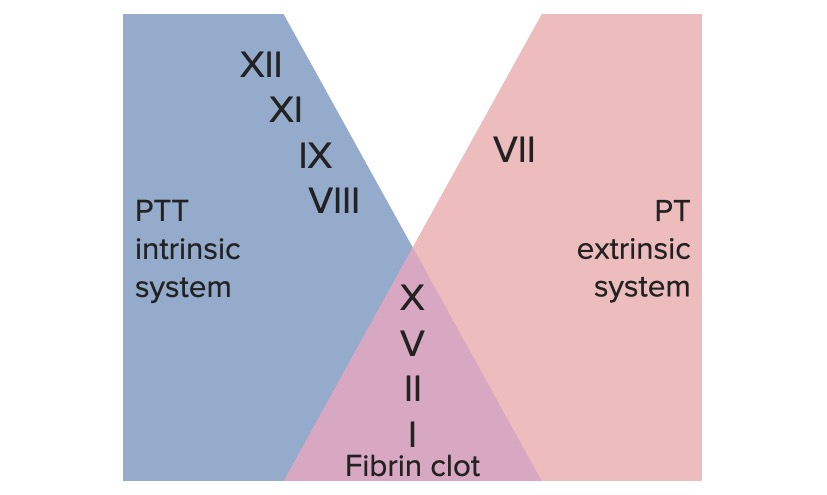
Definition and Phases Definition Hemostasis refers to the innate, stepwise body processes that occur following vessel injury, resulting in clot formation. Phases of the hemostatic process Vasoconstriction and Formation of the Platelet Plug Injured vessels vasoconstrict after endothelial injury. Additionally, exposure of blood to the subendothelial components triggers formation of the platelet plug. Vasoconstriction Endothelial […]