Sideroblastic Anemia
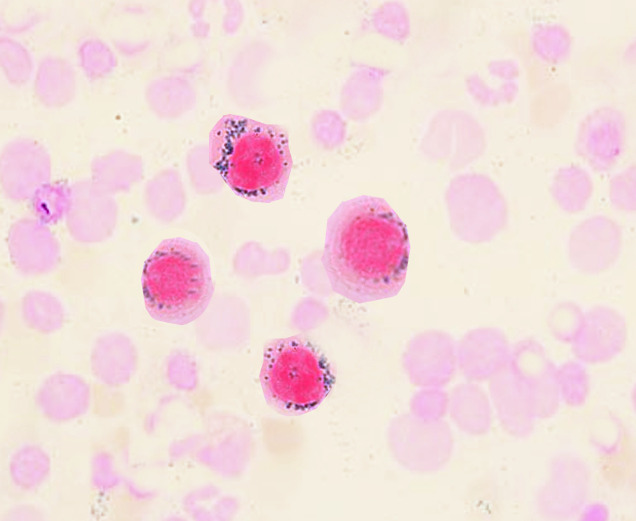
Overview Definition Sideroblastic anemias are a heterogeneous group of bone marrow disorders characterized by abnormal iron accumulation in the mitochondria of erythroid precursors. The distribution of the iron is ringlike around the nucleus, manifested by the precursors (ring sideroblasts) in the bone marrow. Epidemiology A rare disease → incidence and prevalence not well characterized Men […]
Brain Abscess
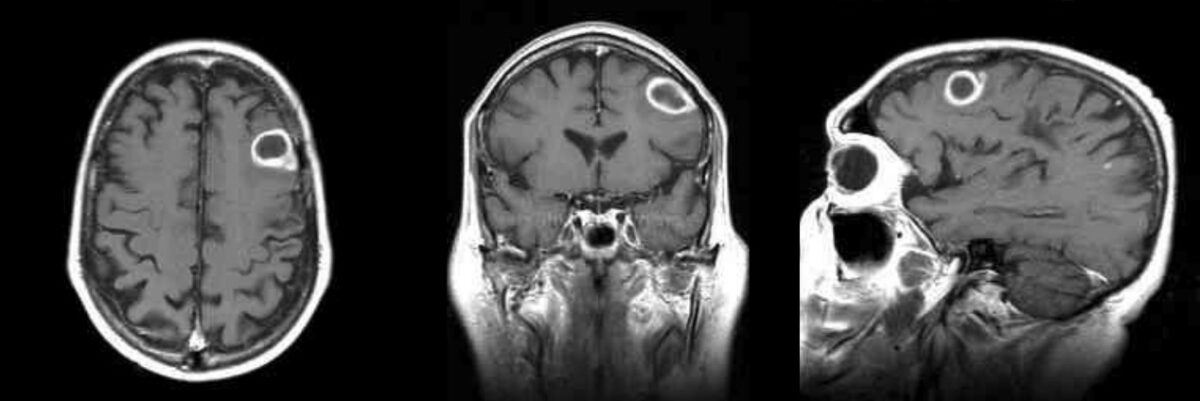
Overview Definition Brain abscess is an uncommon but life-threatening infectious collection of pus in the brain parenchyma. Epidemiology Etiology There are 2 routes of the spread of infection to the brain: Organisms causing brain abscess: Risk factors: Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathogenesis Stages of development of brain abscess after infection Early cerebritis (days 1–3): Late […]
Lungs: Anatomy
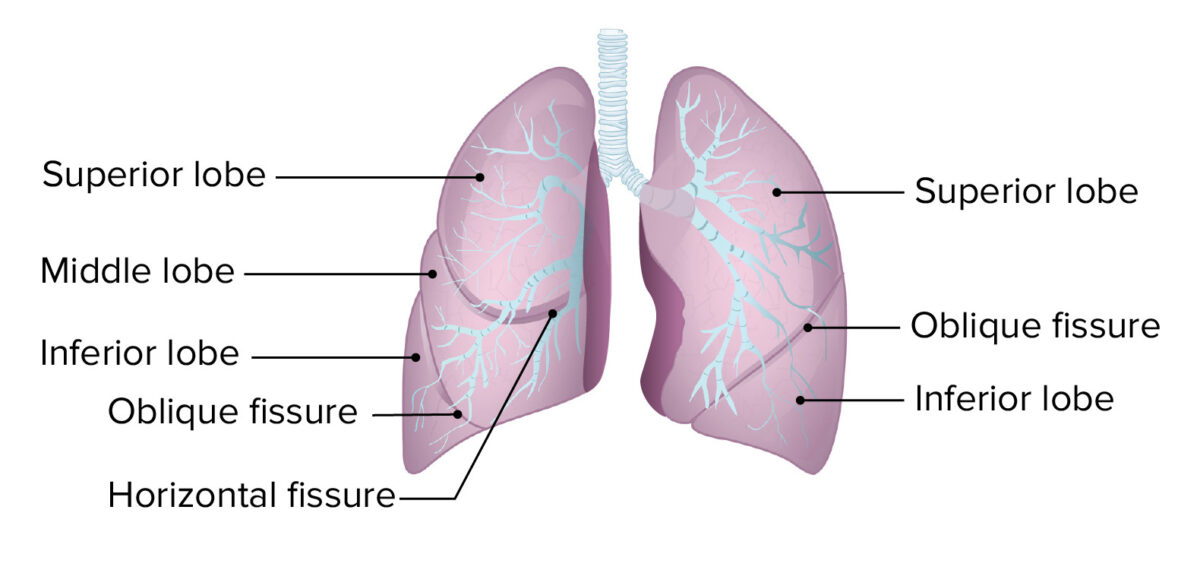
Development Development of the tracheobronchial tree and lungs occurs in 5 stages. The tracheobronchial tree originates from the foregut of the embryonic gut tube, beginning at week 4 of gestation and ending in childhood. Table: Development of the tracheobronchial tree and lungs, and clinical relevance Stage Description Clinical relevance Embryonic period Occurs during weeks 4–7 […]
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
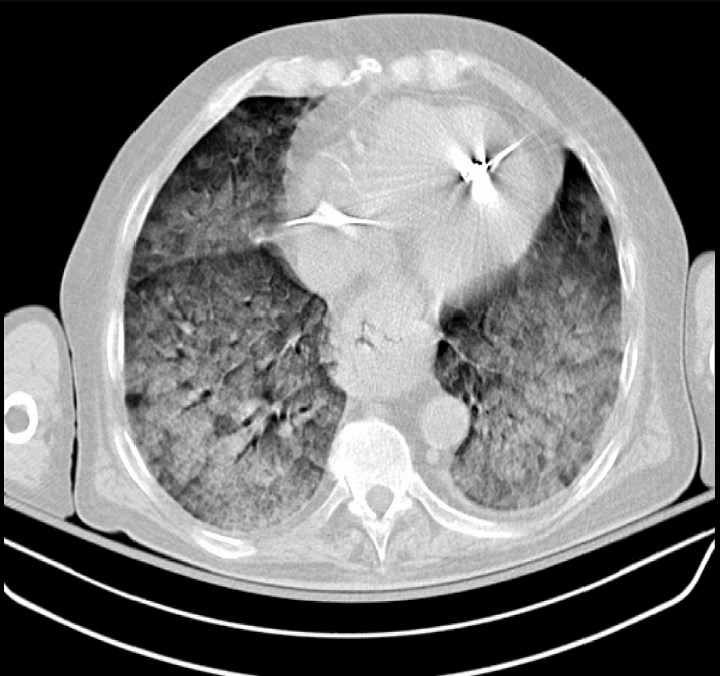
Overview Definition Acute respiratory distress syndrome is a clinical syndrome (not a pathological diagnosis) characterized by a sudden onset of hypoxemia and bilateral pulmonary edema without cardiac failure. The underlying mechanism of ARDS is diffuse alveolar damage (DAD): Acute respiratory distress syndrome is clinically diagnosed using the Berlin diagnostic criteria. Epidemiology Etiology Acute respiratory distress […]
Pulmonary Fibrosis
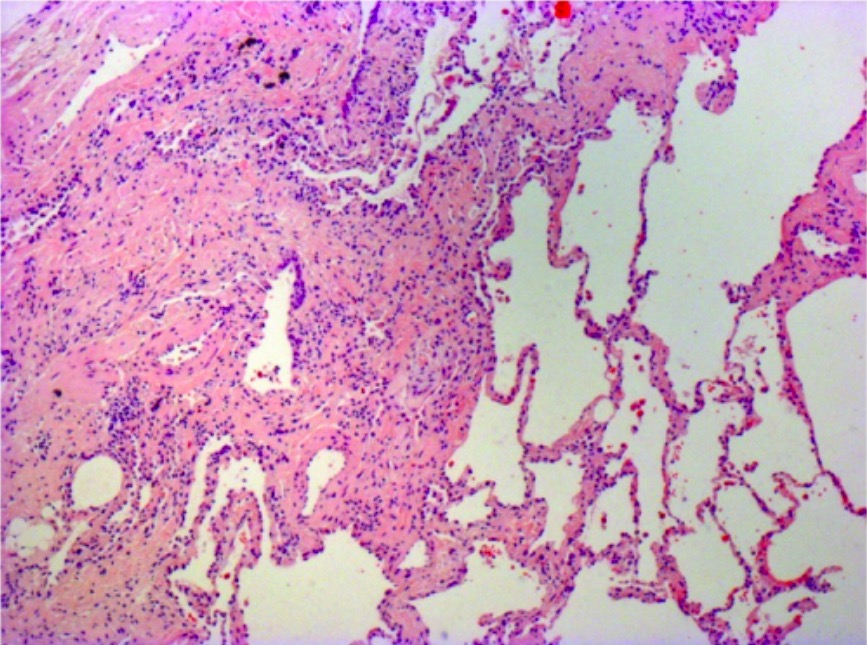
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is the most common type of interstitial lung disease (ILD) and is characterized by chronic, progressive, irreversible fibrosis of the lung parenchyma. Epidemiology IPF has been difficult to study because of its rarity and evolution in diagnostic practices. Etiology and Pathophysiology Etiology The cause of IPF remains […]
Thrombocytopenia
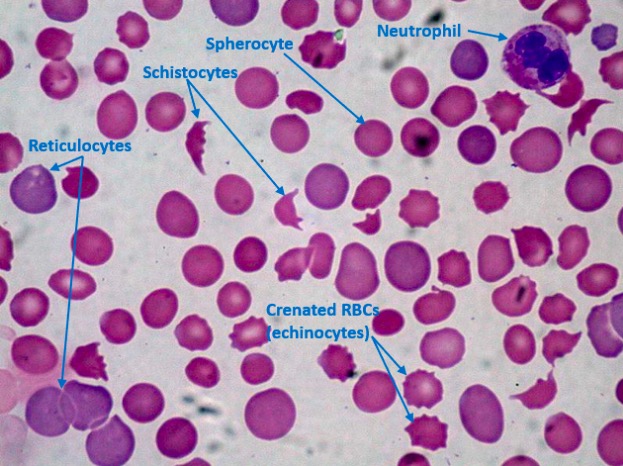
Overview Definition Thrombocytopenia is a deficiency of platelets, typically defined as < 150,000 platelets per microliter of whole blood. Epidemiology Classification Thrombocytopenia can be classified as mild, moderate, or severe on the basis of platelet counts: Etiology Thrombocytopenia can be caused by decreased production, increased destruction, or sequestration of platelets. Causes of thrombocytopenia Table: Causes […]
Dissection of the Carotid and Vertebral Arteries
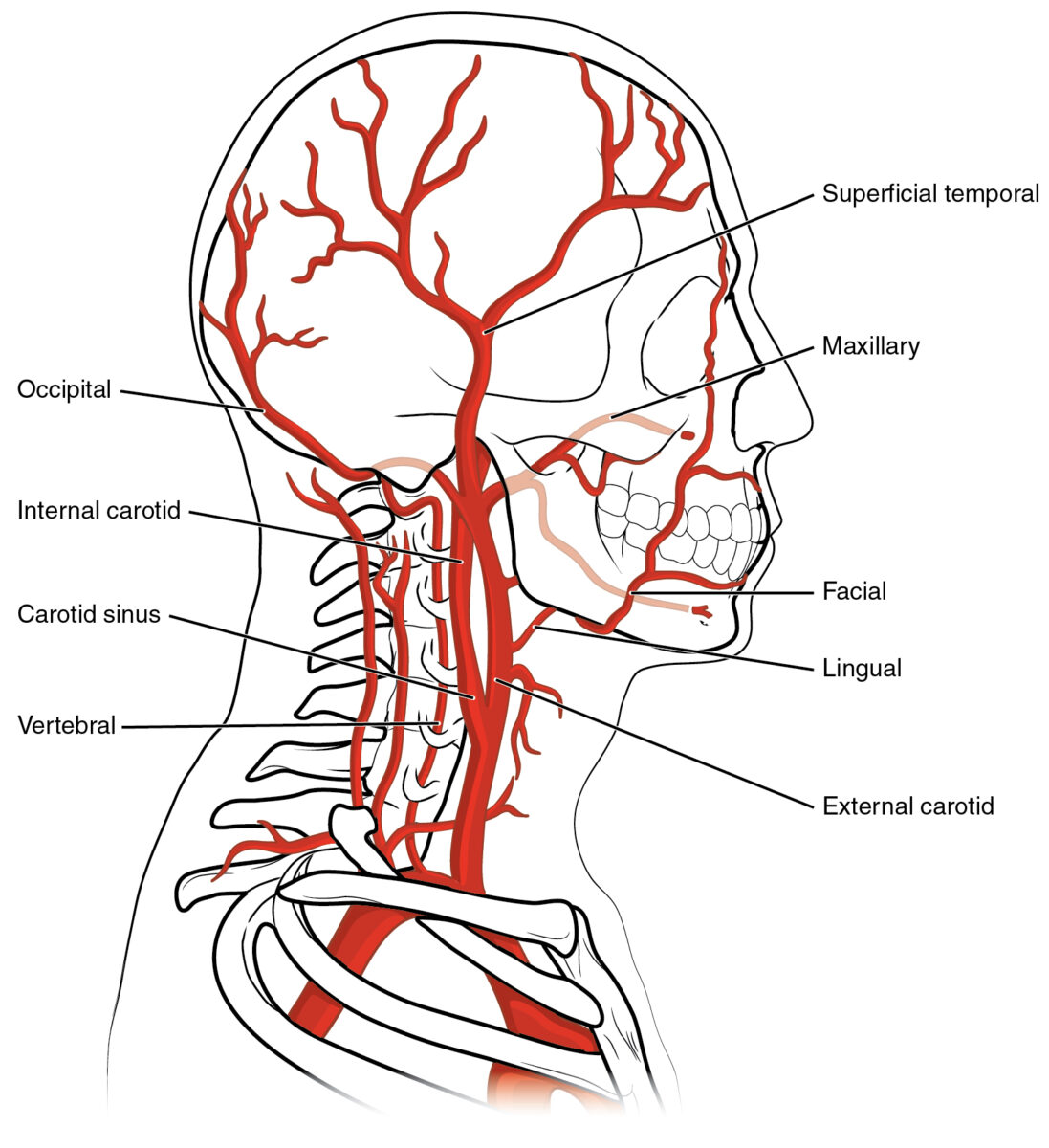
Overview Definition Arterial dissection is a violation of the structural integrity of the arterial wall that results in blood accumulating between the layers. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathophysiology Dissection formation: Most common locations: Pathophysiologic effects: Clinical presentation Local symptoms: Ischemic symptoms: Subarachnoid hemorrhage: Diagnosis History Physical exam Imaging Management Local nonischemic symptoms TIA […]
Atelectasis
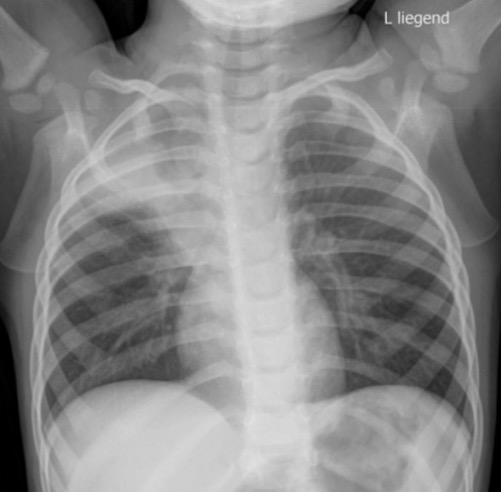
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Atelectasis is the partial or complete collapse of lung tissue. Epidemiology Risk factors Etiology and Pathophysiology Classification Atelectasis is classified on the basis of the underlying pathophysiology. Obstructive atelectasis Etiology: Pathophysiology: Nonobstructive atelectasis Relaxation atelectasis: Compressive atelectasis: Adhesive atelectasis: Cicatricial atelectasis: Replacement atelectasis: Rounded atelectasis: Clinical Presentation Symptoms Physical exam Complications […]
Hemoptysis
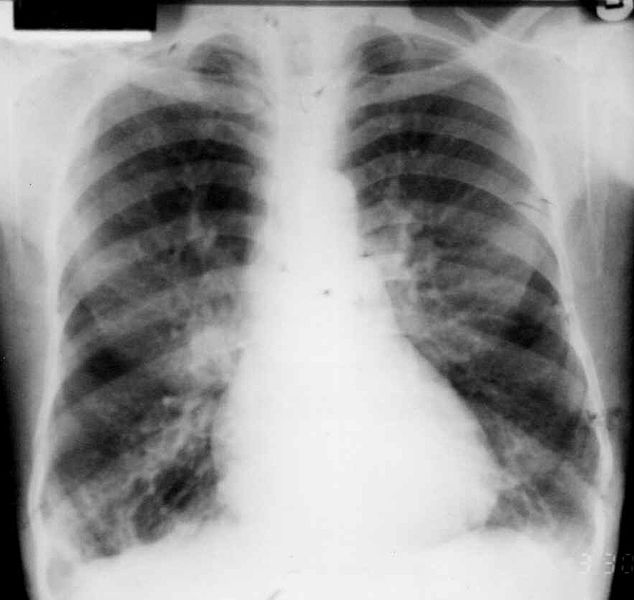
Overview Definition and classification Hemoptysis is defined as the expectoration of blood originating in the lower respiratory tract. Hemoptysis is a consequence of another disease process and can be classified as either life threatening or non-life threatening. Epidemiology Etiology Table: Causes of hemoptysis Airway disease Bronchitis*: acute bronchitis, exacerbation of chronic bronchitis Cystic fibrosis (CF)-related […]
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)

Overview Definition Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a pathogenic process that develops when a microorganism (usually bacteria) enters the body through the urethra and travels to the bladder and/or kidneys. Epidemiology Prevalence: Risk factors Etiology and Pathophysiology Escherichia coli Other bacteria Non-E. coli bacteria are associated with risk factors for drug resistance or in specific […]