Vesicoureteral Reflux
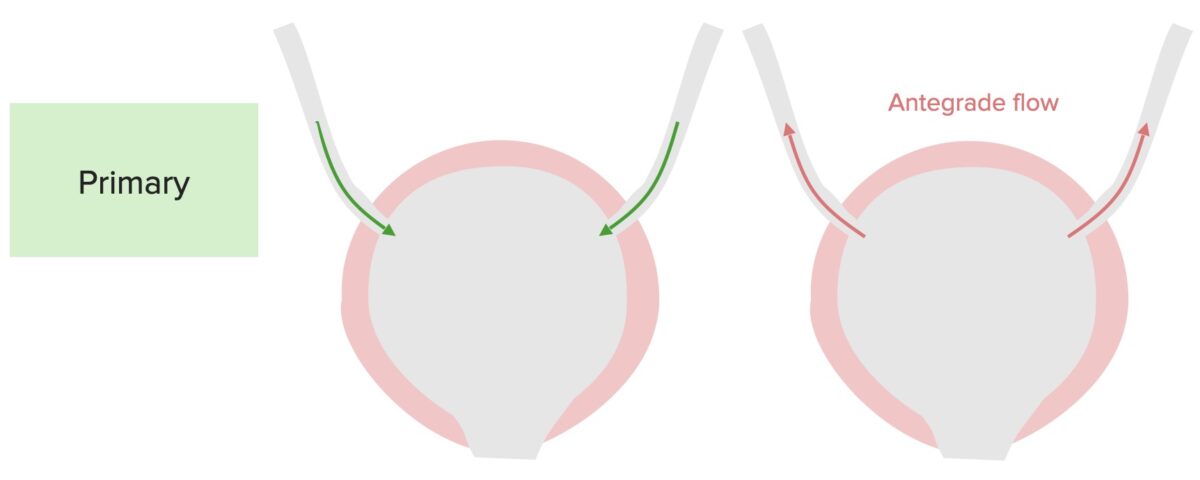
Overview Definition Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) is the retrograde flow of urine from the bladder into the upper urinary tract. Epidemiology Etiology Primary VUR: Secondary VUR: Pathophysiology Normal physiology Primary VUR Potential consequences Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis Clinical presentation There are no specific signs or symptoms for VUR, and the condition may be suspected in the […]
Encephalitis
Overview Definition Encephalitis is an inflammation of the brain parenchyma caused by an infection that is usually viral and presents as diffuse or focal neuropsychologic dysfunction. Epidemiology Classification There are 2 main types of encephalitis: Etiology Viral encephalitis is the most common form of encephalitis. Bacterial, fungal, and parasitic encephalitides are extremely rare. Viral causes: […]
Methemoglobinemia

Overview Definition Methemoglobinemia occurs when RBCs contain elevated methemoglobin levels (normal range in adults is 0%–3%). Methemoglobin is a form of hemoglobin in which ferrous (Fe2+) heme iron is oxidized to the ferric (Fe3+) state, which is unable to bind O2. Etiology Congenital: Acquired due to exposure to oxidizing agents: Epidemiology Pathophysiology Normal hemoglobin Methemoglobin […]
Imaging of the Lungs and Pleura
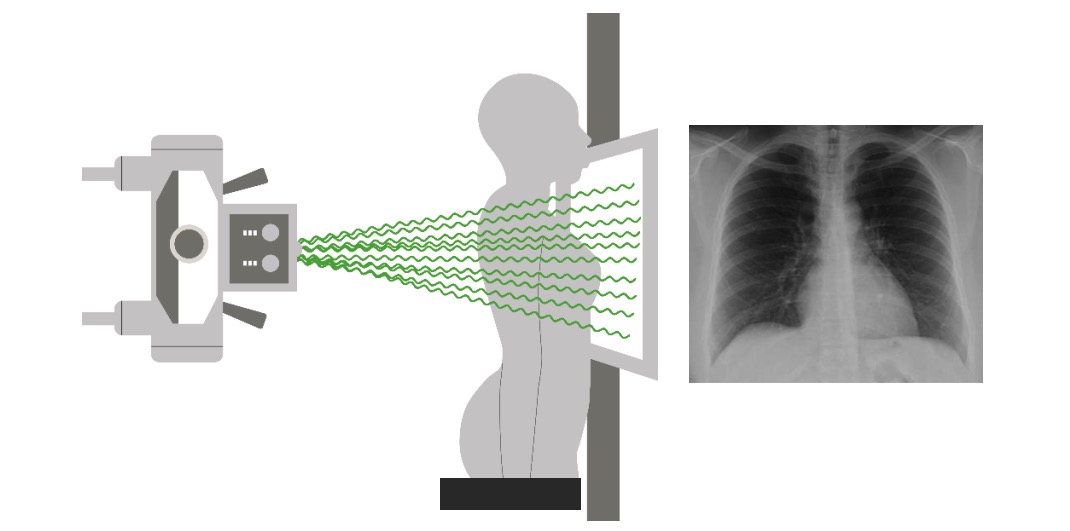
Introduction Before interpreting any image, the physician should take certain preparatory steps. The same systematic approach should be followed every time. Chest X-ray Indication Medical indications: Nonmedical indications: Advantages: Disadvantages: Exam technique Positioning: Positioning for specific views: Penetration: Penetration is the degree to which radiation has passed through body, resulting in a darker or lighter […]
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
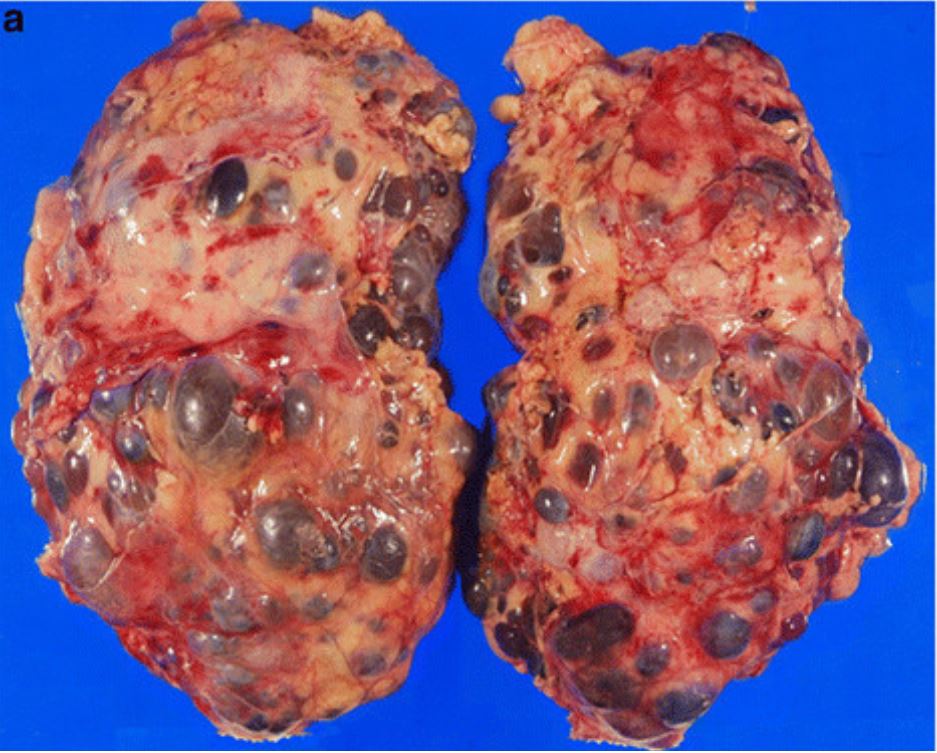
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) affects about 500,000 people in the United States. One of the 2 main types of PKD is autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). Etiology Clinical Presentation The age of symptom onset is variable, but typically in adulthood. Patients with PKD1 mutation present with symptoms earlier than patients […]
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD)
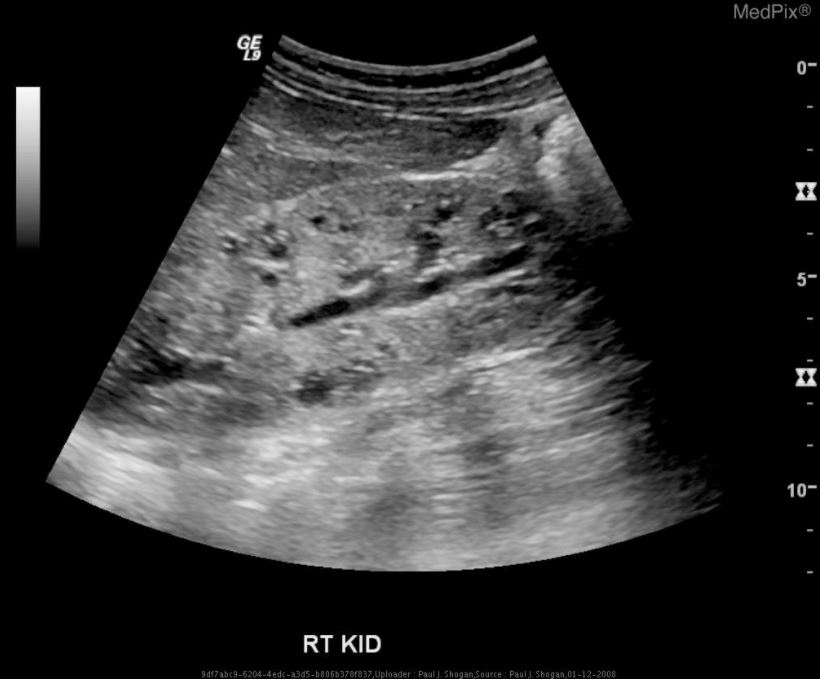
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) affects about 500,000 people in the United States. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) (formerly known as infantile PKD), is 1 of the 2 main types of PKD. Etiology Clinical Presentation General manifestations Manifestations vary by age and affect the following: Antenatal and neonatal Infancy and childhood […]
Bowenoid Papulosis
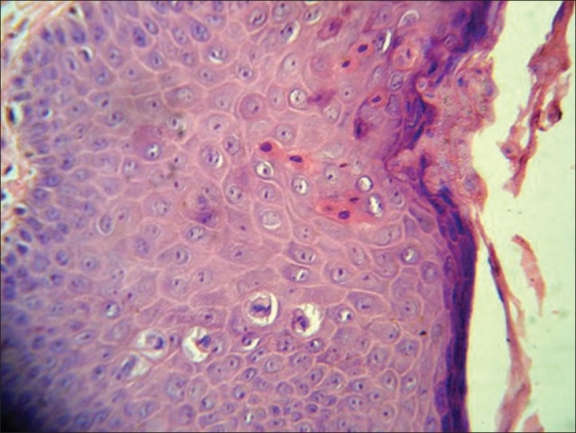
Overview Definition Epidemiology Risk factors Clinical Presentation Table: Clinical presentation Number and morphology Multiple papules Color Red-brown to violaceous Surface Smooth/flat Papillomatous/verrucous Size < 1 cm Distribution Discrete lesions (most common) Annular Linear Location ♂ Penile shaft (most common site) Foreskin Glans Scrotum Perianal skin ♀ (usually bilateral) Labia majora Labia minora Clitoris Vagina Inguinal […]
Bowen Disease and Erythroplasia of Queyrat
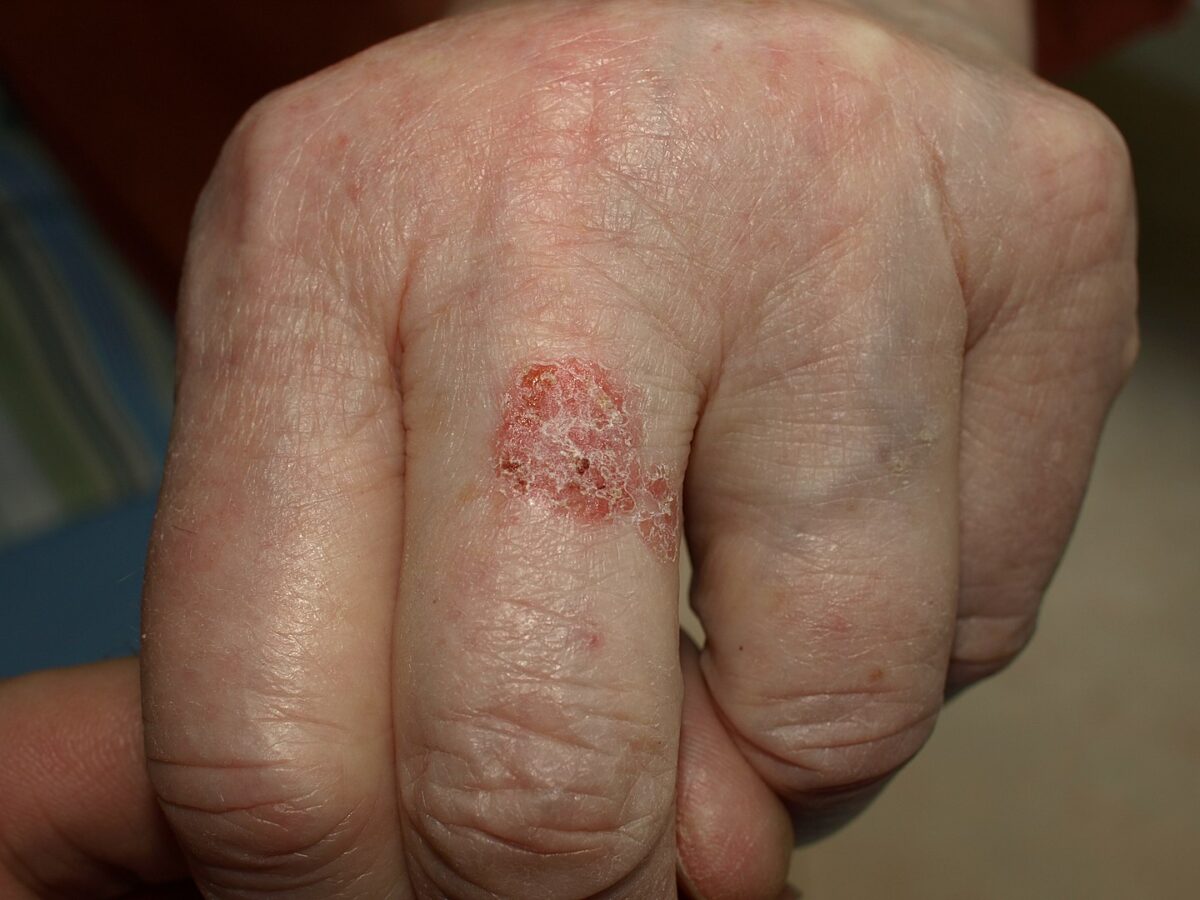
Bowen Disease Erythroplasia of Queyrat Differential Diagnosis References
Leukoplakia
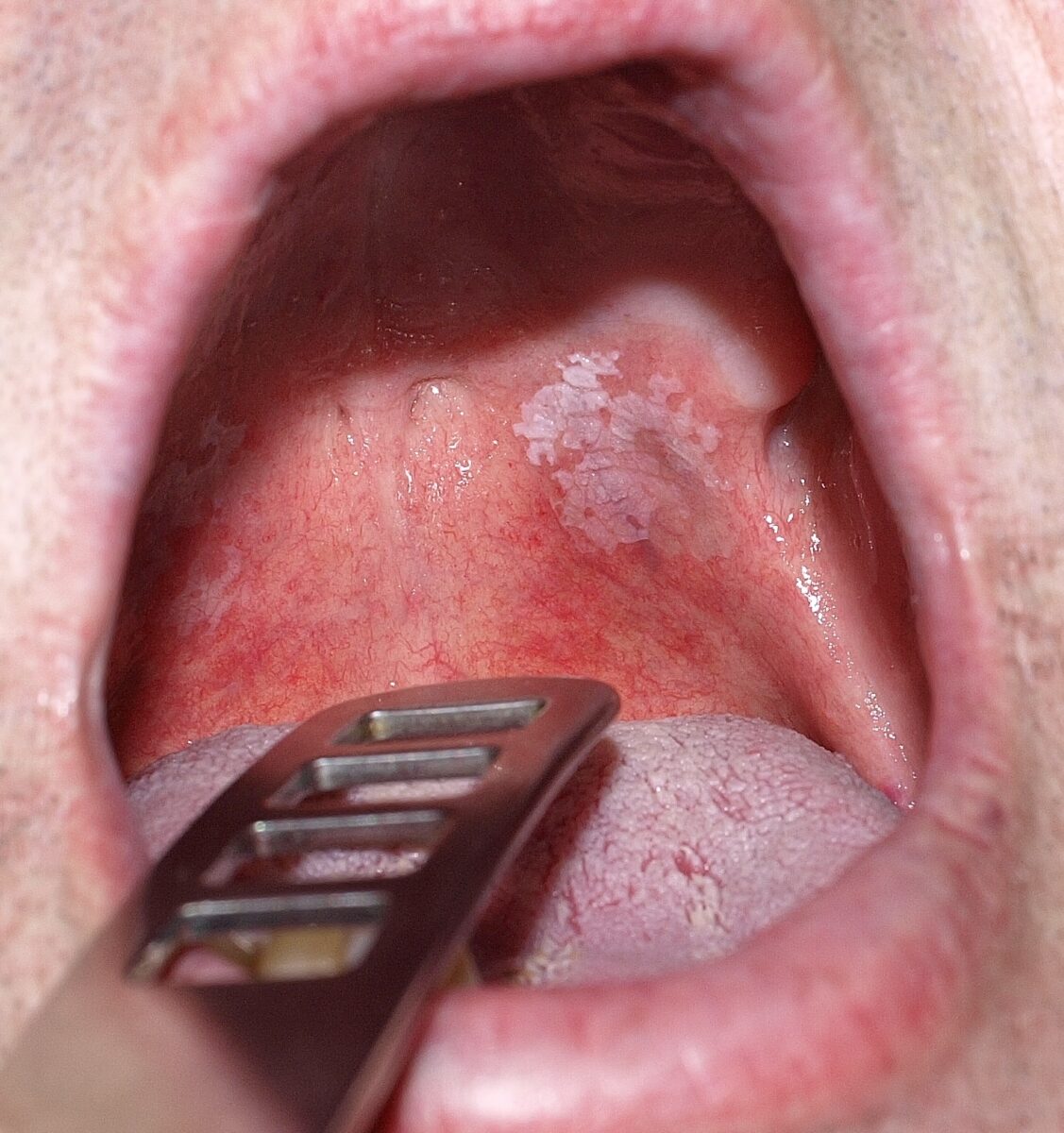
Overview Definition Epidemiology Risk factors Risk factors are similar to those for squamous cell carcinoma. Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation General findings Homogeneous leukoplakia This form is less likely to be malignant and is characterized by: Nonhomogeneous leukoplakia Nonhomogenous leukoplakia presents a higher risk of malignant transformation and may appear: Locations Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Biopsy is […]
Secondary Skin Lesions
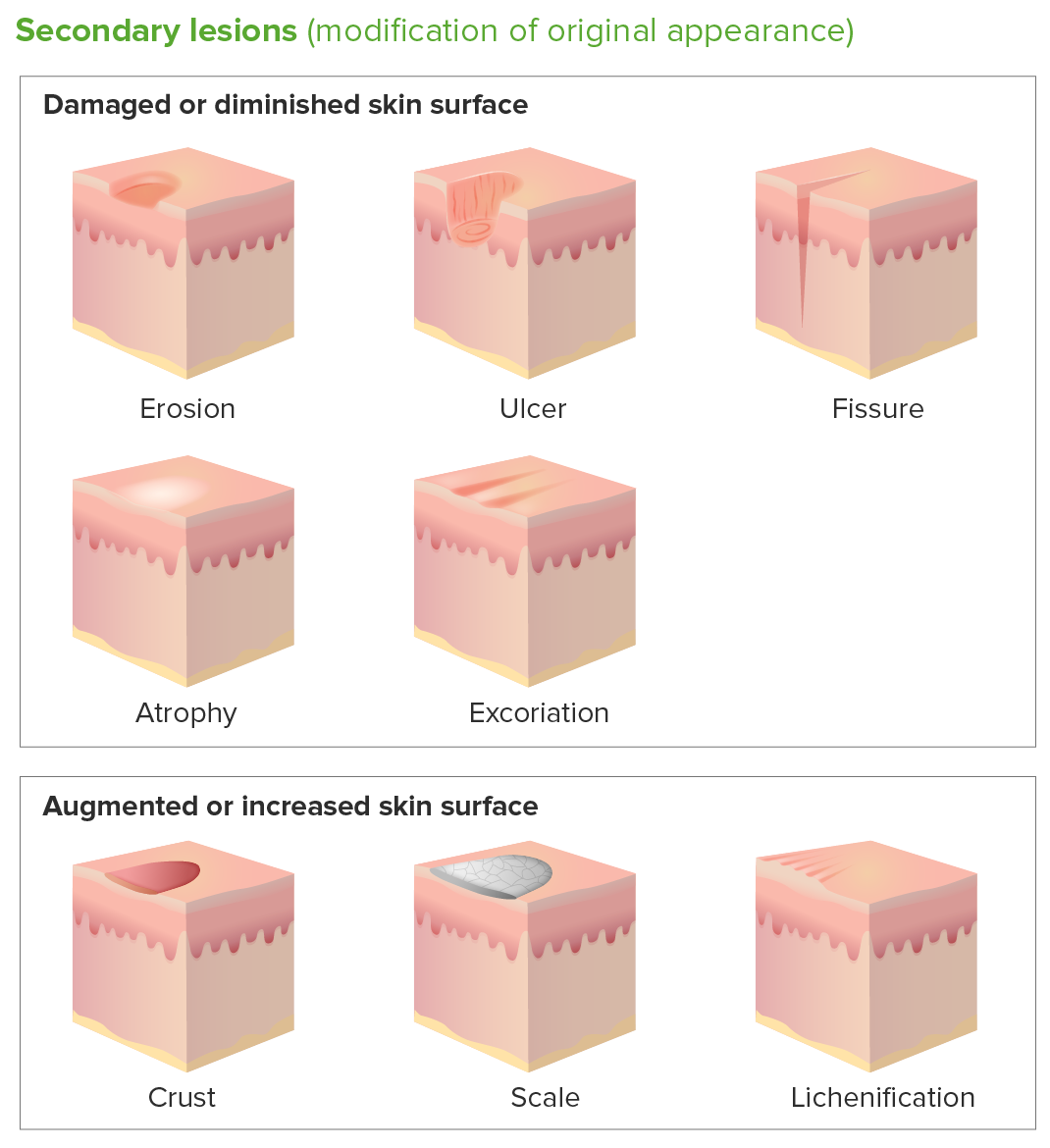
Scales Scales are dry or greasy masses of keratin that represent thickened stratum corneum. Characteristic types of scales are: Crust Erosion Excoriation Excoriation is a linear abrasion produced by mechanical means (scratching, rubbing, or picking) that usually involves only the epidermis but can reach the papillary dermis. Ulcer Fissure Atrophy Lichenification Approach to Diagnosing Skin […]