Primary Myelofibrosis
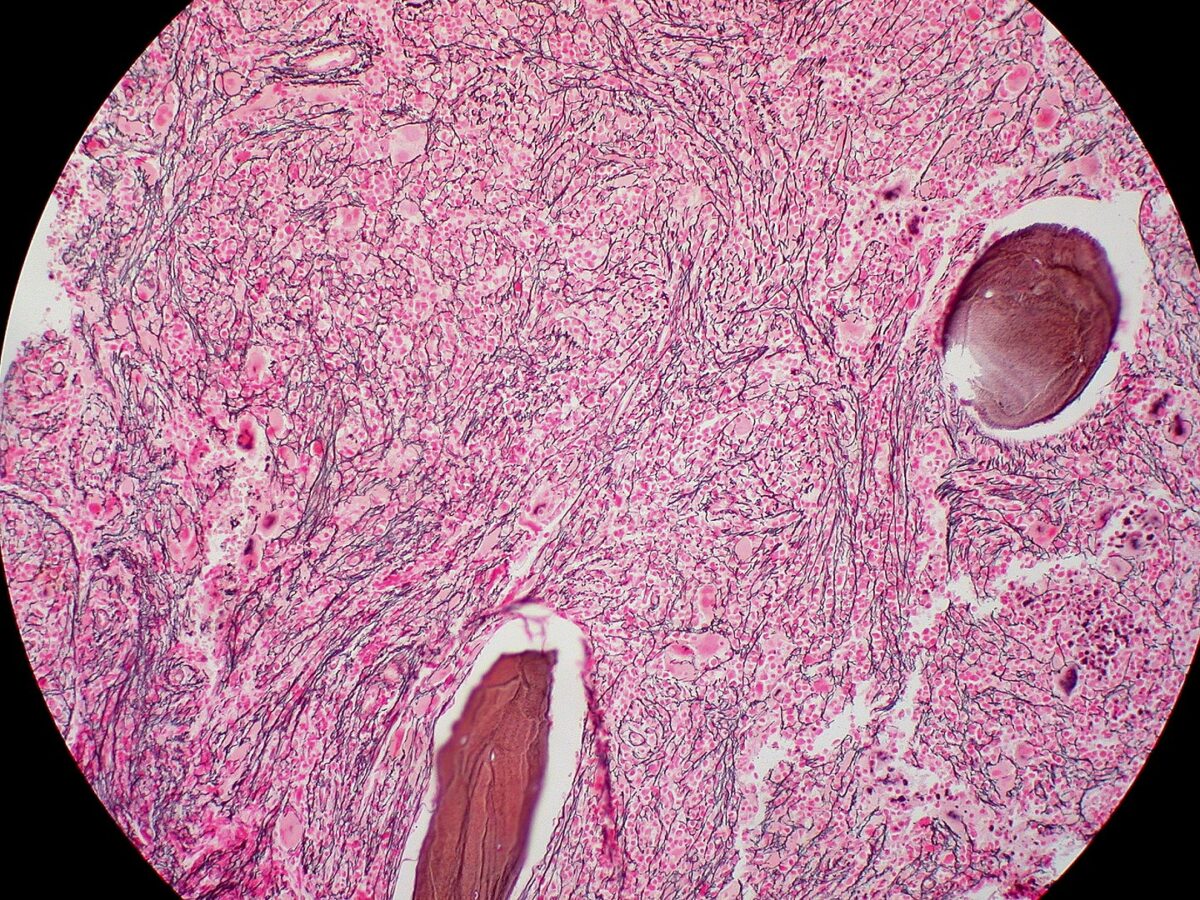
Overview Definition Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm characterized by proliferation of myeloid cells, with nonclonal fibroblast proliferation and hyperactivity, resulting in an obliterative marrow fibrosis. Other names include chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis and agnogenic myeloid metaplasia. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis starts with the hematopoietic stem cell, which is prompted to divide and […]
Lymphocytosis
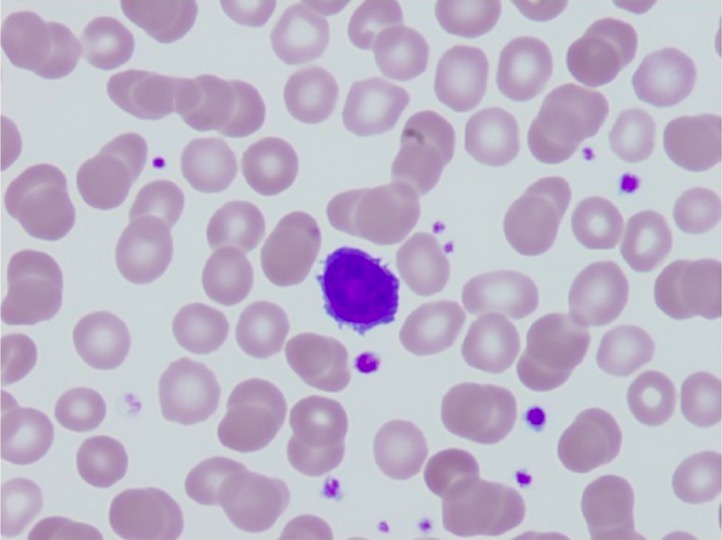
Overview Definition Lymphocytosis refers to elevated levels of lymphocytes. This elevation most often results from increased production. Lymphocyte subsets Epidemiology Etiology and Pathophysiology Lymphocytosis may result from an increased production of lymphocytes (most common) or several additional mechanisms. Increased production of lymphocytes The production of lymphocytes may be increased because of: Table: Infectious processes associated […]
Malassezia Fungi
General Characteristics and Epidemiology General features of Malassezia Formerly known as Pityrosporum Taxonomy: Family: Malasseziaceae Genus: Malassezia Dimorphic: Yeast: spherical or oval Mycelial form: short hyphae Colonies are cream or yellowish in color. Lipophilic Most species are lipid-dependent. Not a dermatophyte Reproduce by unipolar budding Clinically relevant species There are a number of recognized species: […]
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Overview Definition Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a lung disease characterized by airflow limitation resulting from airway disease and/or parenchymal destruction. Types The subtypes may have differing presentations and response to therapy. Patients may have any combination of both. Epidemiology Etiology Risk factors Pathophysiology Chronic bronchitis Inhaled agents cause chronic inflammation in the airways, […]
Hypernatremia
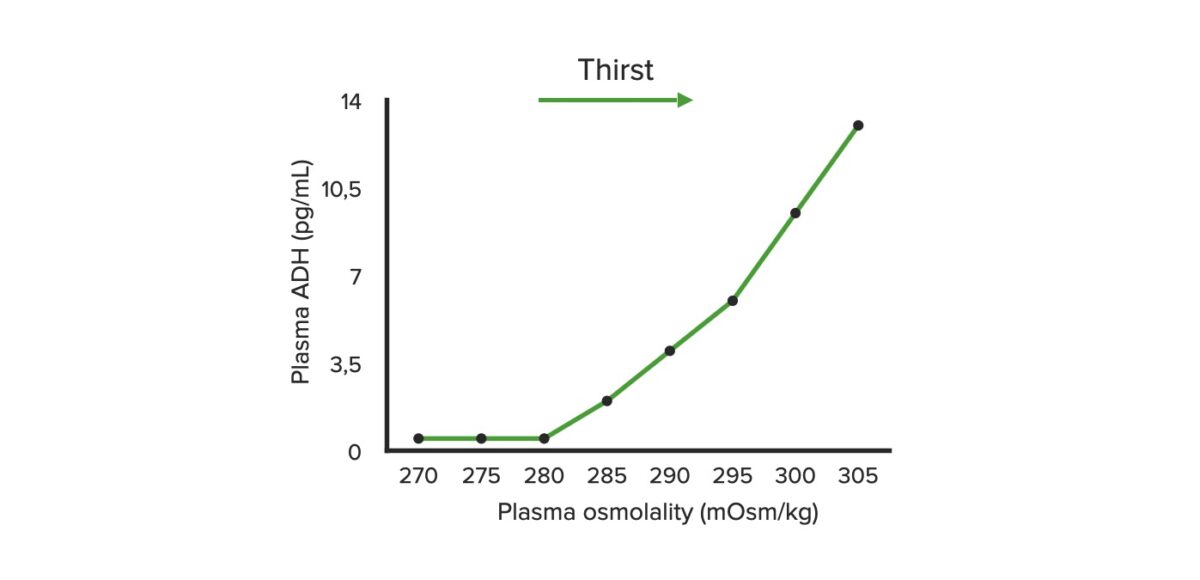
Water Regulation Water regulation is controlled by the interplay between the osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus and the response to antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in the kidneys, resulting in very tight control of serum sodium and plasma osmolality. Hypothalamic osmoreceptors Detect changes in water balance as a result of changes in plasma osmolality: ↑ Water intake causes […]
Equine Encephalitis Viruses
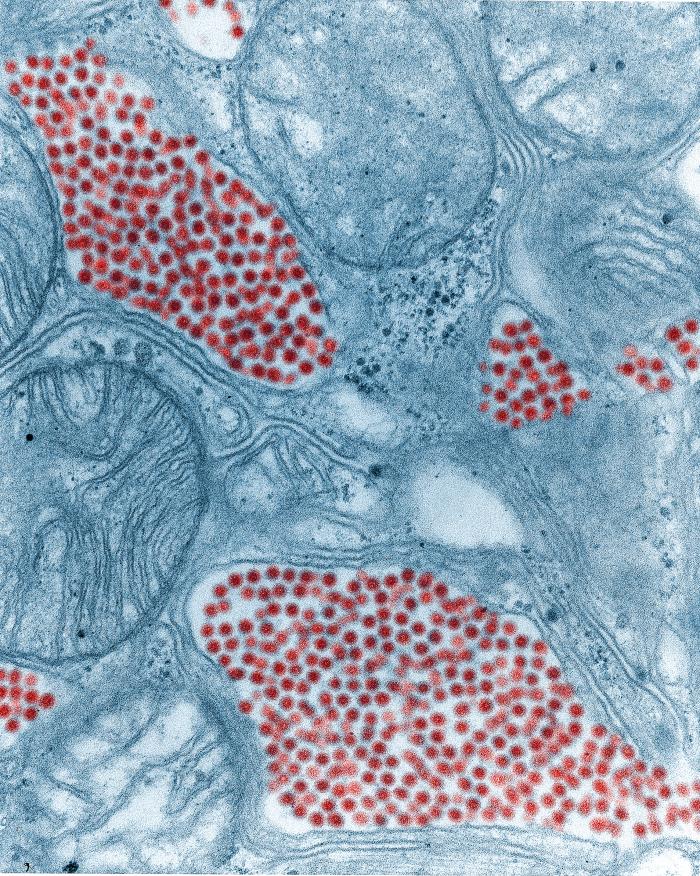
Classification General Characteristics and Epidemiology General features of equine encephalitis virus (EEV) Family: Togaviridae Genus: Alphavirus Genome: Positive-sense, ssRNA 11–12 kb in size Properties: Enveloped Lipid bilayer envelope has viral-encoded glycoproteins E1 and E2. Small icosahedral capsid Clinically relevant viruses and geographic distribution: Eastern equine encephalitis virus (EEEV) complex: Eastern equine encephalitis (EEE) virus: North […]
Rupture of the Spleen
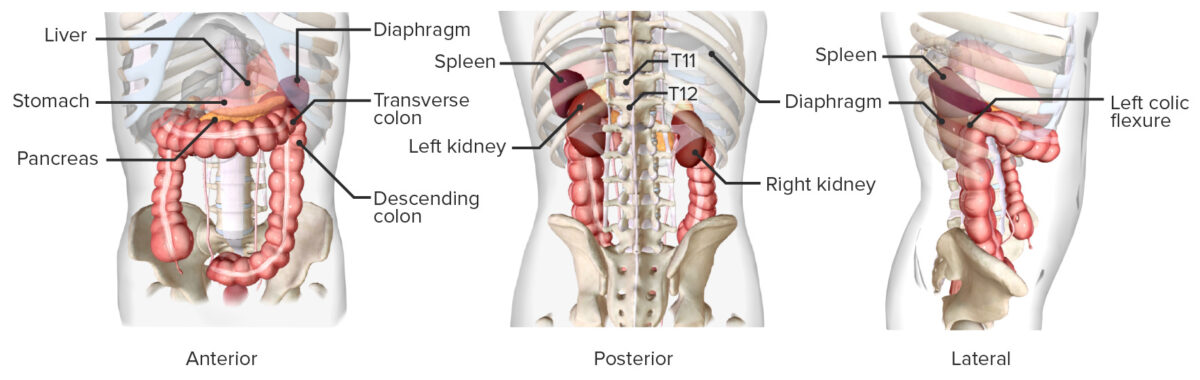
Overview Definition Splenic rupture is often associated with trauma (e.g., motor vehicle accident) that causes a laceration of the organ. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Splenic rupture can have serious consequences because of the unique physiologic function of the spleen. Clinical Presentation History Physical examination Diagnosis Physical examination and history may be useful, but not all patients […]
Antiphospholipid Syndrome
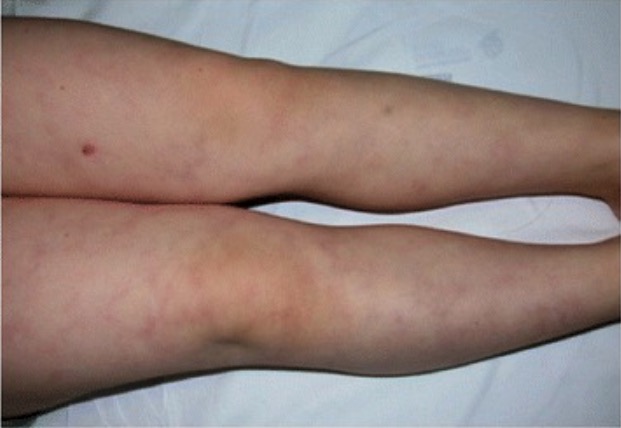
Overview Definition Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune phenomenon that presents with thrombotic events and/or adverse pregnancy outcomes related to the presence of persistent antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL), which produce a hypercoagulable state. Epidemiology In the United States: Classification Patients with APS are classified based on their clinical manifestations. Table: Classification of APS Classification Patients present […]
Insulinomas
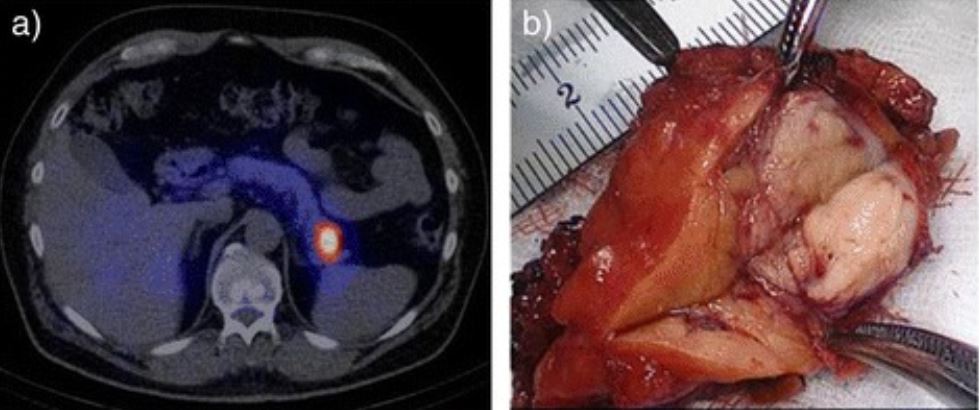
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Insulinomas are pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors that are derived from beta cells and secrete insulin. Epidemiology Incidence: approximately 1–4 cases per million people per year No sex or ethnic predisposition All age groups In 5%–10% of cases, insulinomas are malignant. 6% of cases associated with MEN type 1 (MEN1) syndrome (associated with […]
Meningitis
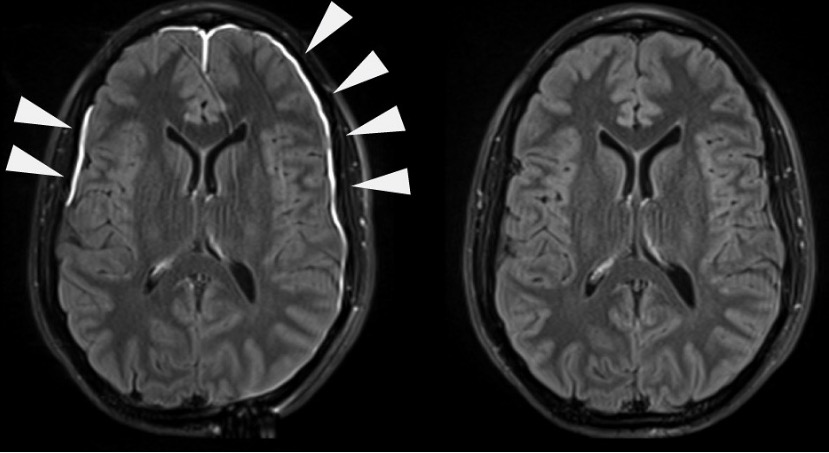
Overview Definition Meningitis is inflammation of the protective membranes of the brain and the spinal cord, collectively called the meninges, that is commonly caused by an acute infection. Epidemiology Etiology Meningitis can be of infectious (most common) or noninfectious origin. Infectious meningitis can be community- or hospital-acquired. Infectious meningitis Bacterial meningitis: Viral meningitis: Fungal meningitis: Parasitic […]