Hairy Cell Leukemia
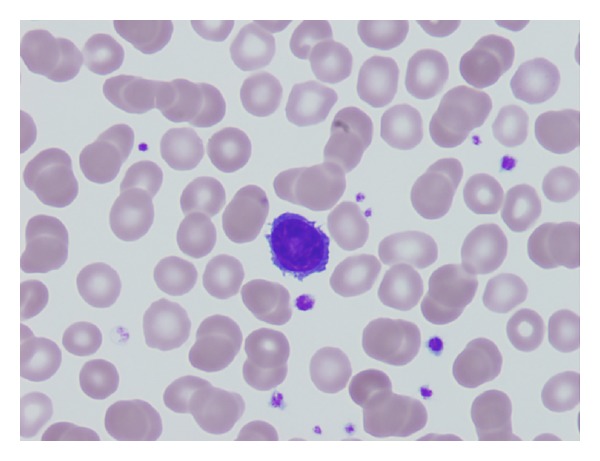
Overview Definition Hairy cell leukemia (HCL) is a rare, chronic B-cell leukemia characterized by the accumulation of small mature B lymphocytes that have hair-like projections visible on microscopy. Epidemiology Incidence: 3 per 1 million persons per year in the United States Rare: approximately 2% of all leukemia cases Median age at diagnosis: approximately 50 years […]
Ependymoma
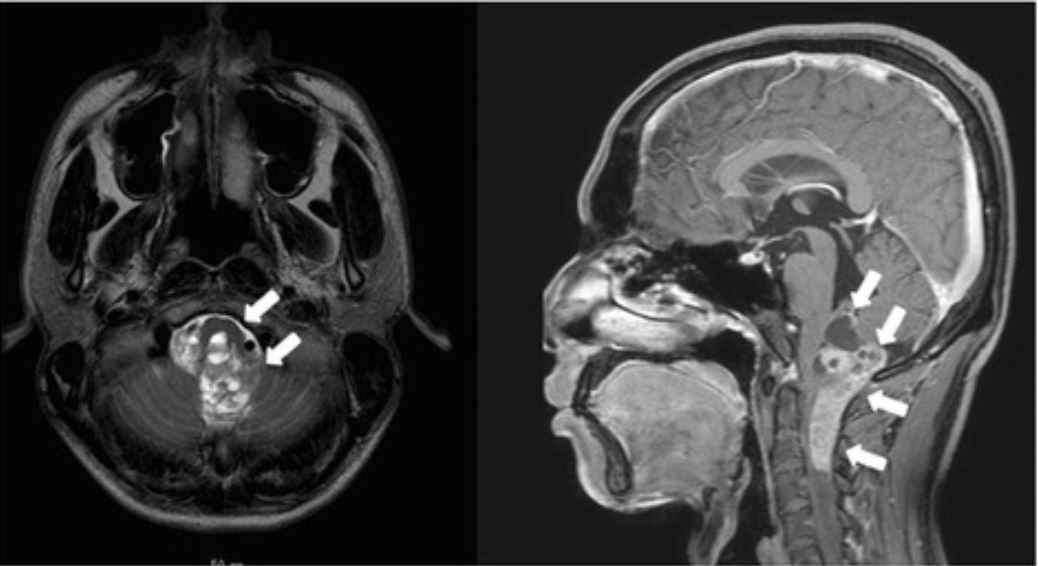
Overview Definition Ependymomas are glial cell tumors in the CNS arising from ependymal cells. Classification of nervous system tumors Table: Classification of nervous system tumors Categories Specific tumors Neuroepithelial tumors in the CNS Astrocytoma, including glioblastoma multiforme Oligodendroglioma Ependymoma and choroid-plexus tumor Medulloblastoma (embryonal tumor) Meningeal tumors Meningioma Hemangioblastoma Sellar-region tumors Craniopharyngioma Pituitary adenoma Pinealoma/pinealoblastoma […]
Bartter Syndrome

Overview Definition Bartter syndrome (BS) is a rare genetic (autosomal recessive) disorder that results from a defect in sodium chloride reabsorption in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, leading to hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis. The disorder mimics long-term ingestion of a loop diuretic. Epidemiology Pathophysiology and Classification Normal physiology in the Loop of […]
Chronic Kidney Disease
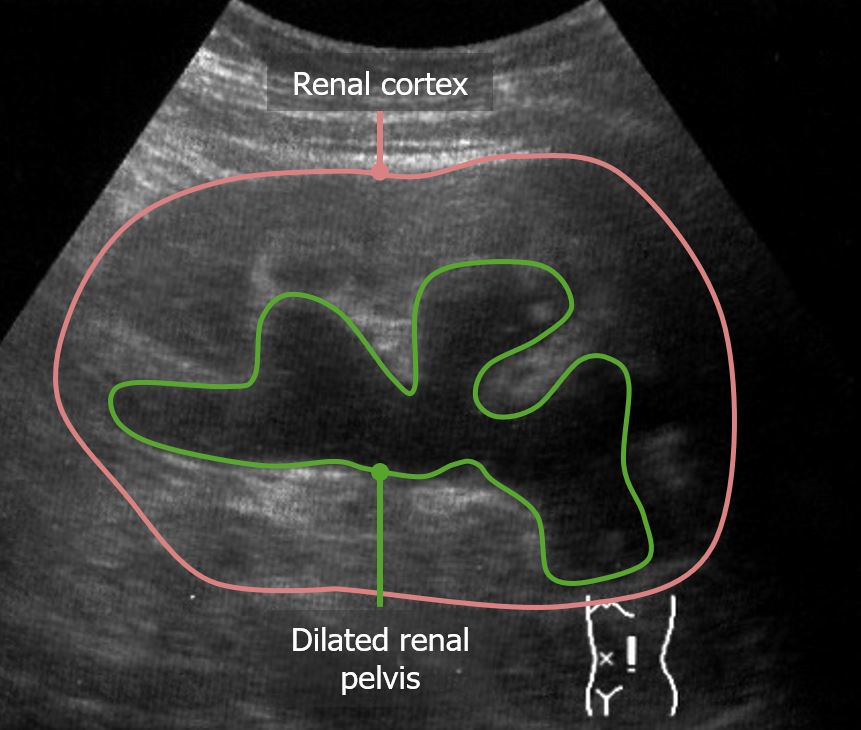
Overview Definition Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is typically defined as a decrease in kidney function and/or other signs of persistent kidney damage for ≥ 3 months. These signs include: Epidemiology Etiology Similar to AKI, the causes of CKD can be classified as prerenal, intrinsic renal, or postrenal. Diabetes and hypertension are, by a large margin, […]
Astrocytoma
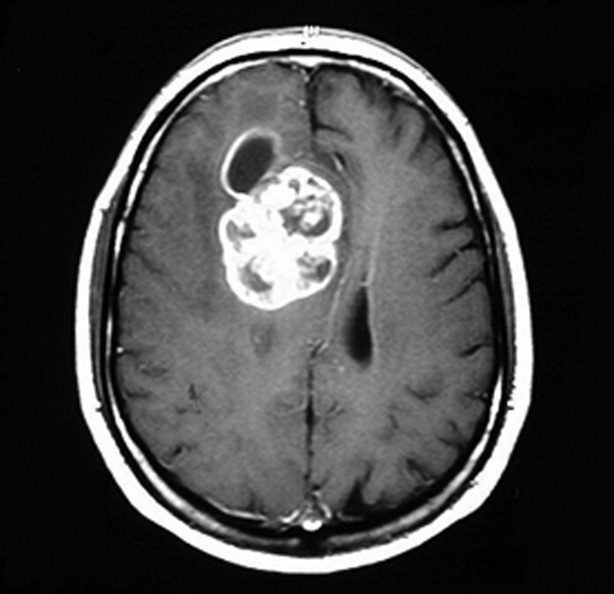
Overview Definition Astrocytomas are neuroepithelial tumors in the CNS arising from astrocytes, a type of star-shaped glial cell. Classification of nervous system tumors Table: Classification of nervous system tumors Categories Specific tumors Neuroepithelial tumors in the CNS Astrocytomas, including glioblastoma multiforme Oligodendroglioma Ependymoma and choroid-plexus tumors Medulloblastomas (embryonal tumors) Meningeal tumors Meningiomas Hemangioblastomas Sellar region […]
Polycythemia Vera
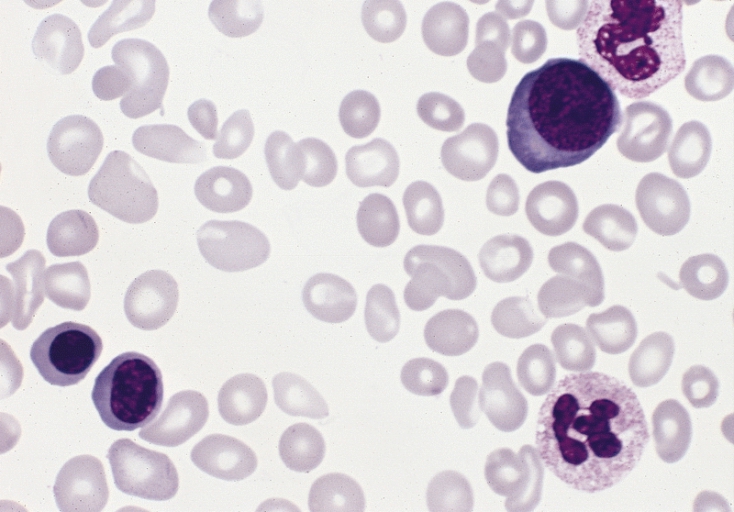
Overview Definition Polycythemia vera (PV) is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm characterized by the overproduction of RBCs (erythrocytosis), WBCs, and platelets. This triad differentiates PV from erythrocytosis seen with chronic hypoxia and other conditions. Classification Epidemiology Etiology and Pathophysiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Polycythemia vera is often diagnosed incidentally when a CBC obtained for other reasons […]
Diseases of the Salivary Glands
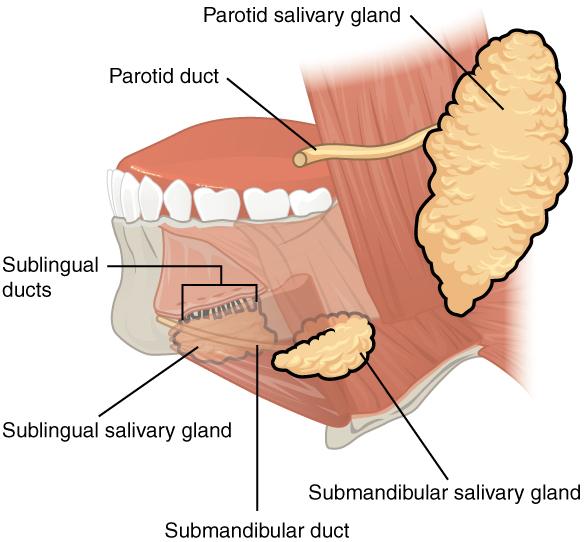
Overview Major salivary glands Physiology The major salivary glands produce > 95% of an individual’s saliva. Terminology for pathologic conditions Since sialadenosis, sialadenitis, and sialithiasis are similar-appearing names, understanding the suffix may aid in differentiating the underlying process. Sialadenosis Definition Sialadenosis (sialosis) is a chronic, benign, noninflammatory hypertrophy of the salivary glands. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology […]
Pancreatic Parameters
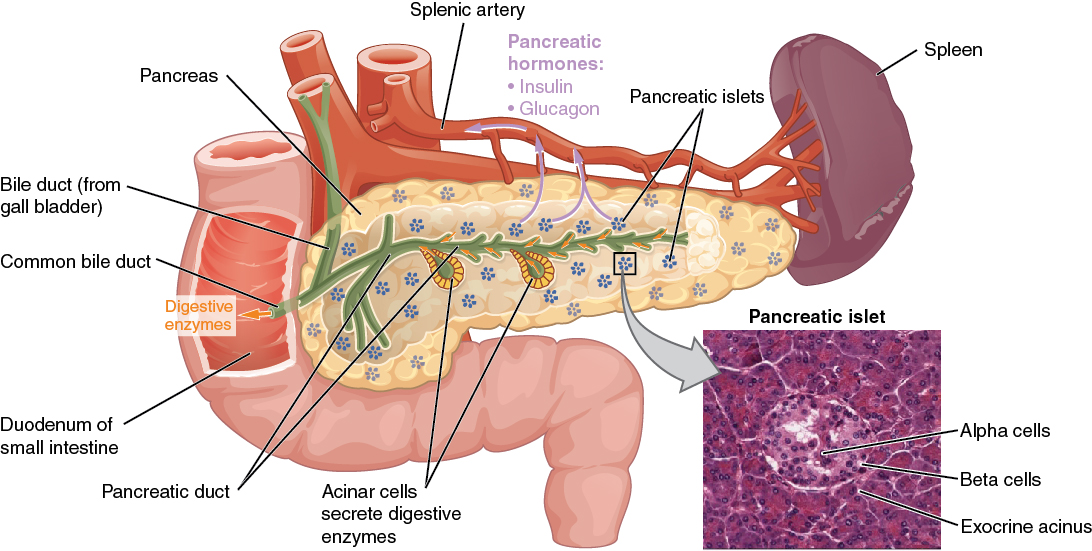
Overview Pancreas The pancreas is an organ positioned across the posterior aspect of the abdomen, behind the stomach and has 2 major functions: Endocrine pancreas physiology The islets of Langerhans, scattered throughout the pancreas, have different types of cells, which correspond to the following hormones: Functions and stimuli differ with each hormone. Exocrine pancreas physiology […]
Hypercalcemia
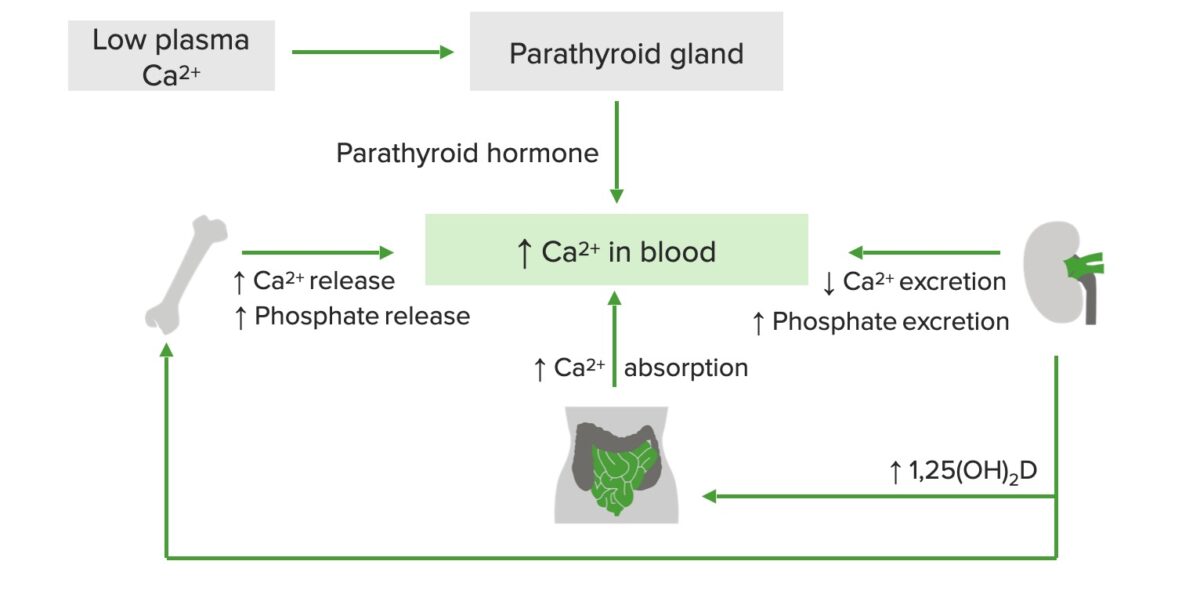
Calcium Homeostasis Calcium Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the human body, with 99% found in bone alone. Calcium in blood exists in 3 forms: Levels: Importance of calcium: Calcium regulation Bone, intestine, and kidneys are involved in homeostasis. Key elements of calcium regulation: Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Mechanisms Hypercalcemia is characterized by elevated […]
Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia
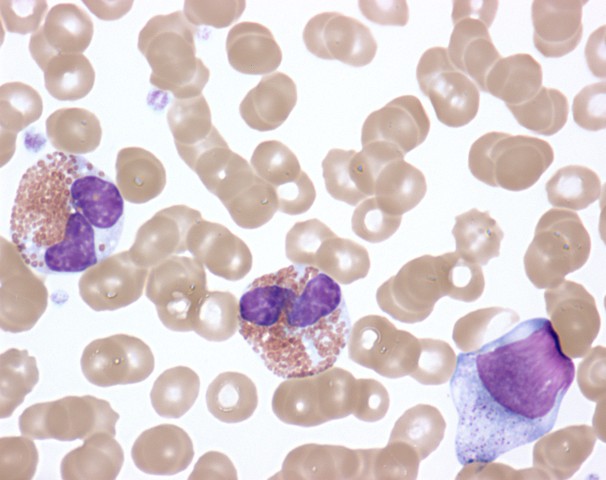
Overview Definition Chronic eosinophilic leukemia, not otherwise specified (CEL, NOS) is a rare chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm typified by clonal eosinophilic expansion in the bone marrow with increased blasts (< 20%). Classifying CEL, NOS Based on eosinophilias: CEL, NOS is classified under chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms (WHO classification): Epidemiology and etiology Pathophysiology Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis starts with a […]