Postinfectious Glomerulonephritis
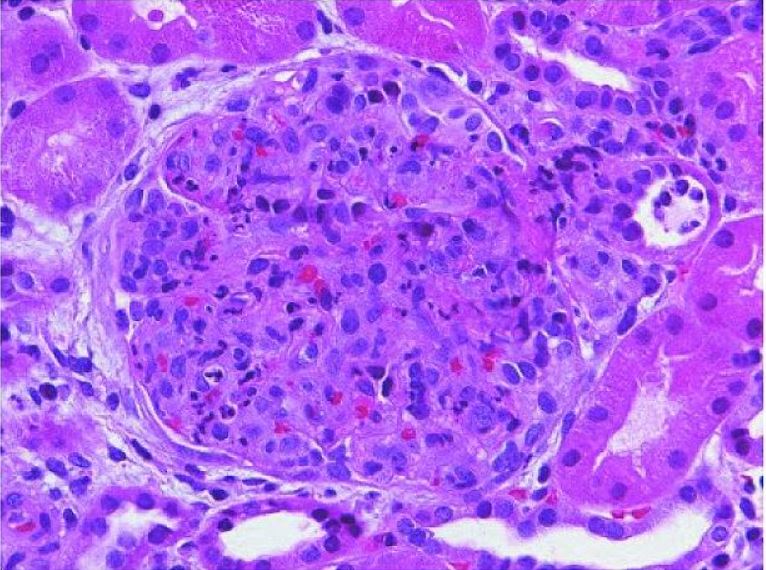
Overview Definition Postinfectious glomerulonephritis has traditionally referred to poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN), which is an immunologically mediated, delayed sequela of clinical pharyngitis or skin infections caused by GAS. In developed countries and older individuals, postinfectious GN is more commonly seen following a Staphylococcus infection, and may follow infections from a variety of different bacteria or viruses. […]
Vasospastic Angina

Overview Definition Vasospastic angina refers to episodes of chest pain (angina), which occur spontaneously while at rest secondary to coronary artery vasospasm, usually in the absence of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease (CAD). Epidemiology Etiology Possible triggers include: Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Manifestations Complications and sequelae Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Management Lifestyle modifications: Medical therapy: Differential Diagnosis […]
Acoustic Neuroma
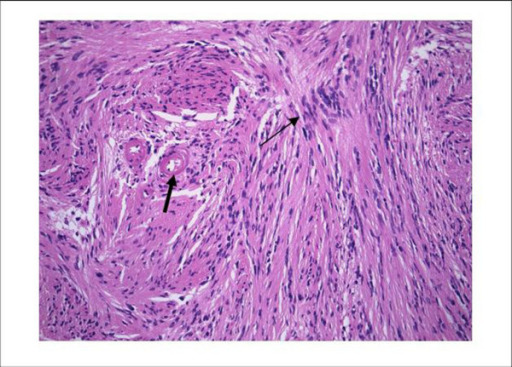
Overview Definition An acoustic neuroma is a benign tumor of Schwann cells that is most commonly found on cranial nerve VIII (vestibulocochlear nerve). Classification of nervous system tumors Table: Classification of nervous system tumors Categories Specific tumors Neuroepithelial tumors in the CNS Astrocytomas, including glioblastoma multiforme Oligodendroglioma Ependymoma and choroid-plexus tumors Medulloblastomas (embryonal tumors) Meningeal […]
Schwannoma
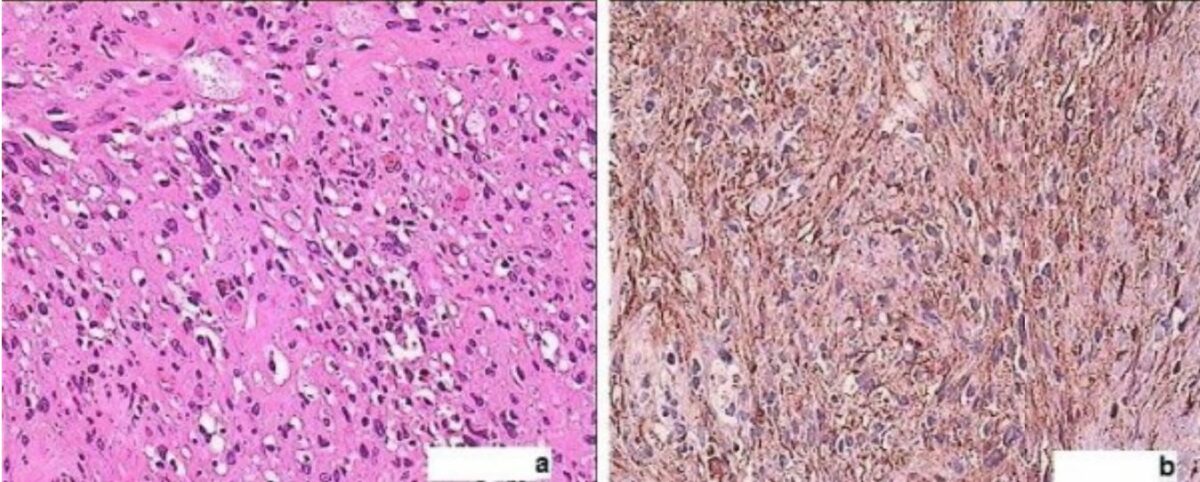
Overview Definition Schwannomas are benign, encapsulated nerve sheath tumors in the peripheral nervous system (PNS), arising from Schwann cells. Classification of nervous system tumors Table: Classification of nervous system tumors Categories Specific tumors Neuroepithelial tumors in the CNS Astrocytomas, including glioblastoma multiforme Oligodendroglioma Ependymoma and choroid-plexus tumors Medulloblastomas (embryonal tumors) Meningeal tumors Meningiomas Hemangioblastomas Sellar […]
Meningioma
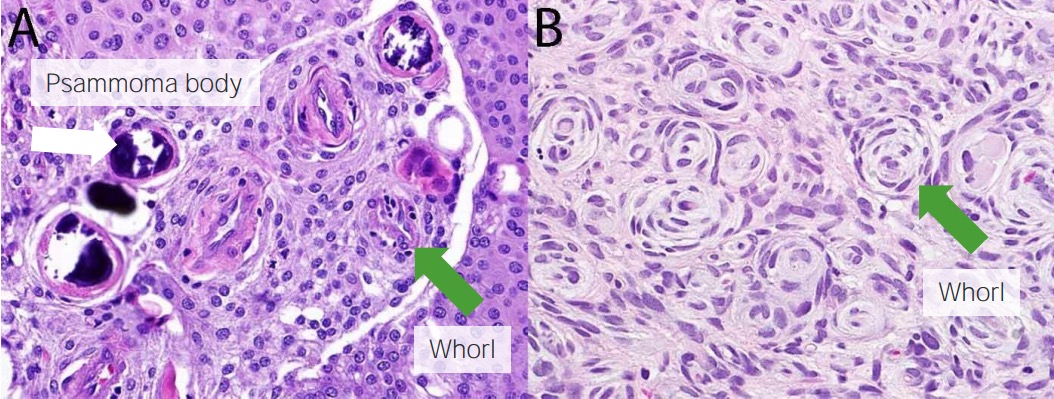
Overview Definition A meningioma is a slow-growing tumor that arises from the meninges of the brain and spinal cord. Meninges are the fibrous layers that encase the brain and spinal cord, and consist of 3 layers: Dura mater: the outer layer, which forms a tough collagenous sheath Arachnoid mater: the middle layer, which consists of […]
Glioblastoma Multiforme
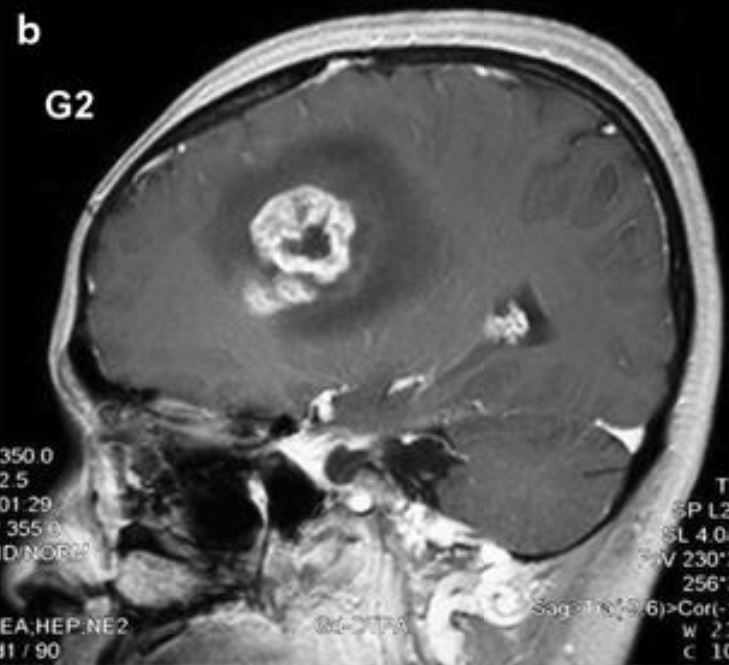
Overview Definition Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is an aggressive, rapidly progressive type of brain tumor arising from astrocytes: Classification of nervous system tumors Table: Classification of nervous system tumors Categories Specific tumors Neuroepithelial tumors in the CNS Astrocytomas, including GBM Oligodendroglioma Ependymoma and choroid-plexus tumors Medulloblastomas (embryonal tumors) Meningeal tumors Meningiomas Hemangioblastomas Sellar region tumors Craniopharyngioma […]
Medulloblastoma
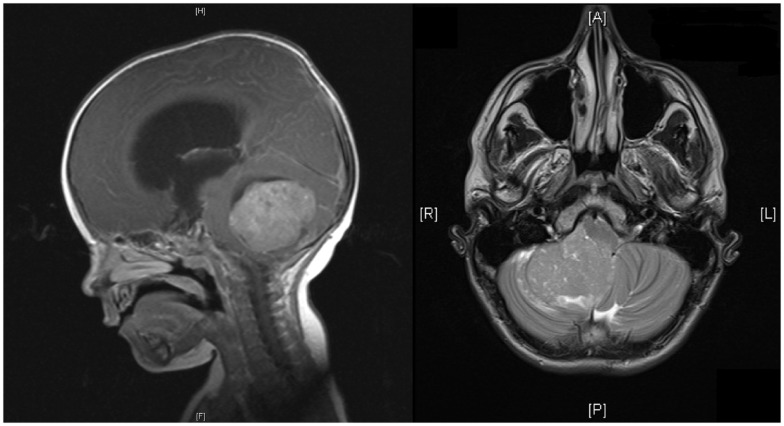
Overview Definition Medulloblastoma is a highly malignant primitive neuroectodermal tumor that develops in the posterior fossa in children. It is an embryonal tumor, arising from neuronal progenitor cells, and generally has a poor prognosis. Classification of nervous system tumors Table: Classification of nervous system tumors Categories Specific tumors Neuroepithelial tumors in the CNS Astrocytomas, including […]
Lymphadenopathy

Overview Definition Lymphadenopathy is lymph node enlargement of usually > 1 cm. It is considered localized if the enlargement is limited to lymph nodes of 1 anatomic region and generalized when ≥ 2 regions are involved. Etiology Most often, lymphadenopathy is a reaction to a local infection. Less frequently, it may be due to a […]
Metabolic Syndrome

Definition and Epidemiology Definition Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of biochemical and physiologic abnormalities associated with the development of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Epidemiology Prevalence: Metabolic syndrome doubles the risk for developing cardiovascular disease. Pathophysiology With obesity, excess adipose tissue releases the following substances, with considerable effects on the body. Nonesterified fatty acids […]
Coronavirus
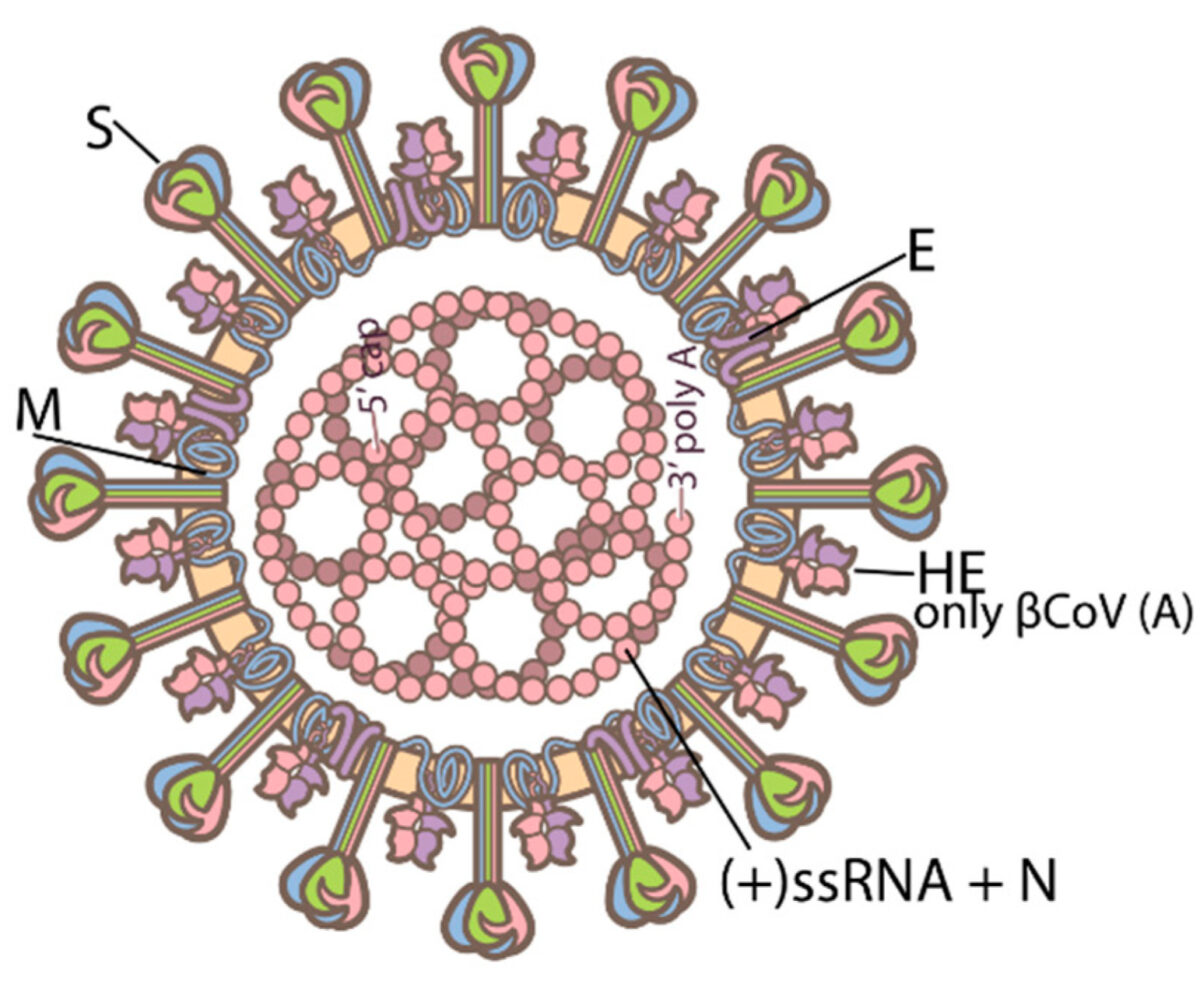
Classification General Characteristics Structure Clinically relevant species Pathogenesis Transmission Virulence factors Most coronaviruses have 4 structural proteins: S, E, M, and N. Replication cycle Diseases Caused by Coronaviruses Table: Epidemiology of respiratory coronavirus diseases MERS-CoV SARS-CoV SARS-CoV-2 Date of first identified case June 2012 November 2002 December 2019 Location of first identified case Jeddah, Saudi […]