Craniopharyngioma
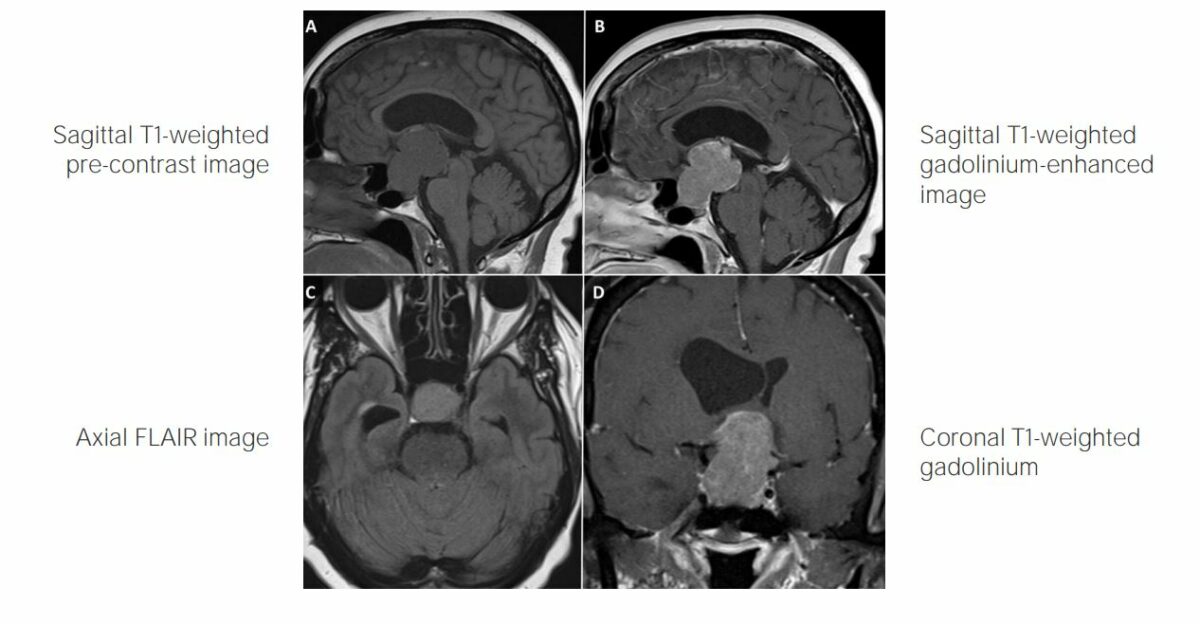
Overview Definition Craniopharyngiomas are rare squamous epithelial tumors with a solid and/or cystic structure, which arise from the remnants of Rathke’s pouch along the pituitary stalk, in line from the nasopharynx to the diencephalon (in the suprasellar region). Craniopharyngiomas have benign histology but malignant behavior, meaning that they tend to invade the surrounding structures and […]
Oral Cancer
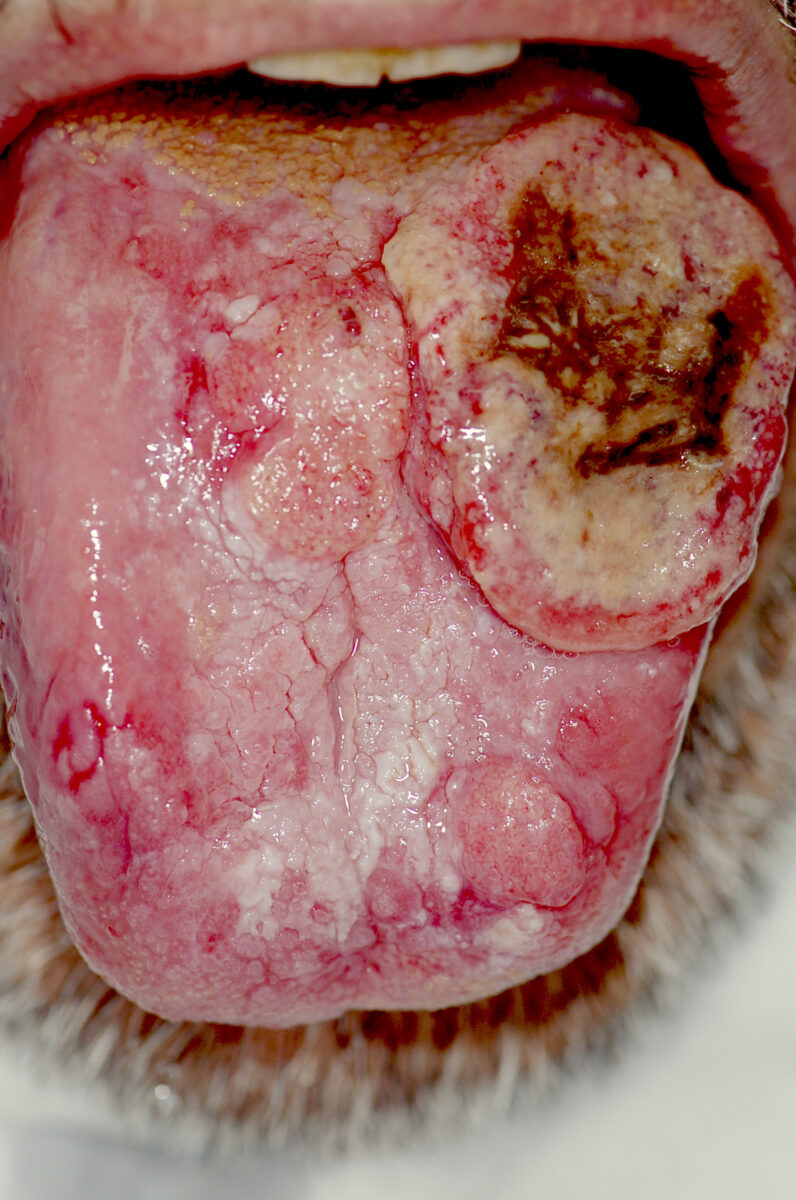
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Mnemonic Biopsy is recommended for suspicious oral lesions lasting 3 or more weeks: Diagnosis Diagnostic approach Staging Table: Staging of oral cancer Stage Description 0 TisN0M0 (in situ or cancer limited to epithelium) I T1N0M0 (lesion ≤ 2 cm and without node involvement or distant spread) II […]
Liddle Syndrome
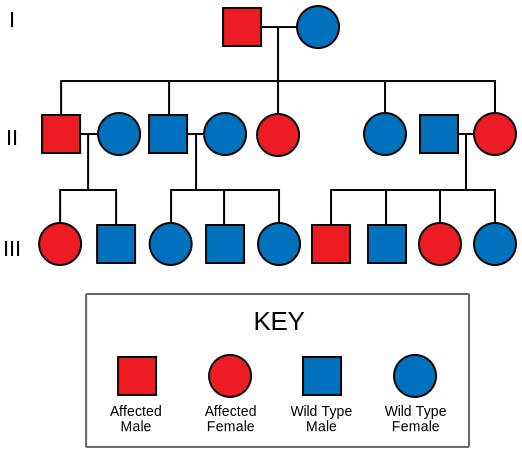
Overview Definition Liddle syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant genetic disorder associated with abnormal increased function of epithelial sodium channels (ENaC) in the collecting tubules. Liddle syndrome is clinically characterized by hypertension, low plasma renin activity, metabolic alkalosis, hypokalemia, and low aldosterone levels. Epidemiology Etiology An autosomal dominant gain-of-function gene mutation changes the structure of […]
Hemangioblastoma
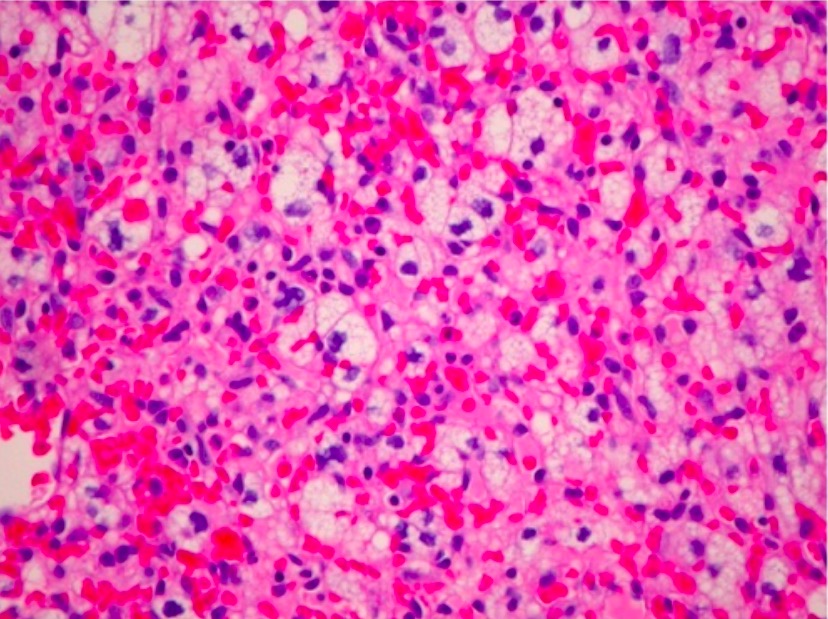
Overview Definition Hemangioblastomas are rare, slow-growing, benign, highly vascular neoplasms of the CNS that have a high association with von Hippel-Lindau disease (VHL), which is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by a variety of benign and malignant tumors. The tumors are most commonly found in the cerebellum. Hemangioblastomas are often found in the parenchyma attached […]
Endophthalmitis
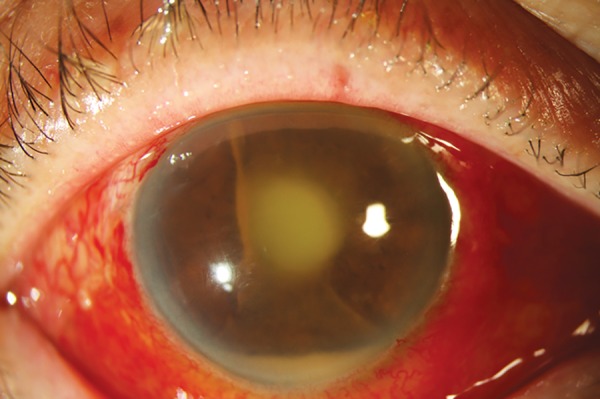
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Endophthalmitis is an inflammatory process of the intraocular cavities (e.g., aqueous and/or vitreous humor) usually caused by bacteria or fungi. Epidemiology Etiology Sterile endophthalmitis Infectious endophthalmitis Exogenous: Endogenous: Pathogenesis Normally, the ocular-blood barrier naturally resists invasive organisms. Exogenous endophthalmitis Pathophysiology: Risk factors: Endogenous endophthalmitis Pathophysiology: In unilateral cases, the right eye […]
Overview of Bone Fractures
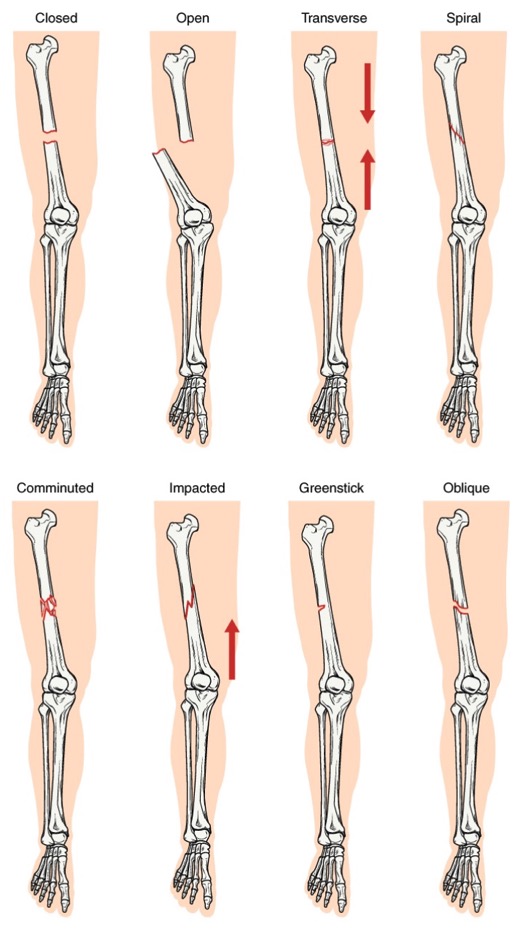
Overview Definition A fracture is a disruption in the cortex of a bone. Epidemiology Classification Risk factors Pathophysiology The general principle behind all fractures is that the bone is subjected to a load that overcomes the bone’s bearing capacity, leading to loss of structural integrity. Clinical Presentation A thorough history with recent injury or fall […]
Oligodendroglioma
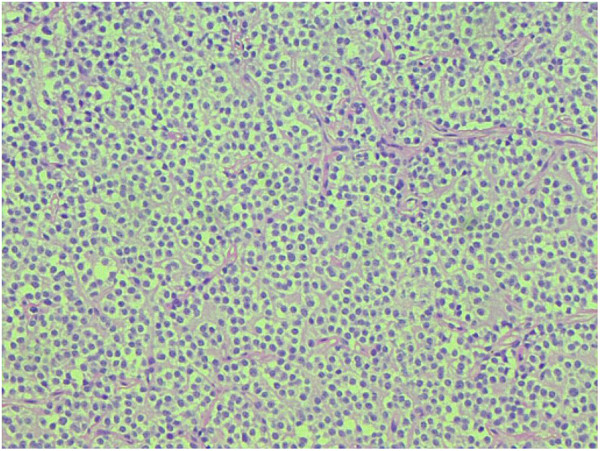
Overview Definition Oligodendrogliomas are malignant neuroepithelial tumors arising from neural glial cell precursors. These tumor cells appear histologically similar to oligodendrocytes, but lack the myelinating ability of oligodendrocytes. Oligodendrogliomas are a type of glioma: Gliomas arise from glial cells, which are supportive tissues within the brain and spinal cord. Oligodendrocytes are glial cells in the […]
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
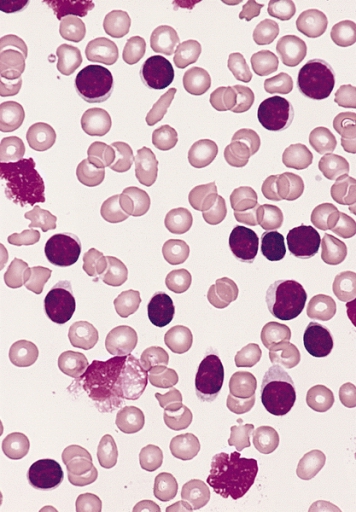
Overview Definition Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a lymphoproliferative neoplasm characterized by accumulation of functionally impaired lymphocytes, often monoclonal in origin. Terminology CLL is identical to small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), both of which are considered manifestations of B-cell neoplasm. The term CLL is used when the disease manifests primarily in the blood. The term SLL […]
Diabetes Mellitus
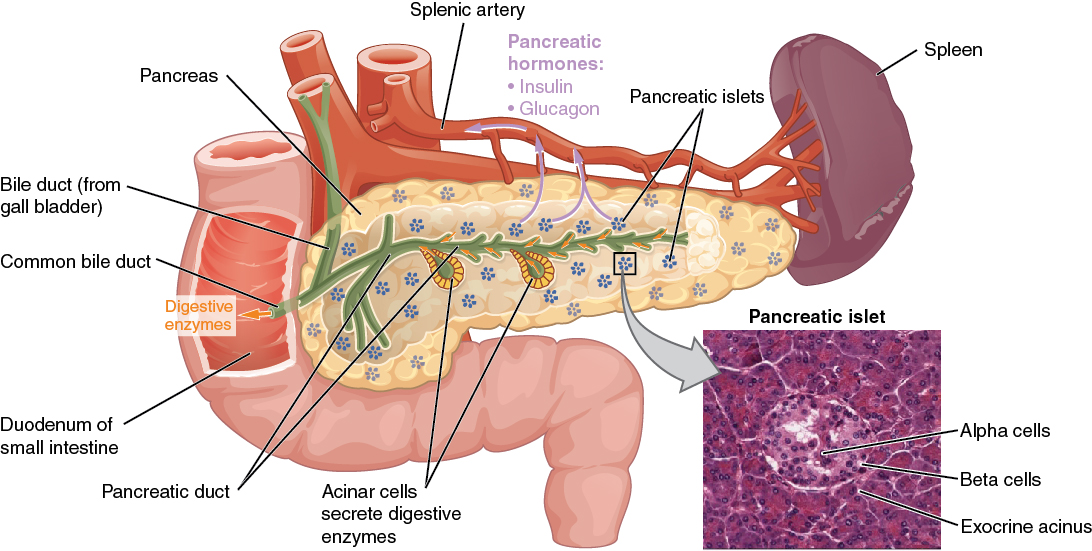
Definition Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a disorder of carbohydrate metabolism. Diabetes mellitus usually occurs in genetically predisposed individuals and is characterized by inadequate production of insulin or resistance to insulin’s action on the pancreas. These features result in hyperglycemia and the long-term pathologic sequelae of DM. Epidemiology Type 1 Type 2 Gestational diabetes Risk factors: […]
X-linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets
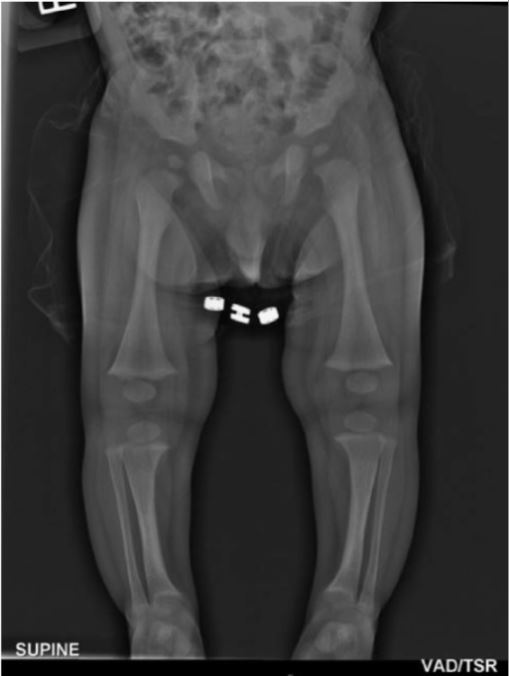
Overview Definition X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets (XLHR) is a rare genetic disorder that causes hypophosphatemia and resultant clinical rickets. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis Clinical presentation The clinical presentation of XLHR may vary from asymptomatic to severely symptomatic. X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets is commonly mistaken for nutritional rickets in infants, and the symptoms include: Diagnosis Family […]