Chronic Pancreatitis (Clinical)
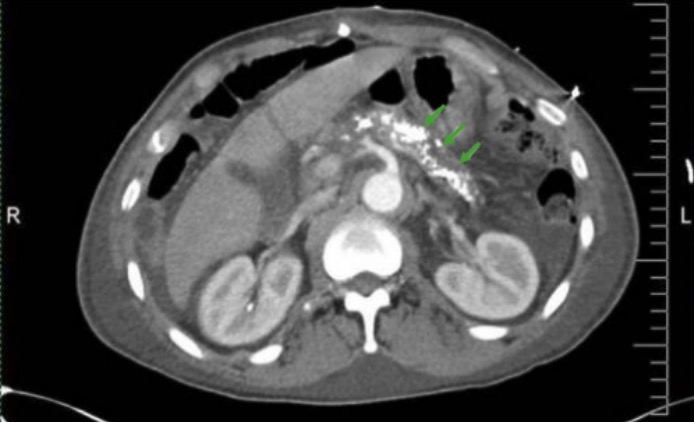
Overview Epidemiology[1,4,5] Etiology[1,4,5,8] Common etiologies of chronic pancreatitis are summarized with the “TIGAR-O” mnemonic: Table: TIGAR-O: Common etiologies of pancreatitis T Toxic/metabolic Alcohol (most common) Tobacco smoking Hypertriglyceridemia Hypercalcemia I Idiopathic May be early- or late-onset G Genetic mutations Autosomal dominant: PRSS1 Autosomal recessive: CFTR SPINK1 A Autoimmune Autoimmune pancreatitis type 1: immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)–related […]
Diarrheagenic E. coli (Clinical)
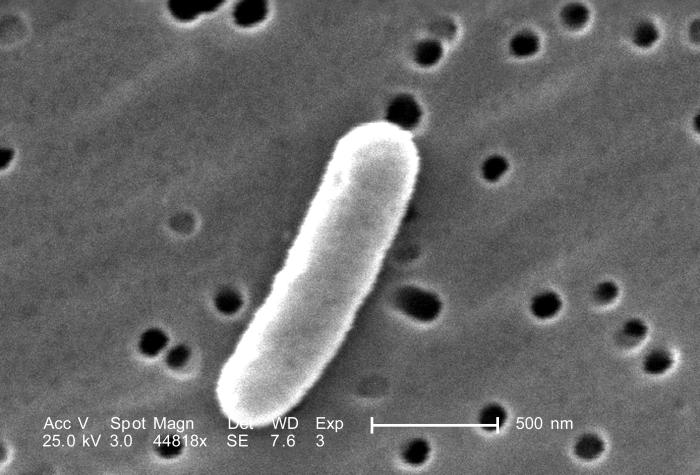
Overview Microbiology[4,6] Classification of diarrheagenic of E. coli[1,3,4,6] Diarrheagenic strains of E. coli can be classified into 5 key “pathotypes,” each of which has unique virulence factors and pathologic mechanisms. Virulence factors[4,6] Virulence traits are distinct for each category of pathogenic E. coli: Transmission[3,4,6] Pathophysiology Each of the 5 main pathotypes has unique pathologic mechanisms. […]
Hyperkalemia (Clinical)
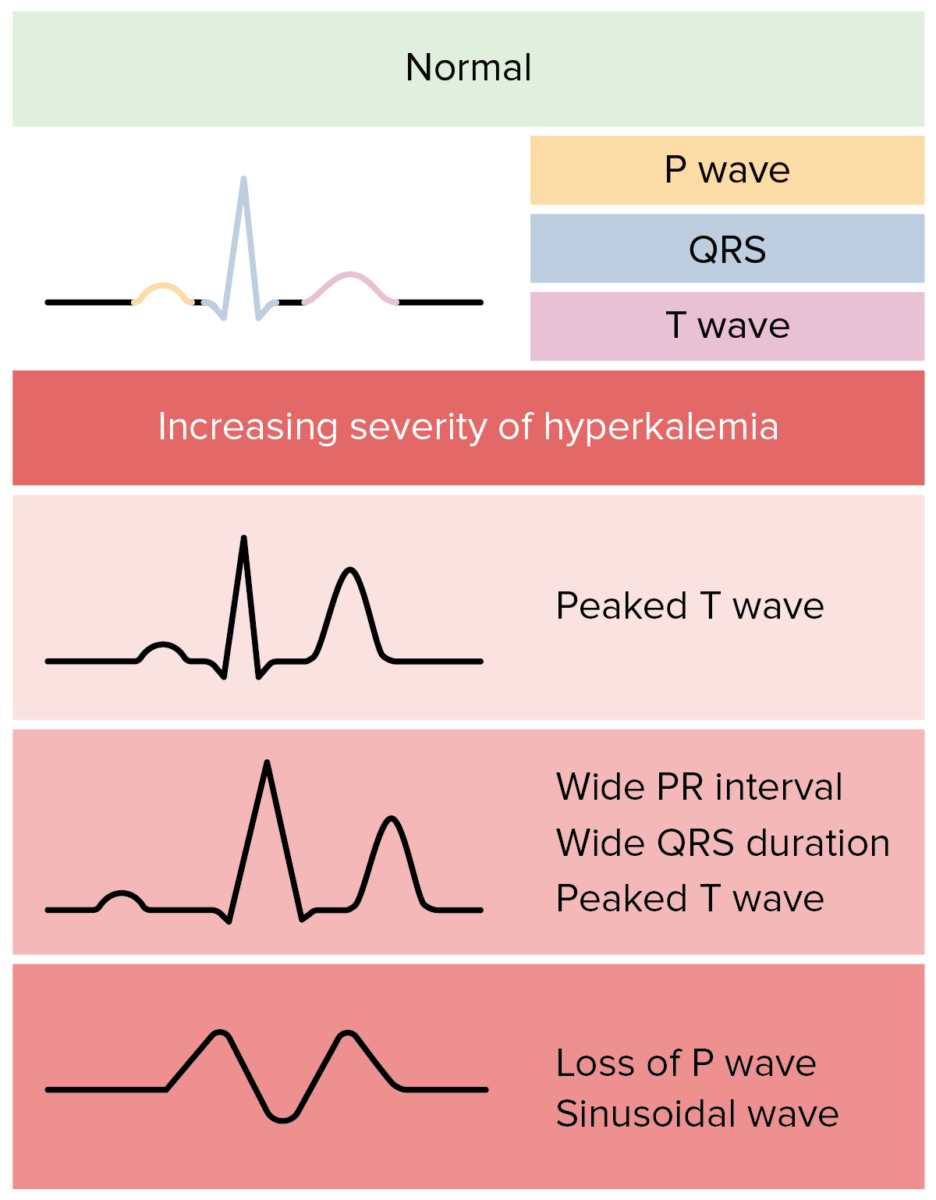
Overview General considerations[2,4] K+ is the main intracellular cation in all cells and is distributed unevenly between the intracellular fluid (98%) and extracellular fluid (2%). Movement of potassium in the kidney[2,4,11] Normal response to ingested K+[2,4,14] A normal Western diet contains approximately 70–150 mmol of K+ per day. This diet is unlikely to lead to […]
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (Clinical)
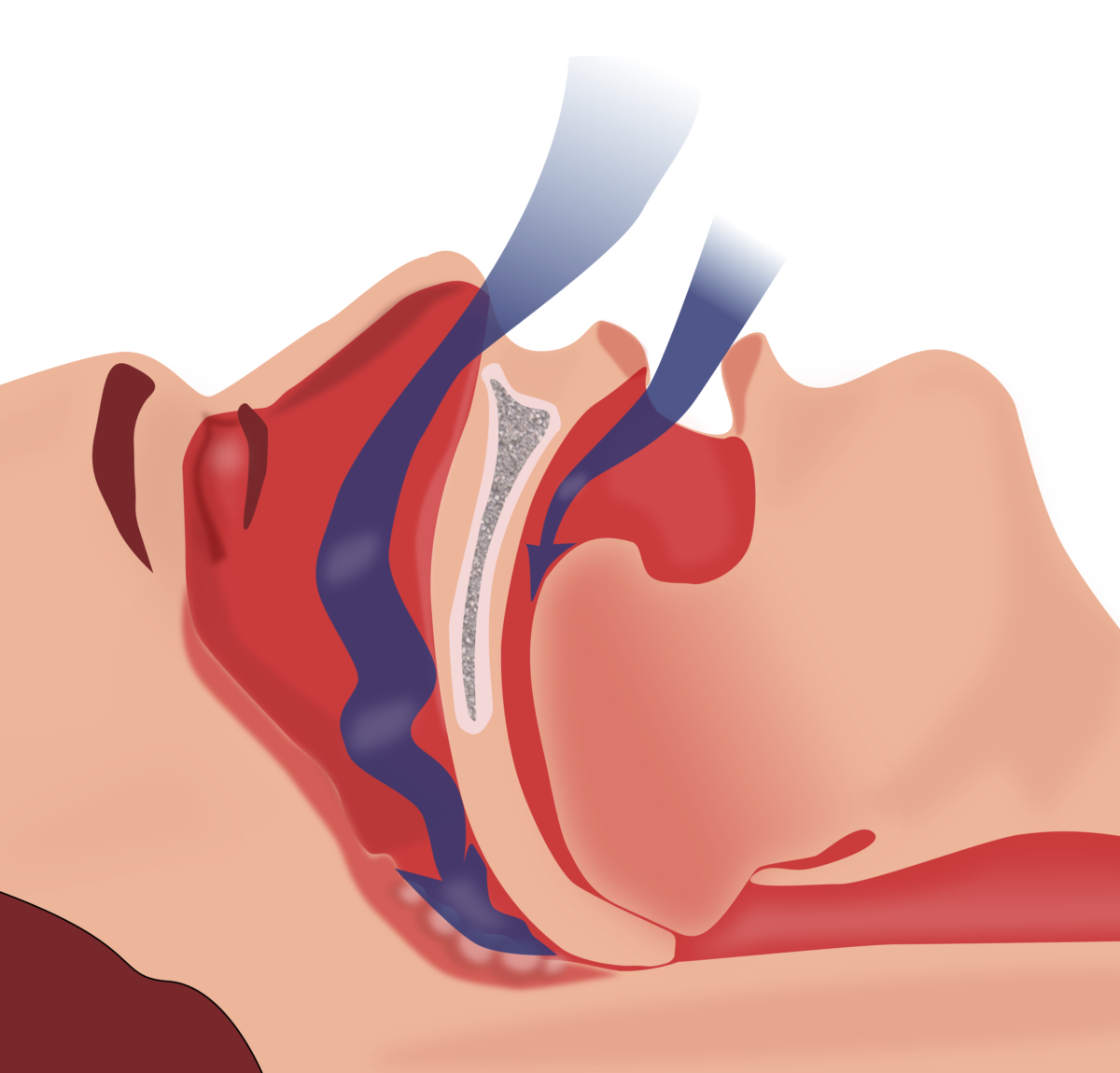
Epidemiology and Classification Epidemiology of OSA[4–6,28] OSA in adults: OSA in children (< 18 years of age):[27] Classification of sleep-related breathing disorders (SRBD)[4,17,24–26] Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) disorders: Central sleep apnea (CSA) syndromes: Hypoventilation syndromes: Hypoxemia syndromes: Risk Factors and Pathophysiology Risk factors[1,5,6] Pathophysiology[5,17] Clinical Presentation Often, the patient is unaware of their symptoms and […]
Necrotizing Fasciitis (Clinical)
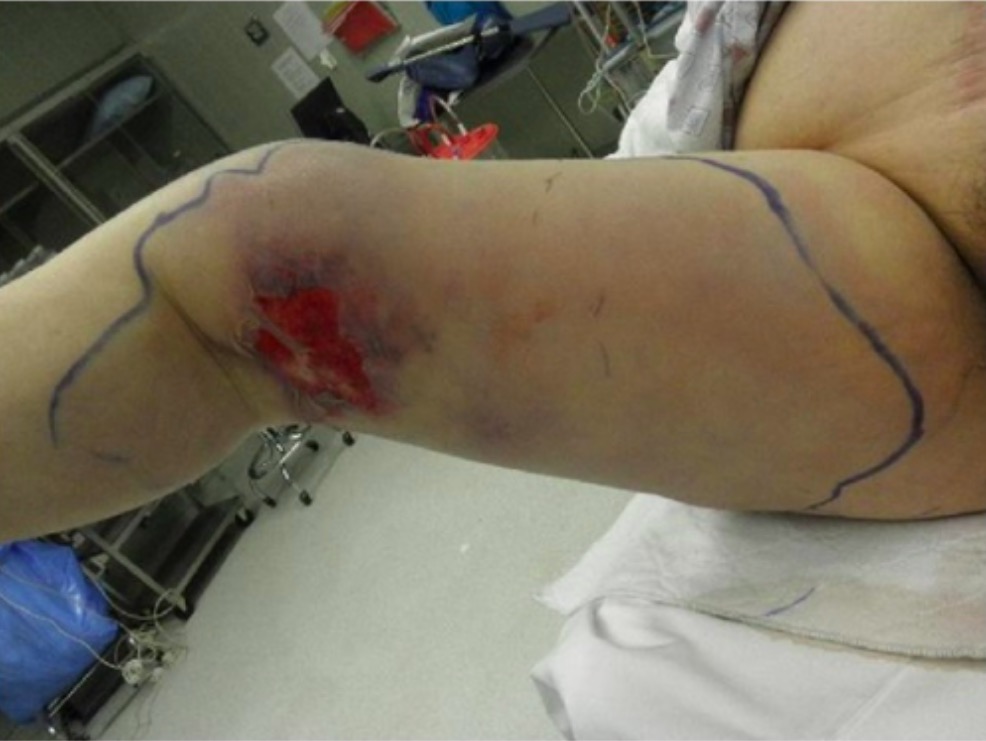
Overview Epidemiology[1] Etiology[1,8,11,13] Necrotizing fasciitis is divided into microbiologic categories based on the causative organism(s): Risk factors[1,2,8,9,11] Pathophysiology[1,2,7,8,11] Clinical Presentation Skin and soft tissue findings[1,8,11] Be sure to mark skin lesions during the physical examination. Early signs: Late signs: Common sites of infection: Evidence of systemic toxicity[8,11] Diagnosis A definitive diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis is […]
Stable Angina (Clinical)

Overview Definition[5,8] Stable angina is episodic chest pain due to transient myocardial ischemia resulting from coronary atherosclerosis. Epidemiology[3–5,12] Etiology[1,7] Angina results from coronary artery disease (CAD), which is the atherosclerotic obstruction of the coronary arteries. Risk factors[10] Cardiac risk factors include: Pathophysiology Angina is a result of mismatched myocardial oxygen demand and oxygen supply.[2,4,5,7,8] Myocardial […]
Kawasaki Disease (Clinical)
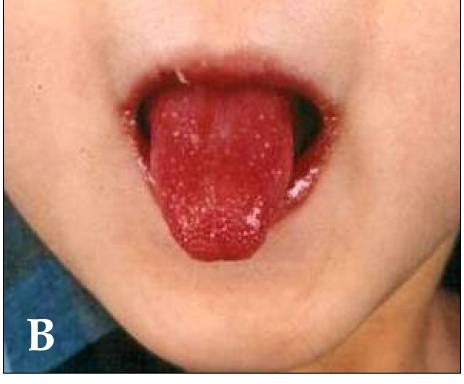
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[1,2,6] Etiology[1,3–5] The etiology of Kawasaki disease (KD) is unknown. There are several theories: Pathophysiology Kawasaki disease is a systemic, inflammatory illness that affects medium-sized arteries, especially the coronary arteries.[3,4] Clinical Presentation Commonly presenting symptoms[6] Less common manifestations Table: Other manifestations of Kawasaki disease[6] System Manifestations Gastrointestinal Diarrhea, abdominal pain, vomiting, liver […]
Hypothyroidism (Clinical)
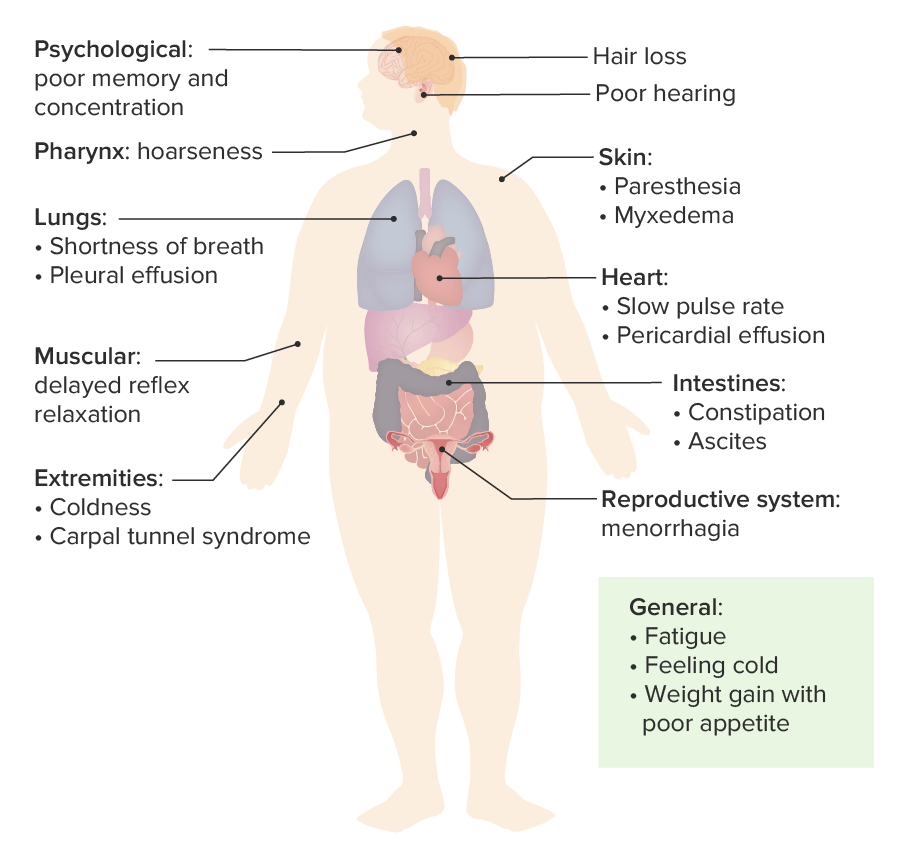
Overview Definition[3,8] Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disorder resulting from thyroid hormone deficiency. Epidemiology[1,2,9] Classification[3,7,8] By onset: By organs affected with disease: Etiology of congenital hypothyroidism[1,8] Etiology of acquired hypothyroidism[2,3] Pathophysiology Hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis[2] Clinical Presentation Underlying processes of manifestations[7,9] Congenital hypothyroidism[1,10] Acquired hypothyroidism Common signs and symptoms:[8,9] In the elderly: Myxedema coma: Diagnosis Congenital hypothyroidism Mandatory […]
Breast Cancer Screening (Clinical)
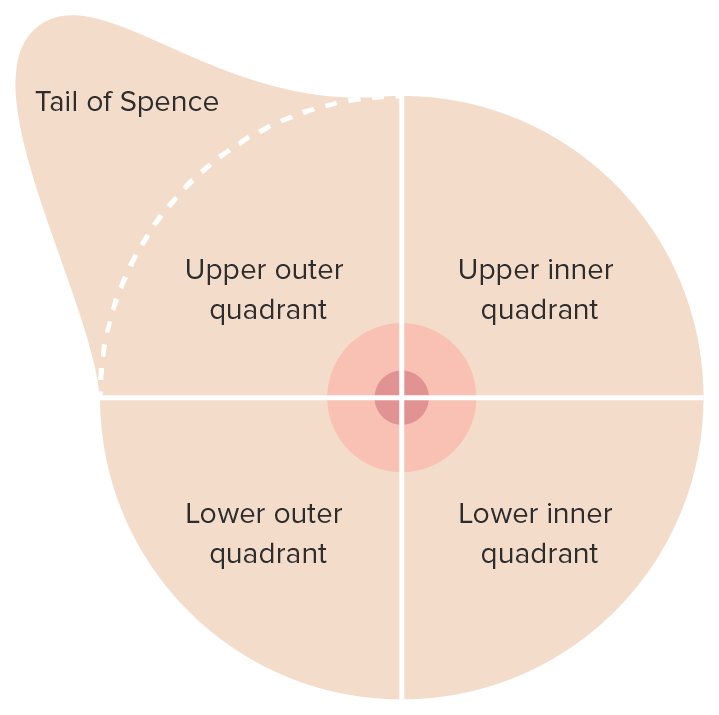
Overview Breast cancer Breast cancer is a disease characterized by malignant transformation of the epithelial cells of the breast. Epidemiology[4,5,8,12] Overview of screening process[4,12] Risk factors for breast cancer[1,4,12] Mnemonic: BReast-CAncer 1 and 2: BRCA1 and BRCA2 are the mutated genes in breast cancer. Initial risk assessment[3,4,12,20] Details of the patient’s medical and personal history […]
Conjunctivitis (Clinical)
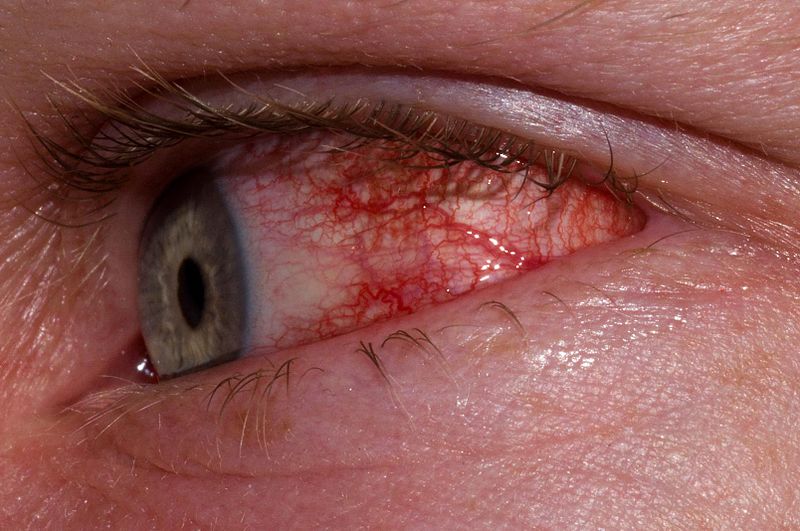
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[1,3] Etiology Infectious conjunctivitis Noninfectious conjunctivitis Clinical Presentation Patients can present with some or all of the following symptoms:[1 –3] Table: Clinical presentation of conjunctivitis based on etiology Viral conjunctivitis Bacterial conjunctivitis Allergic conjunctivitis Discharge Clear, watery discharge Thick, purulent yellow, white, or green discharge with severe crusting (eyes glued shut upon awakening) […]