Renal Cell Carcinoma
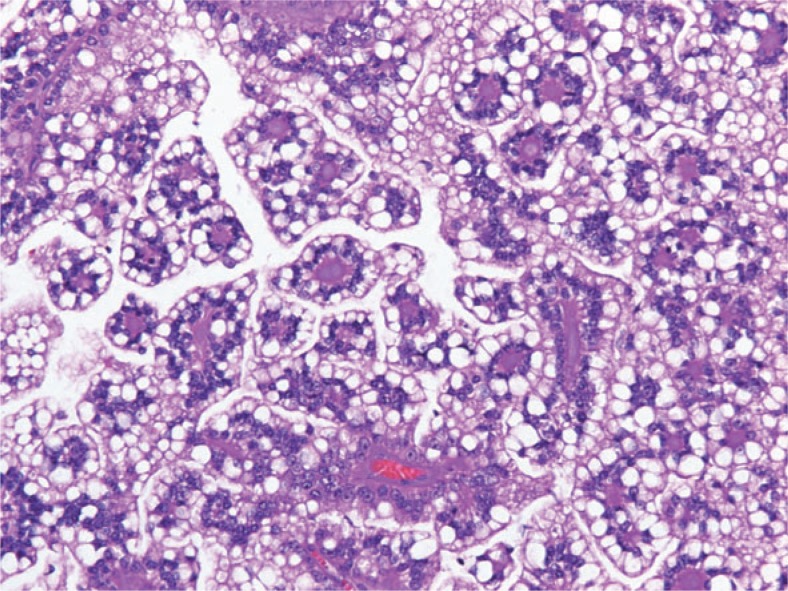
Overview Definition Renal cell carcinoma (RCC), also called hypernephroma and renal cell adenocarcinoma, is a type of cancer that originates from the lining of the small tubules of the renal cortex. Epidemiology Accounts for 80%–85% of all primary renal neoplasms Incidence is highest in North America and the Czech Republic: In North America, RCC is […]
Delirium

Overview Definition Epidemiology Pathophysiology Etiology Predisposing and precipitating factors Predisposing: Precipitating: Etiology The acronym “DELIRIUM” can be helpful in remembering the most common etiologies of the condition. Clinical Presentation Hallmarks of delirium Classification of delirium Based on the main types of symptoms exhibited Diagnosis History and exam Lab studies and imaging Management Overview Nonpharmacologic interventions […]
Infertility
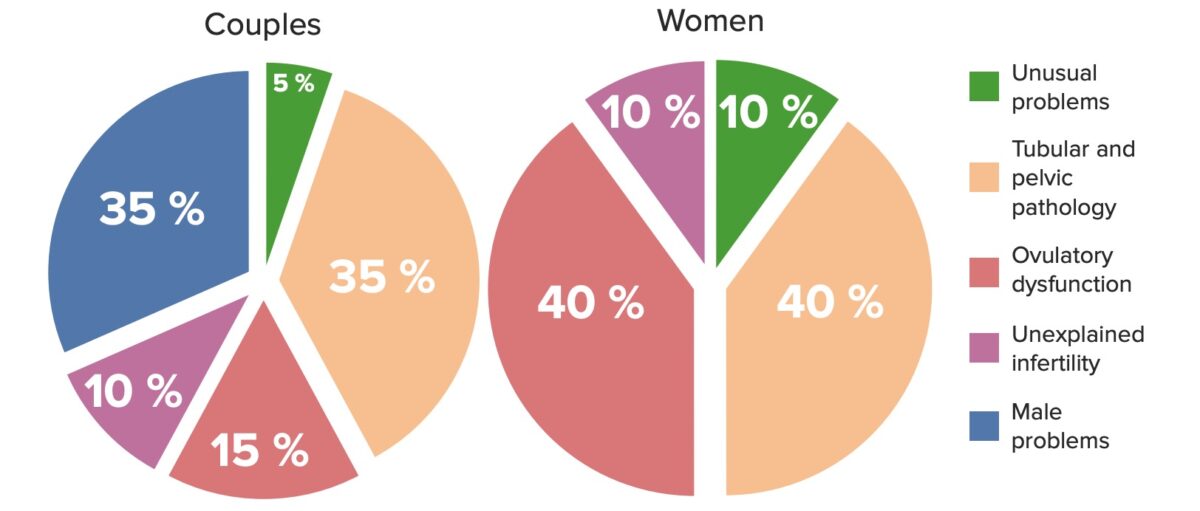
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Infertility is defined as the inability of a couple to conceive after 12 months of regular intercourse, in cases when the woman is < 35 years of age, or after 6 months of regular intercourse in couples when the woman is > 35 years of age. Epidemiology Normal fecundability (the probability […]
Knee Ligament Injuries
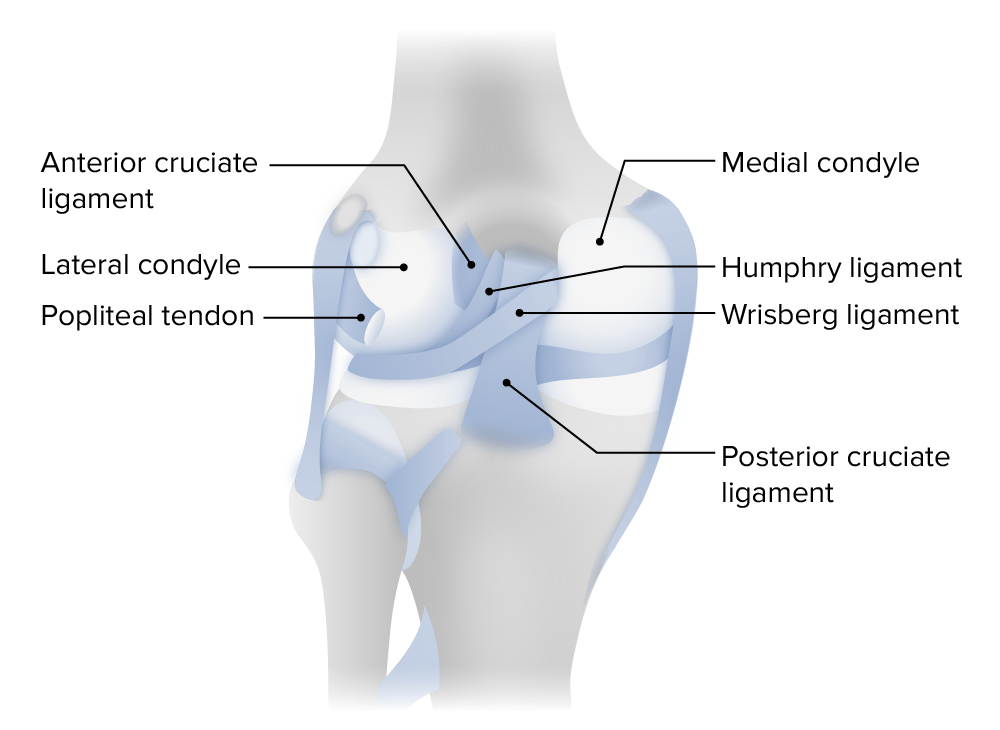
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injury Definition An anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury causes structural damage to the anterior cruciate ligament. The functions of the ligament are to: Anatomy Epidemiology Etiology Clinical presentation Patients with an ACL injury present with pain and report recent high-energy blunt trauma to the knee. History: Physical examination: Diagnosis Diagnosis is […]
Interleukins

Origin and Function of Interleukins Table: Interleukins and their effects on target cells Name Source Target cells Effect on target cells IL-1 Macrophages and monocytes B cells Dendritic cells Endothelial cells Fibroblasts Astrocytes T helper cells B cells Macrophages Endothelium Inflammatory Induces maturation, activation, and proliferation of lymphocytes Pyrogenic Promotes secretion of cytokines and acute-phase […]
Major Neurocognitive Disorders
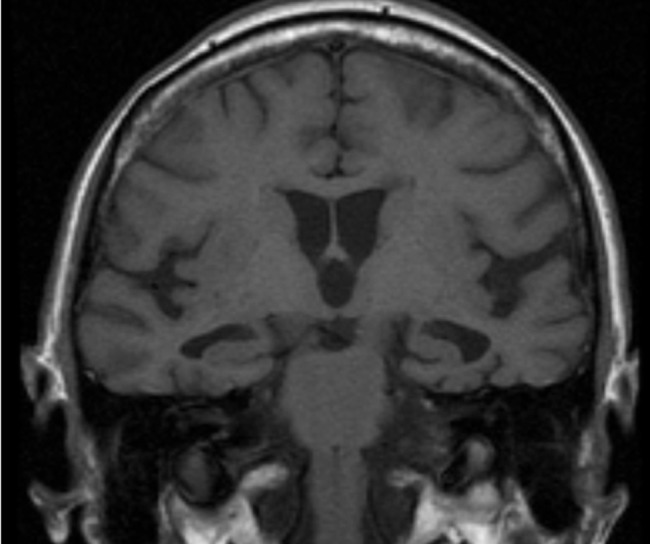
Overview Definition Epidemiology Etiology Most common: Less common: Pathophysiology Pathophysiology of the most common causes of the major NCDs are shortly described below. Alzheimer disease Vascular dementia Dementia with Lewy bodies Parkinson’s disease dementia Frontotemporal dementia Clinical Presentation General features Significant decline in cognition in the following domains: Symptoms are not explained by other medical, […]
Anomalies of the Cornea
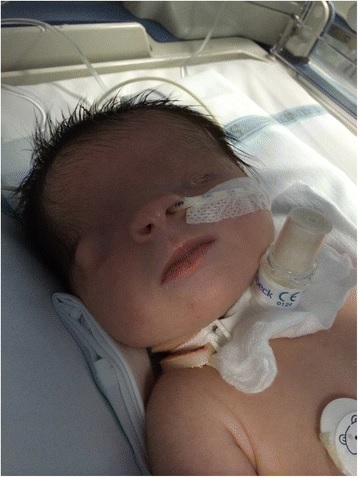
Overview Cornea The cornea is a transparent, avascular, watch glass-like structure that covers the iris, anterior chamber, and pupil. Classification of corneal abnormalities Cryptophthalmos Cryptophthalmos is an autosomal recessive congenital anomaly associated with systemic anomalies and is characterized by an uninterrupted continuity of the skin extending from the forehead to the malar region. Epidemiology Clinical […]
Scoliosis
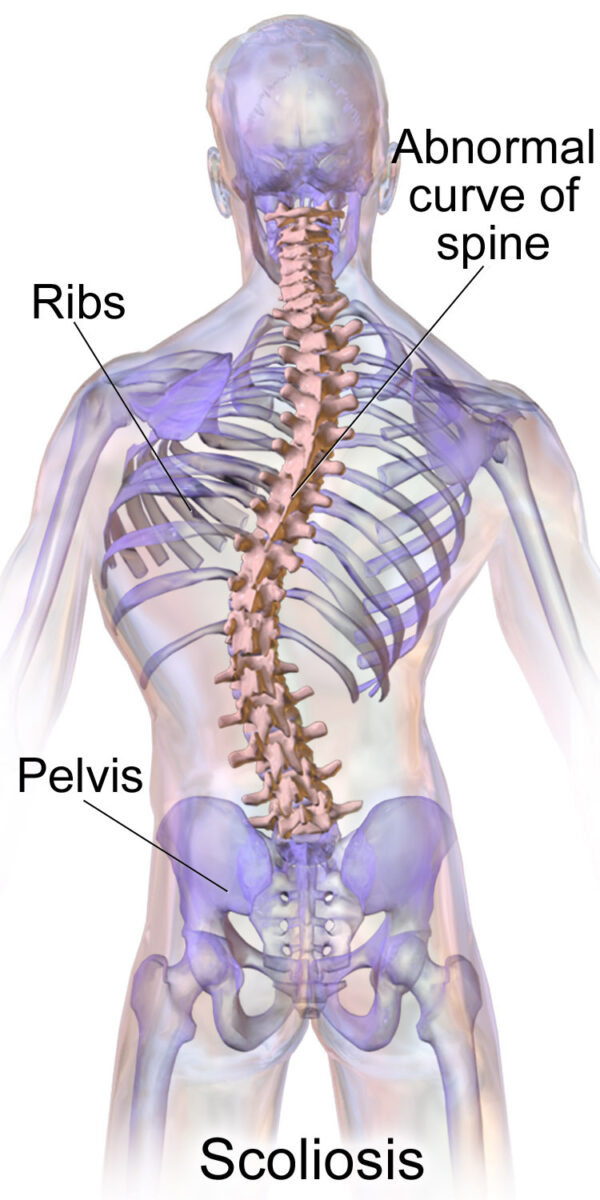
Overview Definition Scoliosis is a lateral spinal curvature of the spine greater than 10 degrees in the coronal plane, usually accompanied by rotation of variable amounts. Epidemiology Classification Pathophysiology Scoliosis can develop de novo or as a continuation of congenital, idiopathic, or early-developed scoliosis. The uneven loading of the spine produces and exacerbates the pathological […]
Clavicle Fracture

Overview Definition A clavicular fracture is a disruption in the integrity of the bony tissue of the clavicle (also called the collar bone). These very common fractures generally heal without incident, although complications are possible. Epidemiology Etiology Classification of clavicular fractures (based on location) Pathophysiology The general principle behind all fractures is that the bone […]
Thalassemia
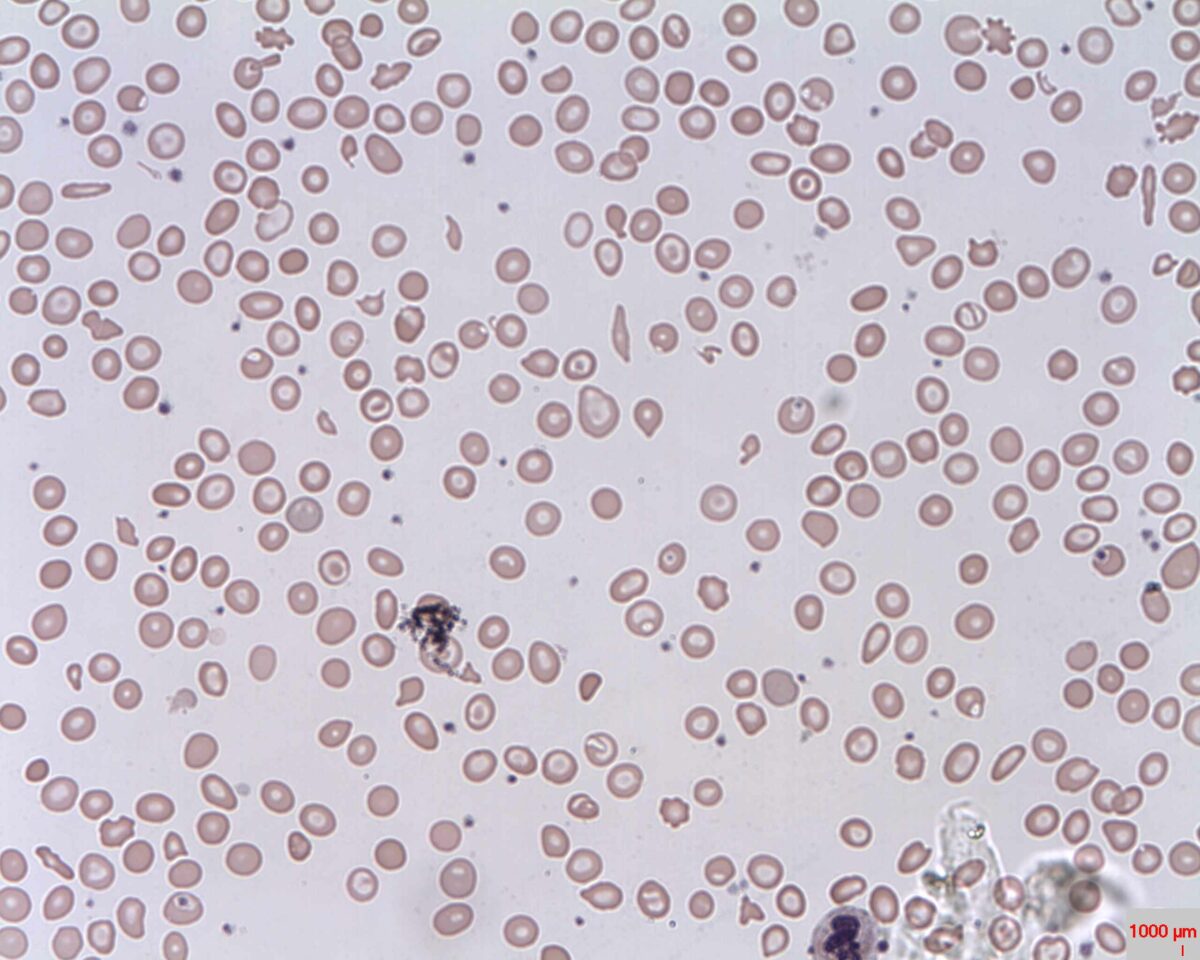
Overview Disease characteristics Thalassemias are hereditary hemoglobin (Hb) disorders of α- or β-globin genes. Defects in these genes lead to abnormal hemoglobin and RBC structure and function. Presents as microcytic hypochromic anemia: Mild cases can be asymptomatic. Severe cases may lead to splenomegaly, hemolysis, and skeletal abnormalities. Epidemiology Worldwide prevalence: α-Thalassemia: 5%; most common in […]