Colon Polyps
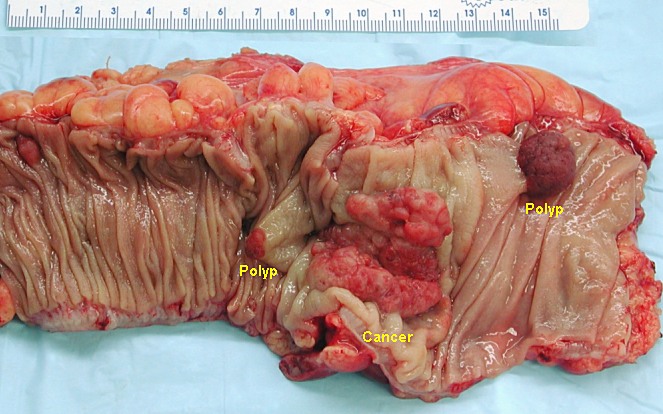
Overview Types of colon polyps Prevalence of colon polyps Risk factors Hereditary polyposis syndromes Each syndrome occurs in < 1% of the population and accounts for 5%–10% of CRCs. Pathophysiology Benign polyps Neoplastic polyps Clinical Presentation Most colon polyps are asymptomatic and discovered on routine colon cancer screening. Diagnosis and Management The definitive diagnosis and […]
Uncontrolled Hypertension
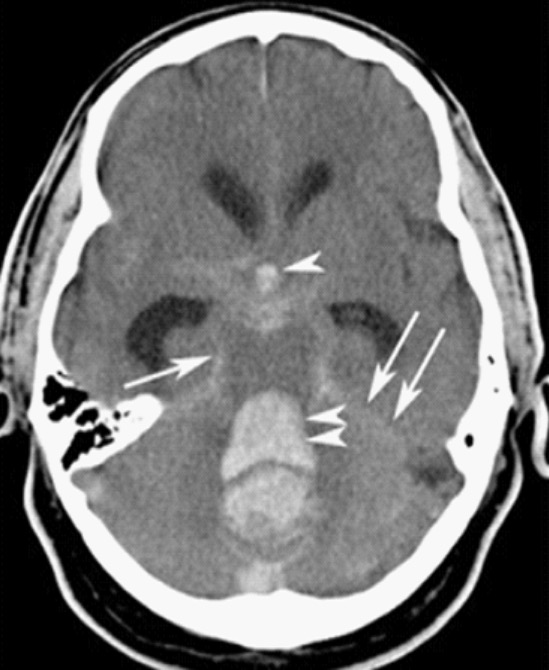
Overview Definitions and classification Etiology Epidemiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Regardless of the manifestation of severe hypertension, by definition, the individual will have a blood pressure ≥ 180 mm Hg systolic and/or ≥ 120 mm Hg diastolic. Hypertensive urgency Hypertensive emergency Evaluation and Diagnosis During the initial assessment of an individual with severe hypertension, it is […]
Hepatitis A Virus
Classification General Characteristics Structure Basic features Epidemiology Pathogenesis Transmission Risk factors Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation General features Specific symptoms The presence of 1 of the following symptoms is a reason to suspect hepatitis A infection, especially in the presence of risk factors: Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Management Prevention Comparison of Hepatitis Viruses Differential Diagnosis References
Hypokalemia
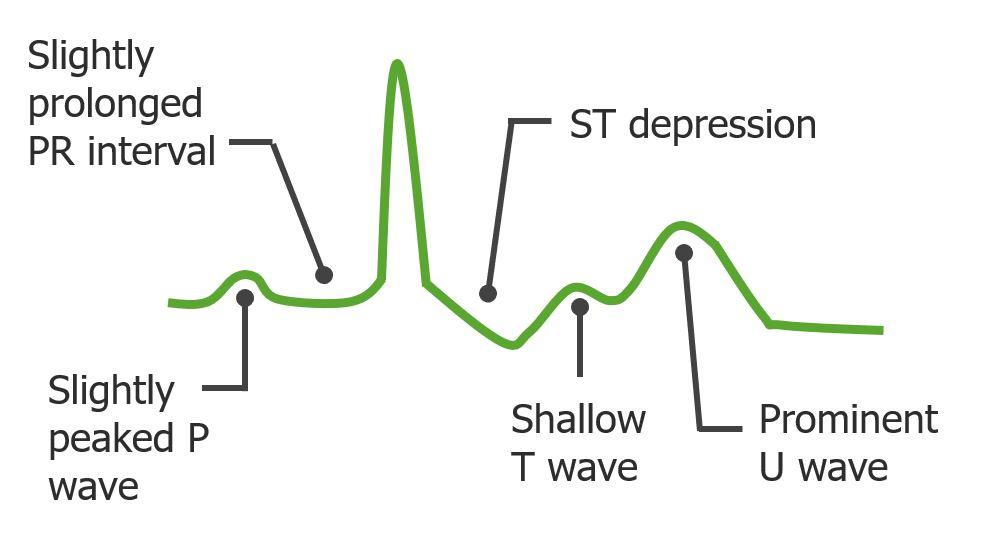
Overview Introduction Potassium (K+) is the main intracellular cation in all cells and is distributed unevenly between the intracellular fluid (98%) and extracellular fluid (2%). The large disparity is necessary for maintaining the resting membrane potential of cells. The GI tract secretes 5%–10% of absorbed K+ daily. Kidneys are responsible for 90%–95% of the overall […]
Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (PanNETs)
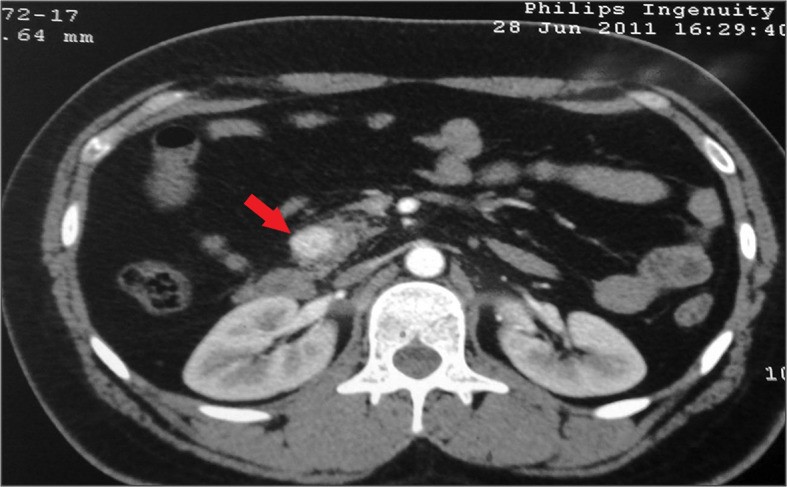
Overview Epidemiology Etiology Pathology and Pathophysiology Pathology Pathophysiology 3 of the most common somatic mutations: Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Patients may present with metastatic disease in the liver, which is then confirmed with biopsy. The diagnostic approach focuses on identifying both the extent of disease spread and the likely primary site of […]
Exocrine Pancreatic Cancer
Overview Classification Epidemiology Etiology Table: Hereditary/genetic factors of exocrine pancreatic cancer Hereditary/genetic factors Germ-line mutations Maximum increased lifetime risk (approximate) Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (PJS) STKII 132 Hereditary pancreatitis PRSS1, others 53 Familial atypical multiple mole melanoma (FAMMM) p16/CDKN2A 38 Family history (increases with the number of 1st-degree relatives and if cancer < 55 years) Unknown 32 […]
Serum Tumor Markers

Overview Definition Uses and limitations Uses: Baseline level should be established at the time of initial presentation. Limitations: Classification Clinical Significance Levels of tumor markers can be useful in monitoring response to treatment for many cancers but have drawbacks and false positives. Common tumor markers Multiple tumor marker testing Comprehensive List of Tumor Markers Table: […]
Hirschsprung Disease
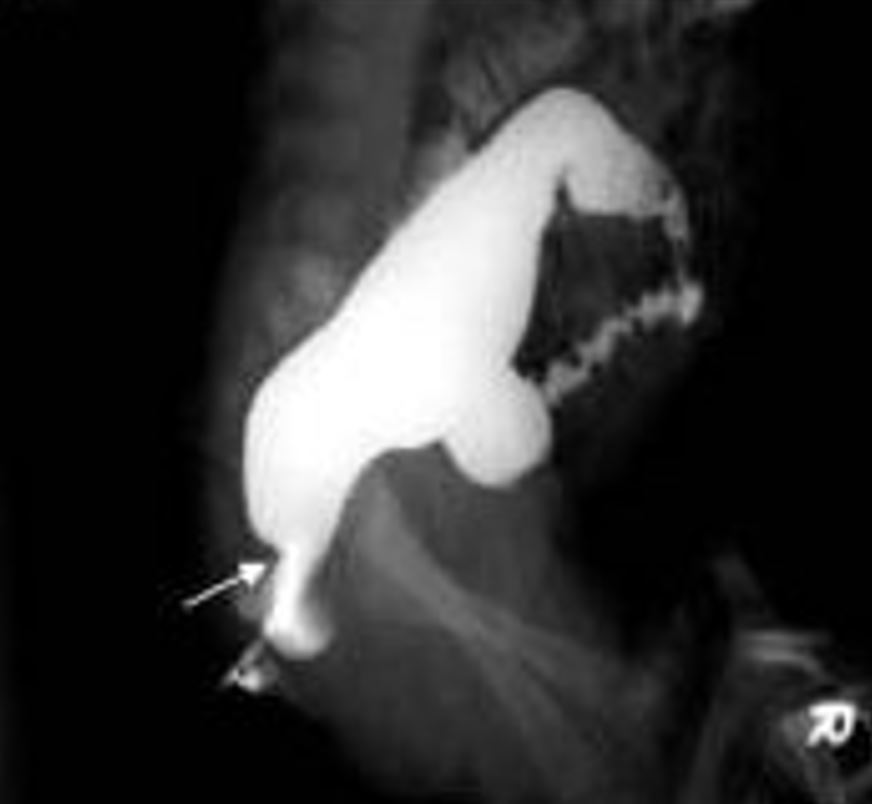
Overview Definition Hirschsprung disease (HD), also known as congenital aganglionosis or congenital megacolon, is a congenital anomaly of the colon caused by the failure of neural crest-derived ganglion cells to migrate into the distal colon. Classification Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology The pathophysiology in HD is the complete absence of ganglion cells (aganglionosis) in the intrinsic nerve […]
Carcinogenesis
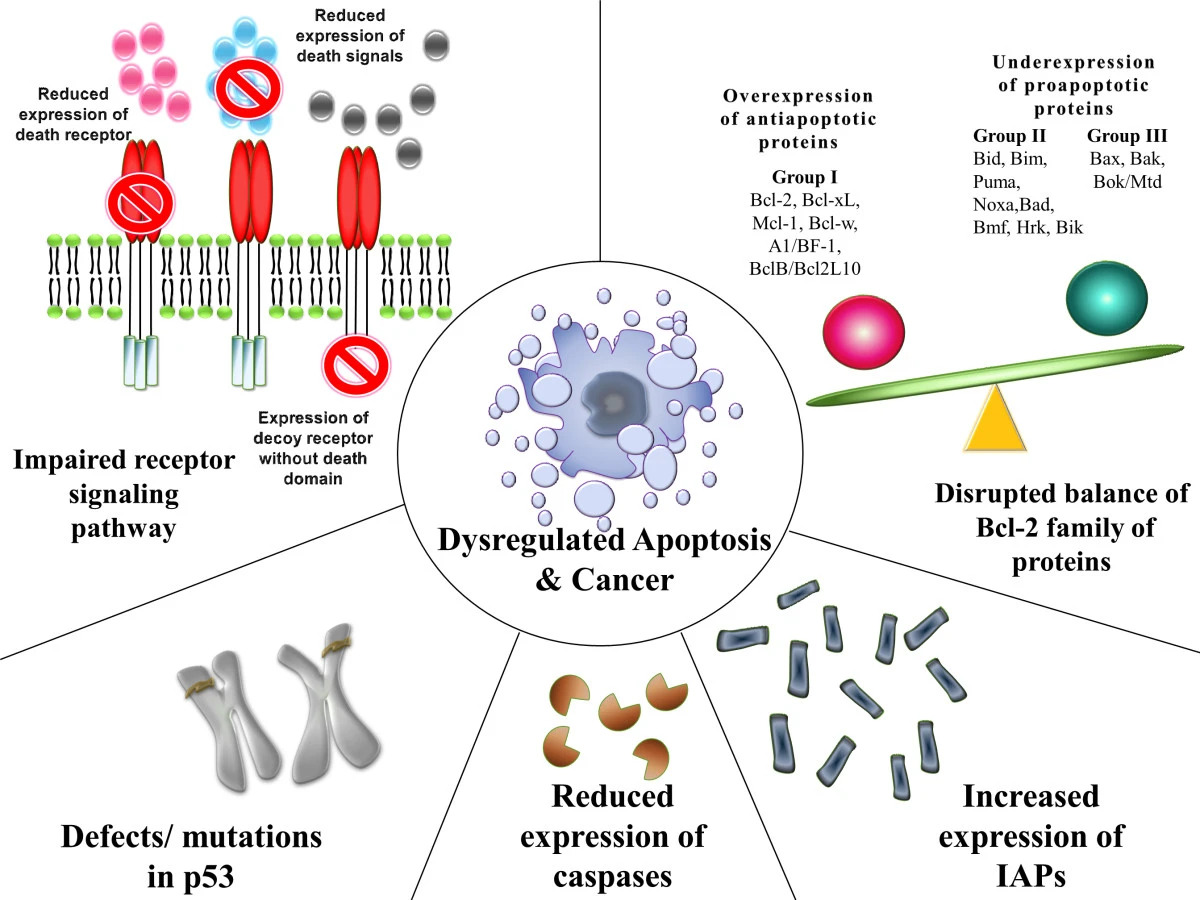
DNA-Damaging Agents Overview Chemical carcinogens Radiation Infections Pathogenesis Overview Cellular changes Regulatory Genes There are 4 classes of normal regulatory genes that are often damaged. Cancer Subtypes Type of cell Common cancers Clinical Relevance References
Glycopeptides
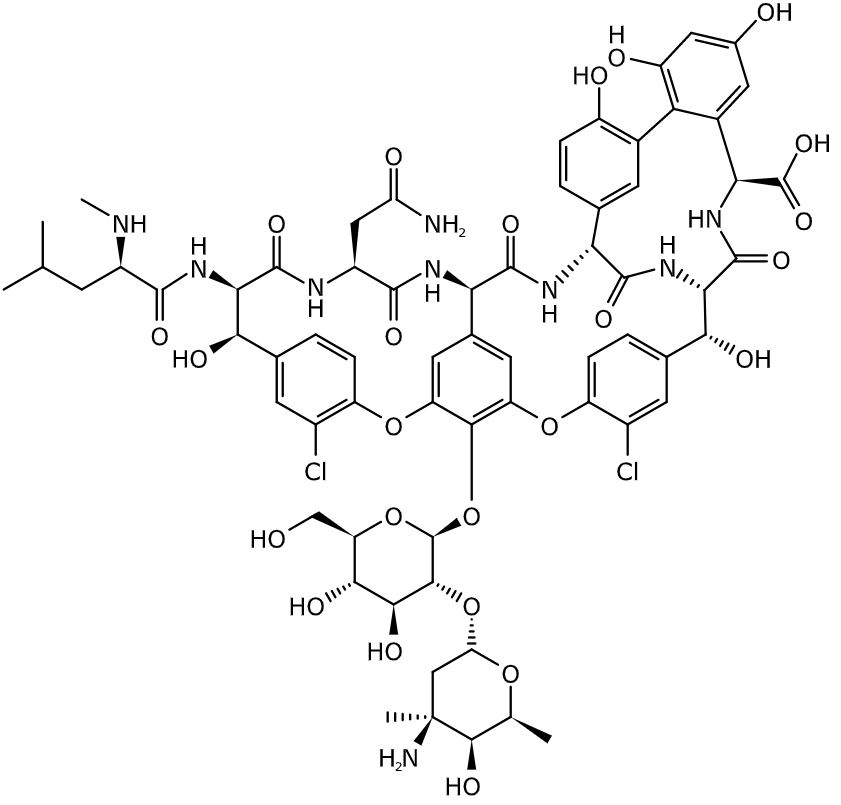
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Definition Glycopeptide antibiotics (GPAs) are actinomycete-derived, glycosylated, nonribosomal peptides, which target gram-positive bacteria by inhibition of cell wall synthesis: Vancomycin Teicoplanin (not available in the United States) Chemical structure Both vancomycin and teicoplanin are heptapeptides, but the carbohydrate groups of each drug differ. Mechanism of action Glycopeptides are bactericidal through inhibition of […]