Chest Pain

Overview Anatomy The anatomy of the chest and thorax includes: heart, lungs, breasts, and chest wall. History Description of chest pain: Typical chest pain descriptions and their clinical significance: Risk factors: Physical examination Vital sign abnormalities and their possible diseases: Examples of important findings in the physical exam: Diagnostic workup Differential Diagnosis Cardiovascular causes Gastrointestinal […]
High-Risk Headaches
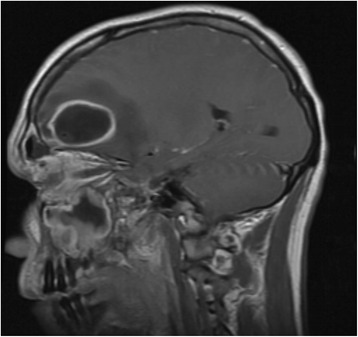
Overview Definition A high-risk headache is any new and sudden onset, typically severe, headache with the potential to cause damage to cerebral or precerebral structures or functions. Etiology There are many etiologies of high-risk headache that the clinician should be aware of and work to rule out when a severe headache is encountered. The most […]
Pyelonephritis and Perinephric Abscess
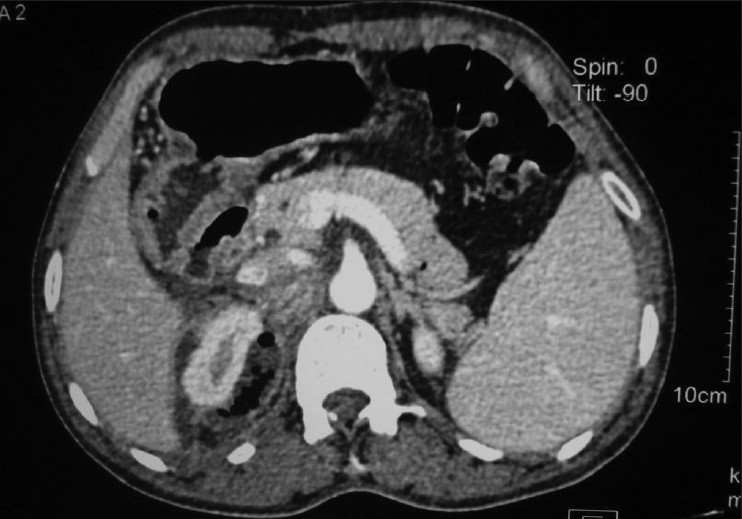
Overview Definitions Types of pyelonephritis Acute pyelonephritis is the sudden-onset infectious process and inflammation of the kidney(s) from ascending infection or hematogenous spread of systemic infections. Epidemiology Etiology Uropathogens Risk factors for urinary tract infections Associated with the development of pyelonephritis and perinephric abscess: Pathophysiology Acute pyelonephritis Chronic pyelonephritis Perinephric abscess Clinical Presentation Clinical features […]
Adrenal Hormones
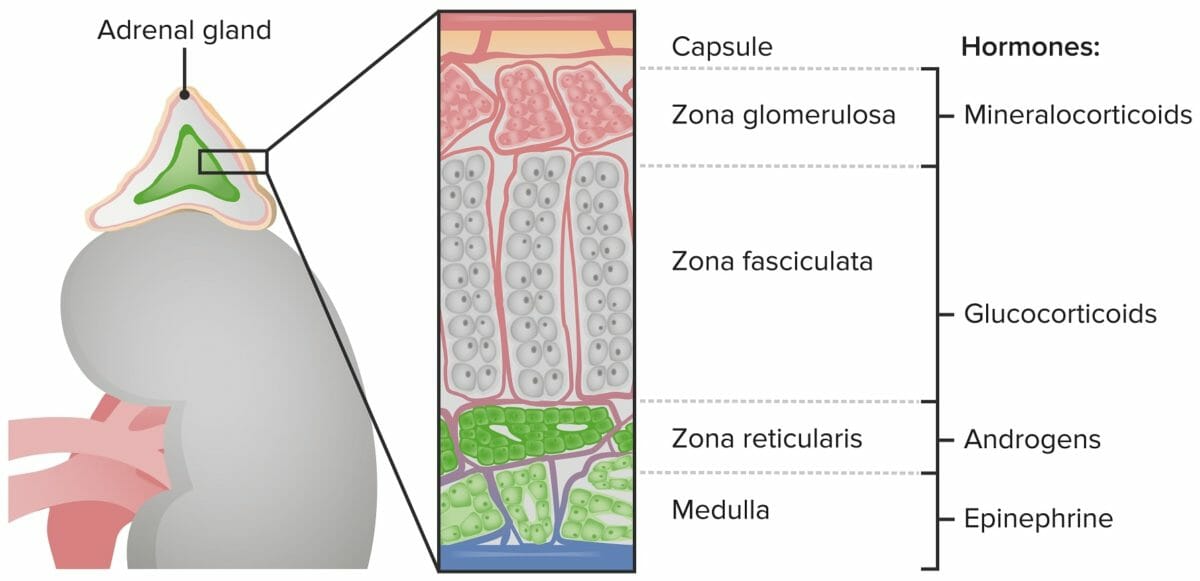
Overview Regions of the adrenal gland The adrenal glands have 2 primary areas with separate functions and regulatory mechanisms. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis Hormones secreted by the adrenal cortex (not the medulla) are controlled by, and help regulate, the HPA axis. Adrenal Cortex Hormones: Mineralocorticoids Mineralocorticoid overview The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) The RAAS is one of […]
Lateral Medullary Syndrome (Wallenberg Syndrome)
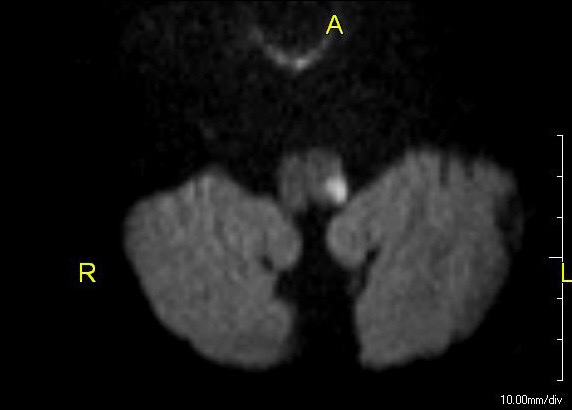
Overview Definition Lateral medullary infarction (also known as Wallenberg syndrome, posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) syndrome, and vertebral artery syndrome) is a neurological constellation of symptoms and signs due to decreased blood flow in vessels supplying the medulla, resulting in brainstem ischemia or infarction. Anatomy Components of the lateral medulla: Blood supply: Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology […]
Pituitary Gland: Anatomy
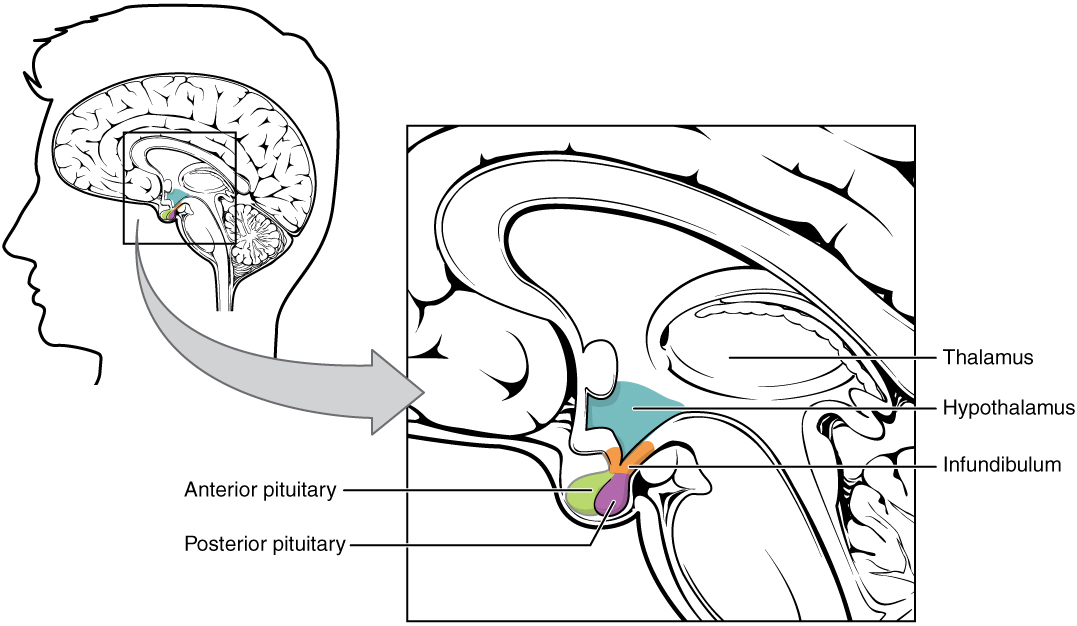
Overview The pituitary gland is known as the “master endocrine gland.” This gland receives stimulatory input from the hypothalamus and secretes multiple different hormones, which target multiple different end organs and have wide-ranging effects throughout the body. Location General structure The pituitary gland is divided into 2 primary components: The 2 halves function independently, as […]
Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)
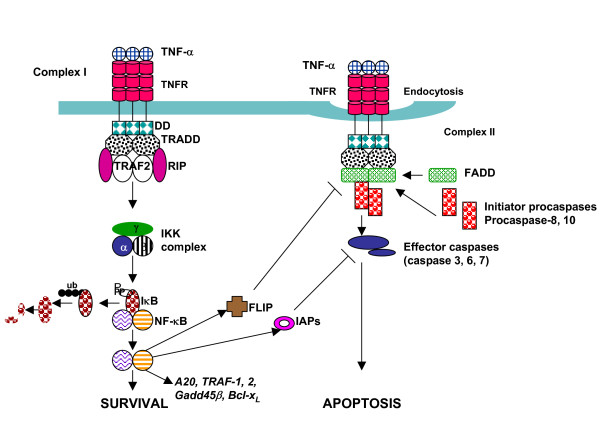
Overview Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) General functions of tumor necrosis factor Tumor Necrosis Factor Superfamily Members of the superfamily Notable members Effects of Tumor Necrosis Factor Induction Tumor necrosis factor receptors Effects Tumor Necrosis Factor and Diseases Diseases Anti–tumor necrosis factor therapy Tumor necrosis factor has multiple biologic effects, and in certain conditions (e.g., rheumatoid […]
Epilepsy
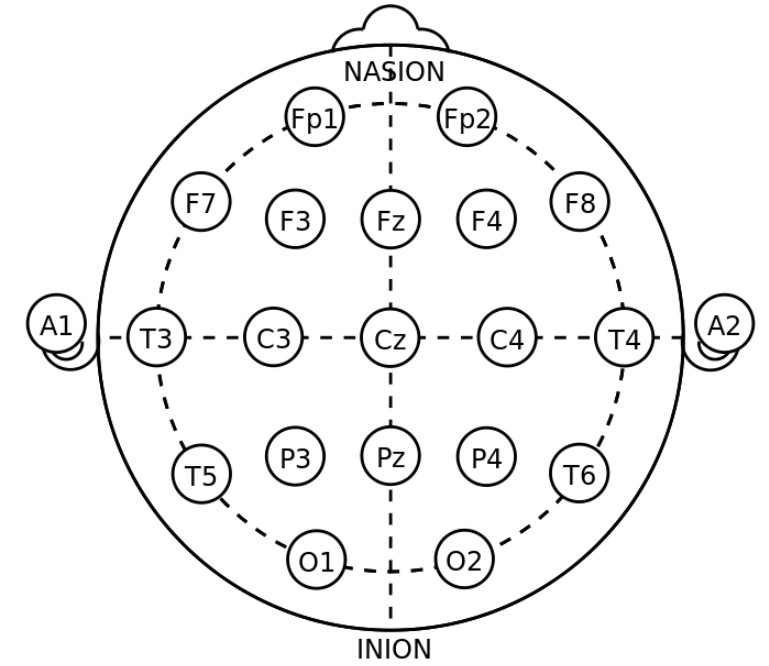
Overview Definition Epilepsy is a chronic brain disorder marked by recurrent and unprovoked seizures. Epidemiology Classification Several features may be used to classify epilepsy, which is useful in considering management options. Clinical Presentation Epilepsy syndromes relate to seizure types and are classified primarily using the clinical history; classification requires input from a family member or […]
Brain Death
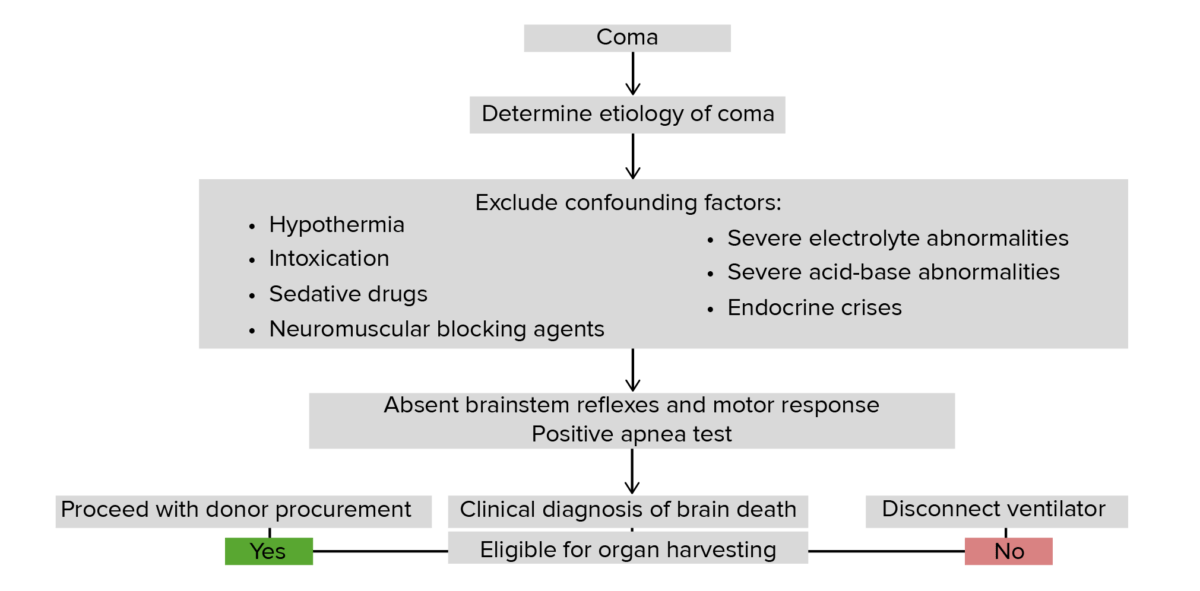
Overview and Pathophysiology Definition Brain death is the complete and permanent loss of all cerebral and brain stem functions, including the ability of the brain stem to regulate vegetative and respiratory activities. Definition of “complete and permanent loss” of brain function: Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation History Physical examination Diagnosis The assessment of brain death in […]
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
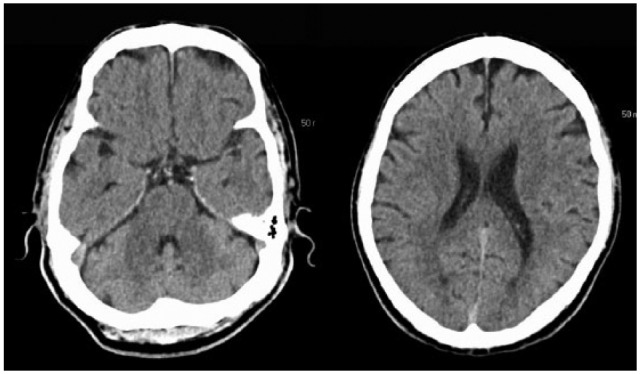
Overview Definition A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a temporary episode of neurologic dysfunction caused by ischemia without infarction that resolves completely when blood supply is restored. Epidemiology Etiology Risk factors Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation The presentation depends on the pathophysiologic mechanism: embolic, lacunar (small penetrating vessel) TIA, or large artery TIA. Pathophysiology Clinical presentation […]