Syncope
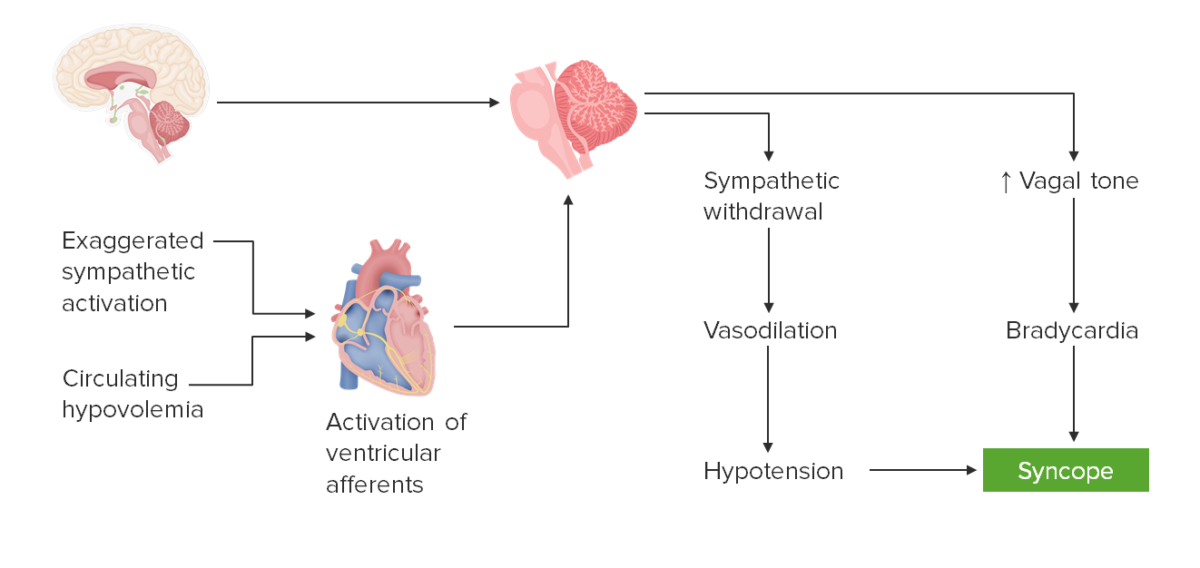
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Syncope is a self-limiting, transient loss of consciousness caused by inadequate cerebral blood flow that results in inadequate cerebral perfusion. Presyncope (also known as near-syncope) is part of the syncope spectrum. Epidemiology Etiology Regardless of the underlying cause, syncope is a manifestation of hypoperfusion to either the cerebral cortex (bilateral) or […]
Ménière Disease
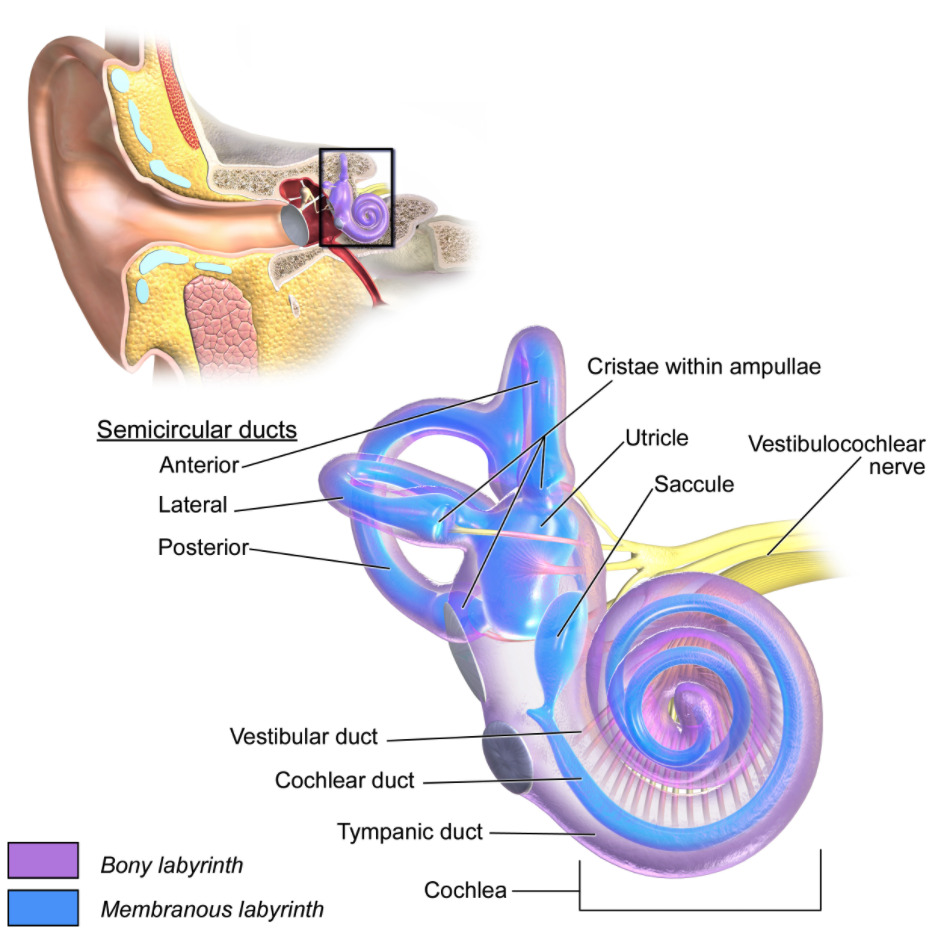
Overview Definition Ménière disease is a triad of episodic vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss likely caused by endolymphatic hydrops of the labyrinthine system of the inner ear. Ménière syndrome is Ménière disease occurring secondary to other inner ear infections. Epidemiology Risk factors Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Diagnostic criteria Clinical diagnosis made by the presence of: […]
Persistent Vegetative State
Overview Definition Persistent vegetative state, also called unresponsive wakefulness, describes the condition of individuals with severe anoxic brain injury who have progressed to a state of wakefulness without any meaningful response to their environment. The definition requires permanence of vegetative state, which is established: 3 months after a hypoxic brain injury 1 year after a […]
Dystonia
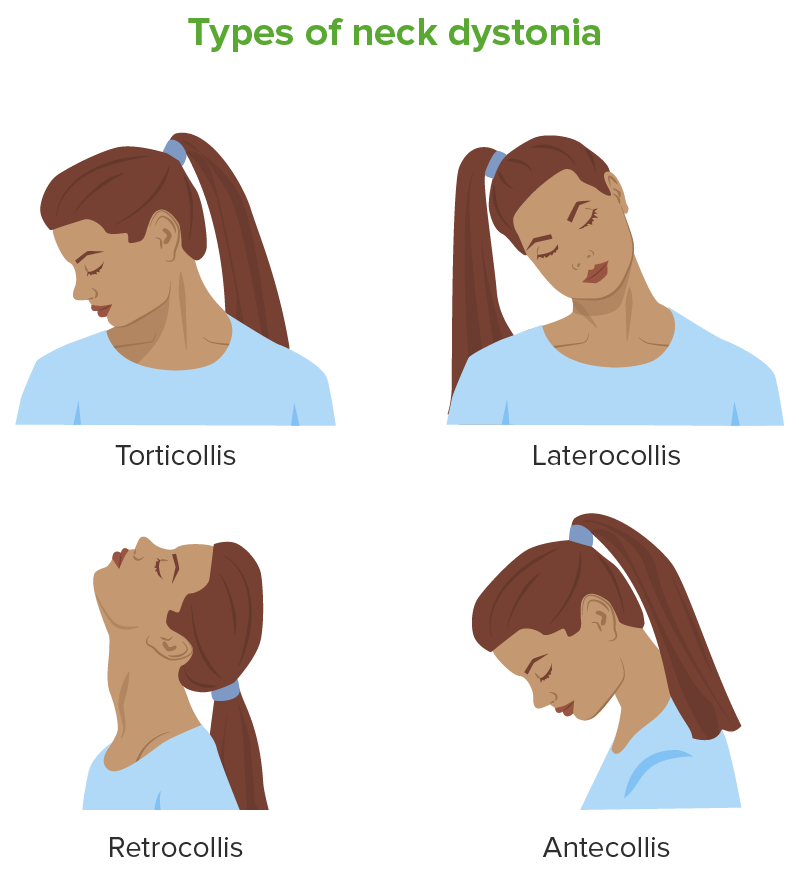
Overview Definition Dystonia is a group of movement disorders characterized by involuntary muscle contractions that cause abnormal control of movement and posture. Dystonia is a focal or generalized hyperkinetic disorder that presents with an excessive muscle-contraction response. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Classification Body distribution Selected types of common dystonias Table: Selected types of common dystonias Name […]
Portal Hypertension
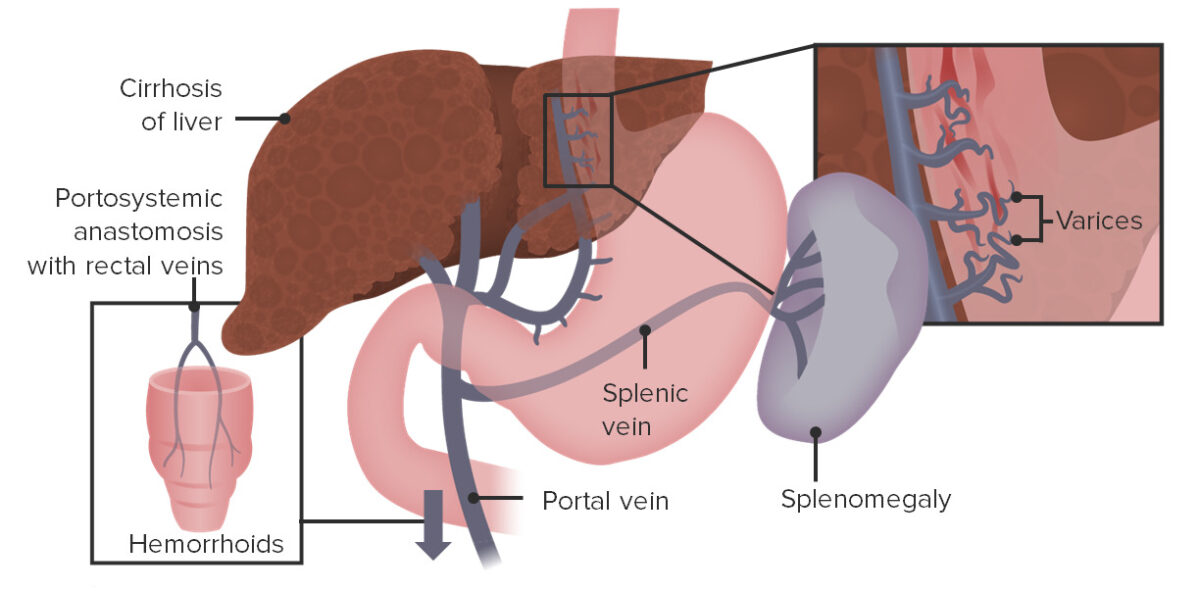
Etiology and Pathophysiology Etiology The etiologies of portal hypertension can be classified based on the location of increased resistance to blood flow through the liver. Prehepatic etiologies: Hepatic etiologies: Posthepatic etiologies: Pathophysiology Anatomy: Portal hypertension: Clinical Presentation Portal hypertension itself usually has no symptoms. Clinical manifestations arise as a result of the underlying etiology and/or […]
Hepatitis C Virus
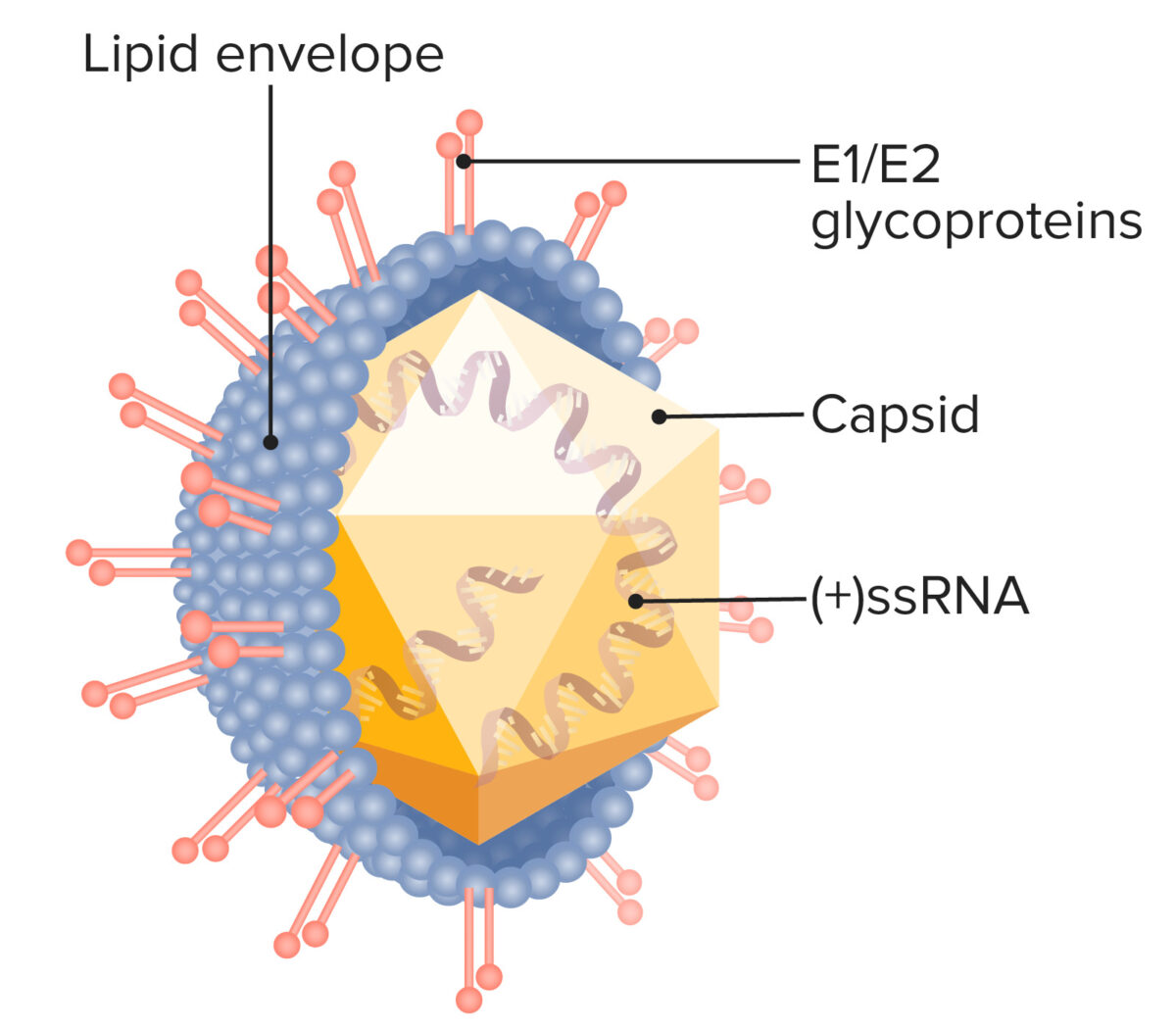
Classification General Characteristics Structure Features Epidemiology Pathogenesis Transmission Humans are the only reservoir for the virus. Modes of transmission include: Host risk factors Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Acute infection Chronic infection Diagnosis Viral markers Further testing Management Pharmacotherapy Prevention Hepatitis Viruses Comparative Table Differential Diagnosis References
Intravenous Fluids
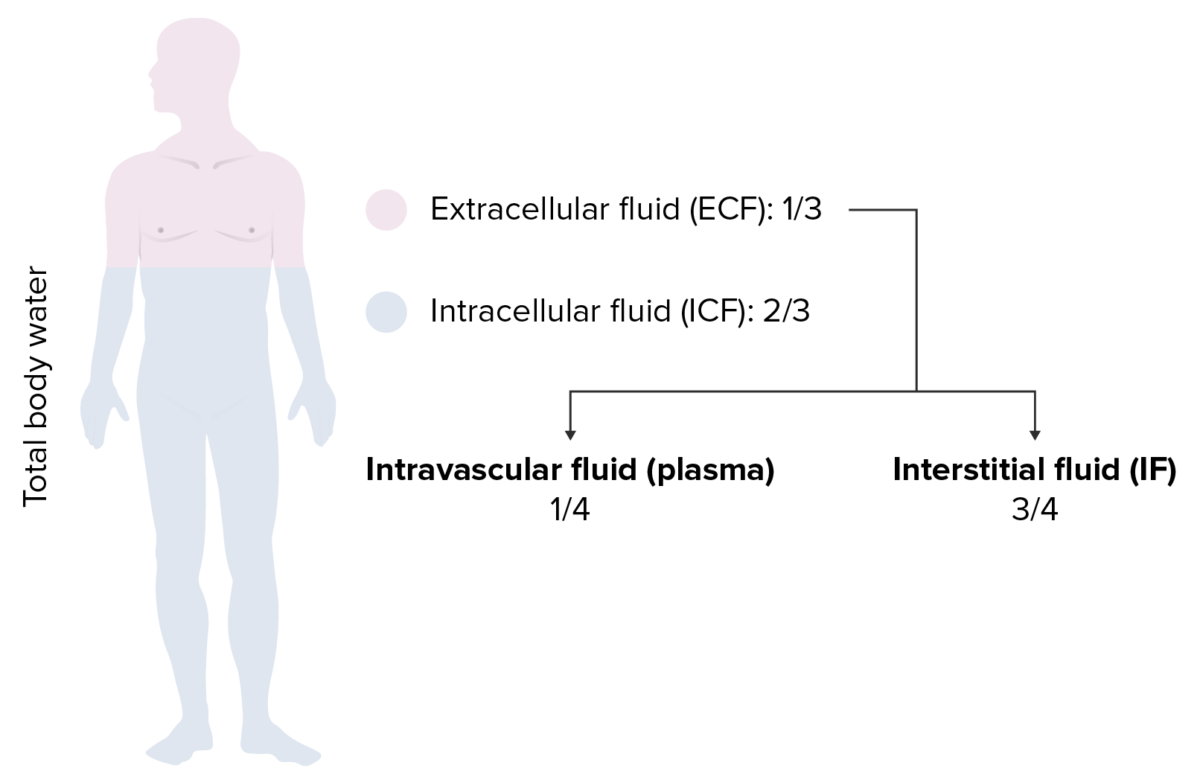
Overview Fluid compartments of the body Movement of water across the compartments Osmolarity, osmolality, and tonicity Crystalloid Fluids Normal saline (0.9% NaCl) Ringer’s lactate (RL) Plasma-Lyte© (PL) Half-normal saline (0.45% NaCl) Quarter-normal saline (0.225% NaCl) 5% dextrose in water Combined solutions Bicarbonate (HCO3) solutions 3% hypertonic saline (3% NaCl) Overview of composition of common crystalloid […]
Trigeminal Neuralgia
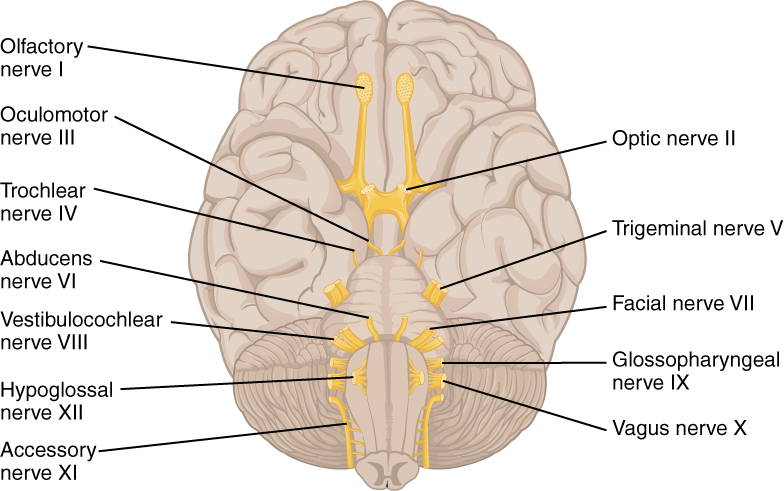
Overview Definition Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a disorder presenting with recurrent, sharp pain in the distribution of the trigeminal nerve. Anatomy of the trigeminal nerve Trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve (CN) V): 3 major divisions of CN V: Epidemiology Etiology Clinical Presentation Main reported symptoms Associated symptoms When other neurologic conditions (e.g., multiple sclerosis or aneurysms) […]
Diarrheagenic E. coli
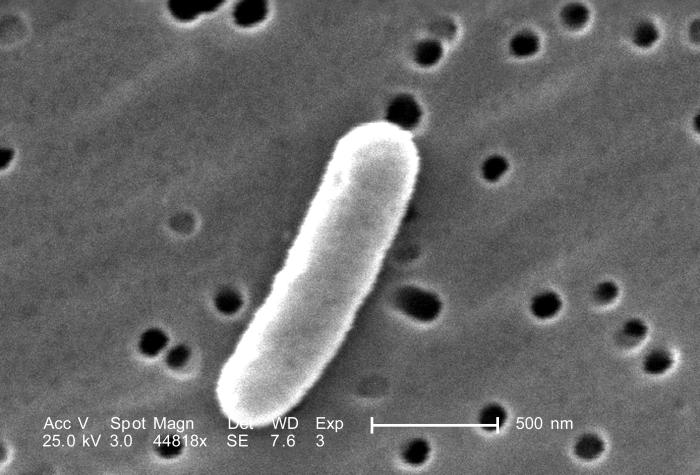
Overview Microbiology Pathogenic strains of E. coli Diarrheagenic strains of E. coli can be classified into 5 key “pathotypes,” each of which has unique virulence factors and pathologic mechanisms. Transmission Table: Comparison of E. coli strains Pathogen Invasive? Toxin? Type of diarrhea ETEC No LT ST Noninflammatory Watery EPEC No No Mild inflammatory Watery EAEC […]
Vertigo
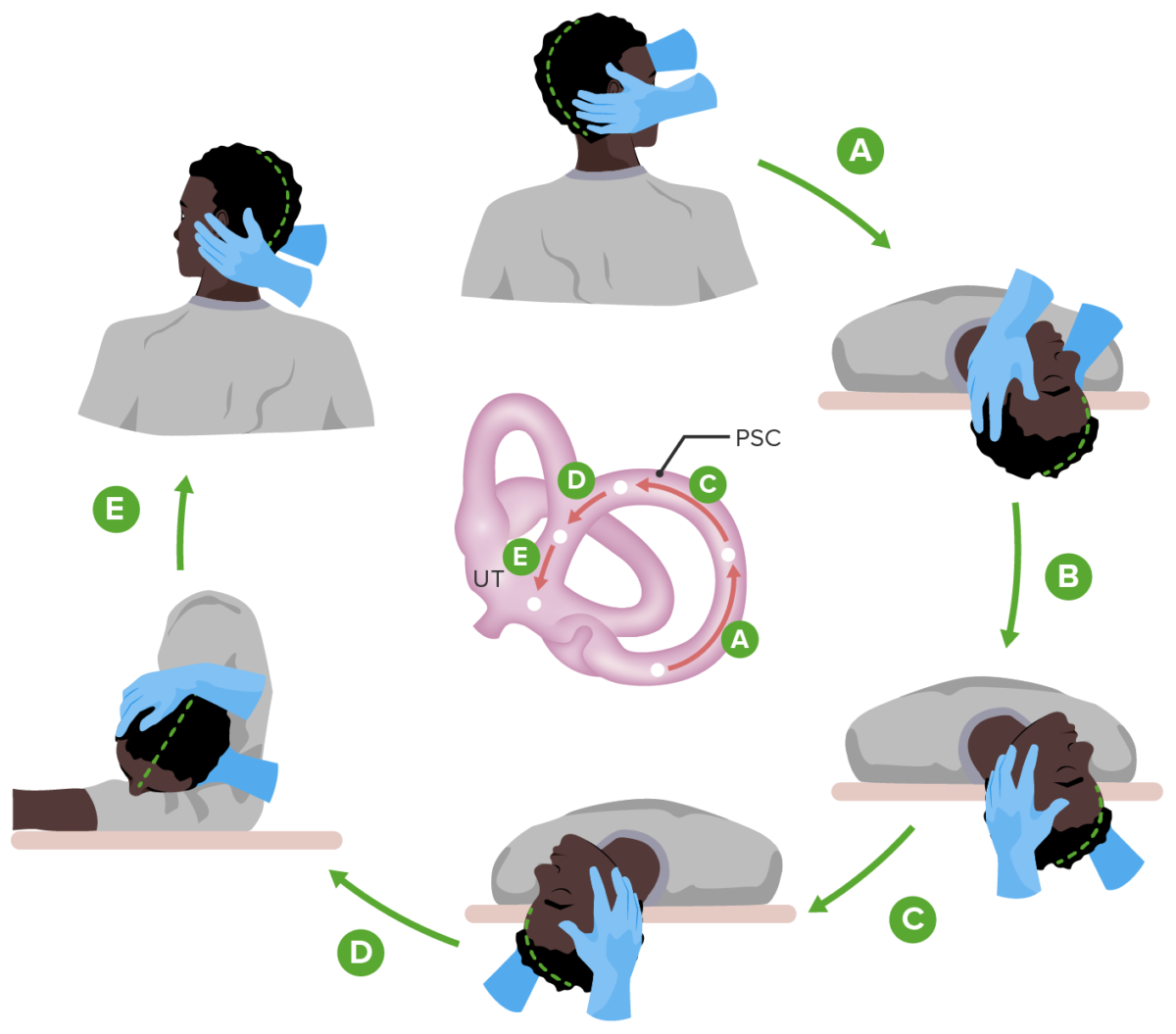
Overview Definition Vertigo is a clinical symptom described as the perceived sensation of rotational motion while remaining still. Epidemiology Classification Etiology Peripheral: Central: Both: multiple sclerosis Pathophysiology To understand the causes of vertigo, it is important to understand how the human body perceives and maintains balance. History of Present Illnesses Chief complaint The chief complaint […]