Liver Function Tests
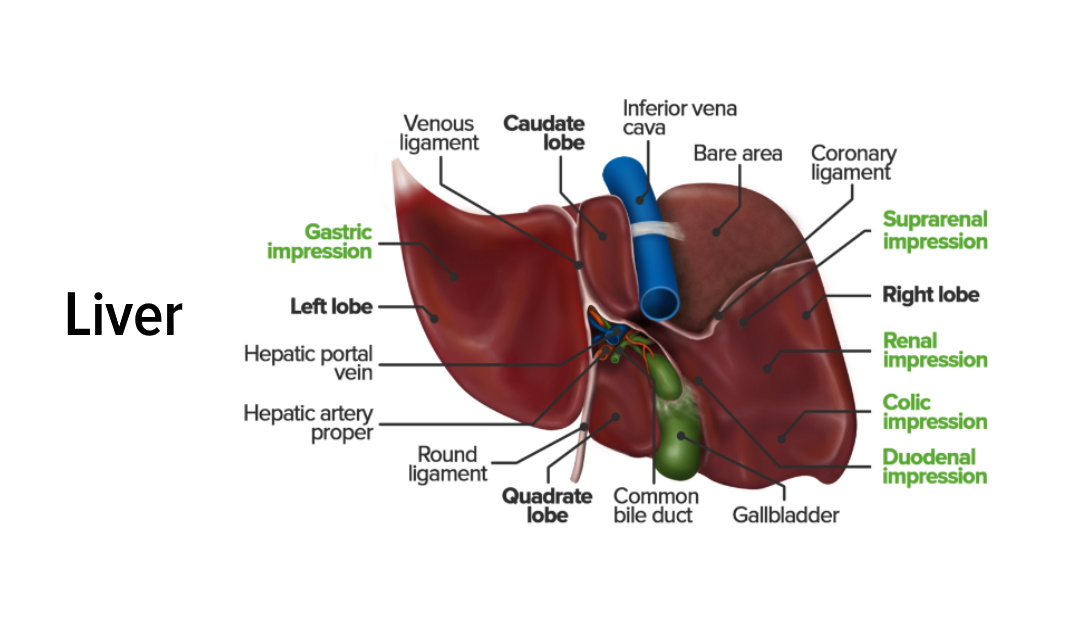
Introduction Hepatobiliary anatomy Hepatobiliary physiology Table: Enzyme patterns in liver disease Liver disease ALT and AST ALP Bilirubin GGTP PT Acute liver damage (e.g., viral hepatitis) ↑↑↑ > 10 times normal level Usually ALT > AST Normal or ↑ Normal or ↑ ↑ Normal Chronic liver damage (e.g., fatty liver) ↑↑ Normal or ↑ Normal […]
Sickle Cell Disease
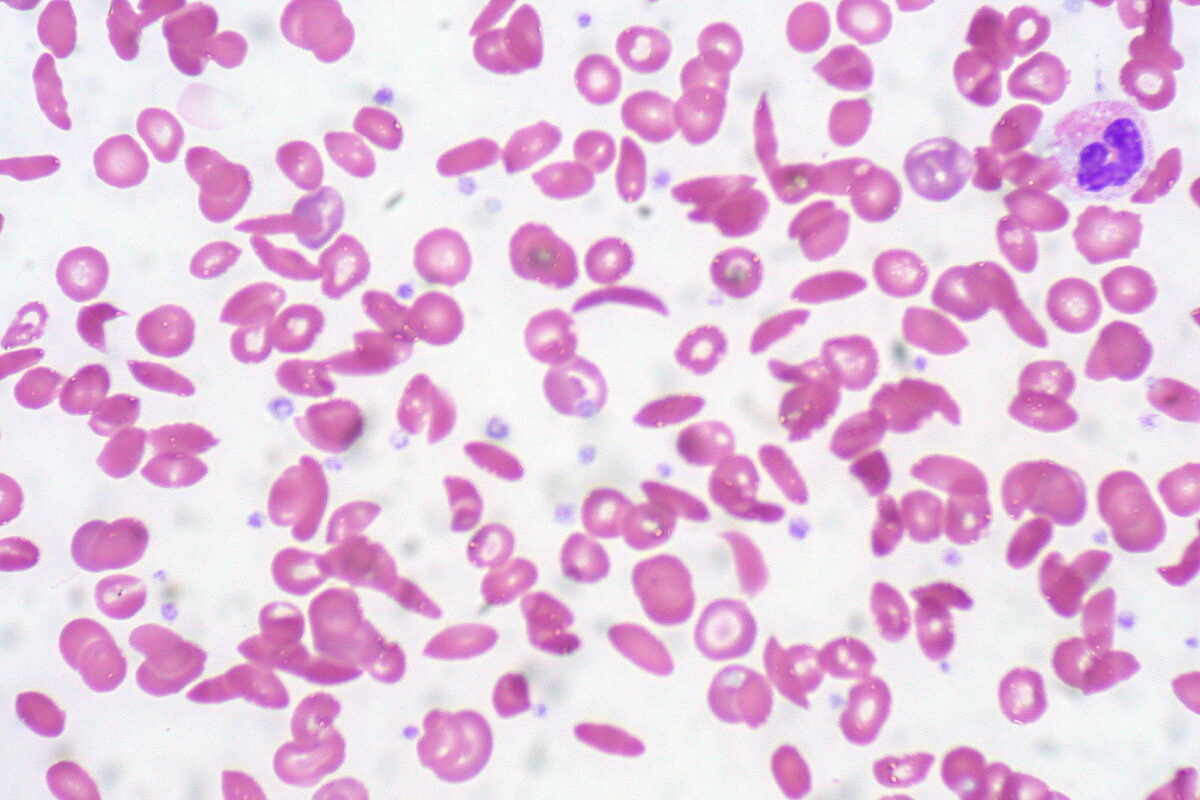
Overview Definition Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of genetic disorders that cause an abnormal Hb molecule (Hb S) that transforms RBCs into sickle-shaped cells, resulting in chronic anemia, vasoocclusive episodes, pain, and organ damage. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Normal adult hemoglobin molecule (HbA1) consists of 2 pairs of chains called alpha and beta. Clinical […]
Extremity and Visceral Aneurysms
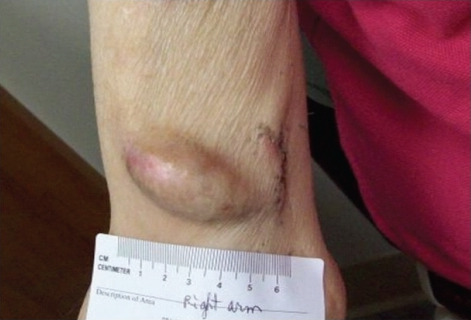
Overview Definition An aneurysm is a bulging, weakened area of a blood vessel, usually an artery, that causes an abnormal widening of its diameter > 1.5 times the size of the native vessel. Classification Types: True aneurysm: involves all 3 layers of the vessel wall with ≥ 1 layer intact Pseudoaneurysm: blood escapes into surrounding […]
Nephritic Syndrome
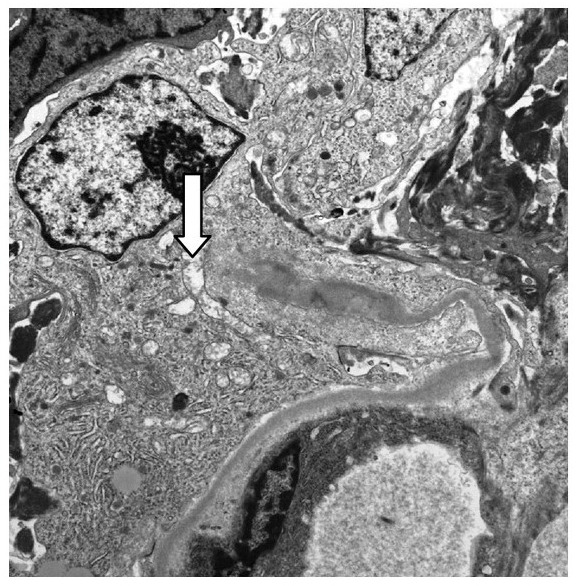
Overview Definition Nephritic syndrome is defined by some or all of the following findings: Glomerular hematuria: active urine sediment Dysmorphic RBCs RBC casts Mild-to-moderate proteinuria (500–3500 mg/day called “subnephrotic”) Hypertension due to: Volume overload/Na retention Suppression of the RAAS Azotemia: Elevated BUN BUN-to-creatinine ratio > 15 Oliguria: < 500 mL of urine/day Etiology Acute glomerulonephritis […]
Nephrotic Syndrome
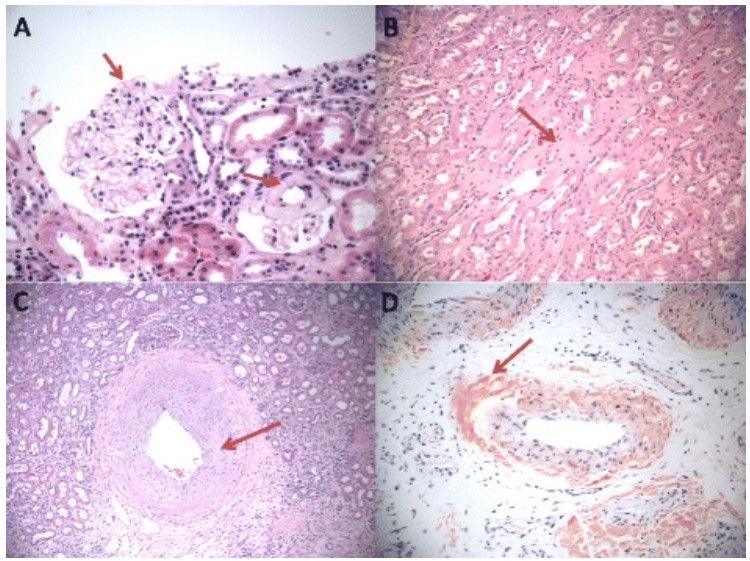
Overview Definition Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by heavy proteinuria (> 3.5 g/day), low serum albumin (< 3 g/dL), and peripheral edema. Epidemiology Primary etiologies (“immune podocytopathies”) Secondary etiologies Pathophysiology The major target of injury in diseases that cause primary nephrotic syndrome is the podocyte. Increased filtration across the glomerular capillary wall results in proteinuria. Nephron […]
Renal Tubular Acidosis
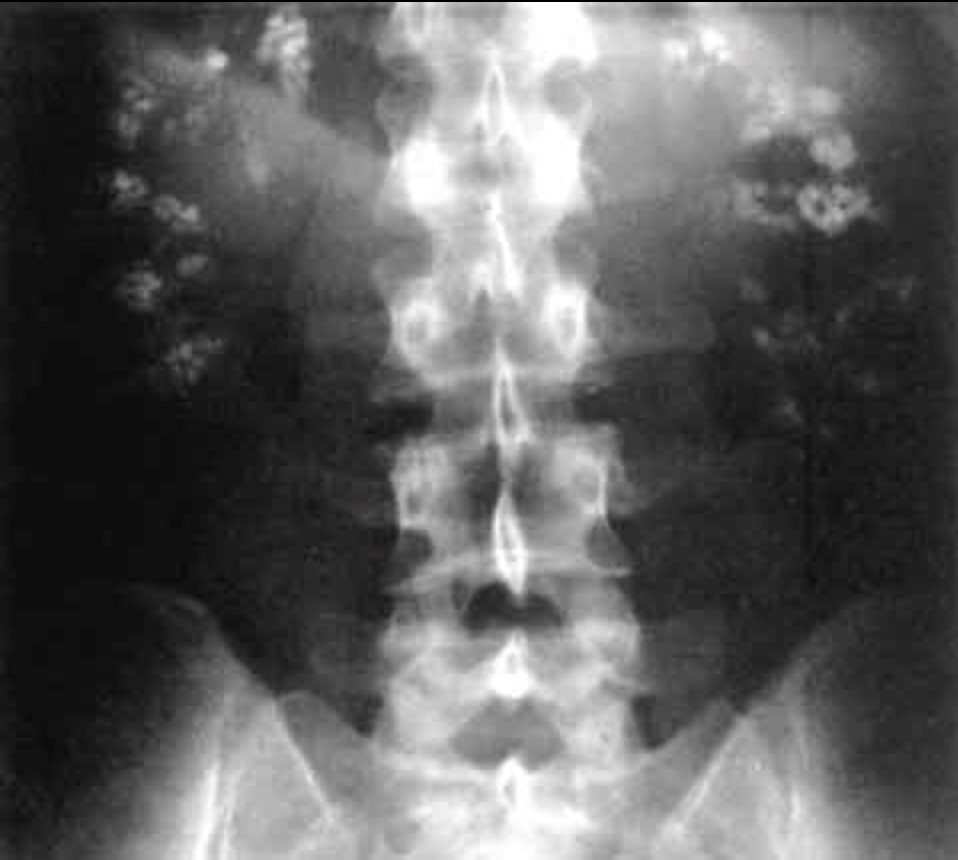
Overview Definition Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) is an imbalance in physiologic pH caused by the kidney’s inability to acidify urine to maintain blood pH at physiologic levels. Classification RTA can be classified based on the clinical characteristics and physiologic defect: Comparison of the types of RTA, including the clinical characteristics, physiologic defects, and potential etiologies: […]
Polyneuropathy
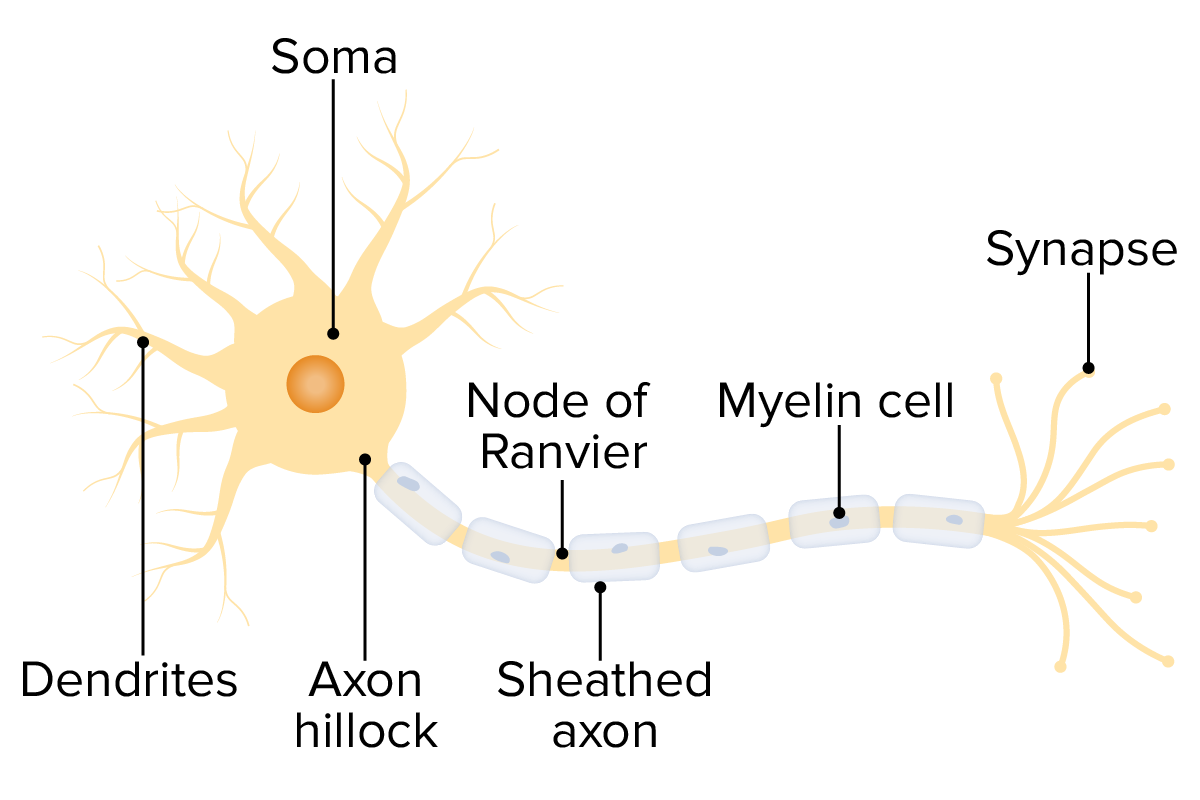
Overview Definition and terminology Polyneuropathy is part of a spectrum of neurologic disorders affecting the integrity and function of the peripheral nerves. The nomenclature corresponds with the number of nerves involved: Epidemiology Classification Polyneuropathies may be classified on the basis of: Etiology and Pathophysiology Etiology There are numerous causes of polyneuropathy; however, diabetes mellitus (diabetic […]
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
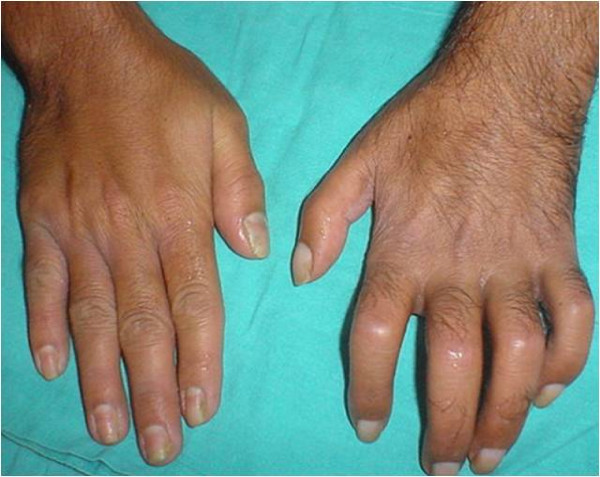
Overview Definitions Epidemiology Classification Etiology Complex regional pain syndrome occurs after an initiating noxious event, such as trauma: Pathophysiology The pathophysiology of CRPS is not completely understood, but there are multiple likely mechanisms. Inflammation (cytokine-mediated): Neurogenic inflammation (neuropeptide-mediated): Central sensitization: Sympathetic dysregulation: Cortical reorganization: Genetic predisposition: Clinical Presentation History Physical examination Stages of complex regional […]
Distal Radius Fractures
Distal Radius Anatomy Overview Epidemiology Etiology Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis Clinical presentation History: Physical exam: Diagnosis Diagnosis is clinical; however, imaging is needed for confirmation and evaluation of severity. Specific examples of distal radius fractures Management Management, whether nonsurgical or surgical, is based on the type of fracture (based on articular involvement and displacement) and […]
Febrile Infant

Overview Definition of fever ≤ 56 days of age, any temperature ≥ 38°C (100.4°F) > 56 days of age, any temperature ≥ 38.5°C (101.3°F) Babies with an underlying immunocompromised state: ≥ 38.5°C once ≥ 38.0°C 3 times in a 24-hour period, 1 hour apart Etiology Infectious: Viral Bacterial Noninfectious: Malignancy Rheumatic disease Drug reaction Systematic […]