Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas
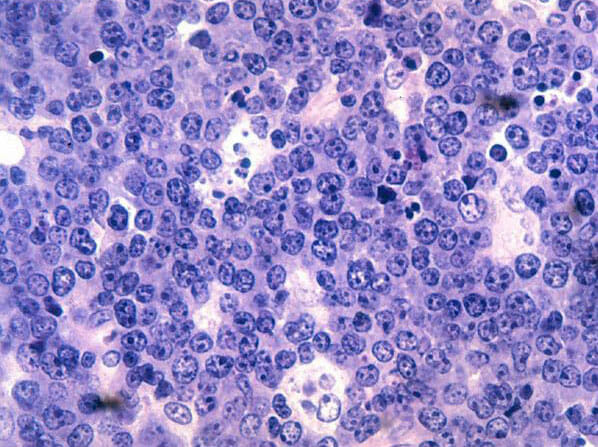
Overview Definition Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) are a diverse group of hematologic malignancies that are clonal proliferative disorders of mature or progenitor B cells, T cells, or natural killer (NK) cells. Epidemiology Incidence in the United States: > 70,000 cases annually (6th most common cancer in the United States) Accounts for 4% of all cancers: The […]
Dermatologic Examination
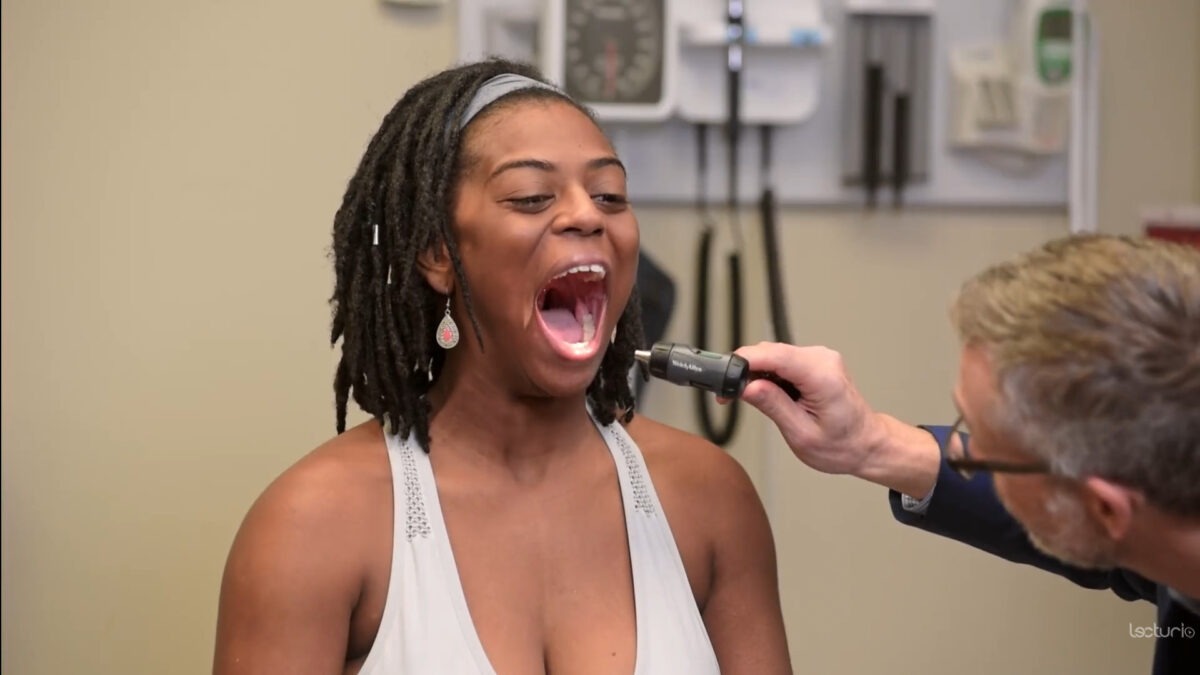
Terminology Primary and secondary skin lesions Primary skin lesions occur as a direct result of a pathologic process, while secondary skin lesions are those that result from manipulation of the skin. Table: Primary skin lesions Primary skin lesion Description Macule Flat, nonpalpable skin lesion ≤ 1 cm in size Differs in color from the surrounding […]
Peripheral Nerve Injuries in the Cervicothoracic Region
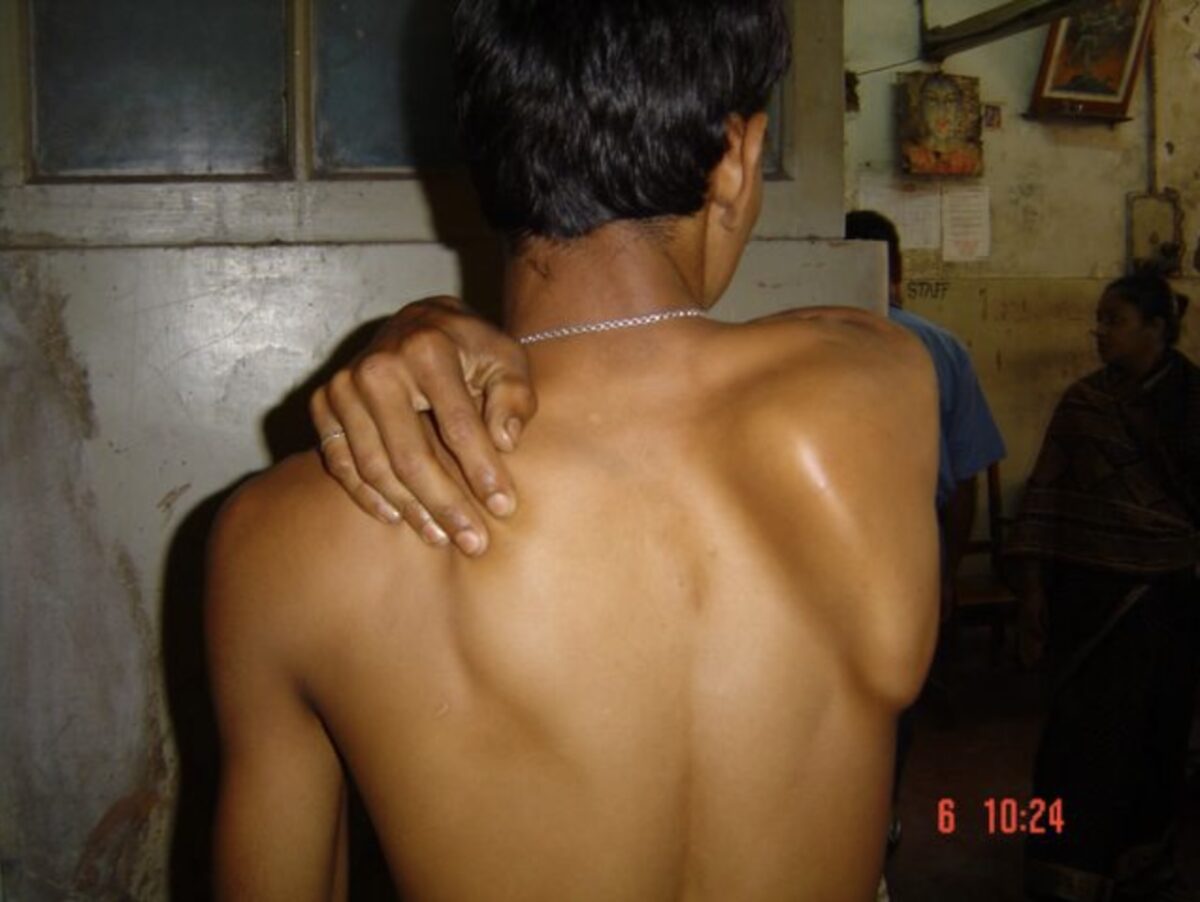
Anatomy Nerve roots emerge from the spinal cord at the C1 level and below. Cervical plexus C1 through C4 nerve roots close to the spinal cord merge to form the cervical plexus. Cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus innervate the skin, transmitting sensory information: Motor branches of the cervical plexus innervate muscles of the shoulders […]
Chronic Diabetic Complications
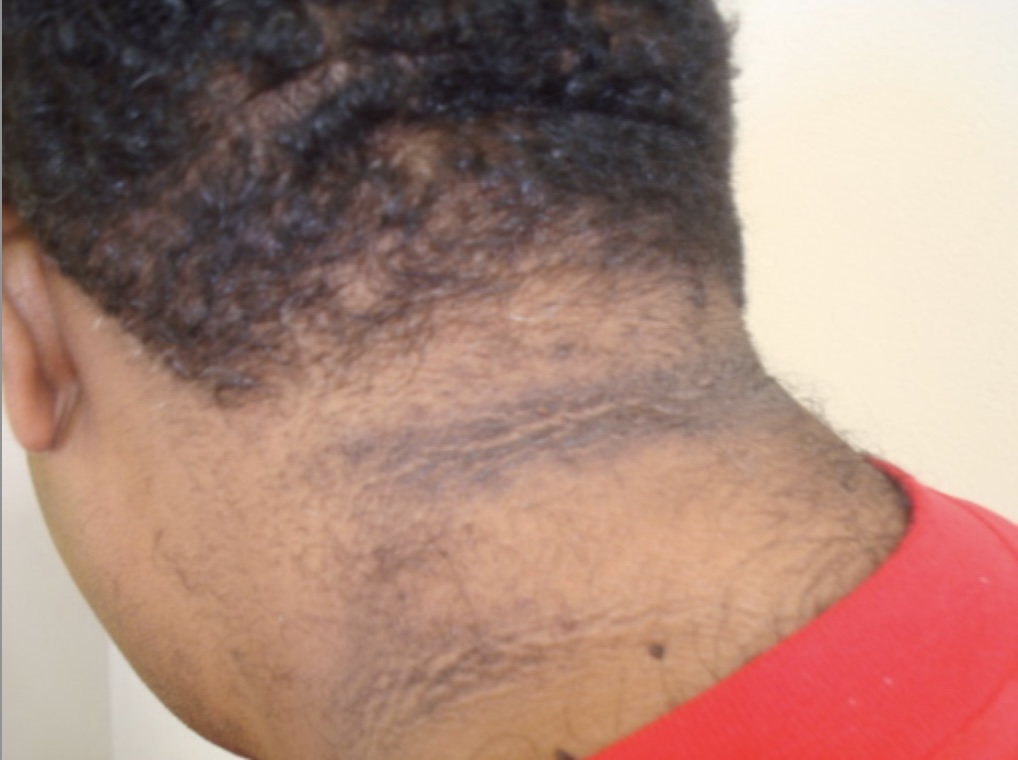
Overview Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a common disease that can lead to multiple serious complications. Long-term glycemic control is imperative to prevent these complications. Pathophysiology Chronic complications of diabetes have unique pathophysiological processes and are dependent on the organ system involved. Cardiovascular Renal There are various forms of kidney disease in diabetes, including nonclassical glomerular lesions […]
Urologic Cancer
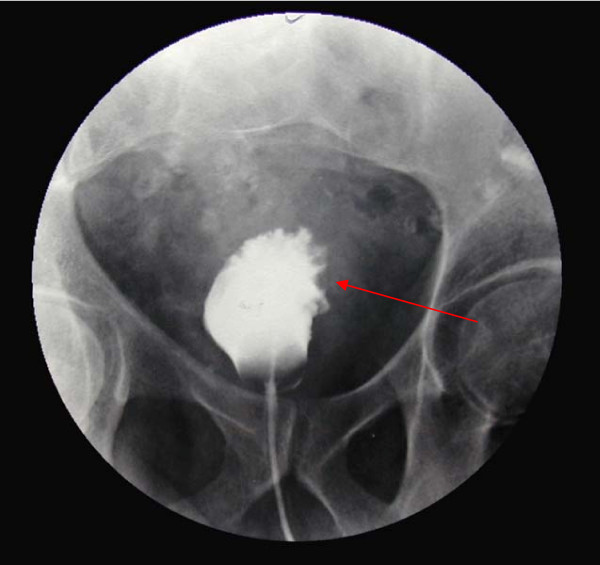
Overview Definition Growth of abnormal cells from the lining of organs of the male and female urinary tracts and the male reproductive organs. Epidemiology Risk factors Types Bladder Cancer Histologic types Clinical presentation Diagnosis Stages of bladder cancer Bladder cancer pathologic stages are based on the TNM staging system. Table: Primary tumor Tumor (T) category […]
Eye: Anatomy
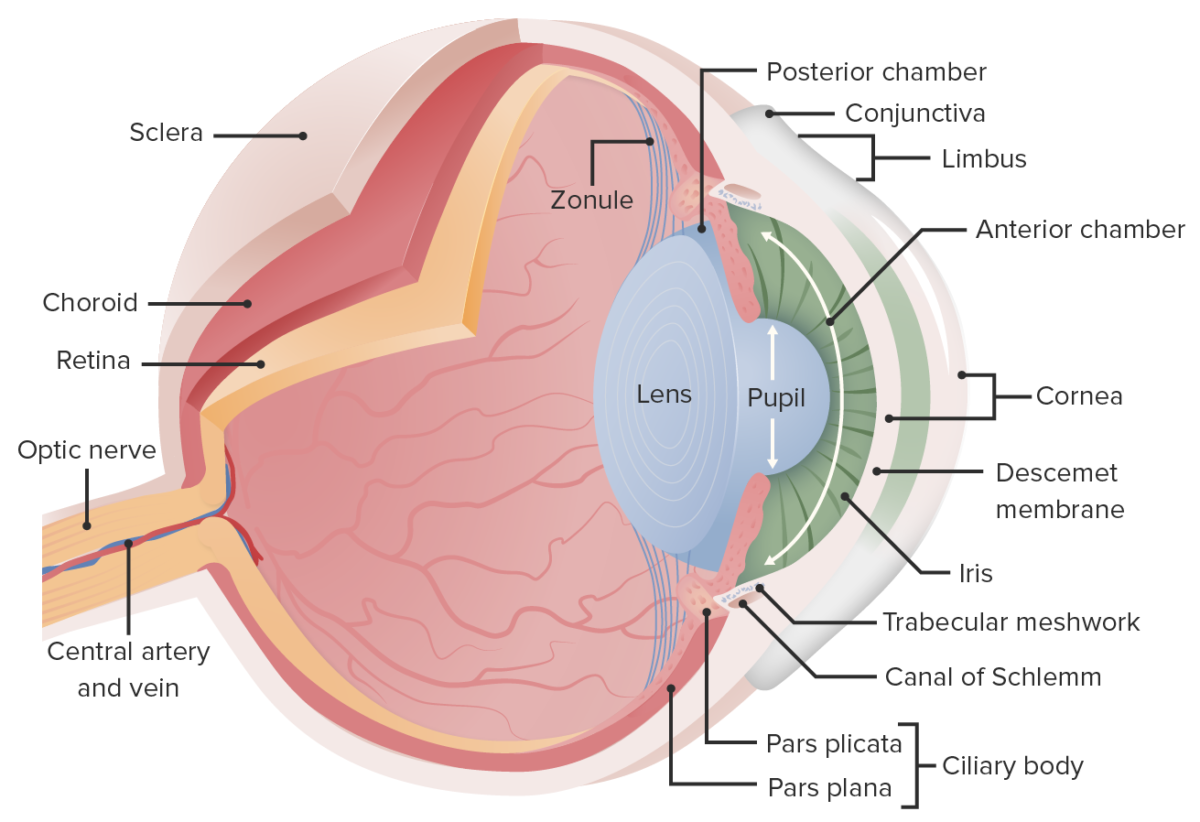
Development General Timeline Gross Anatomy General characteristics The adult eye is a complex organ contained within the orbital cavity (composed of 7 bones). Each eye has multiple layers and chambers and is surrounded by 6 extraocular muscles. Layers of the eye The eye is composed of 3 layers (fibrous, vascular, neural) and a transparent connective […]
Body Fluid Compartments
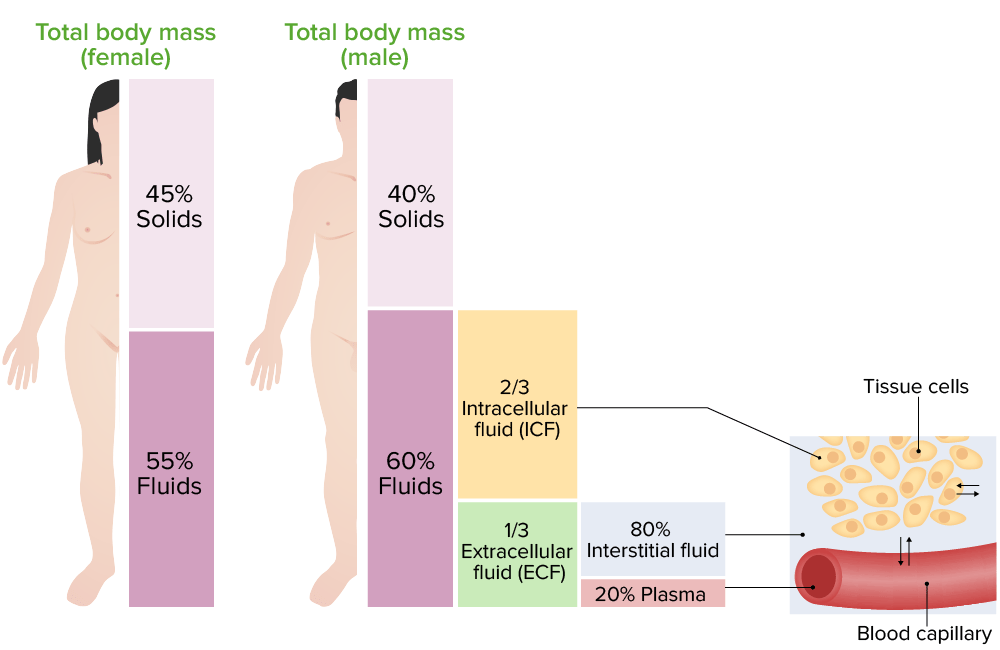
Overview Water in the adult human body makes up approximately 60% of the total body weight. The fluid is distributed in various organs, organ systems, and tissues. The sum of the water in these tissues is known as total body water. Body Fluid Compartments Overview The total body water is distributed primarily between 2 compartments, […]
Glucocorticoids
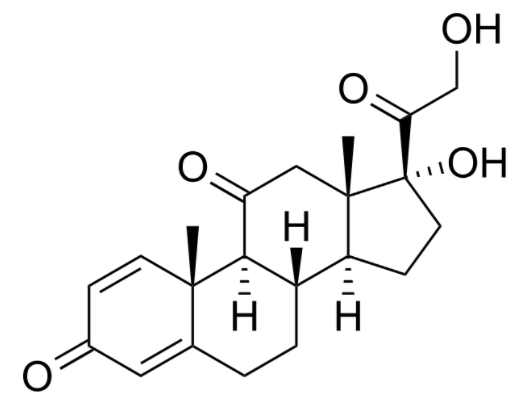
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemical structure Glucocorticoids are synthetic analogs of cortisol and cortisone. Alterations may include: Fluorination (dexamethasone, betamethasone) Methylation (methylprednisolone) Physiology Endogenous glucocorticoids are: Derived from cholesterol (which is synthesized from acetyl-CoA) Secreted from the zona fasciculata Effects: respond to immediate stressors ↑ Immediate available energy through: Fat and protein catabolism → ↑ blood […]
Spinal Disk Herniation
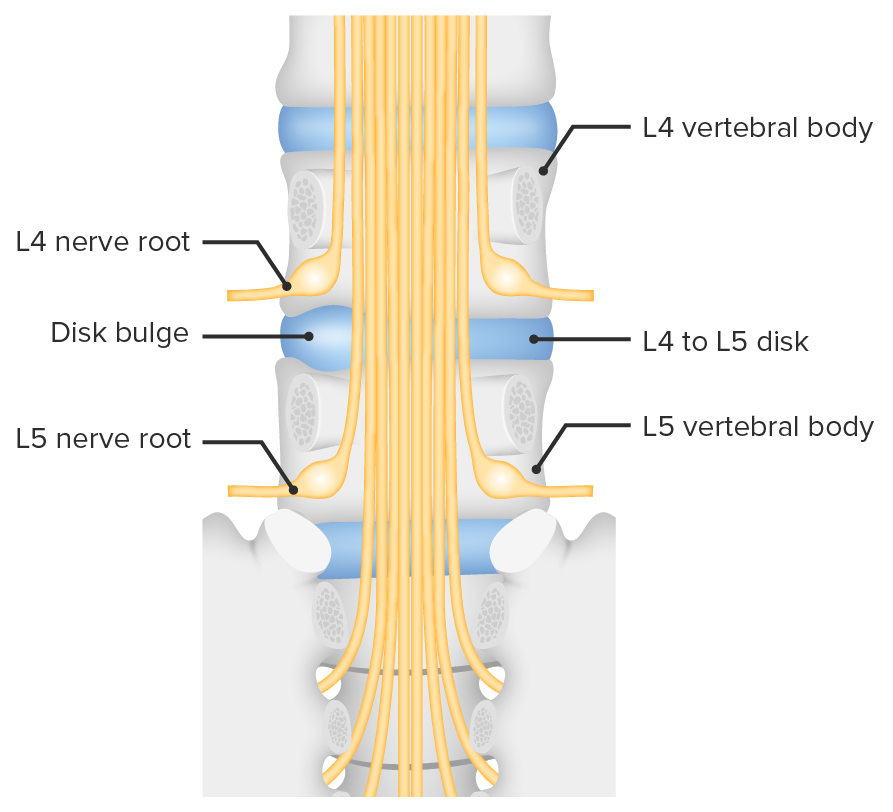
Overview Definition Spinal disk herniation is a condition wherein the gelatinous central portion of an intervertebral disk is forced through a weakened portion of the fibrocartilaginous outer part of the disk, often resulting in back pain and/or nerve root irritation. Spinal disks (intervertebral disks) Structure: Function: Anatomic relationships: Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Spinal disk degeneration (degenerative […]
Tachyarrhythmias
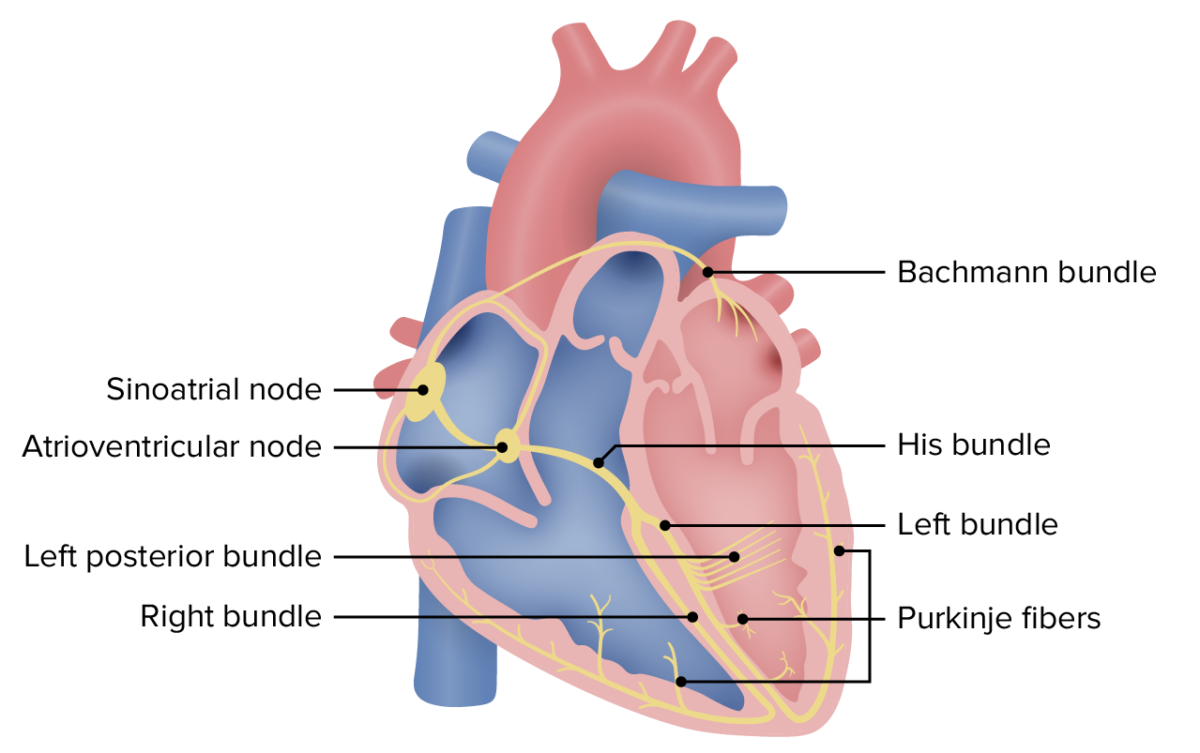
Overview Definition A tachyarrhythmia is a rapid heart rhythm, regular or irregular, with a rate > 100 beats/min. Classification Narrow QRS complex (< 120 msec) tachycardia: Wide QRS complex (≥ 120 msec) tachycardia: Etiology Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy Physiology Sequential events of a cardiac cycle (numbers correlate to the 6 images below): 1. SA node […]