Chronic Venous Insufficiency (Clinical)
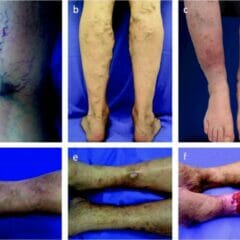
Overview Definition Chronic venous disease is a spectrum of disorders characterized by venous dilation and/or abnormal vein function in the lower extremities resulting from venous hypertension. Epidemiology[2,7,10] Etiology[1,2,10] Pathophysiology Venous hypertension[1,2,7] Skin and soft tissue changes[1,2,7] Clinical Presentation Spectrum of chronic venous disease[1-3] Presenting symptoms[10] Diagnosis and Classification Physical exam[4,7,8,10] Lower extremity appearance: Venous refilling […]
Seborrheic Keratosis (Clinical)
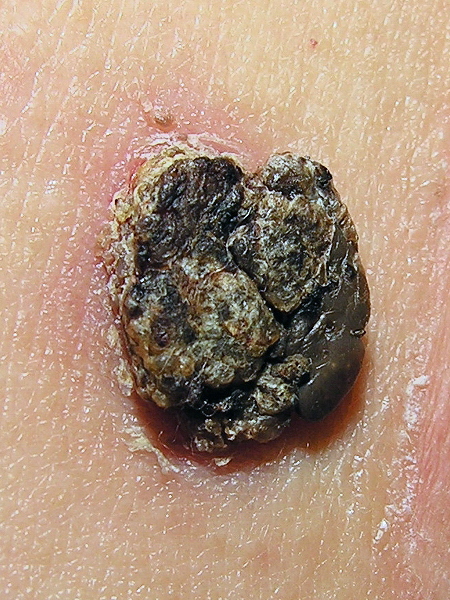
Overview Definition Seborrheic keratosis (SK) is a benign skin tumor consisting of proliferating immature keratinocytes. Epidemiology[2,4] Etiology[1,5,8] Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathogenesis[3,5] Morphology[2,4,5,8] Histology[1,5] Clinical presentation[2,4,8] Diagnosis and Management Although SK is most often diagnosed and managed by dermatologists, it is important for all physicians to be aware of the diagnostic and management options available.[8] […]
Mpox (Monkeypox) (Clinical)
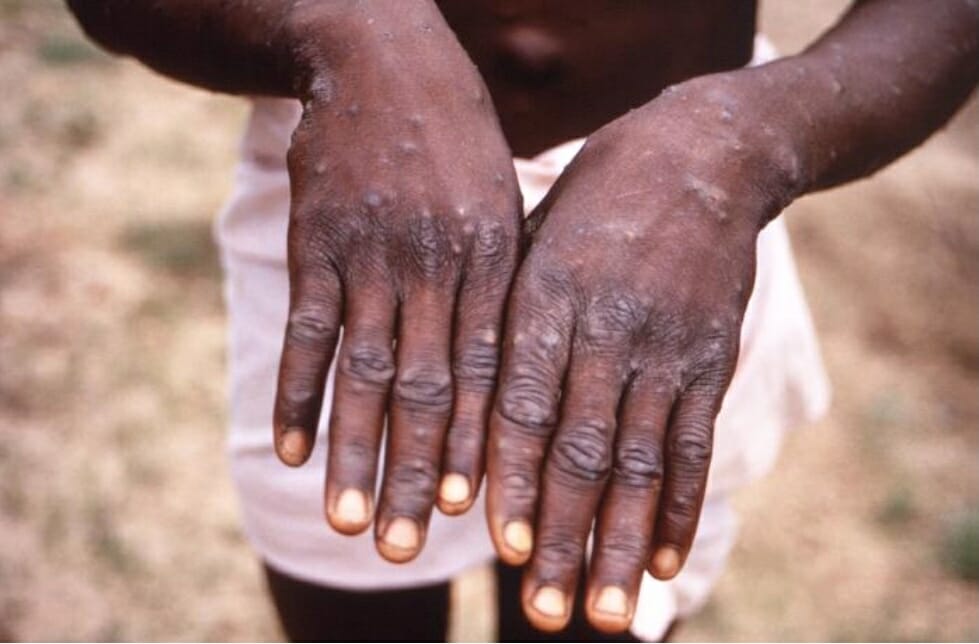
Overview Mpox (formerly known as monkeypox) is a viral zoonotic disease caused by the mpox virus. Mpox has a clinical profile similar to that of smallpox, but is less often fatal. Virology[3,6] Epidemiology Transmission Clinical Presentation General[3,6] Invasion period (0–5 days)[3] Symptoms occurring during this period may include: Cutaneous manifestations[1,3,6,8] The course of illness is followed […]
Lactose Intolerance (Clinical)
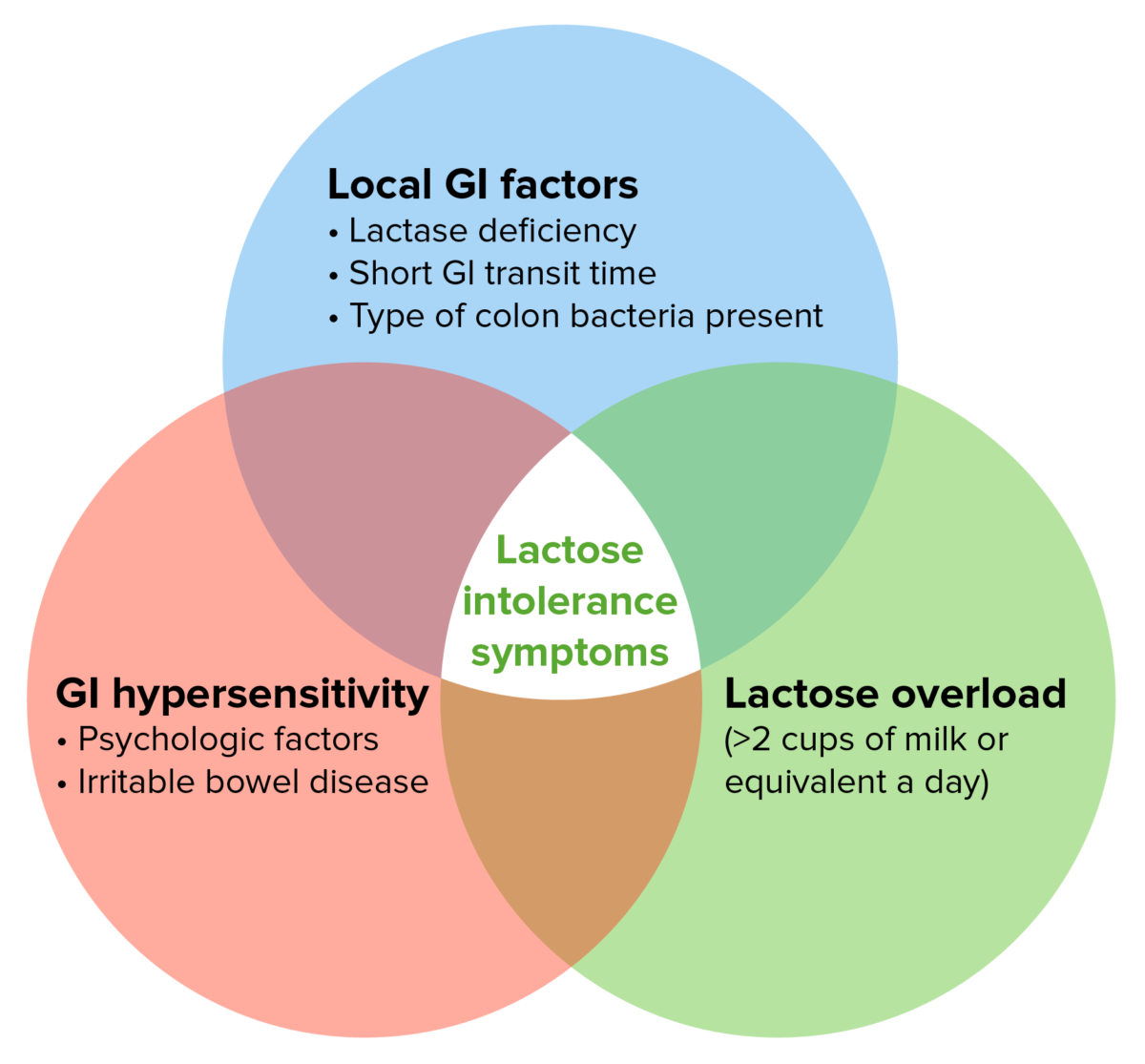
Epidemiology Etiology Primary LD[1,7,8,12] Secondary LD[1,10,12] Less common types of LD[1] Pathophysiology General consideration[5,9,11] Lactase[11,12] Effects of undigested lactose[8,11–13] Clinical Presentation Children and adolescents[7,8,11,13] Adults[10–12] Diagnosis There are no clear consensus guidelines for the diagnosis of LI. The following information is based on the US, UK, and European medical literature. Initial testing[5,10,12] Consider a diagnosis […]
Hyperparathyroidism (Clinical)
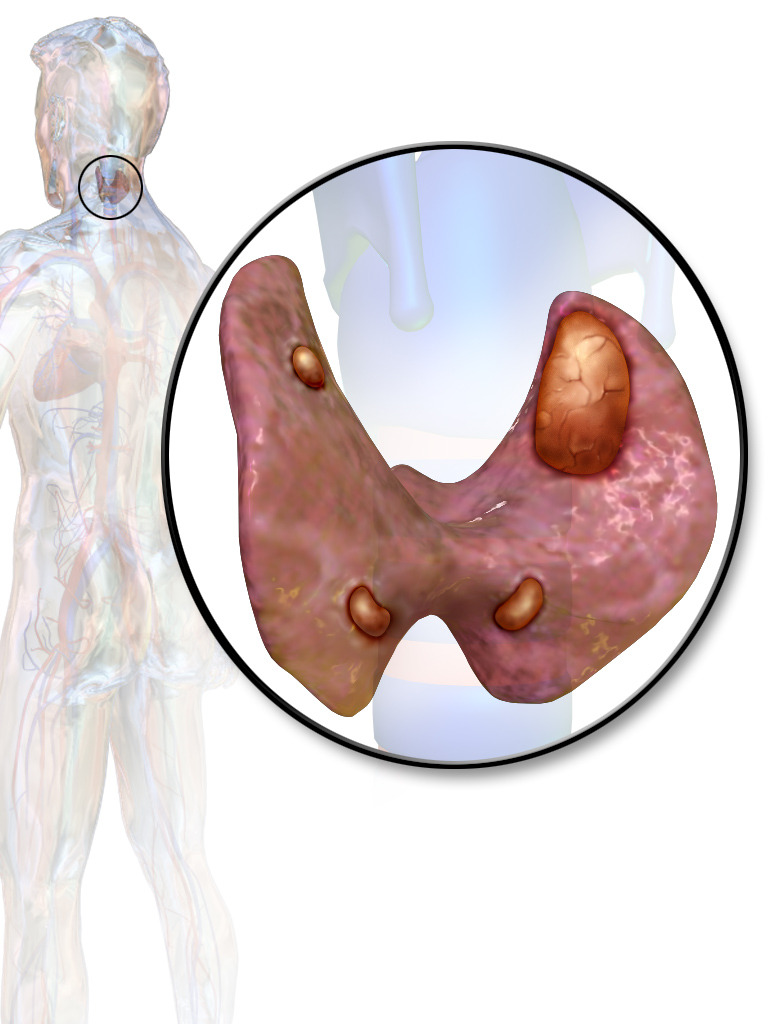
Overview Definition Hyperparathyroidism is a condition associated with elevated blood levels of parathyroid hormone (PTH). Etiology[1,8,12,14] Epidemiology[1,5,8,22] Pathophysiology Normal physiologic effects of PTH[7,14] Pathophysiology Primary hyperparathyroidism:[1,7,10,11] Secondary hyperparathyroidism:[1,7,10,12,14,21] Tertiary hyperparathyroidism:[7,10,14,22] Clinical Presentation Primary hyperparathyroidism (PH) Asymptomatic, mild hypercalcemia (approximately 10.5–12.5 mg/dL) is most often due to primary hyperparathyroidism. Symptoms typically appear in the later stages […]
Aortic Dissection (Clinical)
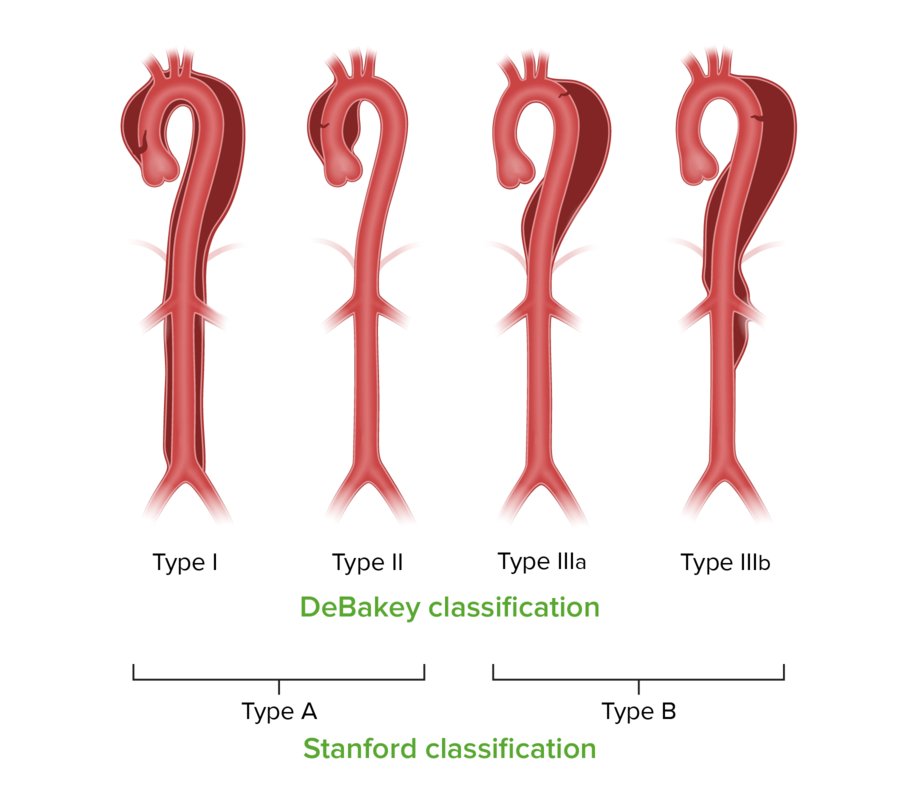
Overview Epidemiology[1,2] Etiology[1,2,5] Classification[2,5] Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Symptoms[1–3,5] Physical exam[1–3,5] Diagnosis Initial studies[1,3,5] Laboratory workup[1–3,5] Pretest probability scoring for acute aortic syndrome (AAS)[15] Pretest probability of aortic dissection may be assessed with the Aortic Dissection Detection-Risk Score (ADD-RS) (calculator) Definitive diagnosis[3,5,12,18] Management Management may vary based on practice location. The following information is based on […]
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) (Clinical)
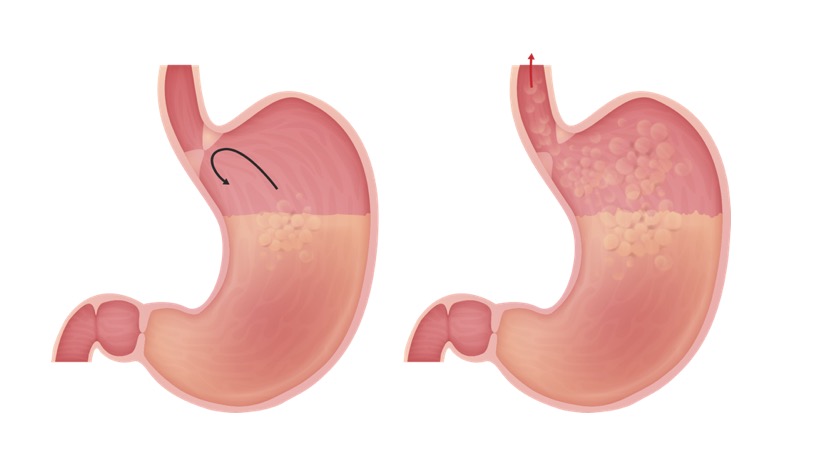
Epidemiology and Etiology Definition Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus that leads to symptoms or complications. Epidemiology[1,2] Etiology[1,2] Hiatal hernia[2,7] Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Physiology Pathophysiology[2,4] Factors leading to increased exposure of esophageal mucosa to gastric acid/contents: Clinical presentation[1,2,4] Alarm signs and symptoms[1,4] Symptoms that should raise suspicion […]
Polyarteritis Nodosa
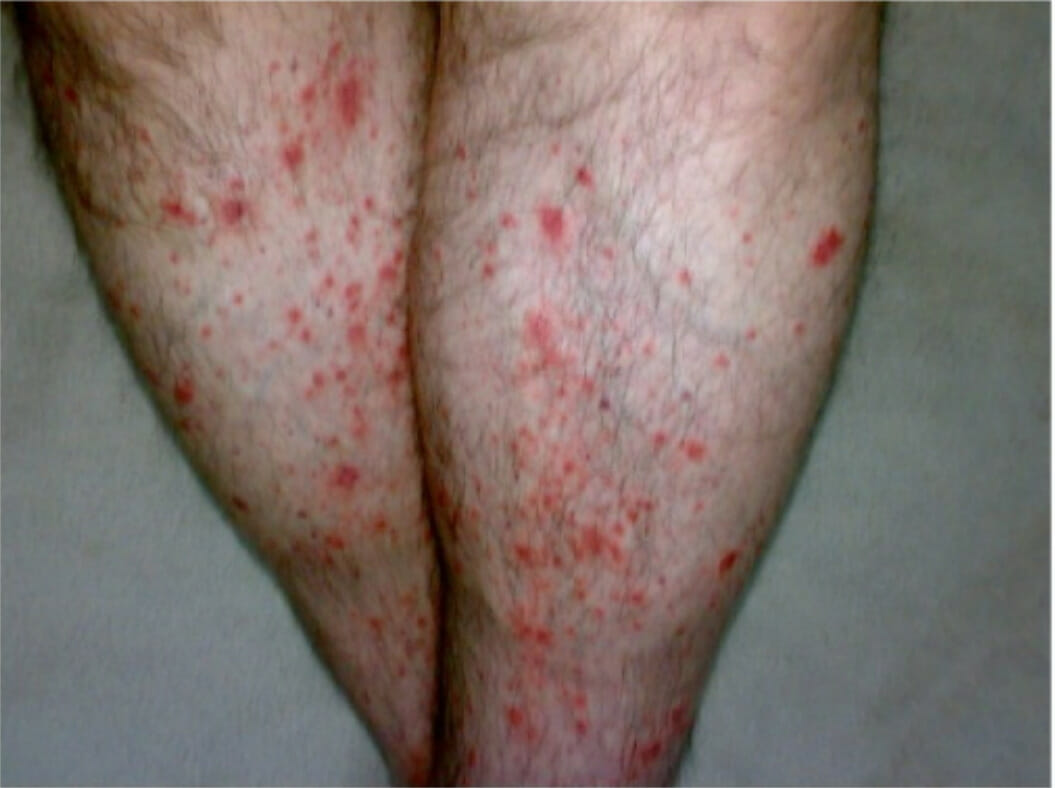
Overview Definition Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) is a systemic, primarily medium-vessel vasculitis characterized by necrotizing inflammatory lesions. This condition eventually results in microaneurysms, which lead to bleeding, thrombosis, organ ischemia, and infarction. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Patients with PAN typically present with multisystem involvement and systemic signs and symptoms. However, there is also a skin-limited […]
Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency
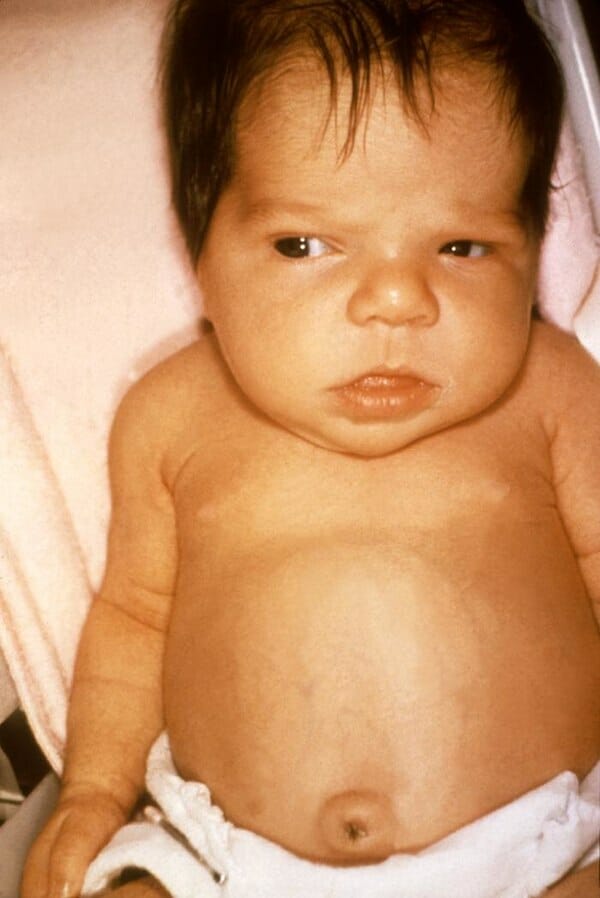
Overview Definition Pyruvate kinase (PK) deficiency is an autosomal recessive enzymatic disorder of erythrocytes that results in chronic hemolysis due to a defect in the PKLR or PKM gene. Epidemiology Etiology and Pathophysiology Classification and etiology Normal physiology Pyruvate kinase is an enzyme required for the conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) into pyruvate and ATP in […]
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis
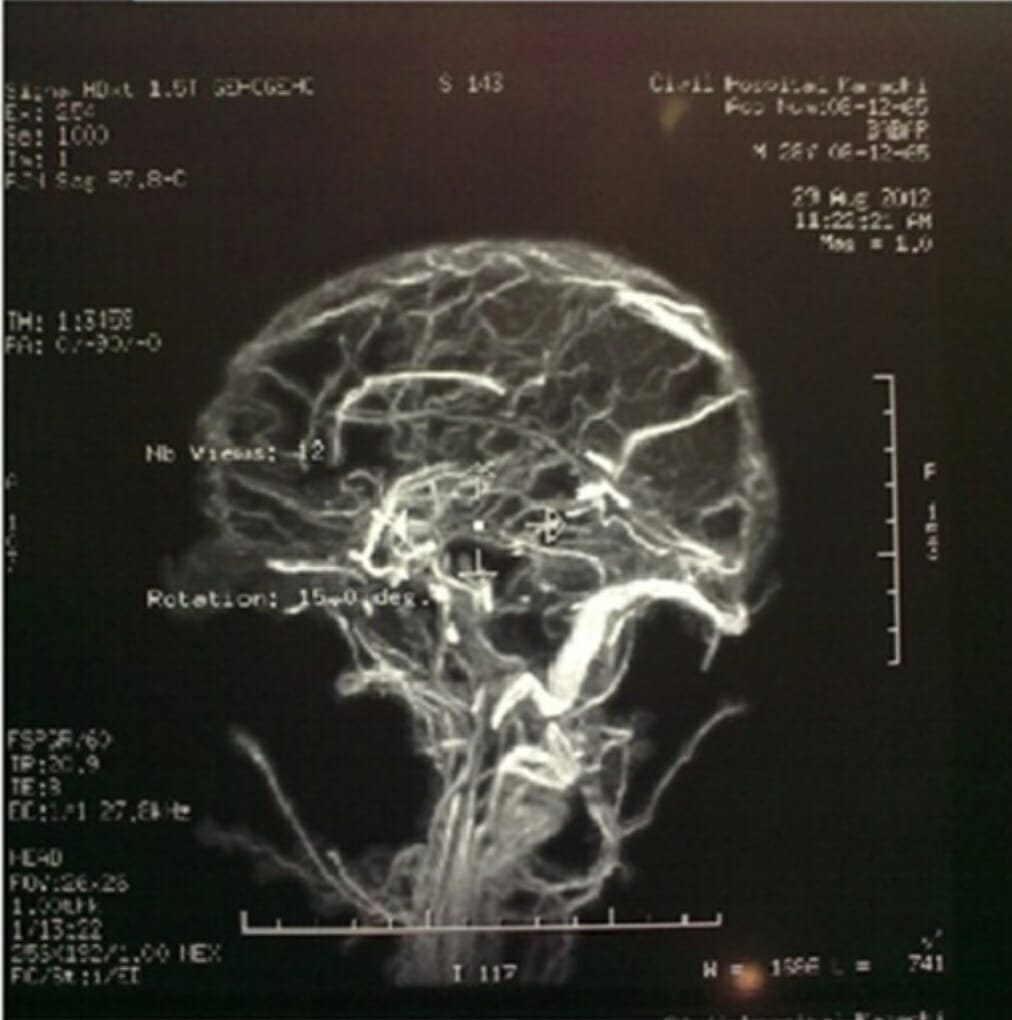
Overview Definition Cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) is a blood clot in the cerebral veins or dural sinuses. Epidemiology Risk factors Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Clinical presentations can vary significantly. Some cases may present with isolated ICP signs, while others have ischemic symptoms. The onset of symptoms can also differ (acute, subacute, chronic). Signs and symptoms Isolated […]