Dacryocystitis (Clinical)
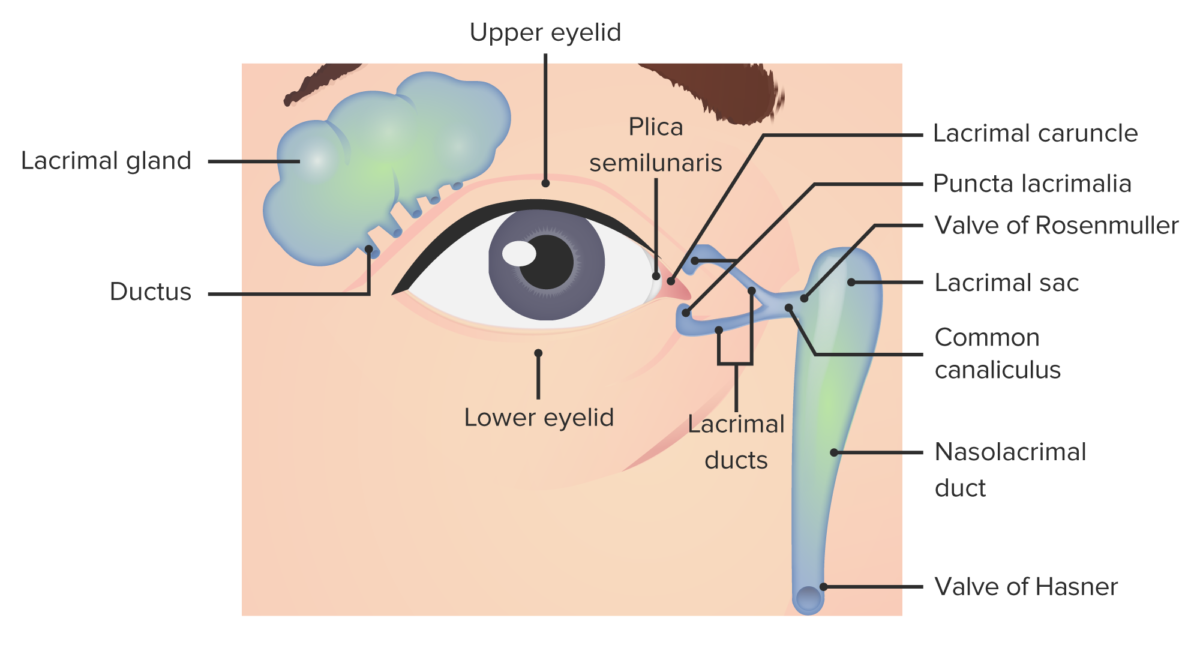
Overview Definition[2,7,8] Dacryocystitis is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac due to nasolacrimal duct (NLD) obstruction and the subsequent stasis of tears. Anatomy and physiology[3,7] Epidemiology[3] Types of Dacryocystitis Based on etiology Based on onset Clinical Presentation Complications Diagnosis Clinical[7,10,13] Testing is based on signs and symptoms. Laboratory tests[7,13] Fluorescein dye disappearance test[7] Imaging[10,13] Nasal […]
Osteoarthritis (Clinical)
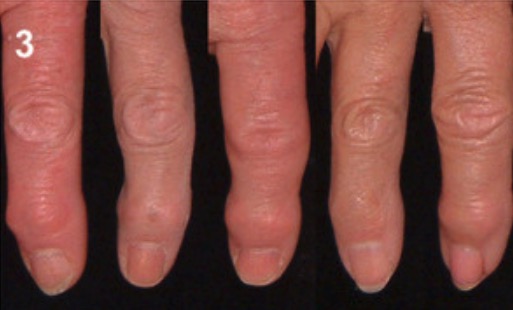
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[1,6,7] Classification and etiology[5,7,12] Risk factors[1,2,6,12,17] Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Commonly affected joints[4‒7] Symptoms[4‒7] Physical exam[4‒7] Diagnosis Clinical criteria[8,9,12] Imaging Osteoarthritis is a clinical diagnosis that is confirmed with imaging. Imaging is not routinely required but may be needed to diagnose atypical presentations of osteoarthritis, such as morning joint-related stiffness > 30 minutes, rapid […]
Hypernatremia (Clinical)
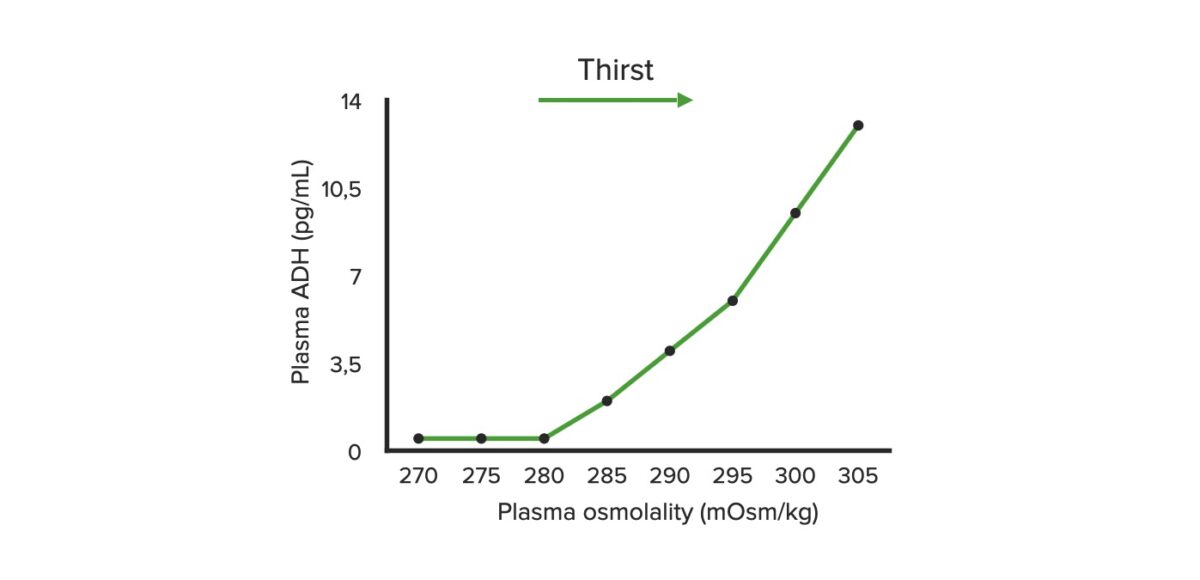
Water Regulation Water regulation is controlled by the interplay between the osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus and the response to antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in the kidneys, resulting in very tight control of serum sodium and plasma osmolality. Hypothalamic osmoreceptors[2–5,16,17] Response to ADH in the kidney[2–5,16] Etiology Etiologies of hypernatremia are organized according to volume status. Hypervolemic […]
Hypokalemia (Clinical)
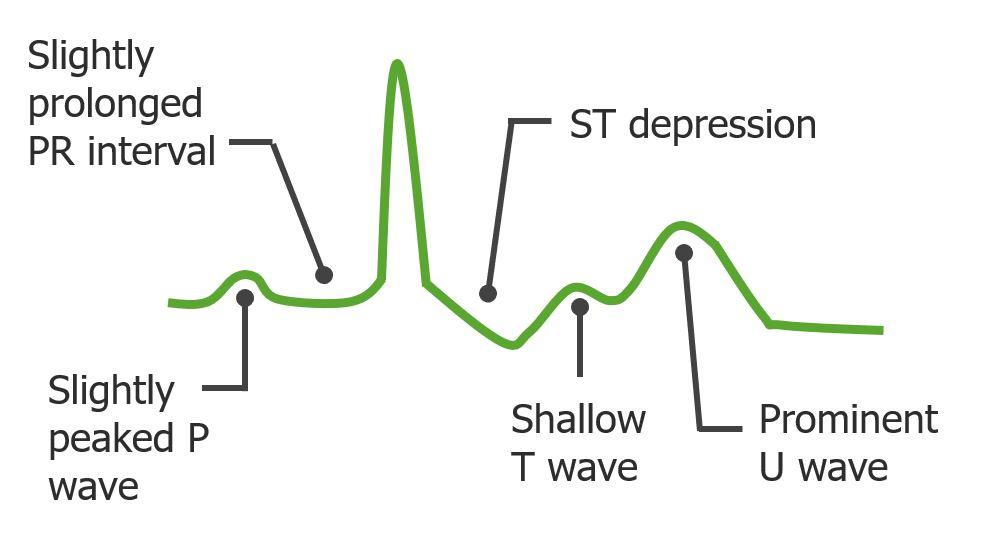
Overview Introduction[10,12] Potassium (K+) is the main intracellular cation in all cells and is distributed unevenly between the intracellular fluid (98%) and extracellular fluid (2%). The large disparity is necessary for maintaining the resting membrane potential of cells. Definition[10] Hypokalemia is defined as plasma K+ concentration < 3.5 mEq/L. Sites of action in the kidney[4,10,12] […]
Hydronephrosis (Clinical)
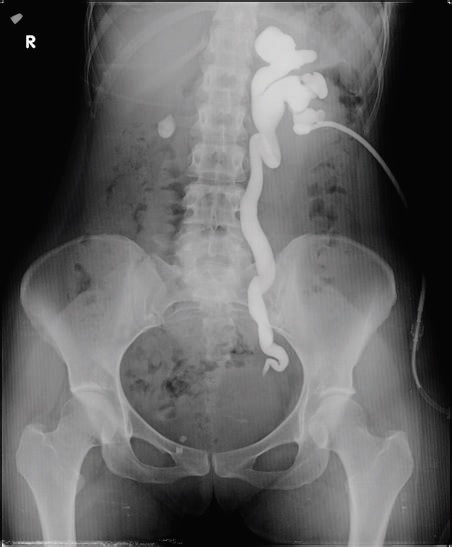
Overview Definition[1] Hydronephrosis is defined as the dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces due to obstruction of urine outflow. Epidemiology[3] Etiology[3,4] Children: Adults: Pathophysiology[2,11] Urinary tract obstruction leading to hydronephrosis is often associated with acute kidney injury; a slower process may result in chronic kidney disease. Clinical Presentation Clinical manifestations vary depending on the […]
Erythema Multiforme (Clinical)
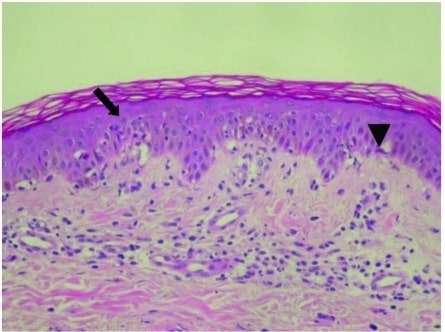
Overview Epidemiology[1,2,7] Etiology[1–3,7] Erythema multiforme (EM) is a cell-mediated immune reaction (type IV reaction) directed against the antigens of the offending agent, which deposit in the skin. A significant number of cases are idiopathic; however, there are many etiologies that may be identified: Classification Etiologies Examples Infectious causes (most common, 90% of cases) Bacterial Mycoplasma […]
Bullous Pemphigoid and Pemphigus Vulgaris (Clinical)
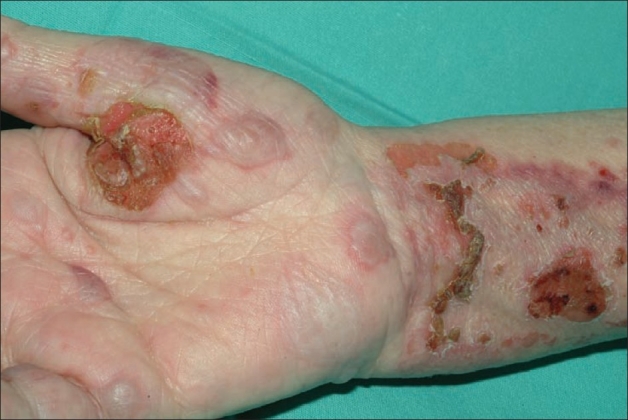
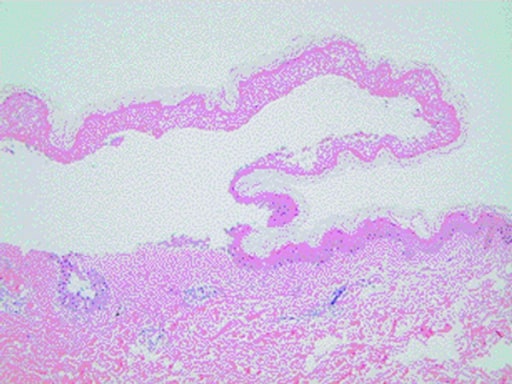
Overview Definition Bullous pemphigoid:[1,2,5,6] Pemphigus vulgaris:[1,7,9,10] Epidemiology and etiology[1,2,5,7,9,11] Bullous pemphigoid Pemphigus vulgaris Incidence per year 6‒13 per 1 million 0.1‒0.5 per 100,000 Age > 60 years old 40‒60 years old Gender predominance Women = men Women = men Racial/ethnic bias None More common in: Ashkenazi Jewish Southeast Europe Middle East India Etiology None have […]
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (Clinical)
Overview Classification[1,10] Table: Classification of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Subtype Involved BSA Stevens-Johnson syndrome 30% of BSA BSA: body surface area SJS: Stevens-Johnson syndrome TEN: toxic epidermal necrolysis Epidemiology[1‒5] Etiology[1,3,4,6,7,10] Table: Major common medication and infectious causes of SJS/TEN Types Examples Medications Antiepileptics Lamotrigine, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, valproate, phenytoin Sulfa Cotrimoxazole, sulfasalazine Other antibiotics […]
Impetigo (Clinical)
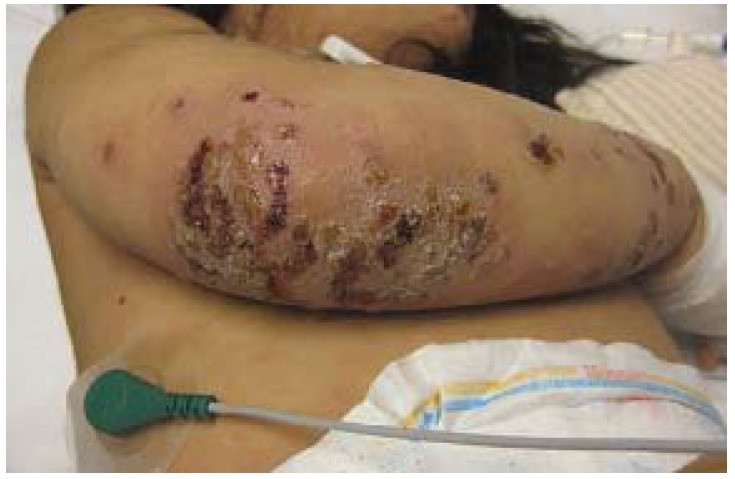
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[1,5,6] Etiology[1,2,5,6] Clinical Presentation There are 3 variants of impetigo: Non-bullous impetigo[1,5,6] Bullous impetigo[1,5,6] Ecthyma[1,5,6] Diagnosis Diagnosis is usually clinical, based on the natural sequence of the lesions and the presence of honey-colored crusts on pediatric patients aged 2–5 years.[5,6] Management and Complications Management Management depends on the type and severity of […]
Cellulitis (Clinical)
Overview Definition[1] Cellulitis is inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissues. It is often due to infection. Epidemiology and etiology[1‒3] Risk factors[2] Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathophysiology[1,2] Clinical findings[1,2] Diagnosis Management and Complications Antibiotic protocols may vary based on the microbiologic susceptibility of the population of the practice location. The following recommendations are based on […]