Irritable Bowel Syndrome (Clinical)
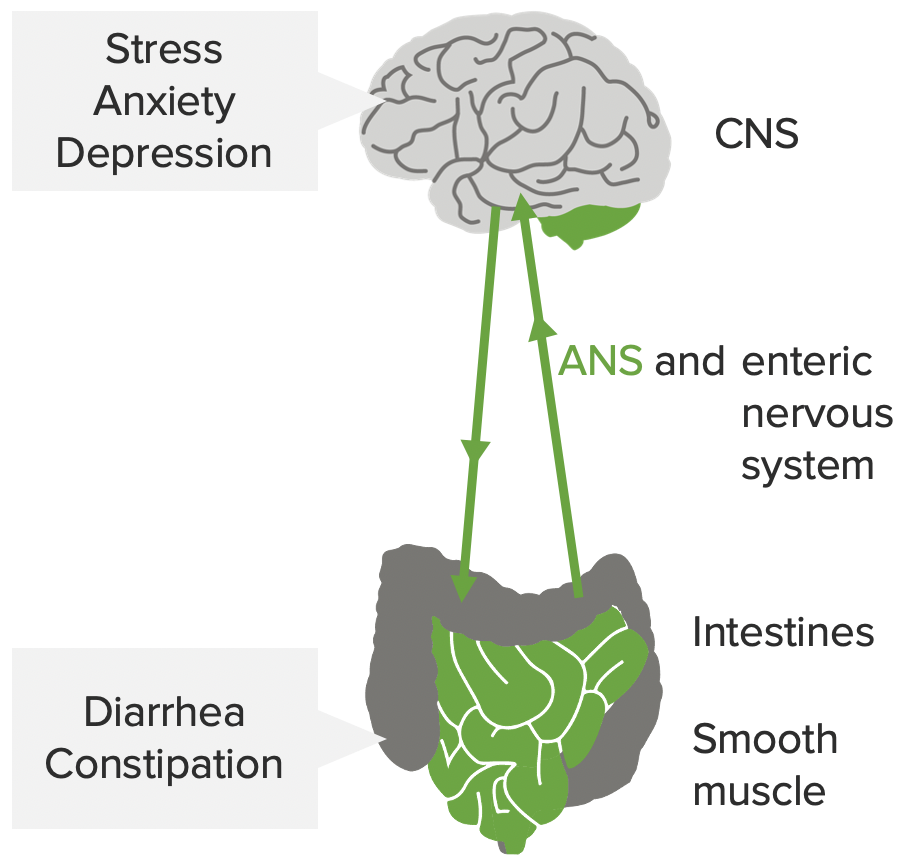
Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Epidemiology[2,3,7] Pathophysiology[1,4,8] Although no specific organic cause has been identified, there are several possible pathogenic mechanisms. Clinical Presentation Classification[7–9] Irritable bowel syndrome is classified based on the clinical presentation. Other signs and symptoms[2,3,9] Diagnosis Criteria for diagnosis[8,9,11,12] Irritable bowel syndrome is a diagnosis of exclusion, but the Rome IV criteria (calculator) help […]
Liddle Syndrome (Clinical)
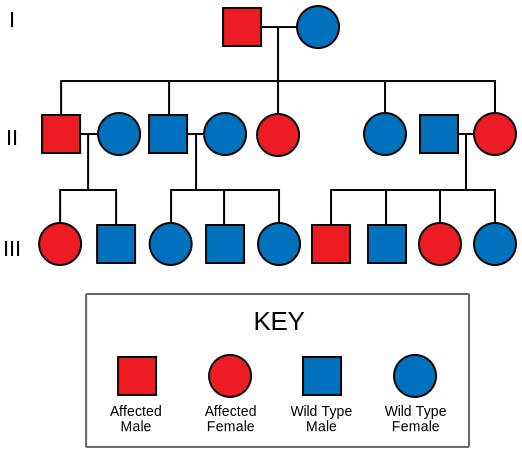
Overview Definition[1–5] Liddle syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant genetic disorder associated with abnormal increased function of epithelial sodium channels (ENaC) in the collecting tubules. Liddle syndrome is clinically characterized by hypertension, low plasma renin activity, metabolic alkalosis, hypokalemia, and low aldosterone levels. Epidemiology[1,3,4] Etiology[1–5,7] An autosomal dominant gain-of-function gene mutation changes the structure of […]
Migraine Headaches (Clinical)
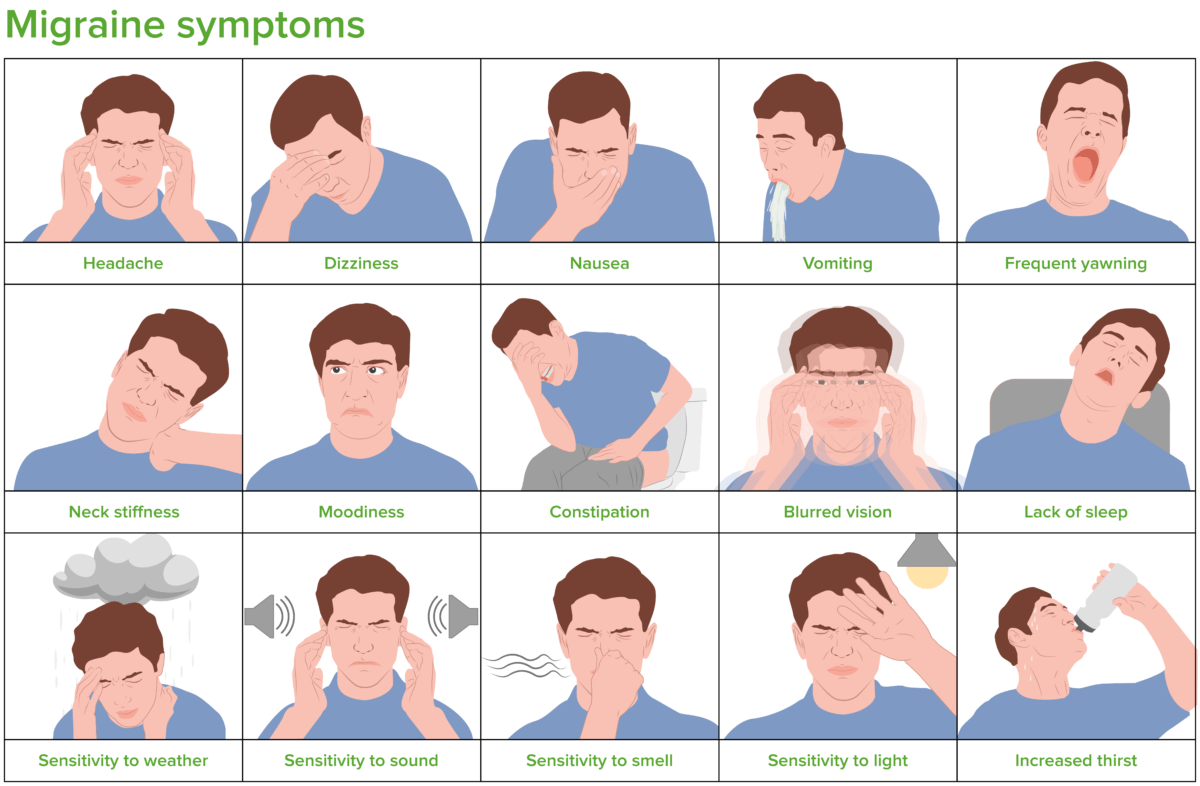
Overview Definition Migraine headaches are primary headaches commonly associated with nausea, photophobia, phonophobia, and exacerbated by physical activity. Distinguishing features:[4,5,11,18] Migraine-related terminology:[11,13,18] Epidemiology[3,8,14] Classification[4,5] Migraine headache is classified among the primary headache disorders as well as having subtypes of its own. Primary headache disorders: Subtypes of migraine headache: Pathophysiology Current consensus holds that a primary […]
Bartter Syndrome (Clinical)

Overview Definition[1–4] Bartter syndrome (BS) is a rare genetic (autosomal recessive) disorder that results from a defect in sodium chloride reabsorption in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, leading to hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis. The disorder mimics long-term ingestion of a loop diuretic. Epidemiology[2–4] Pathophysiology and Classification Normal physiology in the Loop of […]
Trigeminal Neuralgia (Clinical)
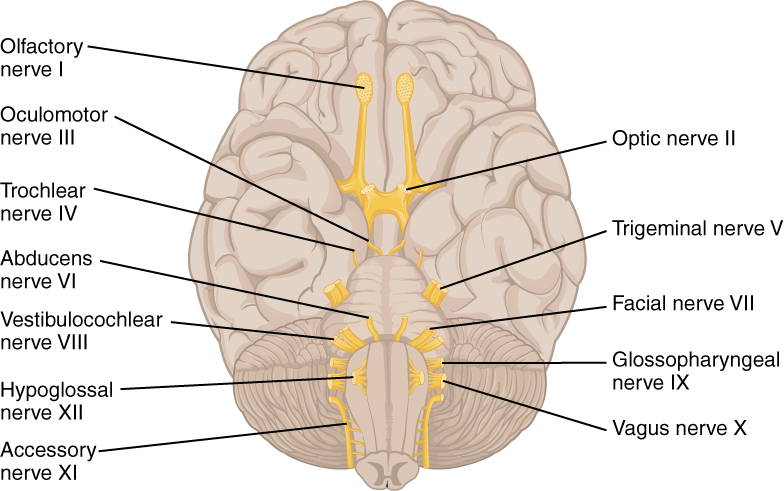
Overview Definition[1,2,5,12] Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a disorder presenting with recurrent, sharp pain in the distribution of the trigeminal nerve. Anatomy of the trigeminal nerve[7,12] Trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve (CN) V): 3 major divisions of CN V: Epidemiology[1,2,5] Etiology[1–3,5,13] Clinical Presentation Main reported symptoms[1,2,5,7] Associated symptoms[1,2] When other neurologic conditions (e.g., multiple sclerosis or aneurysms) […]
Brain Death (Clinical)
Overview and Pathophysiology Definition[1,2,4] Brain death is the complete and permanent loss of all cerebral and brain stem functions, including the ability of the brain stem to regulate vegetative and respiratory activities. Definition of “complete and permanent loss” of brain function: Etiology[1,3] Pathophysiology[1,3] Clinical Presentation History[4,5] Observation time prior to clinical testing[4,5] There is insufficient […]
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)(Clinical)
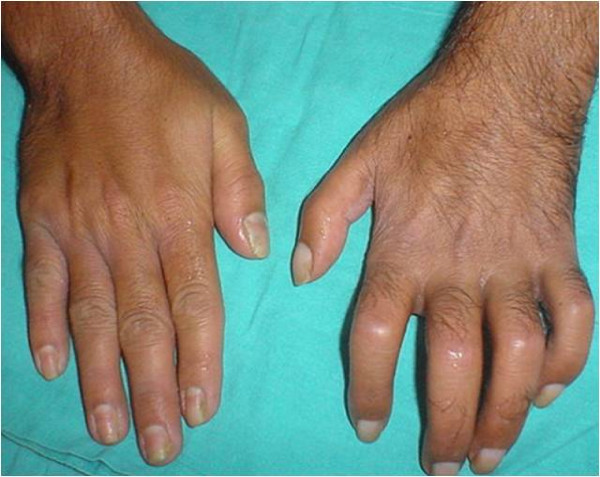
Overview Definitions[1,3,6] Epidemiology[1,3,6,8] Classification[1,8] Etiology[1,3,6,8] Complex regional pain syndrome occurs after an initiating noxious event, such as trauma: Pathophysiology The pathophysiology of CRPS is not completely understood, but there are multiple likely mechanisms. Inflammation (cytokine-mediated):[1,3,6] Neurogenic inflammation (neuropeptide-mediated):[1,3,6] Central sensitization:[1,3,6,11] Sympathetic dysregulation:[1,3,6,11] Cortical reorganization:[1,3,6,11] Genetic predisposition:[6] Clinical Presentation History[1,3,8,10,11] Physical examination[1,8,10,11] Stages of complex regional […]
Fibromyalgia (Clinical)
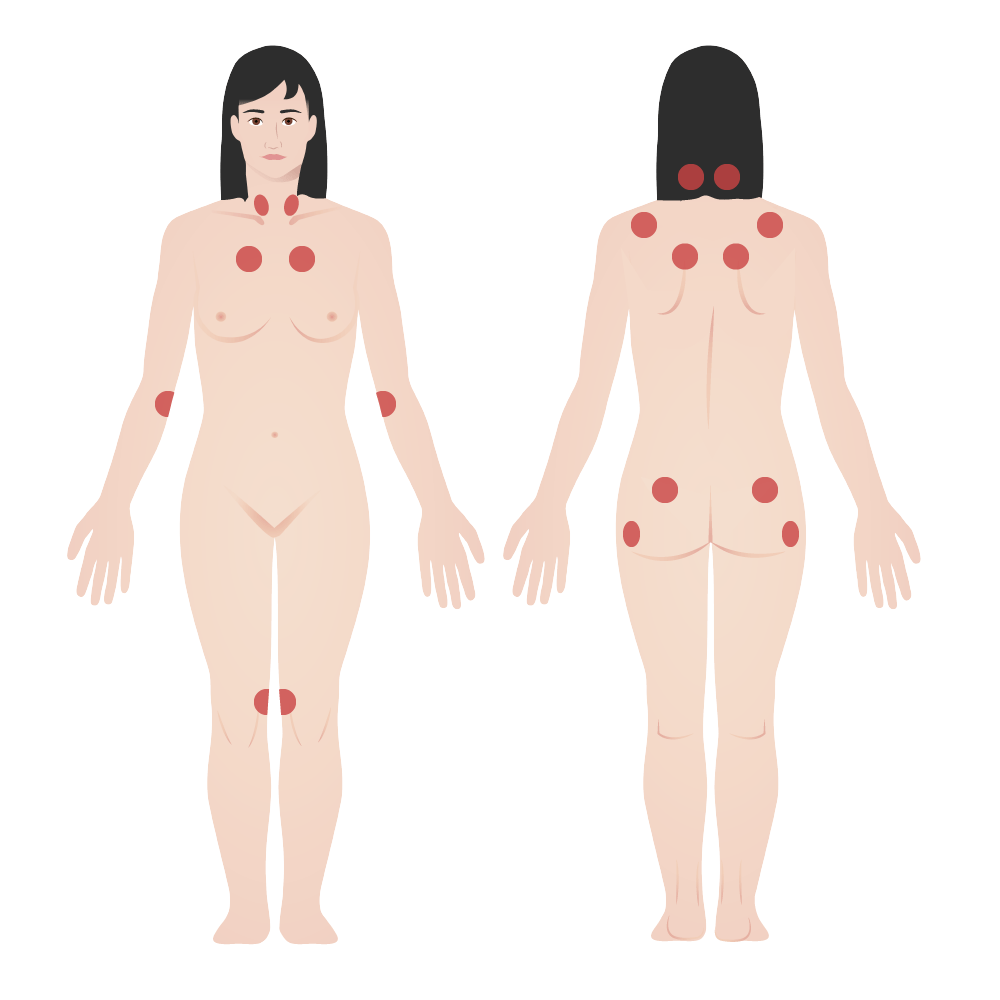
Overview Epidemiology[1,10] Etiology[1,5] While the cause is unknown, the following environmental triggers have been associated with the onset of fibromyalgia. Pathophysiology[1,5] Clinical Presentation Diagnosis History and physical exam Fibromyalgia is a chronic syndrome; therefore, diagnosis determination is recommended over multiple visits after sequential observation and physical exams. A history evaluation should include:[9] A physical examination […]
Lichen Planus (Clinical)
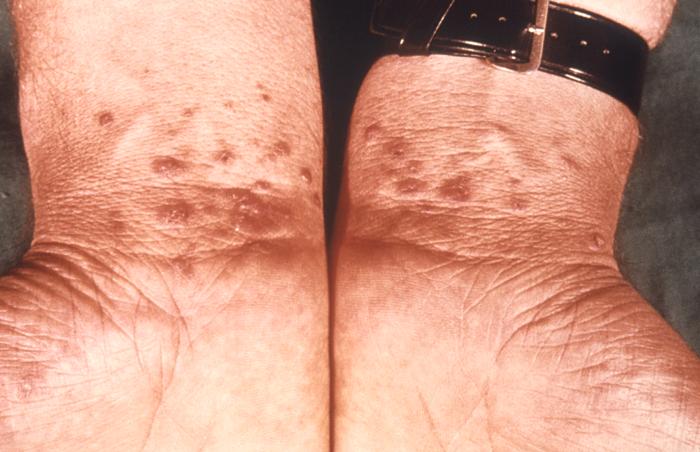
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[5,6,8] Etiology[1–3,5,14] Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Cutaneous LP[5,6] Cutaneous variants by morphology[5,6,8] Oral LP[5–7,13] Genital LP[5–7] Other forms of LP[5–7] Diagnosis Definitive diagnosis is made based on typical morphologic lesions on exam, in combination with associated histopathologic findings at the affected site.[8,9] History and clinical findings[5,8] Mucocutaneous biopsy[5,6,8] Other tests[5,8] Management Management may […]
Pseudomembranous Colitis (Clinical)
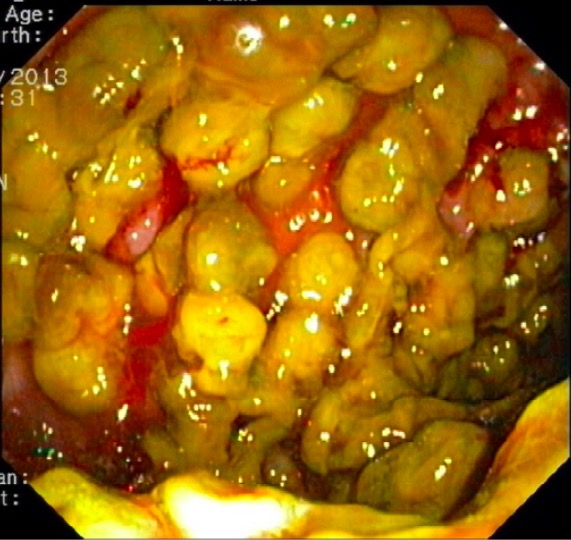
Overview Definition Pseudomembranous colitis is inflammation of the colon caused by overgrowth of the bacterium Clostridioides difficile. Epidemiology[8,10–12] Etiology[8,11,12] Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathogenesis[11–13] Clinical presentation[8,13] Table: C. difficile infection (CDI) classification based on severity Characteristics Mild-to-moderate colitis Severe colitis Fulminant colitis Number of loose stools/day < 6 ≥ 6 ≥ 6 Fever – +/– […]