Otitis Externa (Clinical)
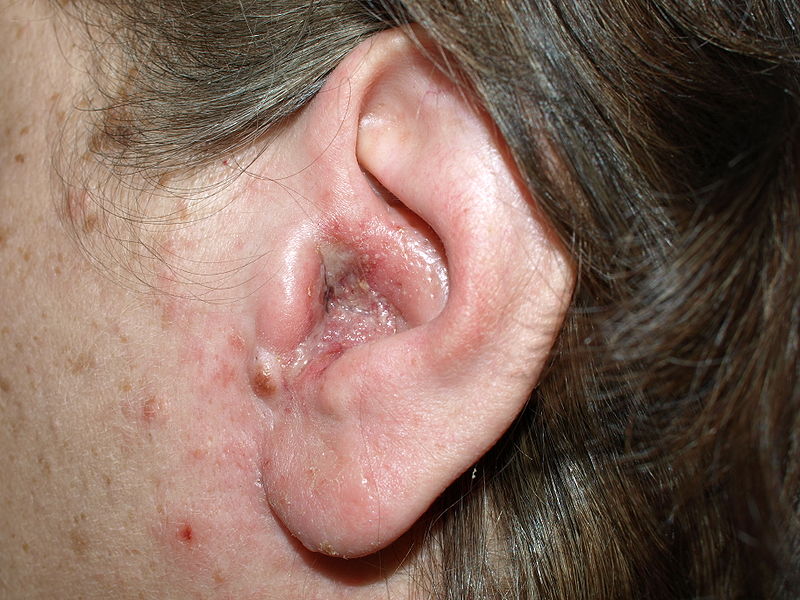
Overview Definition Otitis externa is an infection of the external auditory canal. Epidemiology[1,6,7,9,11] Etiology[1,6,7,9,11] Risk factors[1,6,7,9,11] Pathophysiology Defense mechanisms of the ear[1,9,11] Pathogenesis of otitis externa[1,9,11] Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis Symptoms[1,6,7,9,11] Physical examination[1,6,7,9,11] Diagnosis The diagnosis of otitis externa is based on the history and physical examination. Culture of the ear canal or discharge is […]
Horner Syndrome (Clinical)
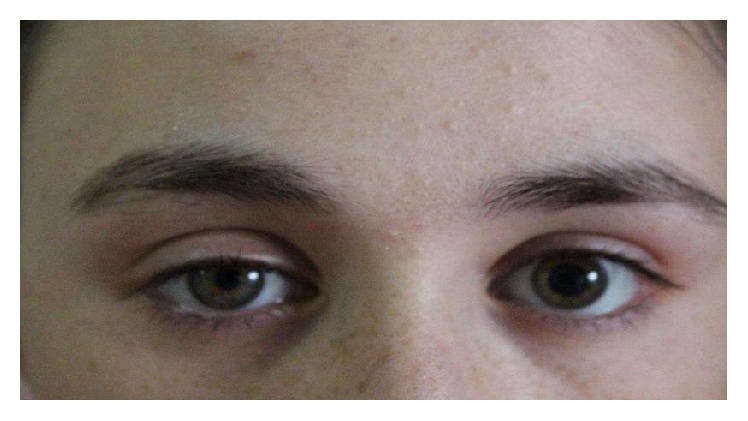
Overview Definition[1–4] Horner syndrome, also known as oculosympathetic paresis, is a condition resulting from the interruption of the sympathetic innervation to the eyes. The syndrome is characterized by the classic triad of: Epidemiology[2,3] Neuroanatomy[1,4,6,7] Horner syndrome can result from a lesion anywhere on the 3-neuron sympathetic pathway supplying the eye. The nerve supply starts from […]
Botulism (Clinical)
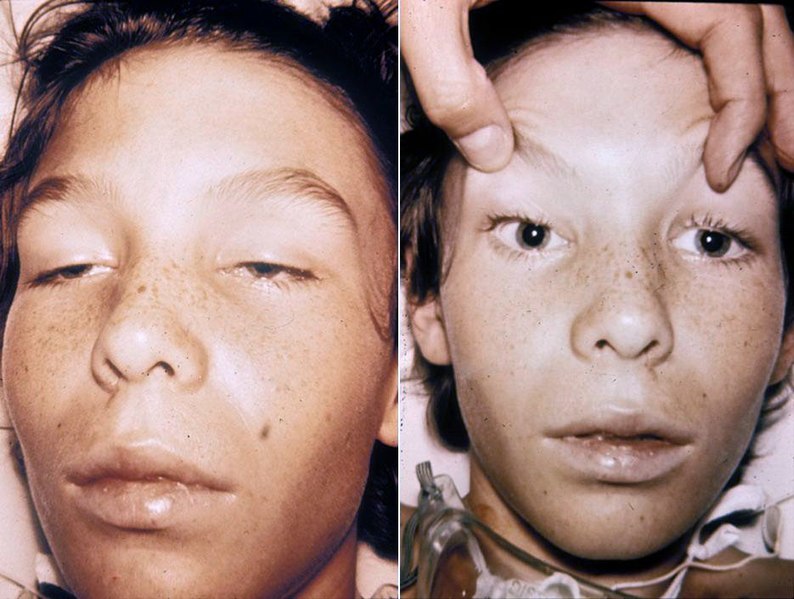
Overview Definition Botulism is a rare, neuroparalytic syndrome caused by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum (C. botulinum), which releases a fatal neurotoxin (botulinum toxin), resulting in varying degrees of muscle paralysis and distinct clinical syndromes. Epidemiology[1–4] Etiology[1–4] Classification Infant botulism[1–4] Foodborne botulism[1–4] Wound botulism[1–4] Iatrogenic botulism[2–4] Adult intestinal toxemia[3,4] Inhalation botulism[2–4] Pathophysiology The means of exposure […]
Brain Abscess (Clinical)
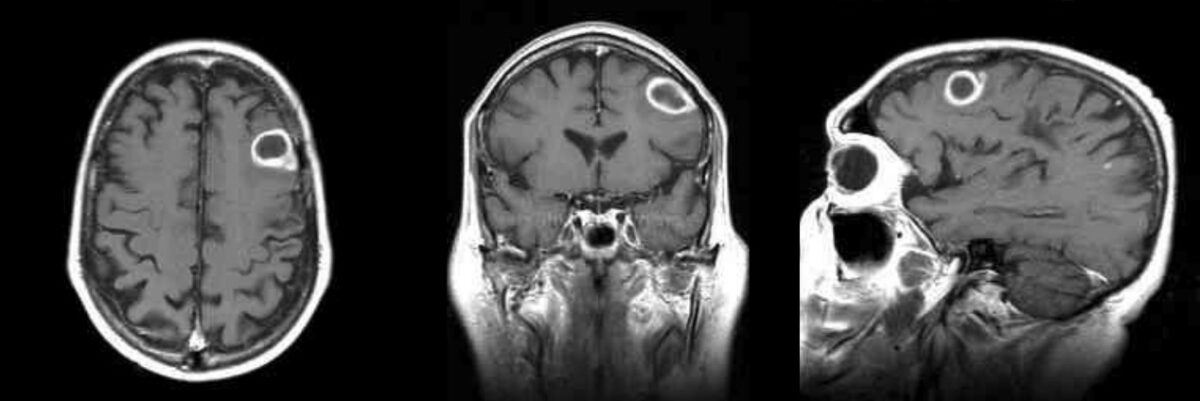
Overview Definition[1,3–5] Brain abscess is an uncommon but life-threatening infectious collection of pus in the brain parenchyma. Epidemiology[3,5] Etiology There are 2 routes of the spread of infection to the brain: Organisms causing brain abscess:[1,3,5] Risk factors:[1,3–5] Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathogenesis[6,7] Stages of development of brain abscess after infection[6,7] Early cerebritis (days 1–3): Late […]
Megacolon (Clinical)
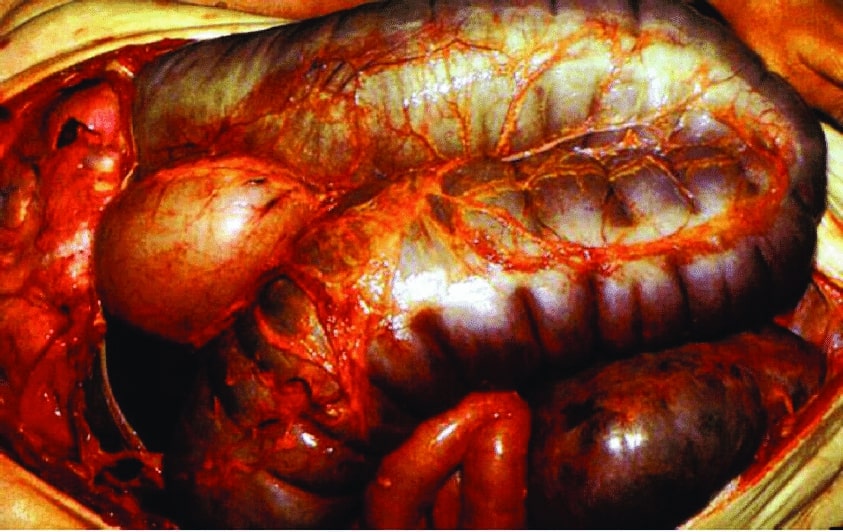
Overview Definition and classification Megacolon is a severe dilatation of the colon secondary to impaired motility or an inflammatory process. The condition is classified based on the time course and duration: Epidemiology[1,3,7] Etiology of acute megacolon[1,6–8] Etiology of chronic megacolon[2–4,14] Pathophysiology Toxic megacolon[1,6,7] Acute colonic pseudo-obstruction[2,8] Congenital aganglionic megacolon[3,4,5] Chronic acquired megacolon[2,5] Clinical Presentation Symptoms[1,3–7,15] […]
Acute Otitis Media (Clinical)
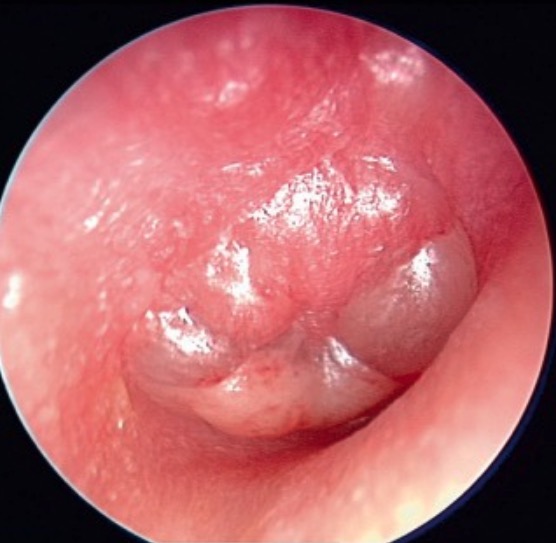
Overview Definition[1,7] Acute otitis media (AOM) is an infection characterized by the accumulation of fluid and inflammation within the middle ear. Epidemiology[2,7] Etiology[2,7,8] Acute otitis media is an inflammatory condition of the middle ear with an infectious etiology that may be bacterial (most common) or viral. Bacterial: Viral: Risk factors[1,2,5,7] Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathophysiology[2,7] […]
Tension Headaches (Clinical)
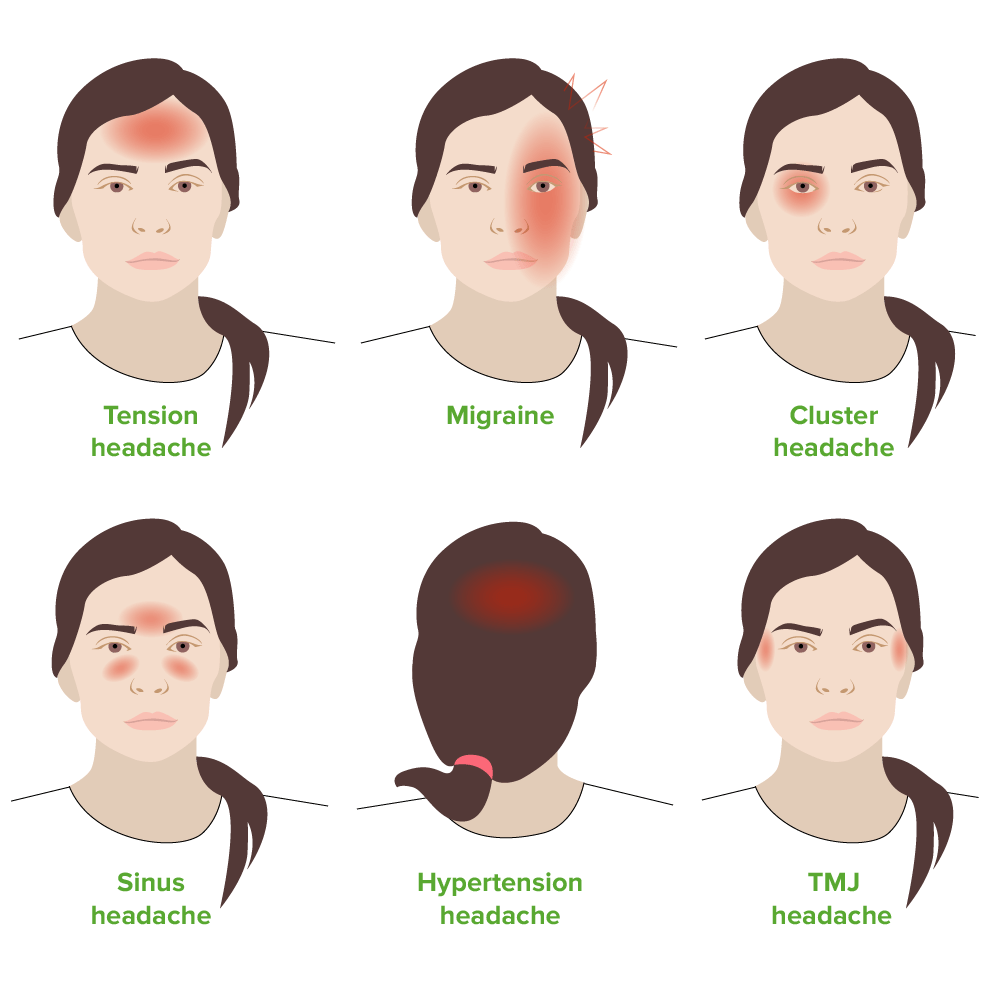
Overview Definition[1,6] A tension headache attack is defined by the following features: Classification[7,9] Tension-type headaches are 1 of the 3 primary headache disorders. 3 primary headache disorders: 3 tension headache subtypes: Epidemiology[1] Pathophysiology The pathophysiology of tension headache is multifactorial, but the precise mechanisms are largely unknown. Pain mechanisms are dynamic and vary from 1 […]
Cluster Headaches (Clinical)
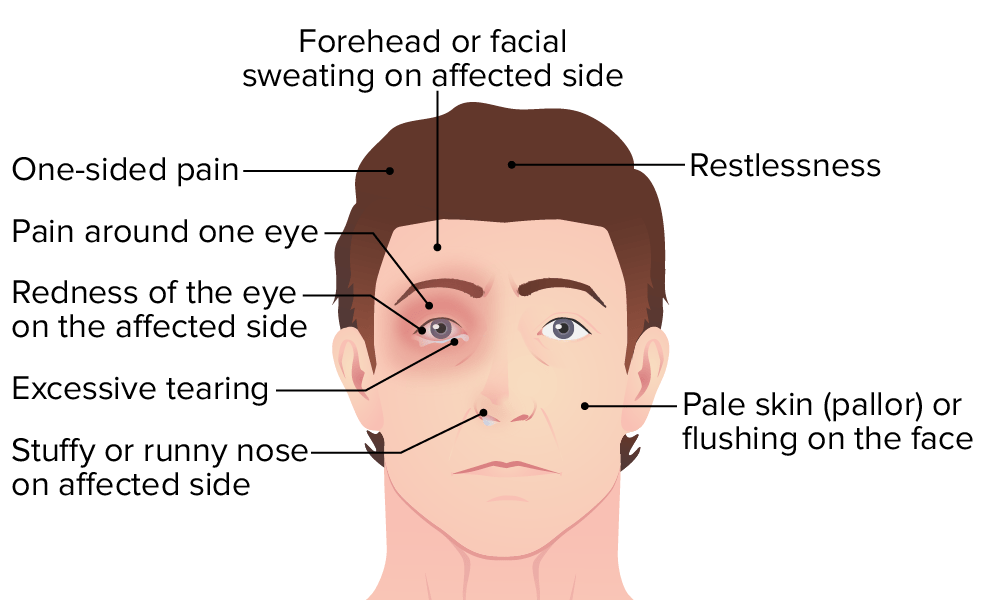
Overview Definition[1,5,6] Cluster headaches are named based on their tendency to occur in clusters lasting from weeks to months, and interrupted by periods of remission. The defining features include: Classification[1,4] Cluster headache belongs to 2 distinct classification schemes: primary headache disorders and trigeminal autonomic cephalgias (TACs). Primary headache disorders: Trigeminal autonomic cephalgias: Epidemiology[1] Pathophysiology The […]
Volvulus (Clinical)
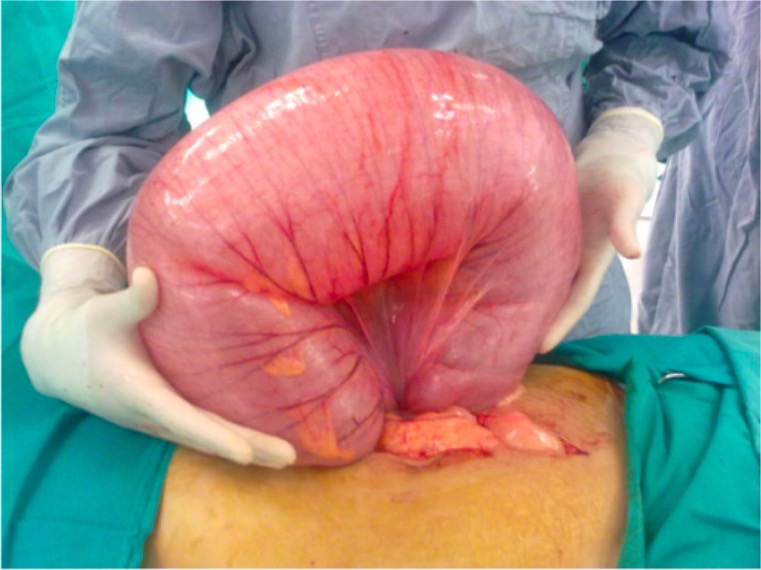
Overview Definition A volvulus is the twisting of a segment of bowel on its mesentery, which results in bowel obstruction. Epidemiology[1–4] Etiology[2–4] Sigmoid volvulus: Cecal volvulus: Pathophysiology Colonic volvulus not only leads to luminal occlusion, but it also increases the risk for bowel ischemia, gangrene, and perforation.[2–4] Clinical Presentation Sigmoid volvulus[3,4] Cecal volvulus[2,4] Diagnosis History[2–4,8] […]
Large Bowel Obstruction (Clinical)
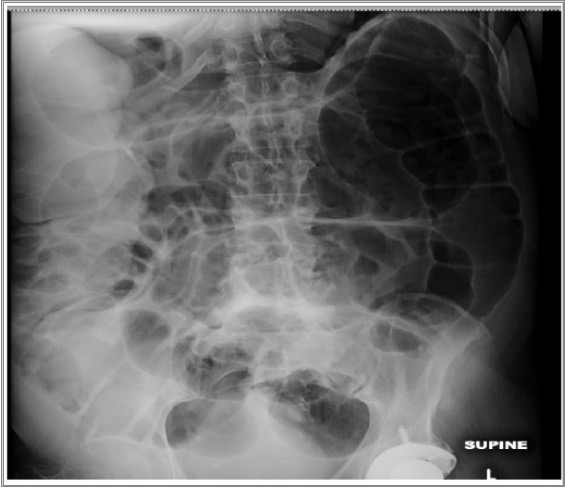
Overview Definition A large bowel obstruction (LBO) is an interruption in the normal passage of bowel contents through the colon and rectum. Epidemiology[1–6] Etiology[1–6,11] Pathophysiology Pathogenesis[3,4,11] Pathophysiology for specific etiologies Clinical Presentation Acute obstruction symptoms[1,3–6] Chronic obstruction syndrome[1,4] Physical exam[1,4–6] Diagnosis Relevant history Laboratory studies[3,8–10] Imaging Colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy Management Initial supportive management[6,7] All patients […]