Type IV Hypersensitivity Reaction
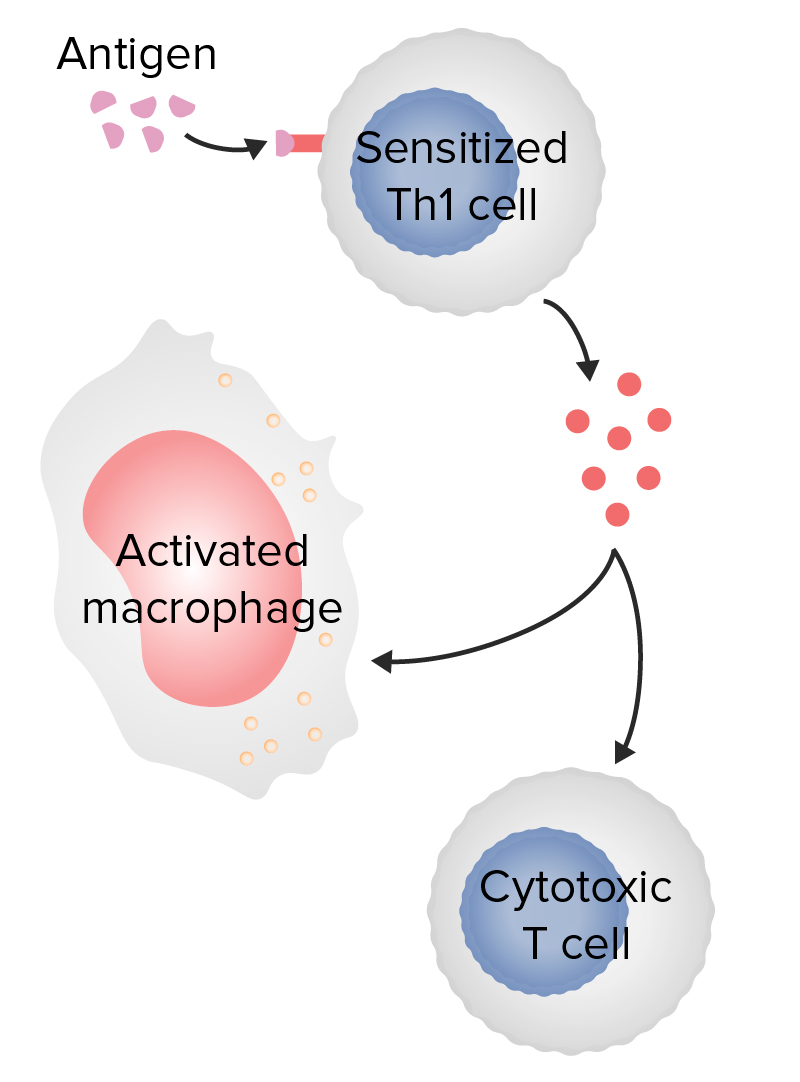
Overview Pathophysiology T cell function Pathogenesis Sensitization phase Effector phase Clinical Presentation Allergic contact dermatitis Tuberculin Granulomatous diseases Autoimmune myocarditis Diabetes mellitus type I Drug hypersensitivity Guillain-Barré syndrome Disease Target antigen Effects Allergic contact dermatitis Environmental chemicals such as urushiol (from poison ivy and poison oak), metals (e.g., nickel), topical medication Epidermal necrosis, inflammation, skin […]
Type III Hypersensitivity Reaction
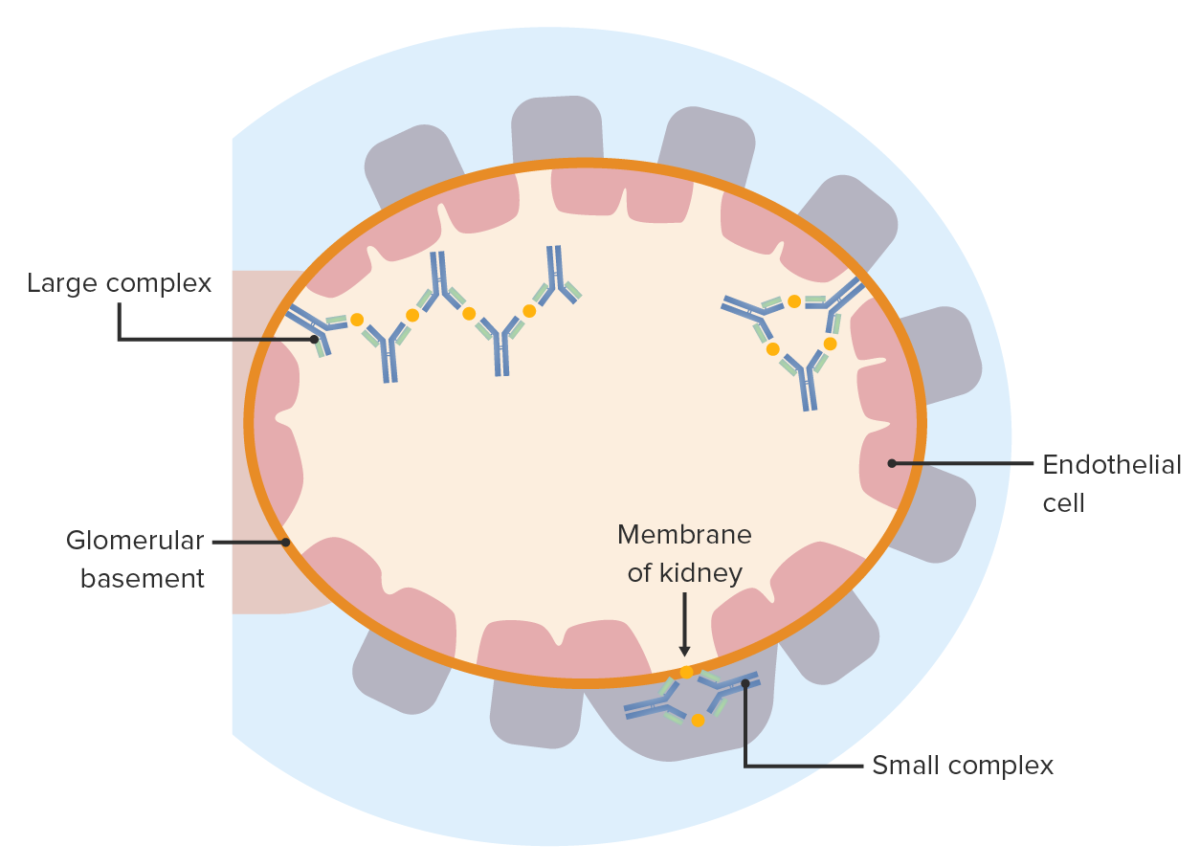
Overview Pathophysiology Physiology Pathogenesis Immune complex formation: IC formed by the binding of Ag and Ab Immune complex deposition Immune complex deposition depends on: Immune complex inflammatory reaction Clinical Presentation Manifestations are affected by the route of entry, site(s) of IC deposition, and persistence of antigen(s). Arthus phenomenon/Arthus reaction Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis […]
Type II Hypersensitivity Reaction
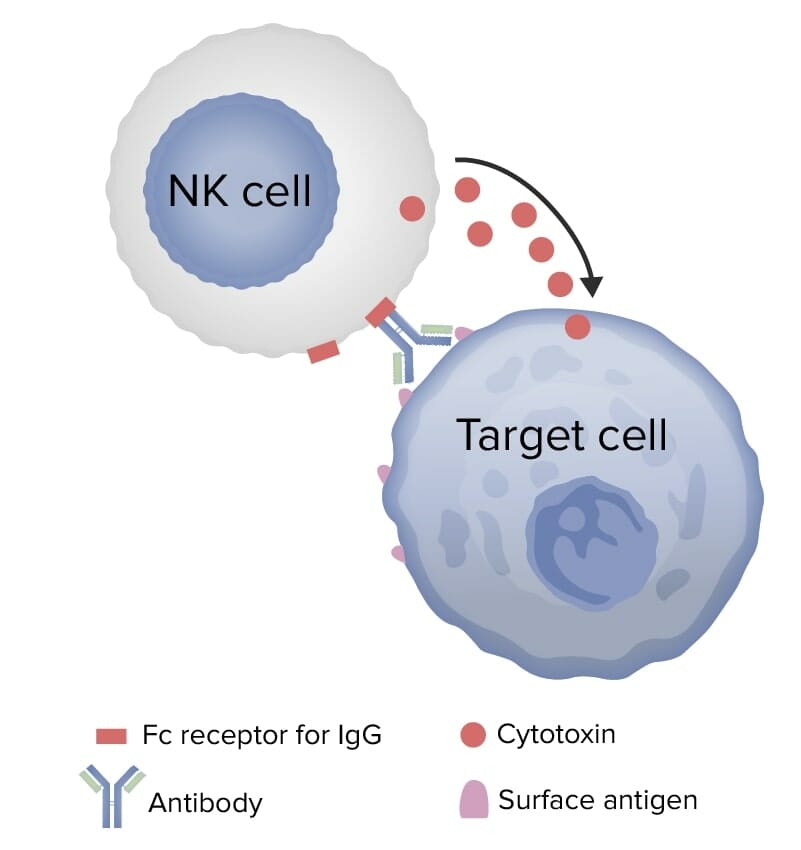
Overview Pathophysiology Activation of the complement system The following mechanisms are triggered by the binding of Ab-antigen complexes: Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) Antibody-mediated cellular dysfunction Clinical Presentation Type II hypersensitivity can result from the following conditions: Transfusion reactions (ABO or blood group incompatibility) Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (against RBCs) Pernicious anemia (against intrinsic factor) Hemolytic disease […]
Type I Hypersensitivity Reaction
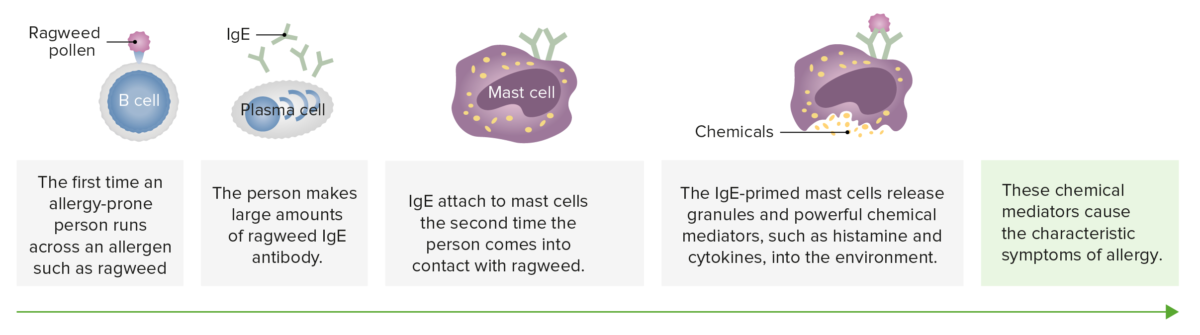
Overview Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Sensitization stage Reaction or effector stage Causes Types of hypersensitivity Table: Comparison of type I hypersensitivity to other types of hypersensitivity Type I Type II Type III Type IV IgE-mediated hypersensitivity IgG-mediated cytotoxic hypersensitivity Immune complex-mediated hypersensitivity Cell-mediated hypersensitivity IgE is bound to mast cells via its fragment […]
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)

Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology At least 12 genes are known to cause severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) if mutated, including those that encode for the following: The pattern of inheritance depends on the type of genetic mutation involved: Pathophysiology Table: Possible SCID phenotypes Phenotype Genetic defect T–B+NK– γC, JAK3 T–B–NK+ RAG-1, RAG-2, Artemis, DNA ligase […]
DiGeorge Syndrome
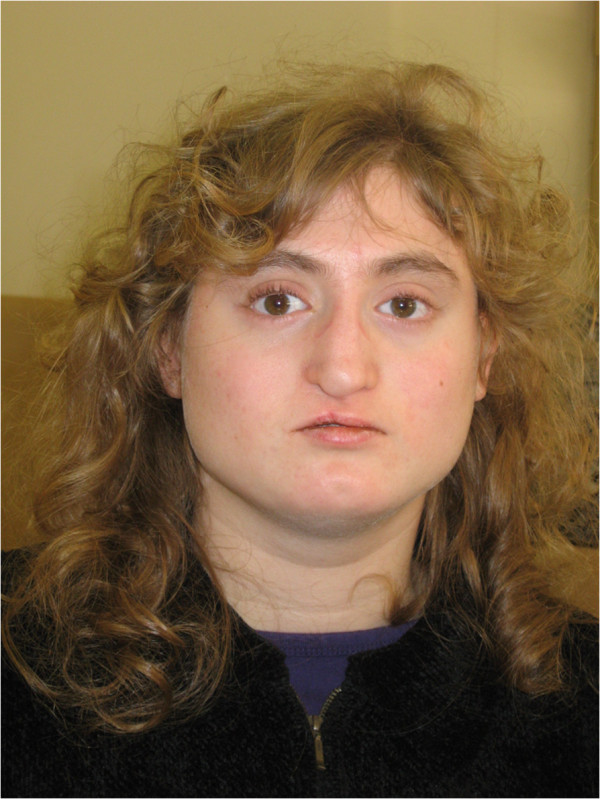
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation DiGeorge syndrome has a marked variability in clinical expression among different individuals. Manifestations can include the following: Mnemonic DiGeorge syndrome signs can be summarized using the mnemonic CATCH-22: Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Establishing a diagnosis is difficult due to the variability of phenotypes. A diagnosis of DiGeorge is […]
Autosomal Dominant Hyperimmunoglobulin E Syndrome
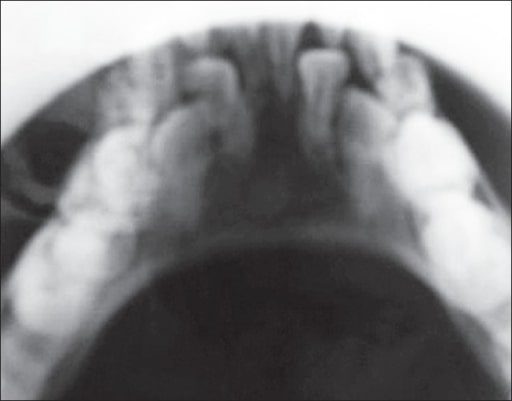
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Clinical Presentation Symptoms may be apparent at birth or become apparent during infancy or early childhood. Patients present with various clinical manifestations and abnormalities: Mnemonic A helpful mnemonic of the clinical manifestations of AD-HIES is FATED: Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis The diagnosis of AD-HIES is based on clinical evaluation, especially […]
IL-12 Receptor Deficiency
Etiology and Pathophysiology Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Management Differential Diagnosis The following conditions are differential diagnoses for IL-12 receptor deficiency: References
IPEX Syndrome
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Signs of systemic autoimmunity begin presenting in the 1st year of life. Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Diagnostic testing for IPEX syndrome follows systematic criteria consistent with: Management Numerous medications are used and administration depends on each patient’s manifestations: Differential Diagnosis The following conditions are differential diagnoses for […]
Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome
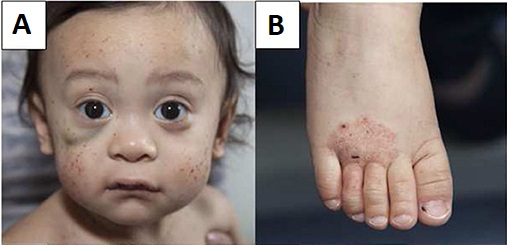
Etiology and Pathophysiology Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Management Differential Diagnosis The following conditions are differential diagnoses for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: References