Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation
Overview Immune system The immune system provides defense (immunity) against invading pathogens ranging from viruses to parasites, and components are interconnected by blood and the lymphatic circulation. There are 2 lines of defense (that overlap): Innate versus adaptive immunity Table: Innate versus adaptive immunity Innate immunity Adaptive immunity Genetics Germline encoded Gene rearrangements involved in […]
Humoral Adaptive Immunity
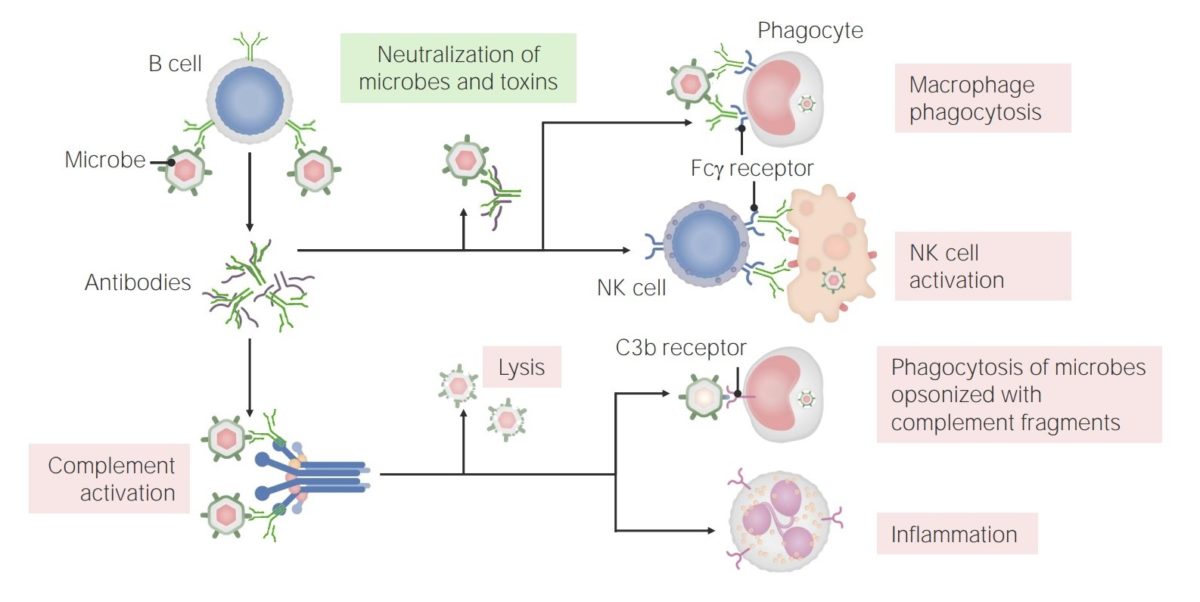
Overview Immune system: definition The immune system provides defense (immunity) against invading pathogens ranging from viruses to parasites. The components of the system are interconnected by blood and the lymphatic circulation. 2 lines of defense (that overlap): Innate immunity (which is nonspecific) Adaptive immunity (based on specific antigen recognition): Cell-mediated immunity: adaptive response in the […]
Adaptive Cell-mediated Immunity
Overview Immune system definition The immune system provides defense (immunity) against invading pathogens ranging from viruses to parasites. Components are interconnected by blood and the lymphatic circulation. Two lines of overlapping defense: Innate immunity (nonspecific) Adaptive immunity (based on specific antigen recognition): Cell-mediated immunity: adaptive response in the cells/tissues involving the T cells Humoral immunity: […]
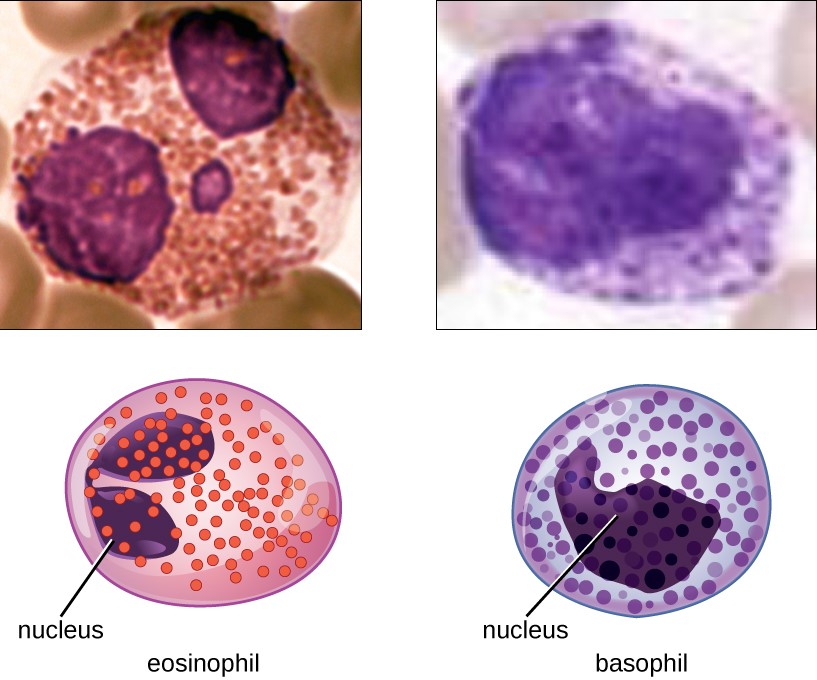
Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions
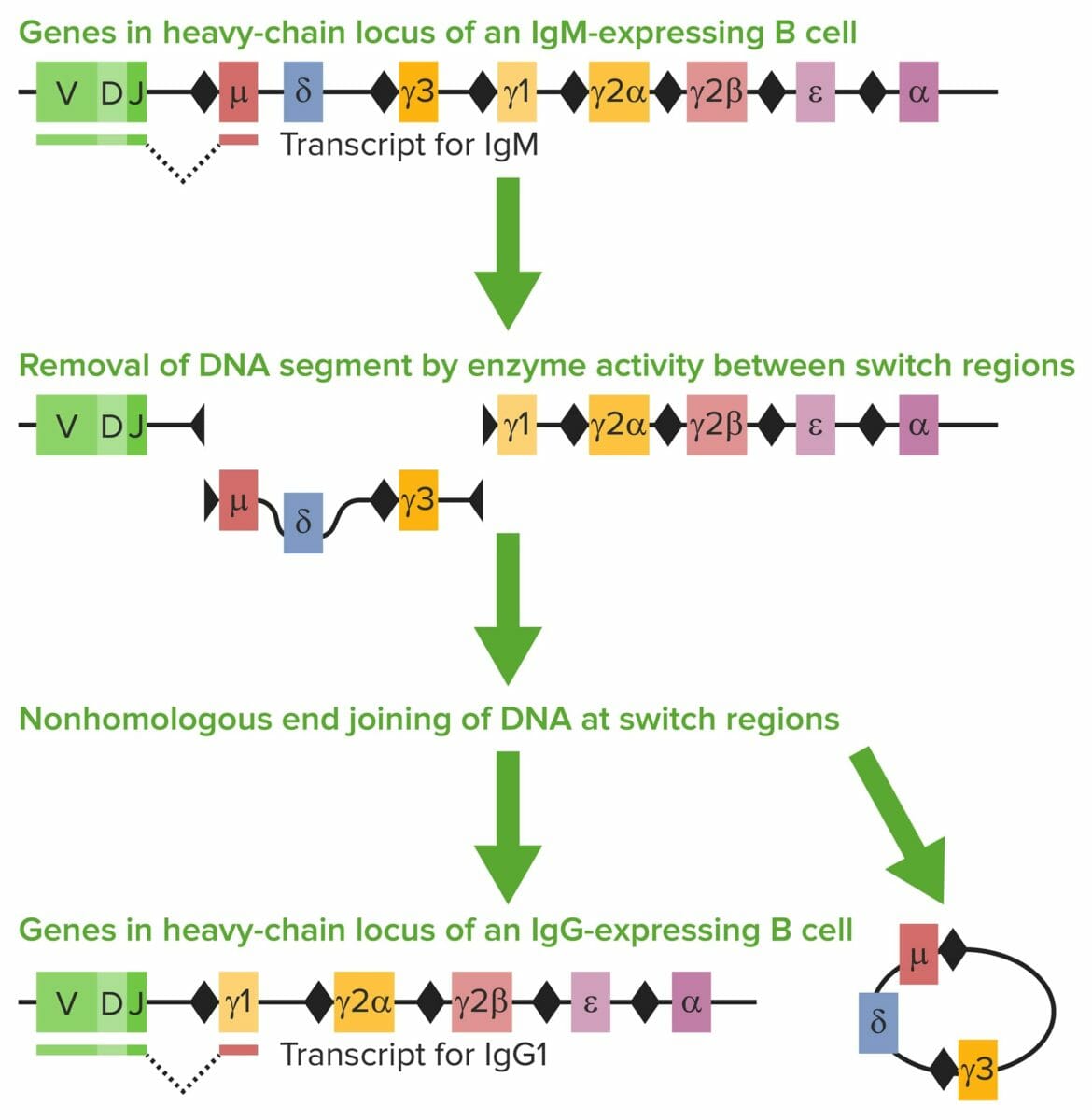
Overview Immunoglobulins (Igs) Ig regions and fragments Immunoglobulin Genes Ig gene segments Gene rearrangements Class-switch recombination (CSR) Processes of class-switch recombination Antibody Diversity and Specificity Antibodies that are created have important properties (diversity and specificity) that are essential in the immune response. Antibody diversity Unique mechanisms creating antibody diversity include: Specificity Classes and Characteristics Classes […]
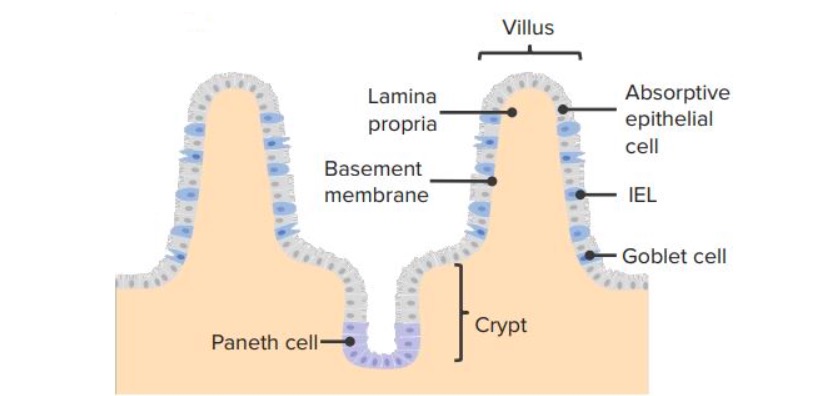
Innate Immunity: Barriers, Complement, and Cytokines
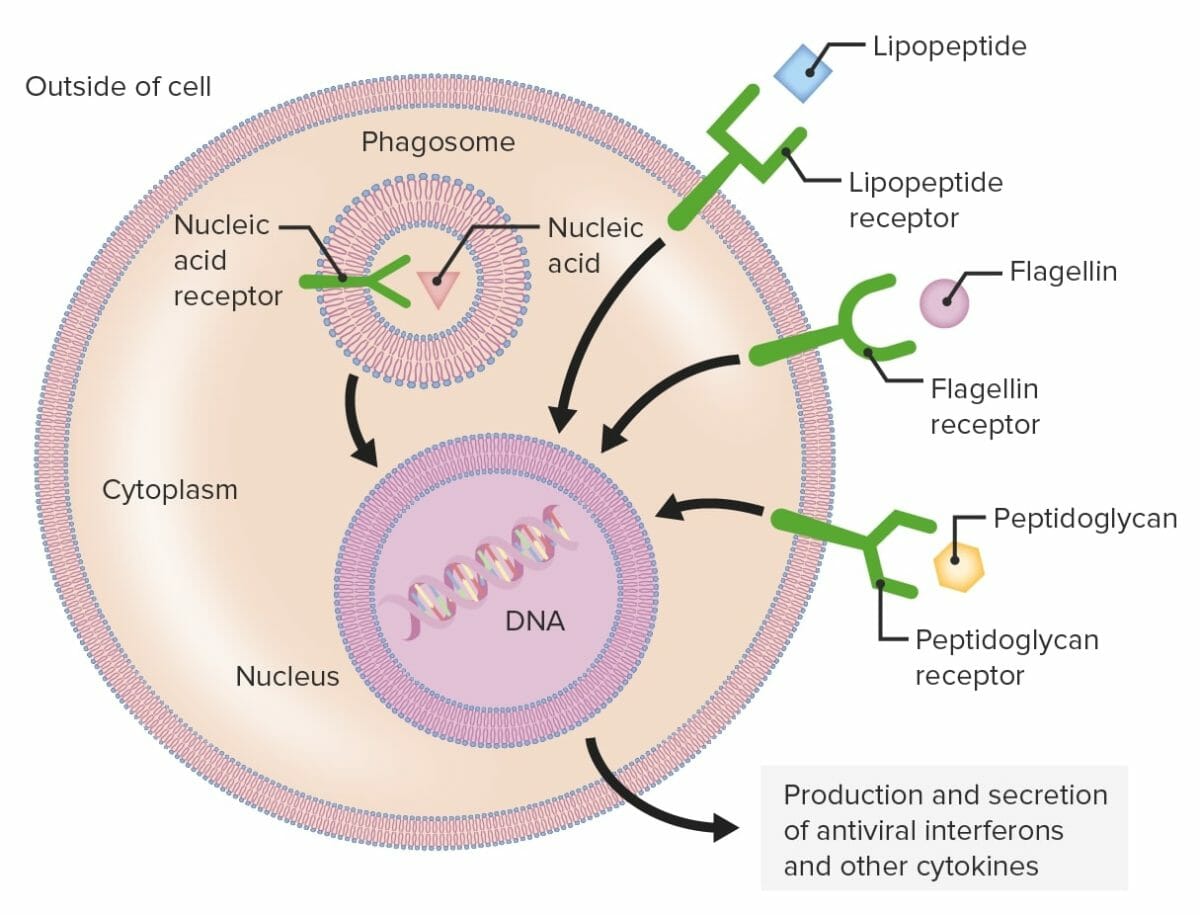
Overview Immune system The immune system provides defense (immunity) against invading pathogens ranging from viruses to parasites; components are interconnected by blood and lymphatic circulation. Two lines of overlapping defense: Innate versus adaptive immunity Table: Innate versus adaptive immunity Innate immunity Adaptive immunity Genetics Germline encoded Gene rearrangements involved in lymphocyte development Immune response Nonspecific […]
T cells: Types and Functions
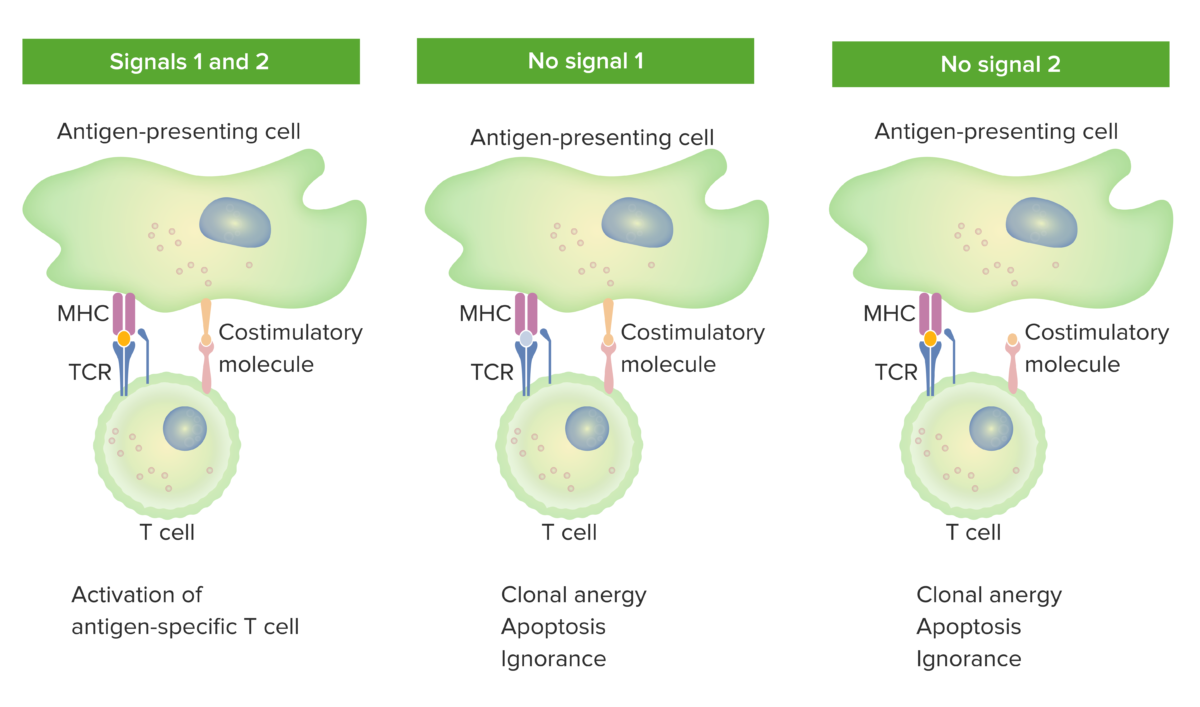
T-Cell Development Introduction Development The initial process takes place in the outer cortex of the thymus, and the cells move into the deeper cortex as they mature. Stages To reach functionality, the T cell goes through stages, released from the bone marrow as progenitor cells to continue development in the thymus. The table summarizes the […]
B cells: Types and Functions
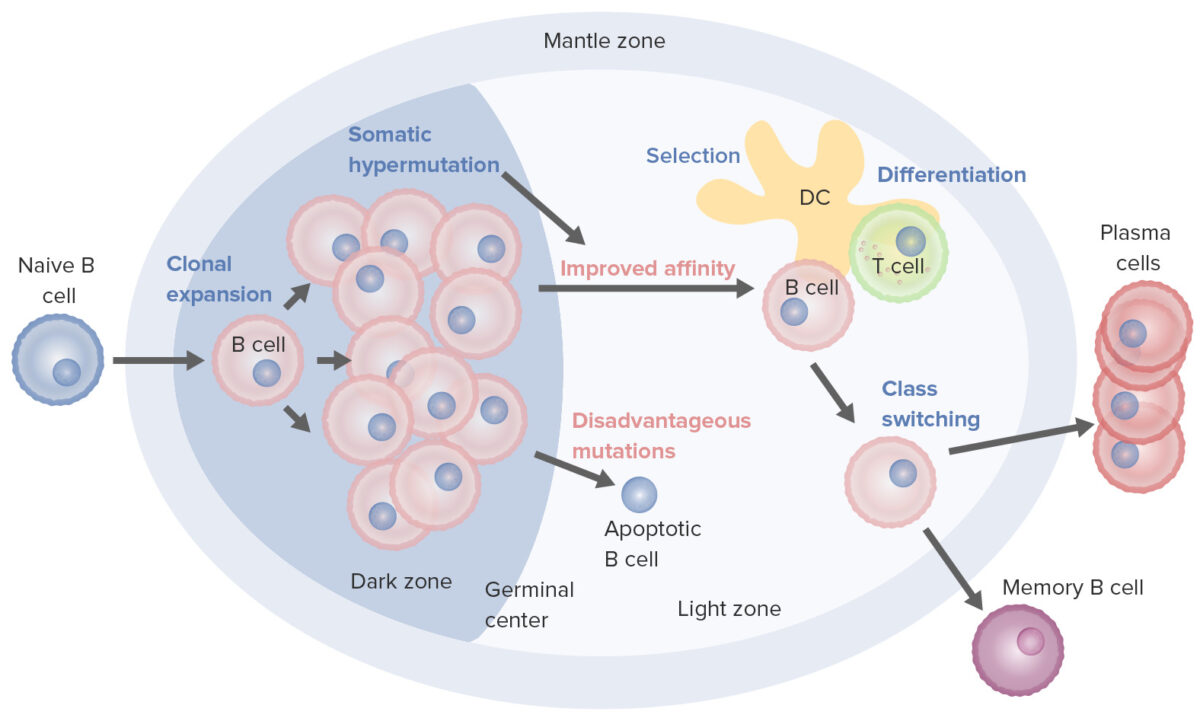
B-Cell Development Definition B (bursa-derived) lymphocytes, or B cells, are a type of lymphocyte that arises from the common lymphoid progenitor. Development Stages To reach functionality, the B cell goes through stages in the bone marrow and the secondary lymphoid organs: Table: Stages of B-cell development Maturation stage Ig genes B-cell receptor (BCR) Associated events […]
Severe Congenital Neutropenia
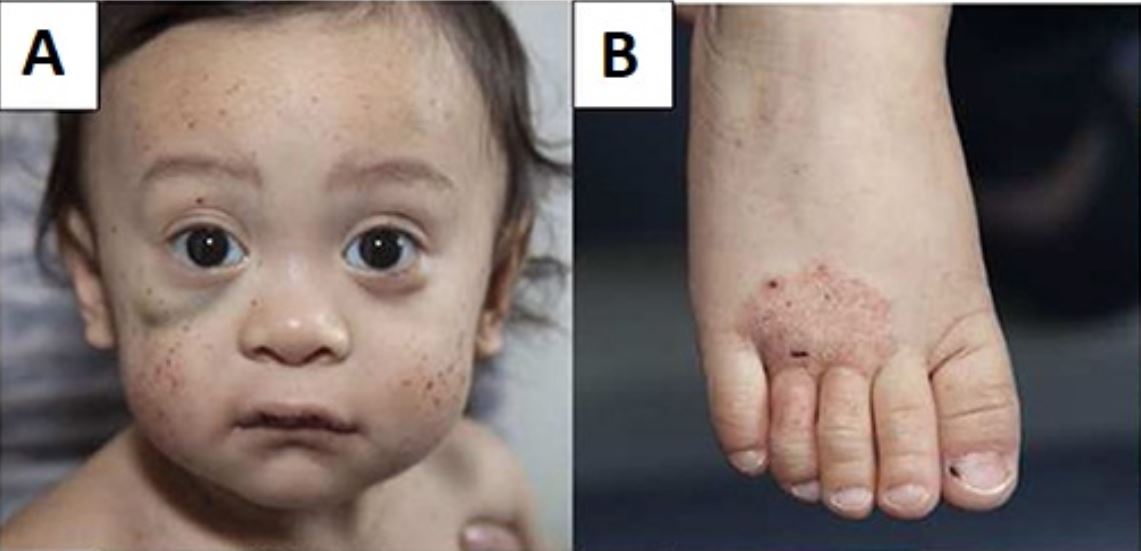
Etiology General facts In 50%–60% of cases, severe congenital neutropenia (SCN) is due to an autosomal dominant ELANE gene mutation. However, the initial mutation described by Kostmann was in HAX1, which is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. X-linked recessive inheritance is due to mutations in the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS) gene protein (WASP). Subtypes The […]
Chronic Granulomatous Disease
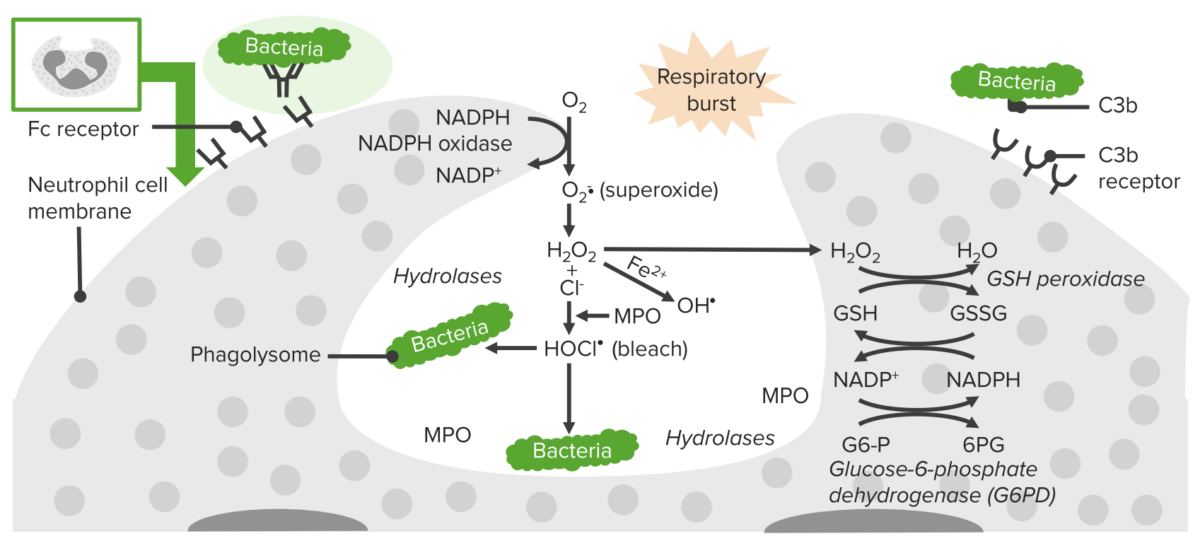
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is caused by mutations in the genes encoding for proteins that make up the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase: Pathophysiology Normal phagocytosis pathway Pathophysiology of CGD The NADPH-oxidase enzyme is impaired in phagocytic cell → ↓ production of superoxide anion O2–, which affects other oxidants. […]
Terminal Complement Pathway Deficiency
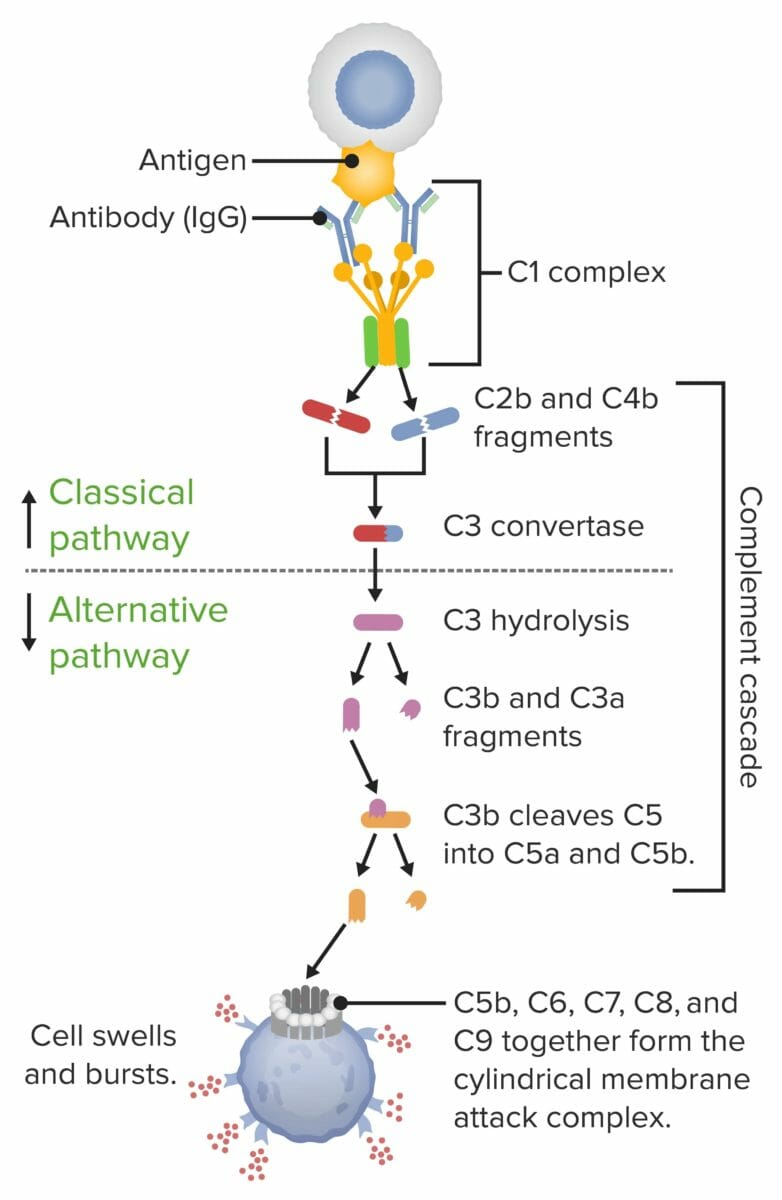
Etiology and Pathophysiology Epidemiology and etiology Genetic disorder with autosomal recessive inheritance Deficiency of 1 of the terminal complement proteins Most common deficiencies in the United States: C5, C6, or C8 Pathophysiology Membrane attack complex (MAC) structure and function: Structure: ring-like structure formed by activated terminal complement proteins (C5b, C6, C7, C8, and C9) Function: […]