The Cell: Cytosol and Cytoskeleton
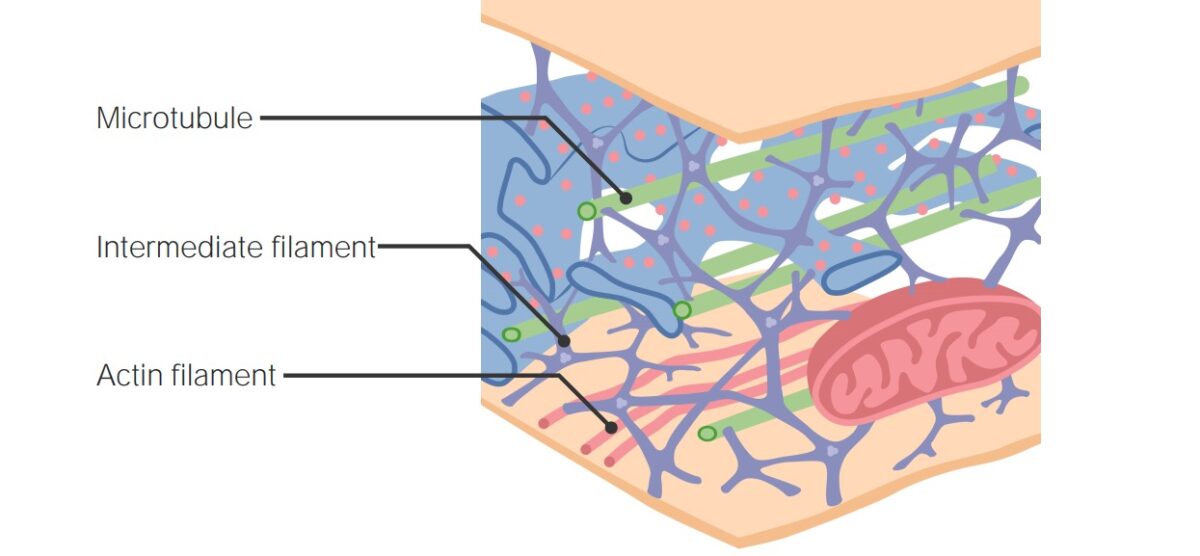
Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is composed of different protein fibers that extend through the cytosol. Three different types of fiber proteins provide the framework along which molecular motor proteins move. Protein fibers Molecular motors Specialized proteins “walk” along the microtubule highways, transporting organelles, substrates, or chromosomes within the cell. Cytosol References
Arteries: Histology
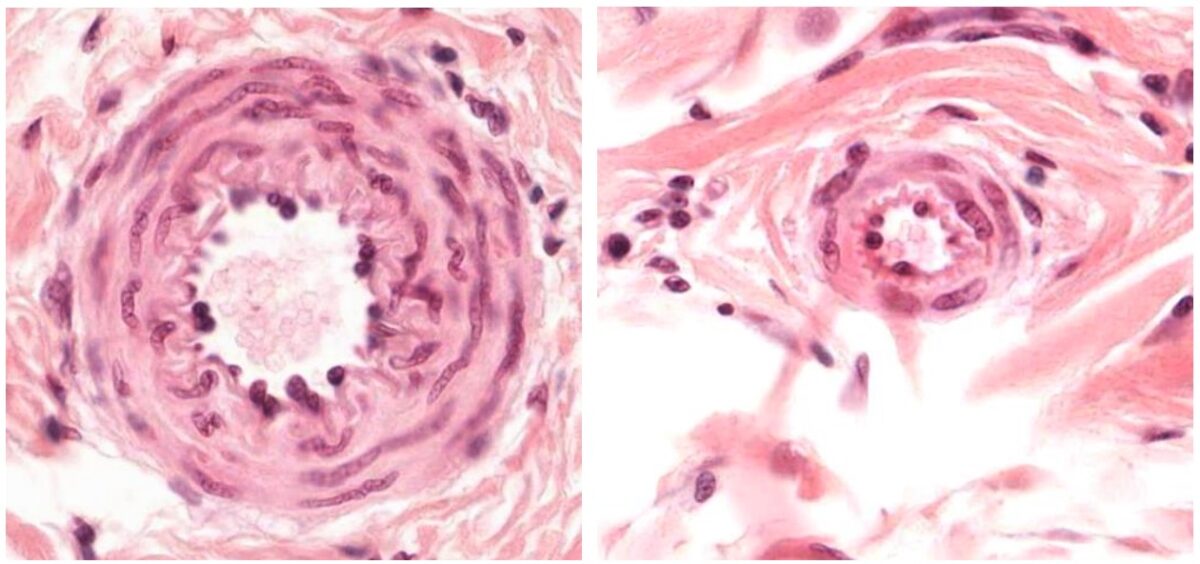
Overview Definition Arteries are tubular collections of cells that transport oxygenated blood and nutrients from the heart to the tissues of the body. General characteristics All arteries have the following characteristics: Layers of the Vessel Wall All arteries have the same basic structure and are made up of three primary layers: the tunica intima, tunica […]
The Cell: Organelles
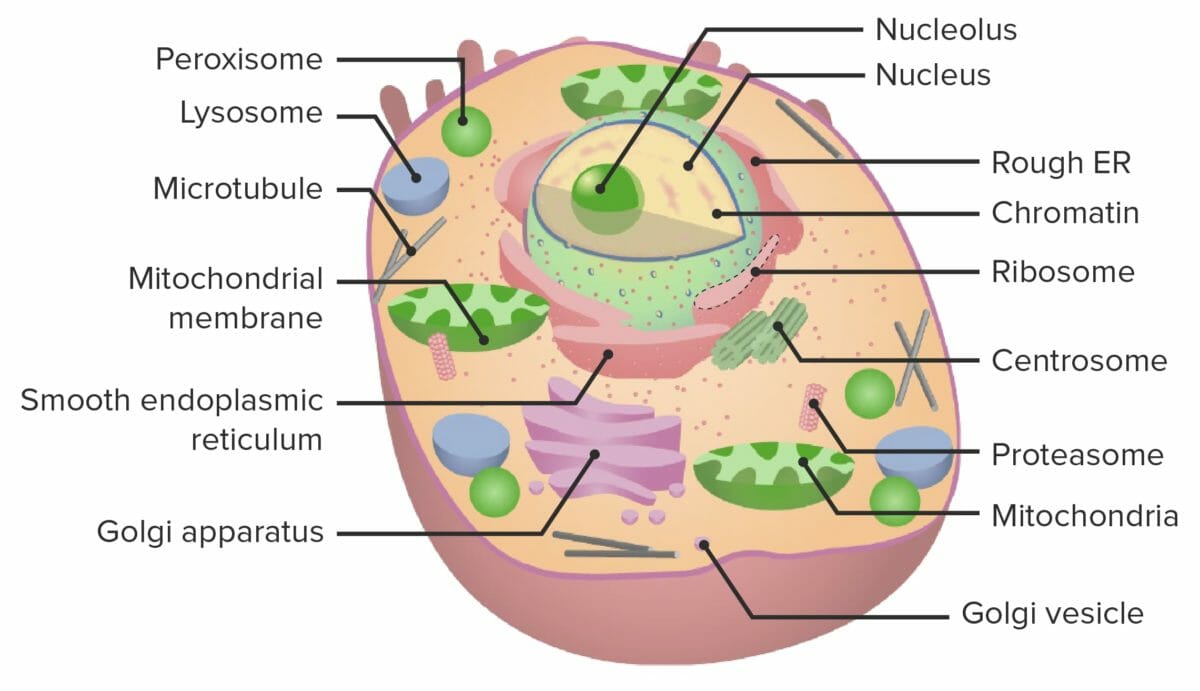
Overview Definition Organelles are specialized structures within the eukaryotic cell that carry out specific functions (cell’s “internal organs”). Classification Membrane-bound organelles: Non-membrane-bound organelles: Membrane-bound Organelles Plasma membrane Nucleus Structure: Functions: Endoplasmic reticulum Structure: Functions: Golgi complex Structure: Functions: Mitochondria Structure: Functions: Vacuoles Structure: Functions: Lysosomes Peroxisomes Non-membrane-bound Organelles Ribosomes Structure: Function: Nucleolus Proteasomes Flagella and […]
The Cell: Cell Membrane
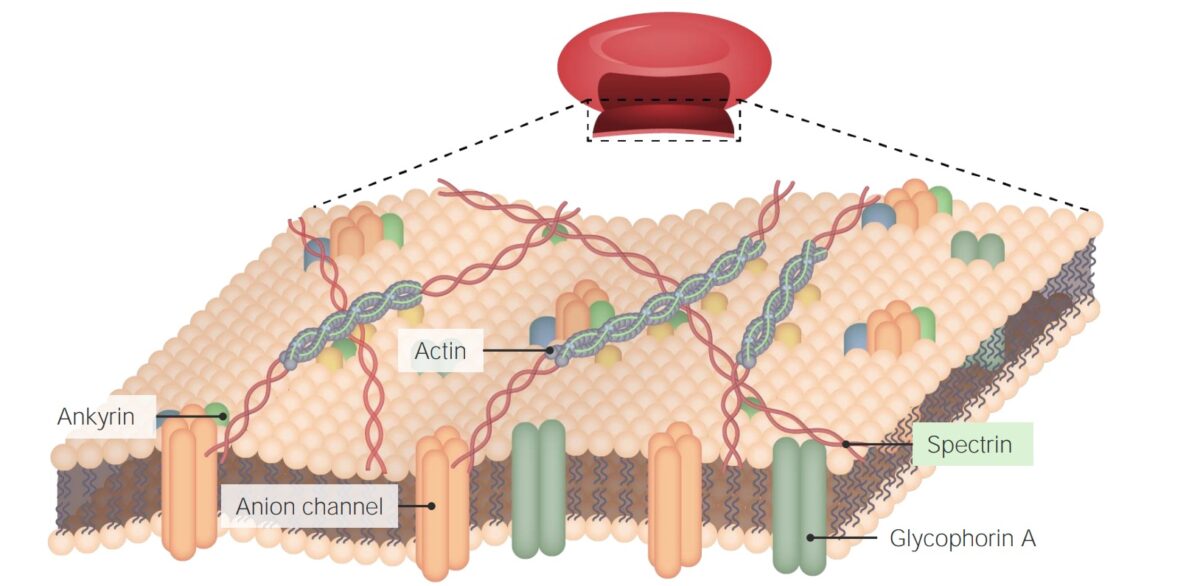
Characteristics and Structure Definition Cell membrane (also known as plasma membrane or plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates the contents of the cell from the outside environment. Functions Composition The composition of the cell membrane can change depending on the environment and the stage of cell development. By weight, it is composed of approximately […]
Cell Types: Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic
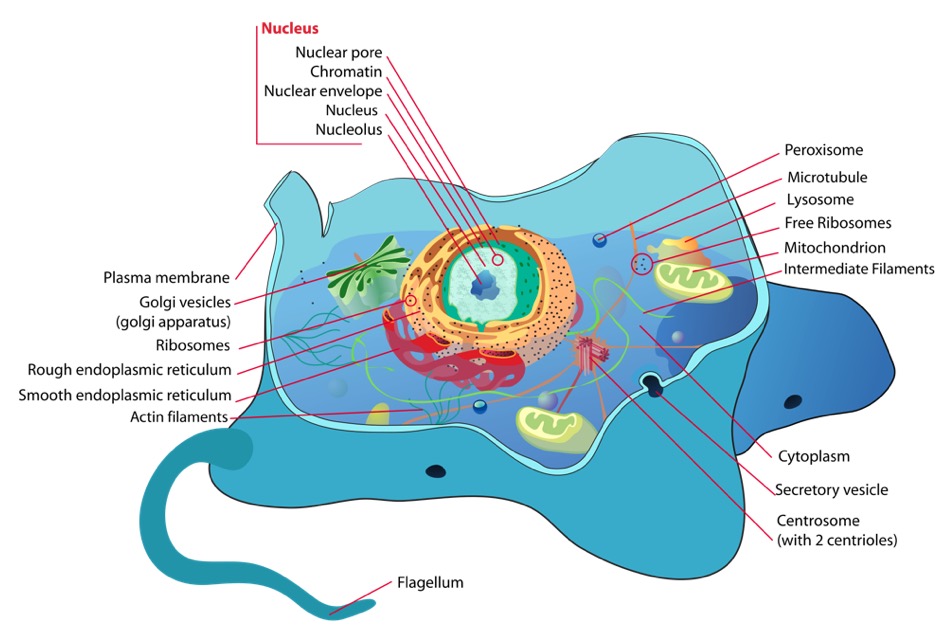
Eukaryotic Organisms Eukaryotic organisms include: Cellular organization Cellular characteristics Prokaryotic Organisms Prokaryotic organisms include bacteria and archea. The cellular organization is unicellular. Cellular characteristics Clinical Relevance References
Adipose Tissue: Histology
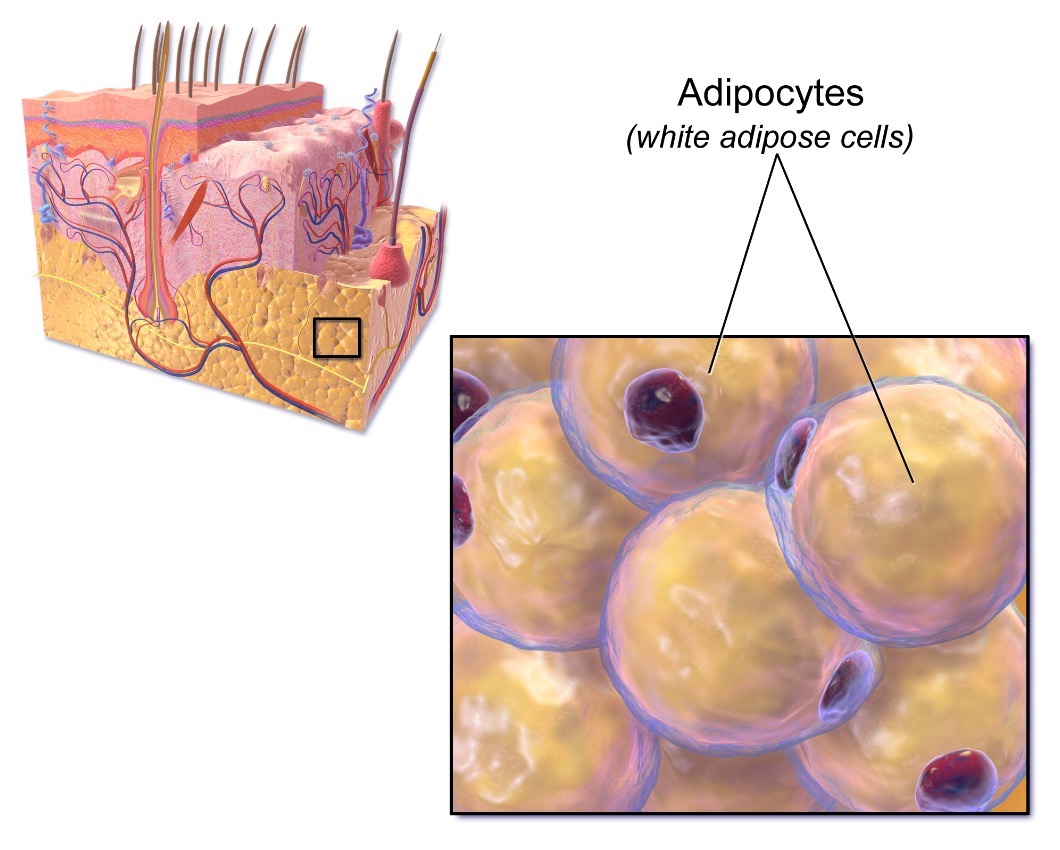
Overview Definition Adipose tissue is a type of loose connective tissue composed mainly of cells called adipocytes. Composition Types of adipose tissue Two classic types: 3rd, recently described, transitional type: Anatomic distribution Development Embryonic development White adipose tissue: Brown adipose tissue: Postembryonic development Gender differences Females: Males: Morphology and Histology Morphology White adipose tissue: Brown […]