Primary Lymphatic Organs
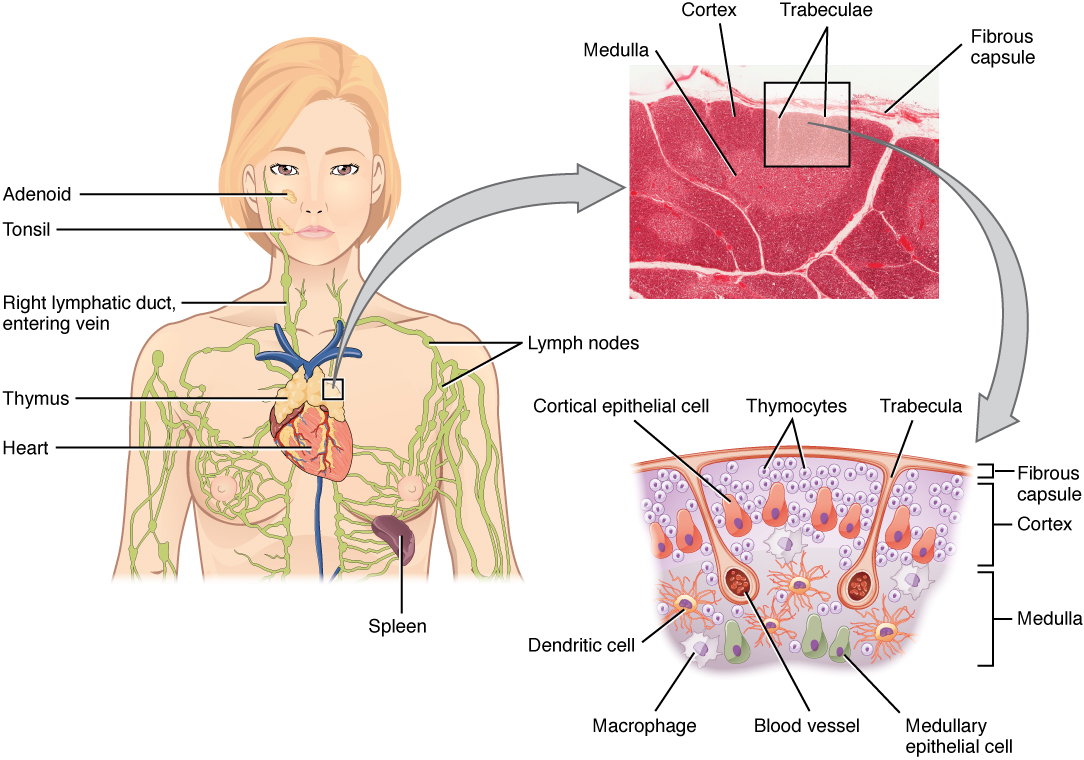
Overview Immune system Lymphatic system The lymphatic system (lymph vessels, lymph fluid, and lymphoid organs) is part of the body’s immune system. Bone Marrow Anatomy Bone marrow is the spongy tissue found in the medullary canals of long bones and cavities of the cancellous bones. Main Functions Structures Thymus Anatomy Main function The main function […]
Lymphocytes: Histology
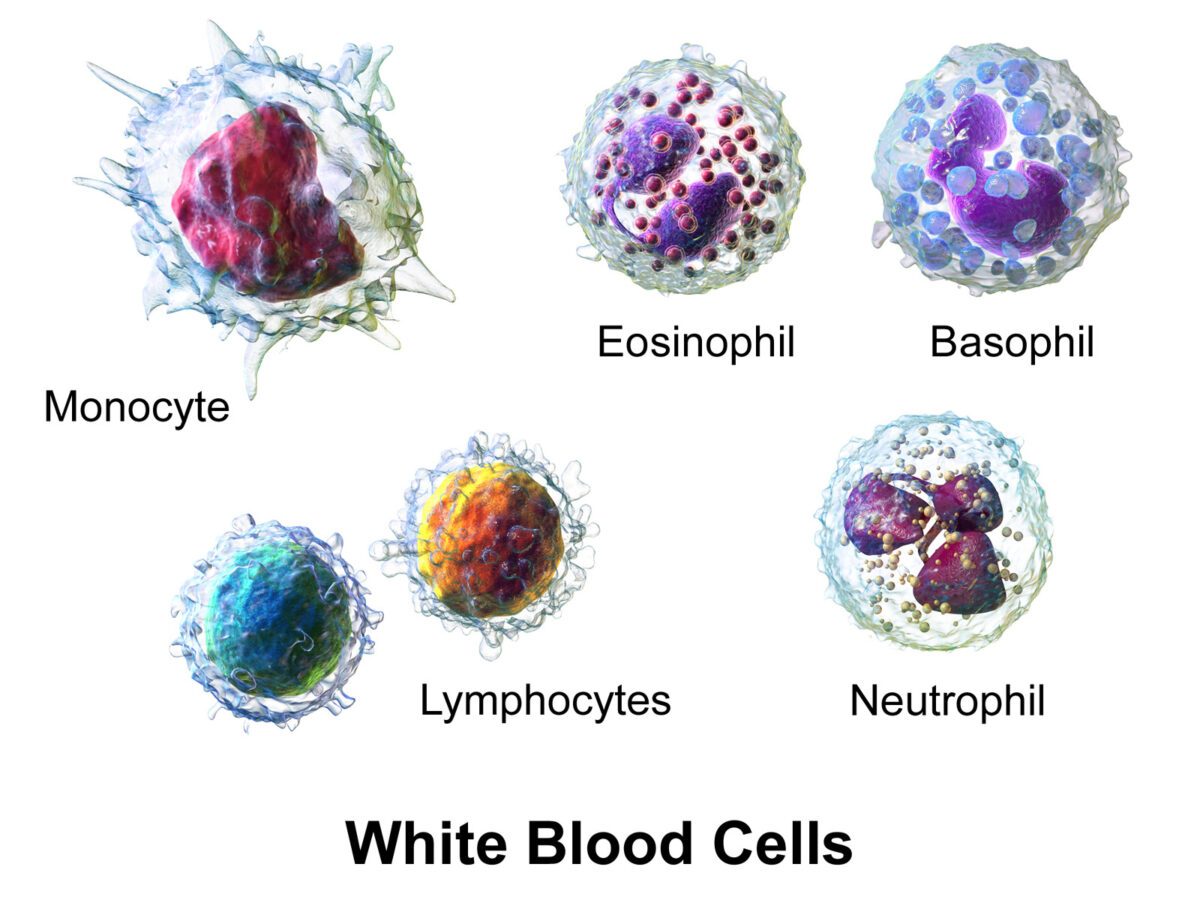
Overview Definitions and description Lymphocytes are blood cells involved in immune response, which arise from the common lymphoid progenitor (CLP). Description: 30% of circulating WBCs Spherical and/or ovoid cells Diameter: 6–15 μm Lifespan: weeks to years Belong to a heterogeneous group of cells called leukocytes (WBCs), which are divided as follows: Granulocytes: derived from the […]
White Myeloid Cells: Histology
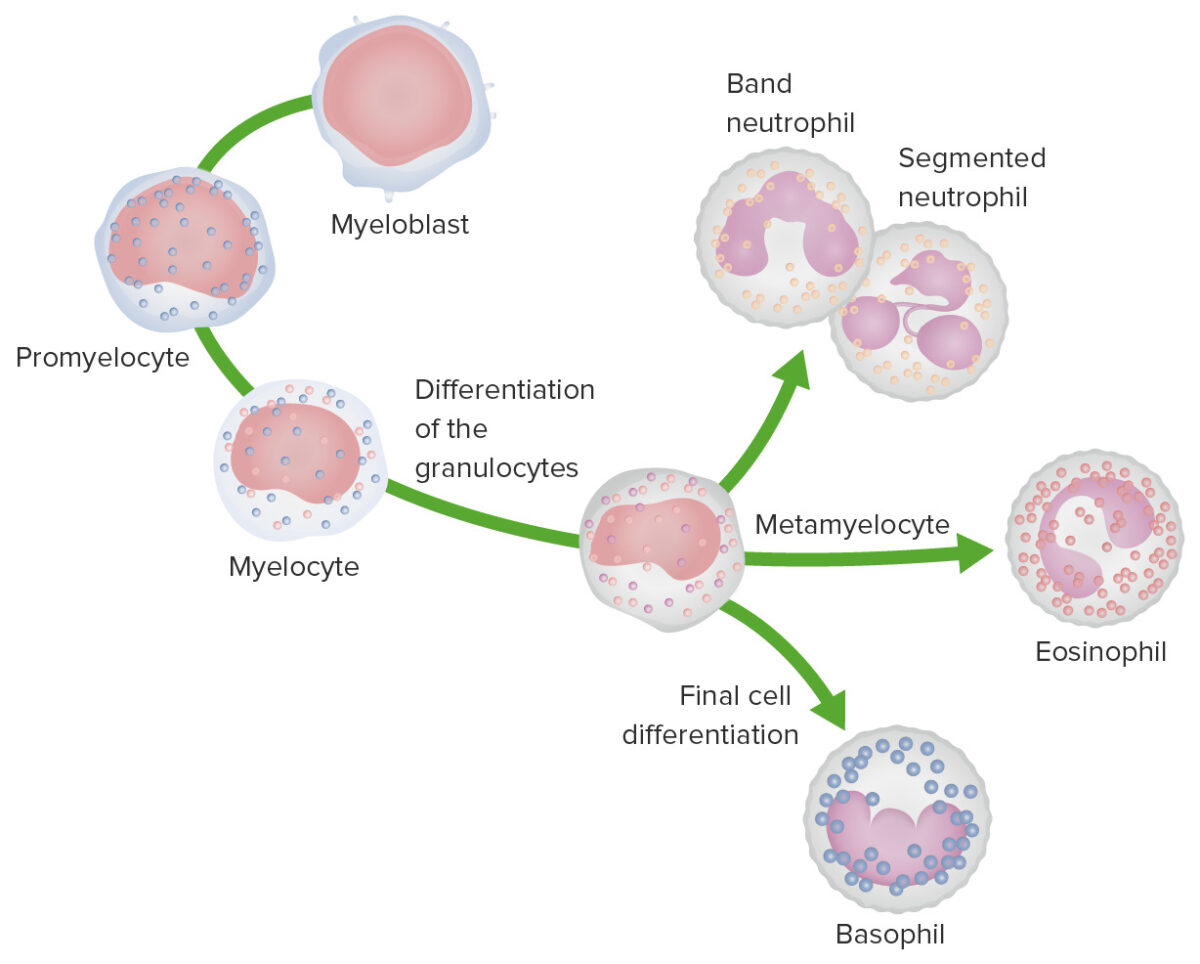
Overview Definition White myeloid cells are leukocytes developed from the common myeloid progenitor (CMP), which is derived from hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) of the bone marrow. Cell description Table: Cell description of agranulocytes Type Nucleus Granules Characteristics and functions Monocyte (3%–7% of differential count) Kidney shaped (indented or C shaped) None Characteristics: Lifespan: hours to […]
Erythrocytes: Histology
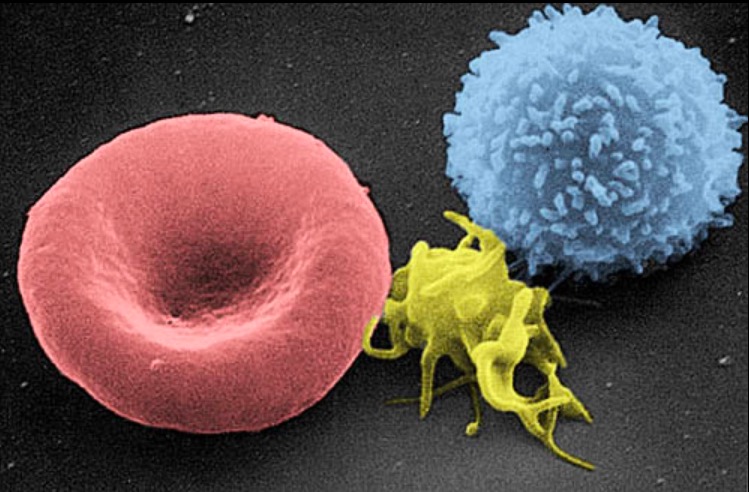
Overview Definition and description Erythrocytes, also called red blood cells (RBCs), are terminally differentiated structures lacking nuclei but filled with oxygen-carrying hemoglobin. Erythrocytes are the most abundant cells in the blood. Diameter: 7.5 μm Biconcave shape: Gives RBCs high surface-to-volume ratio Sets up most hemoglobin within a short distance from the cell surface, facilitating efficient […]
Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis
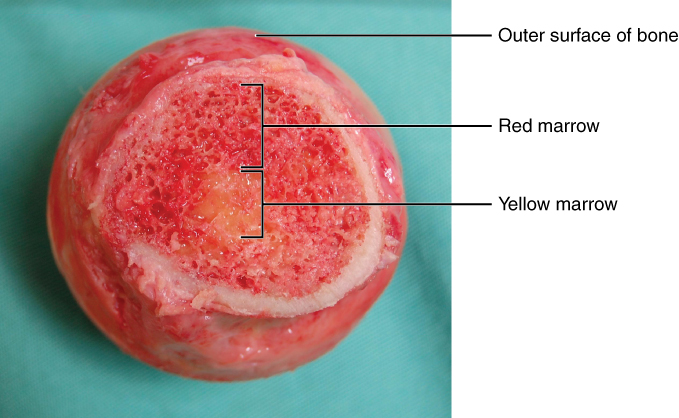
Overview Definition Bone marrow is the spongy tissue found in the medullary canals of long bones and the cavities of cancellous bones. Types of marrow Bone Marrow Cells and Structures Hematopoietic Nonhematopoietic Structures that provide a microenvironment that supports the differentiation of hematopoietic cells and proliferation of blood cells: Hematopoiesis Production of blood cells Hematopoiesis […]
Platelets: Histology
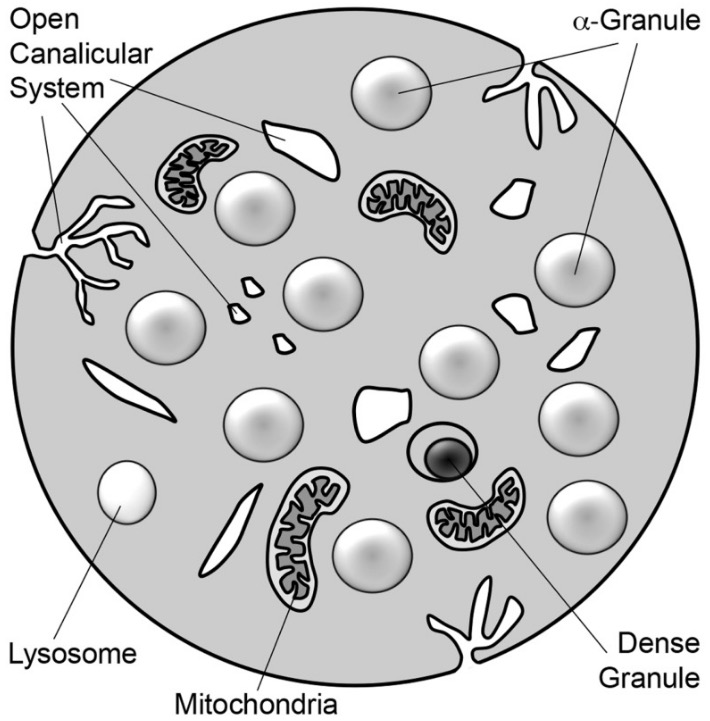
Overview Definition Platelets are small cell fragments without nuclei, but with a variety of organelles. Platelets are involved in primary hemostasis by adhering to damaged blood vessels and aggregating with one another (platelet plug). Description: Diameter: 2–3 µm Lens-shaped biconvex discoid Normal count: 150,000–450,000 platelets/µL Lifespan: up to 10 days Structure Outer membrane: Receptors facilitate […]
Cartilage: Histology
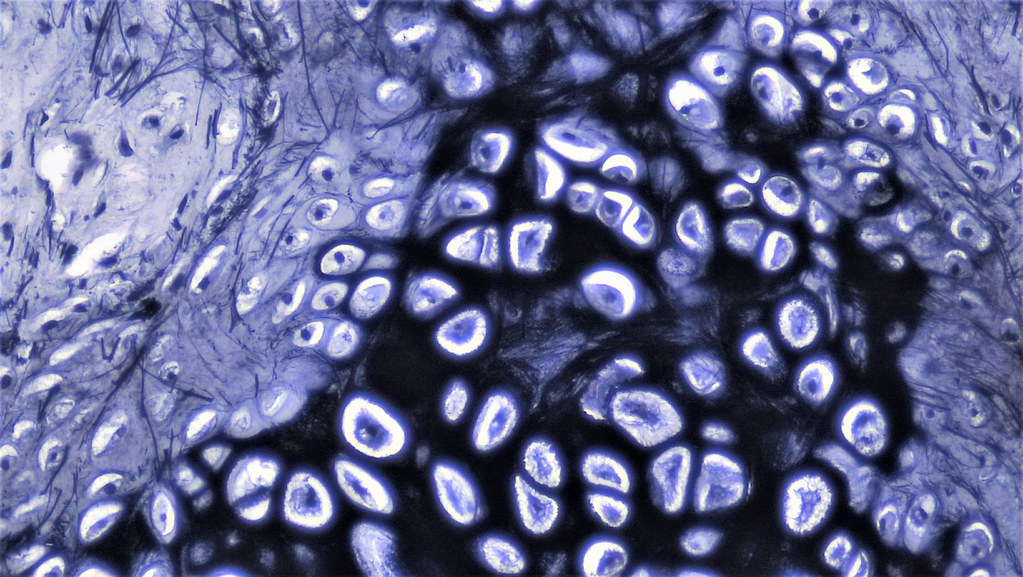
Overview Definition Cartilage is a type of connective tissue that forms structural components of the human skeleton and provides support to various organs. Composition Chondrocytes: The major cell type of the cartilage tissue Synthesize extracellular matrix (ECM) components and become embedded in them (lacunae) Young chondrocytes retain the ability to divide; daughter cells secrete new […]
Connective Tissue: Histology
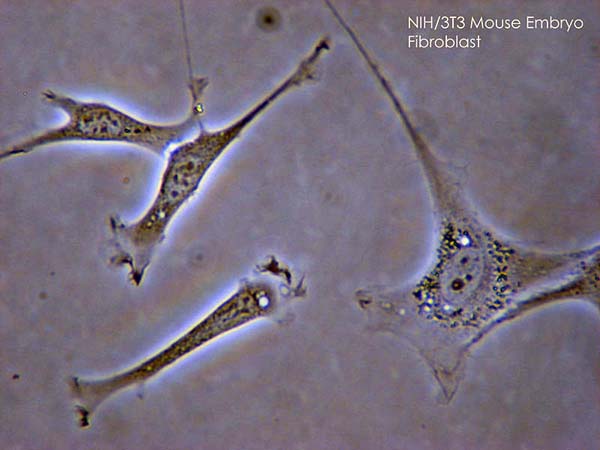
Overview Definition Connective tissue refers to a group of tissues of mesenchymal origin (rather than a single tissue type), whose main function is providing structural support to the organs of the body. Structural elements Connective tissue consists of 3 major elements: ground substance, fibers, and cells. The types and proportions of these elements determine the […]
Capillaries: Histology
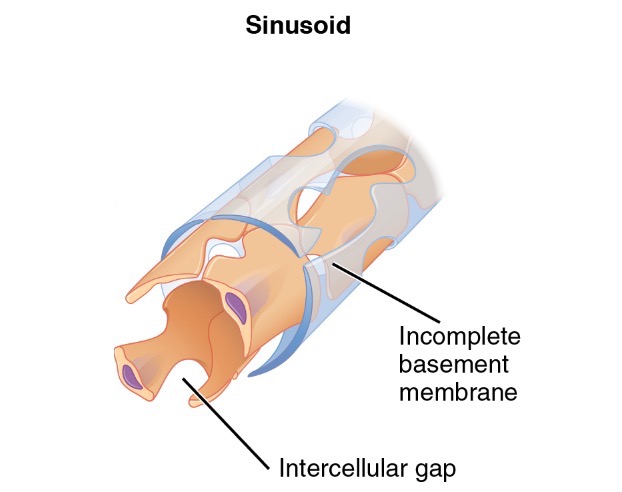
General Characteristics Definition Capillaries are the smallest of the blood vessels. Capillaries are the primary structures in the circulatory system that allow the exchange of gas, nutrients, and other materials between the blood and the extracellular fluid (ECF). Structure Blood flow through and around capillaries Location Physiology Types of Capillaries 3 primary types of capillaries: […]
Veins: Histology
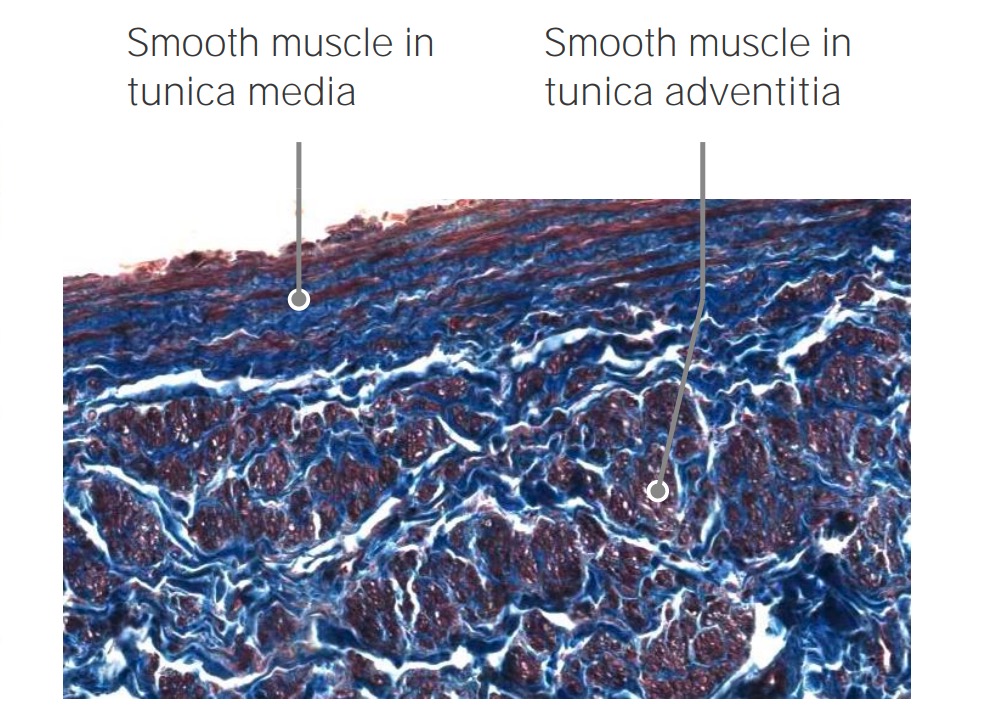
Overview Definition Veins are tubular collections of cells transporting deoxygenated blood and waste products from capillaries in the periphery of the body back to the heart. General characteristics Characteristics of veins and the venous system include: Pressure within the venous circulation Layers of the Vessel Wall All veins have the same basic structure and are […]