Population Pyramids
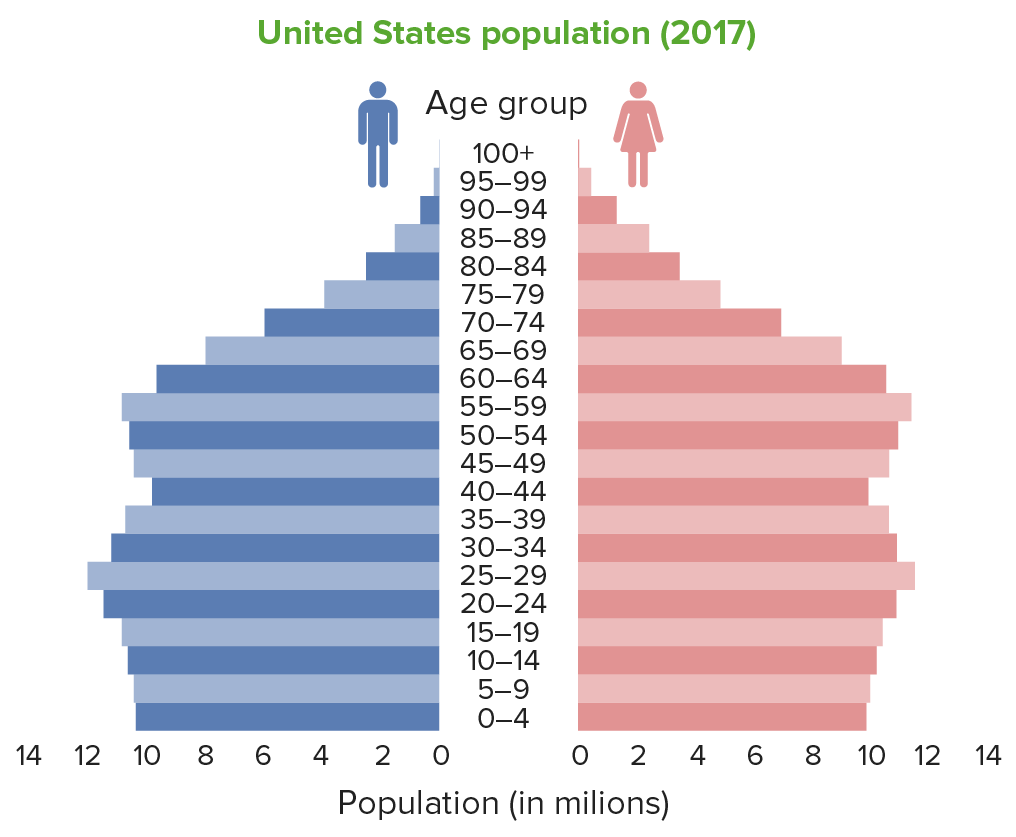
Overview Definitions Structure Uses of the Population Pyramid Population trends Future needs Types of Population Pyramids Stationary pyramid Expansive pyramid Constrictive pyramid Stages of Population Pyramids Demographic transition model Sequence of stages Stage 1: high stationary Stage 2: early expanding Stage 3: late expanding Stage 4: low stationary Stage 5: References
Types of Biases
Definition of Bias Bias is an error in the design, conduct, or analysis of a study that results in a deviation of the test statistic from its true value. This results in an incorrect estimate of an association between an exposure and the target population such that the test statistic generated deviates from its true […]
Epidemiological Studies
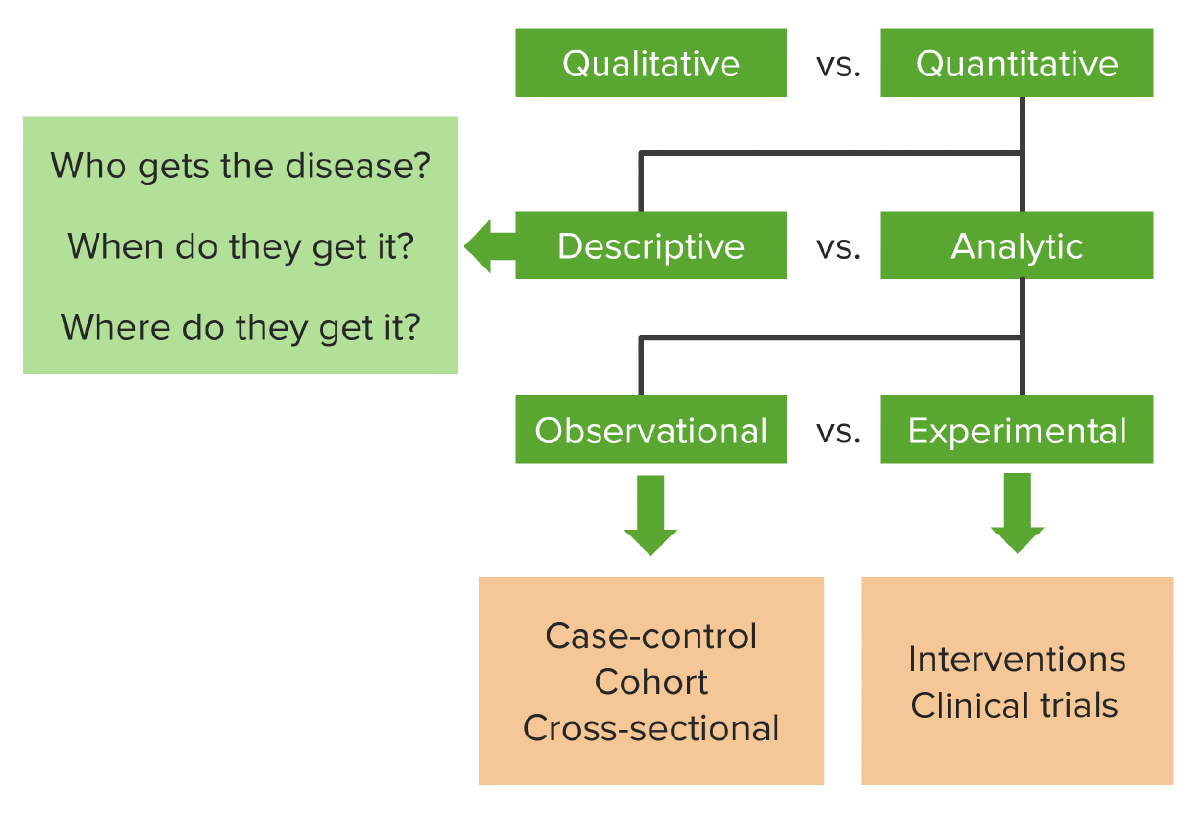
Observational Studies Observational studies are used to observe and measure outcomes in a cohort with no control over risk factors or variables. They are often retrospective. Types of observational studies include cross-sectional studies, case-control studies, and cohort studies. Cross-sectional studies Case-control studies Cohort studies Table: Advantages and disadvantages of cohort studies Advantages Disadvantages Direct calculation […]
Measures of Health Status
Mortality Measures of mortality are statistical measures that specify how many people are dying from a disease or particular exposure over a specific period of time and are scaled to the size of the selected population (usually per 1,000 or 100,000 people). Mortality rate (MR) Case fatality rate Proportionate mortality Standardized mortality ratio (SMR) Years […]
Measures of Disease Frequency
Incidence Definition Incidence refers to the number of new cases of a certain disease or event in a population over a specified period of time. There are 2 ways of measuring incidence: cumulative incidence (CI) and incidence rate (IR). Both are measures of the risk of contracting a disease or condition. Examples Cumulative incidence Over […]