Hemothorax
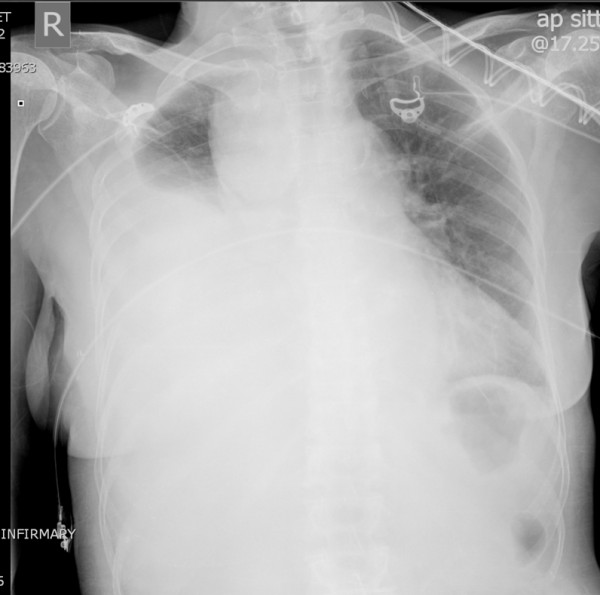
Overview Definition A hemothorax is defined as a collection of fluid with a hematocrit of at least 50% accumulated in the potential space between the parietal and visceral pleura of the lungs. Epidemiology Etiology The source of blood may be the chest wall, lung parenchyma, heart, or great vessels from either traumatic or non-traumatic causes. […]
Toxic Shock Syndrome
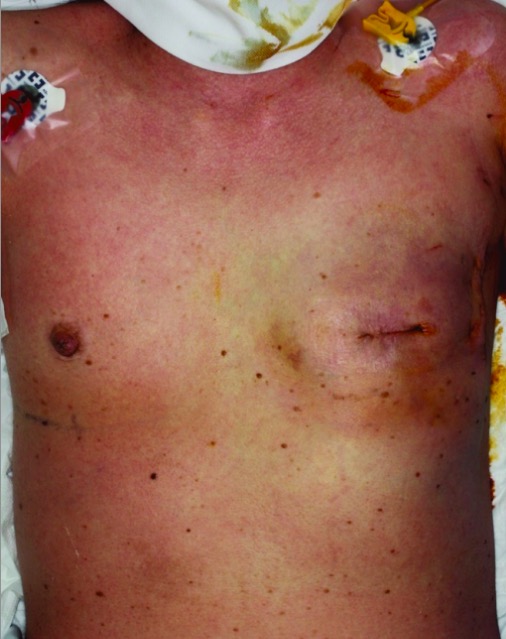
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is an acute, multi-systemic disease caused by toxin-producing bacteria: Risk factors: Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Both staphylococcal and streptococcal TSS present similarly, with a rapid onset of signs and symptoms (within hours). General signs and symptoms Multi-organ involvement Diagnosis Laboratory evaluation Supporting workup Clinical criteria The following […]
Hypothermia
Overview Definition Hypothermia is a decrease in core body temperature to below 35°C (95°F). Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Mechanisms of heat loss Pathogenesis Clinical Presentation General manifestations Stages of hypothermia Diagnosis Physical exam Laboratory studies Other studies Management Mild hypothermia (32°C–35°C (89.6°F–95°F)) Moderate hypothermia (29°C–32°C (84.2°F–89.6°F)) Severe (22°C–28°C (71.6°F–82.4°F)) and profound (< 22°C (< 71.6°F)) hypothermia […]
Head Trauma
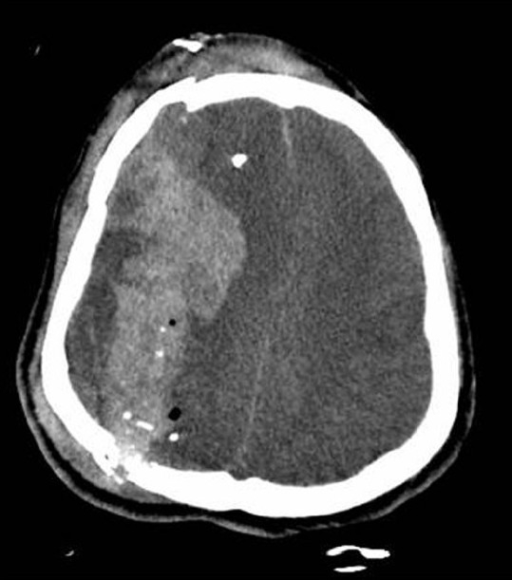
Overview Definition Head trauma is an injury to the skull, brain, and/or intracranial structures. Epidemiology Etiology Classification of Severity Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) Table: Glasgow Coma Scale Feature Response Score Eye opening Open spontaneously 4 Open to verbal command 3 Open to pain 2 No eye opening 1 Verbal response Oriented and appropriate 5 Disoriented […]
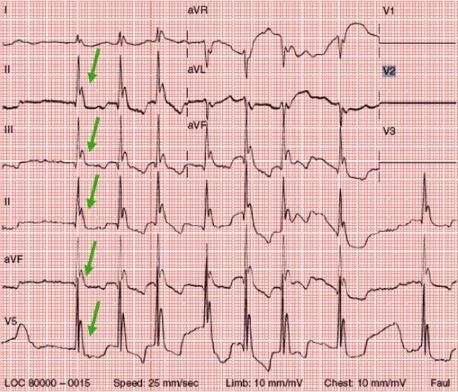
Cardiac Arrest

Overview Definition Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is the abrupt cessation of cardiac activity. Epidemiology Risk factors Etiology and Clinical Presentation Cardiac causes of cardiac arrest Non-cardiac causes of cardiac arrest Mnemonics The 5 Hs and 5 Ts of the common reversible causes of SCA: Clinical presentation Cardiac Rhythms Four major cardiac rhythms are associated with […]
Flail Chest
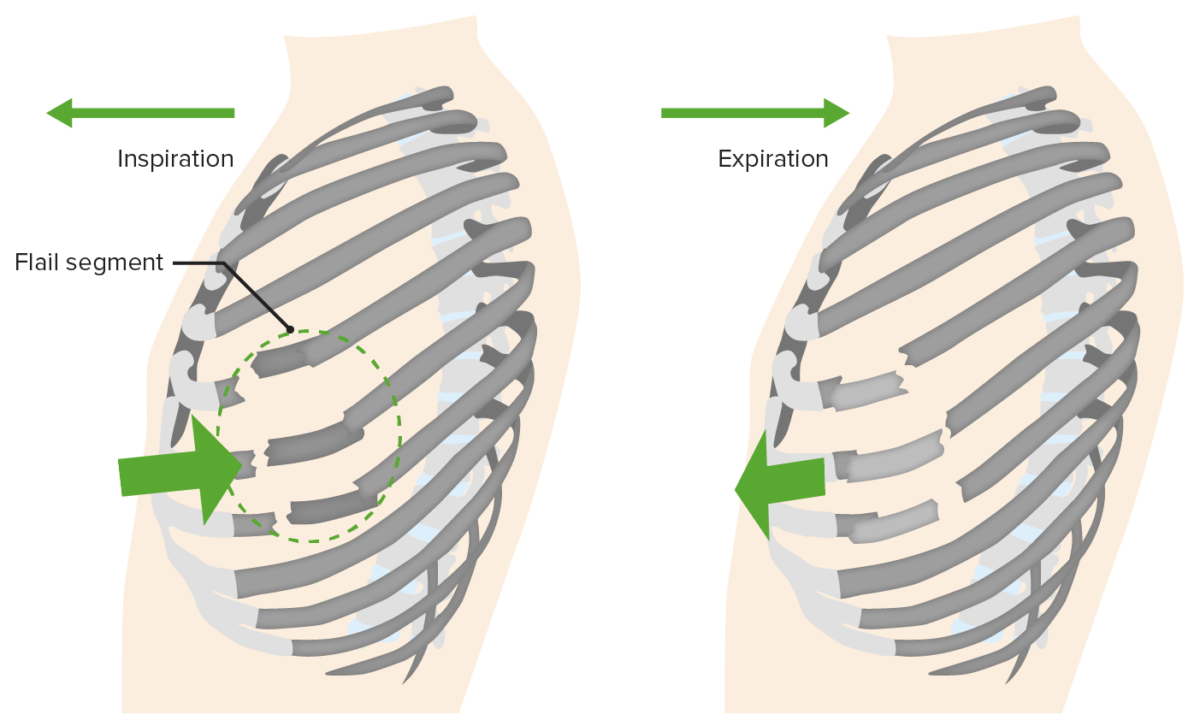
Overview Definition Flail chest is defined as 3 or more contiguous ribs that are fractured in 2 or more different locations, resulting in a freely moving segment of the chest wall that is discontinuous from the rest of the thoracic cage. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis Flail chest is a clinical diagnosis (confirmed by imaging) made […]
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
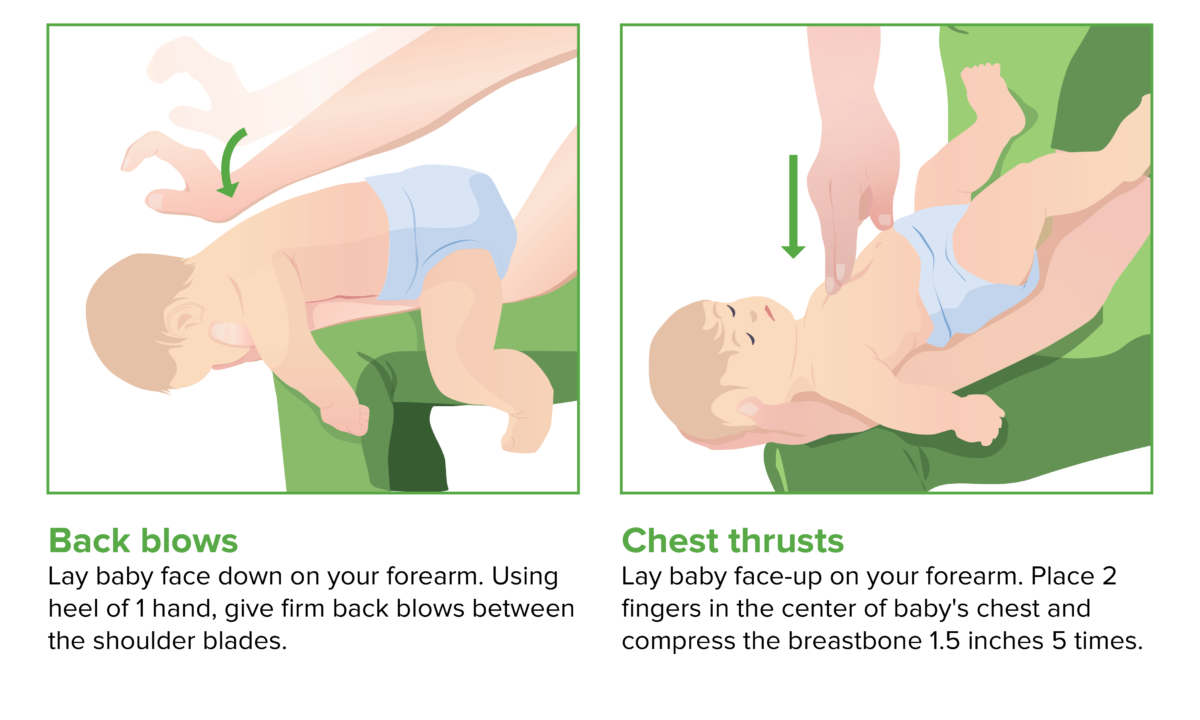
Overview Introduction Cardiopulmonary resuscitation sequence overview Cardiopulmonary resuscitation consists of chest compressions and rescue breaths carried out sequentially. Rescue Breaths Rescue breath technique Heimlich maneuver If patient’s chest does not rise, foreign object may be obstructing airway: Chest Compressions Positioning Technique Limit pauses during CPR Defibrillation Early defibrillation has been shown to significantly improve morbidity […]
Blunt Abdominal Injury
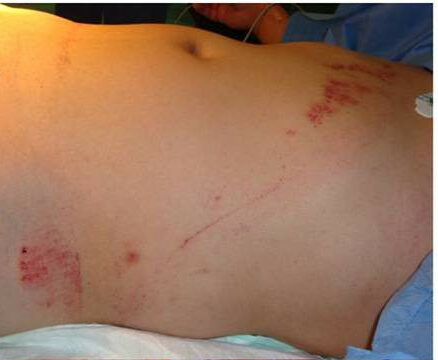
Overview Definition Blunt abdominal injury is defined as damage to the abdomen and/or abdominal organs secondary to impact with a blunt (not penetrating) object or surface. Epidemiology and etiology Anatomy Pathophysiology Blunt abdominal trauma can occur due to several pathologic processes: Diagnosis Because of the wide variety and severity of injuries associated with blunt abdominal […]
Pneumothorax
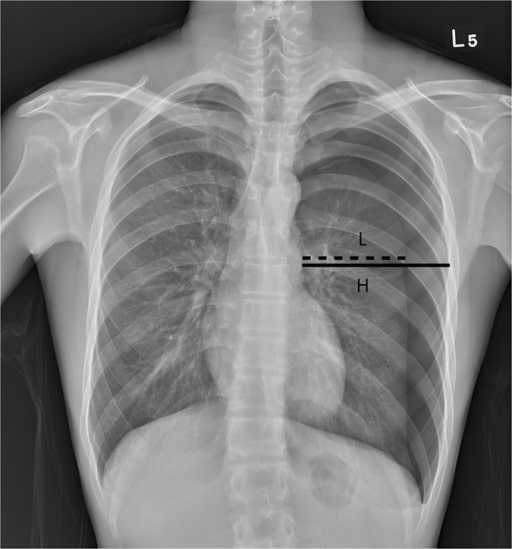
Classification and Epidemiology Classification Epidemiology Etiology Traumatic pneumothorax Spontaneous pneumothorax Pathophysiology As air enters the pleural space, which normally has a negative pressure, the elastic recoil in the lung tissues causes either a partial or full lung collapse. Normal physiology Traumatic pneumothorax Spontaneous pneumothorax Tension pneumothorax Clinical Presentation The clinical presentation will depend on the […]
Hyperglycemic Crises
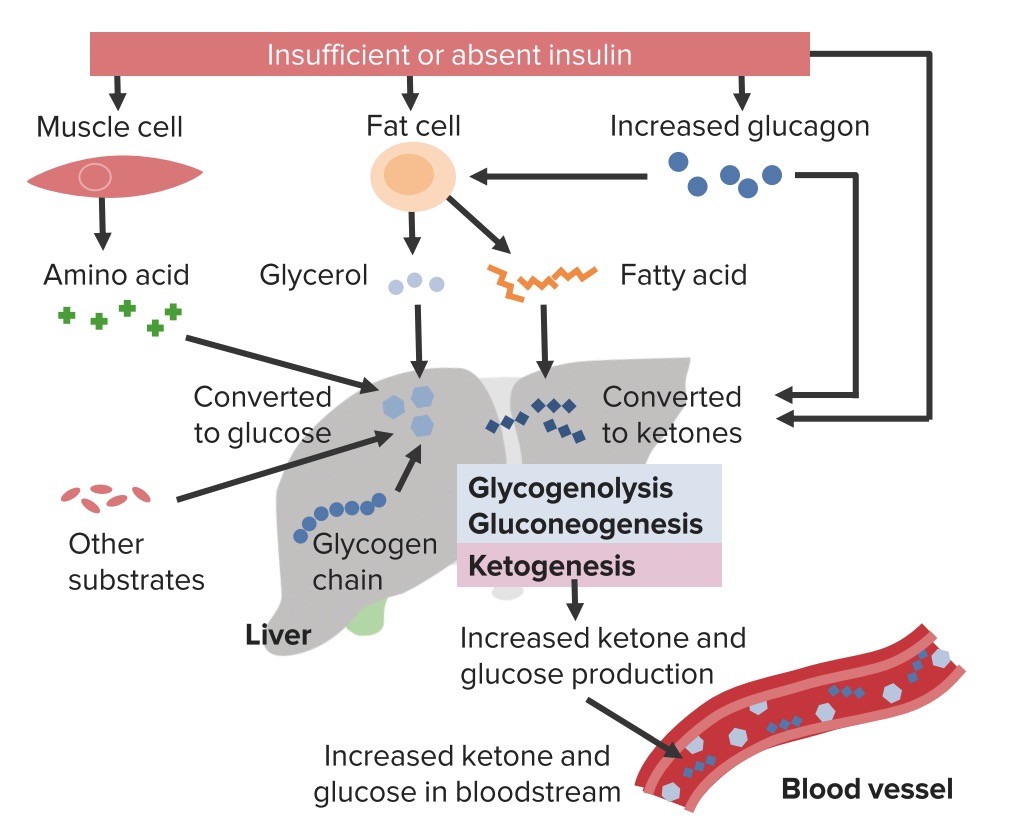
Overview Definition Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) are serious, acute complications of diabetes mellitus. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Normal physiology The normal response to increased serum glucose involves the release of insulin by pancreatic beta cells. This leads to: Pathophysiology of DKA Pathophysiology of HHS Clinical Presentation Clinical presentation of DKA Clinical presentation […]