Caustic Ingestion (Cleaning Products)
Overview Introduction Caustics and corrosives cause tissue injury by a chemical reaction. Injury by alkaline chemicals is overall more toxic than that caused by acidic substances: Caustic ingestion: Epidemiology Etiology Common acid-containing products: Common alkali-containing products: Pathophysiology Tissue injury occurs by changing the ionized state and structure of molecules, thereby disrupting the covalent bonds. Alkaline […]
Snakebites
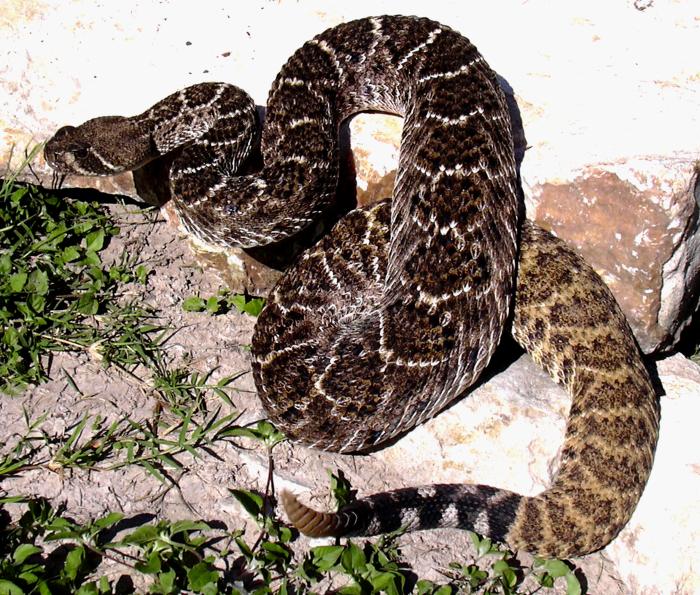

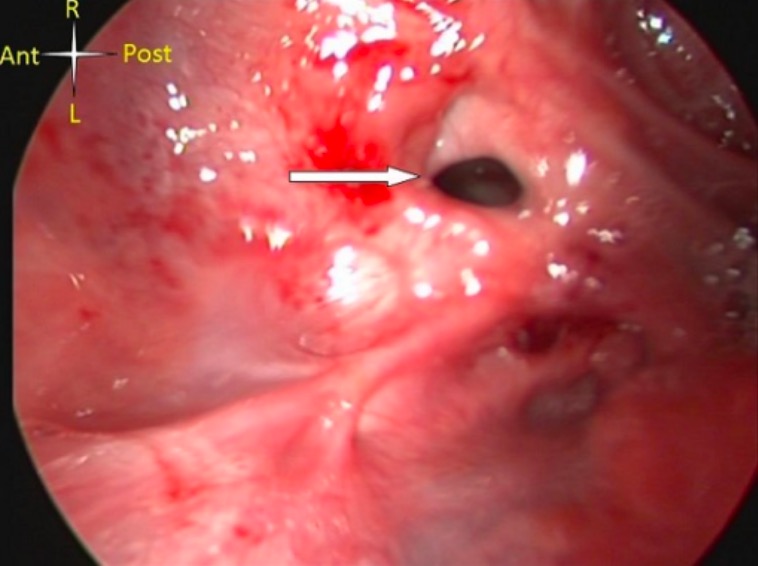
Overview Epidemiology Clinically relevant species Some important venomous snakes in the United States include: Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation General presentation Local signs of envenomation Systemic signs and symptoms of envenomation Complications Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis The diagnosis of a snake bite is clinical and aided by the identification of the snake. Photos of the snake (if […]
Heatstroke
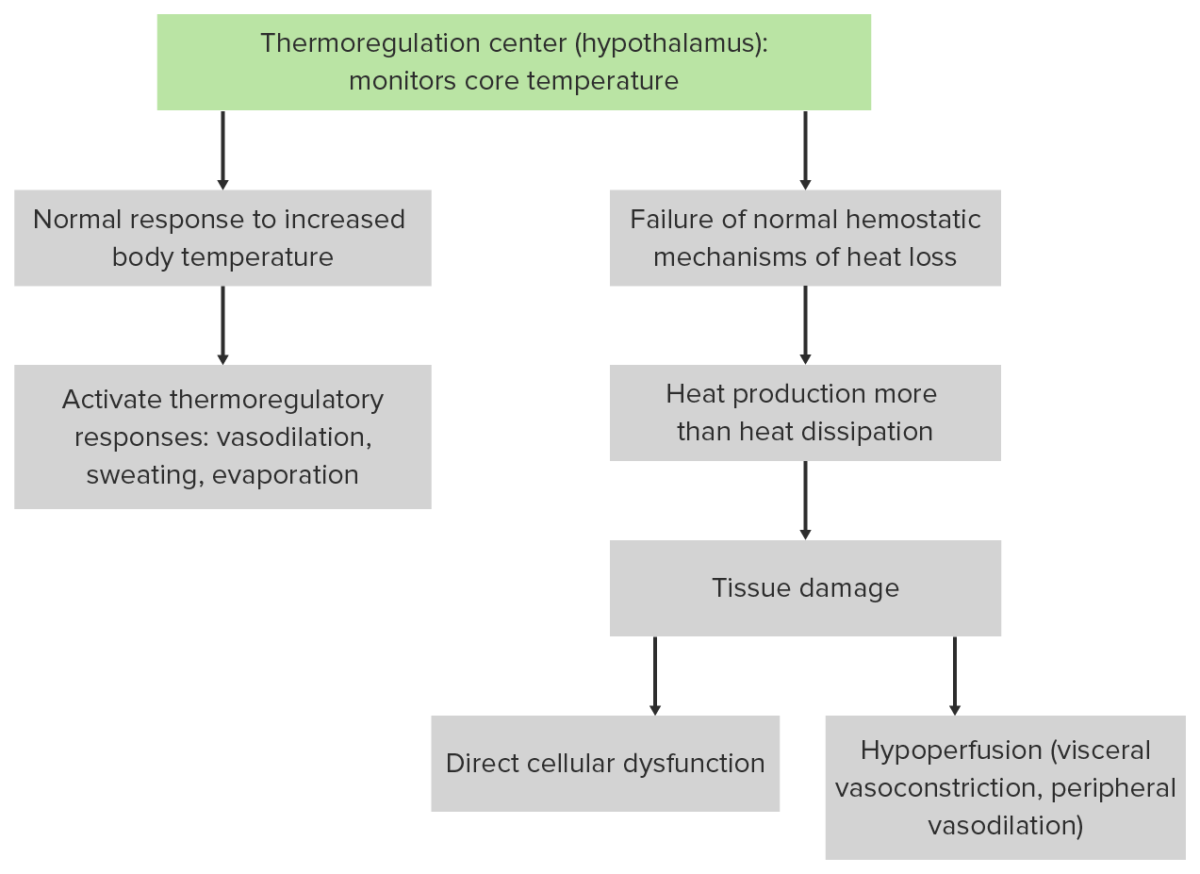
Overview Definition Heatstroke is a temperature-related illness caused by the body’s failure to maintain temperature homeostasis. Heatstroke is characterized by body temperatures approaching and exceeding 40ºC (104ºF) and neurological symptoms including seizures, delirium, and ataxia. Epidemiology Incidence in the United States is difficult to determine due to lack of reporting: Risk factors for heatstroke: Etiology […]
Perforated Viscus
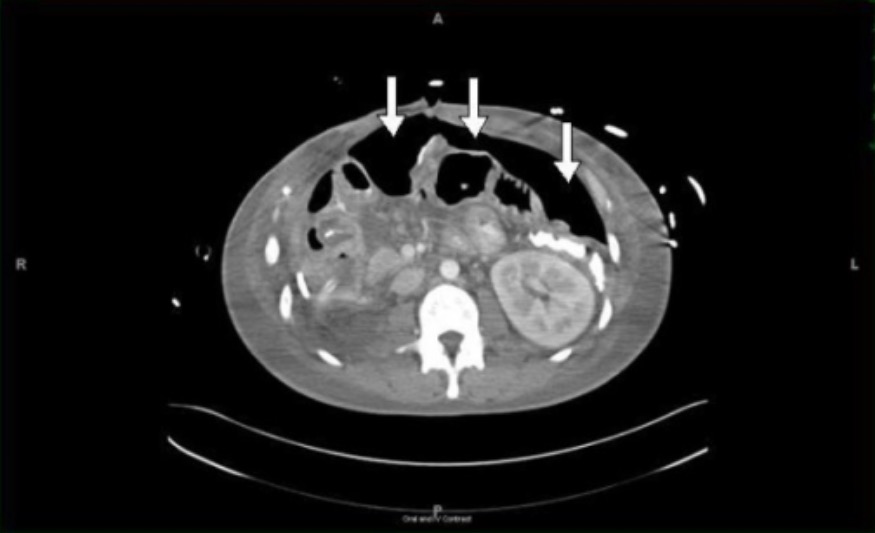
Overview Definition A perforated viscus, also known as intestinal or bowel perforation, is a full-thickness disruption of the intestinal wall, with subsequent leakage of enteric contents into the peritoneal cavity, resulting in a systemic inflammatory response, peritonitis, and possibly sepsis. Epidemiology Etiology Clinical Presentation History Physical exam Vitals: Abdominal exam: Atypical presentation: Diagnosis Laboratory workup […]
Pulmonary Edema
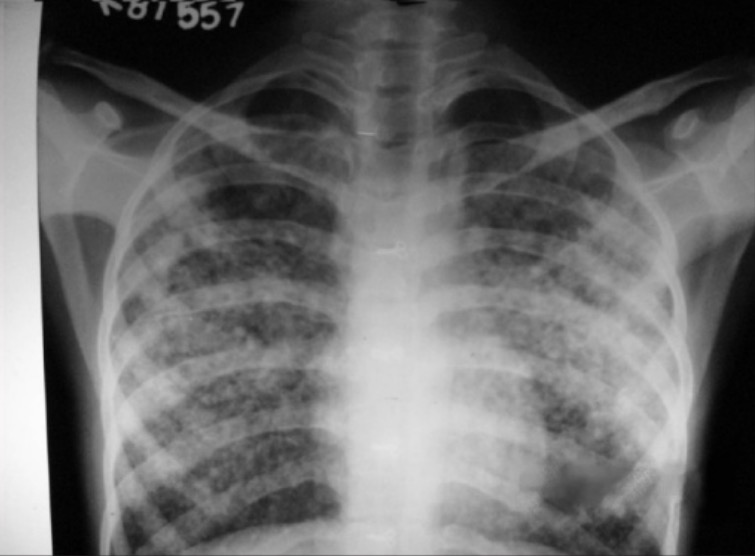
Overview Definition Pulmonary edema is the accumulation of excess fluid within the lung parenchyma and alveoli. Epidemiology Etiology Pulmonary edema is classified based on the underlying etiology. Pathophysiology Starling forces Starling forces explain how fluid moves from the blood into extravascular spaces, which leads to pulmonary edema. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema Depending on […]
Mediastinitis
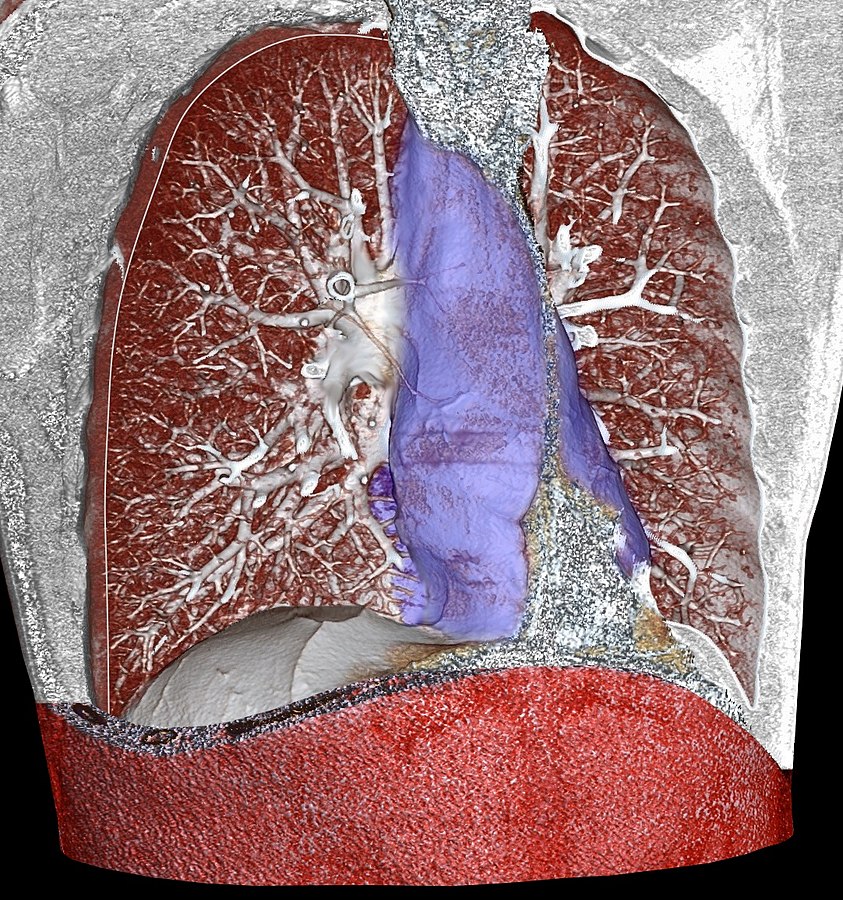
Anatomy and Etiology Anatomy Mediastinum: Etiology Acute mediastinitis: Chronic mediastinitis: Fibrosing mediastinitis: Diagnosis History Physical exam Acute mediastinitis: Chronic mediastinitis: Laboratory tests Imaging Management Acute mediastinitis: Chronic fibrosing mediastinitis: Clinical Relevance References
Crush Syndrome
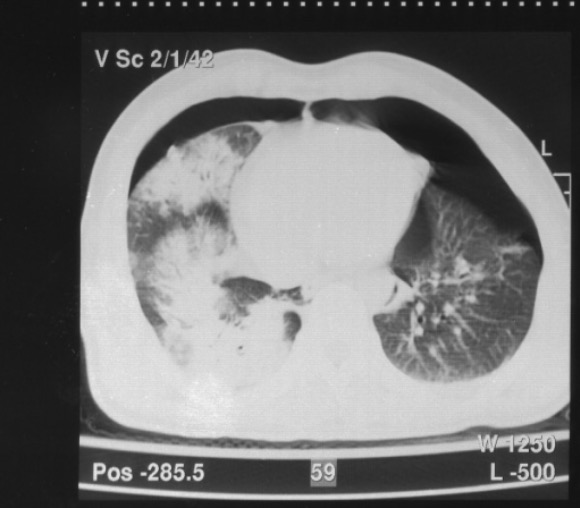
Definition and Etiology Definition Crush syndrome is a condition of systemic manifestations (including shock and renal failure) that develop from high-degree crush injury or traumatic compression of the torso, extremities, or other parts of the body. Etiology Pathophysiology Initial events Systemic effects Clinical Presentation Chest and abdominal crush injury Extremity crush injury Other clinical features […]
Serotonin Syndrome
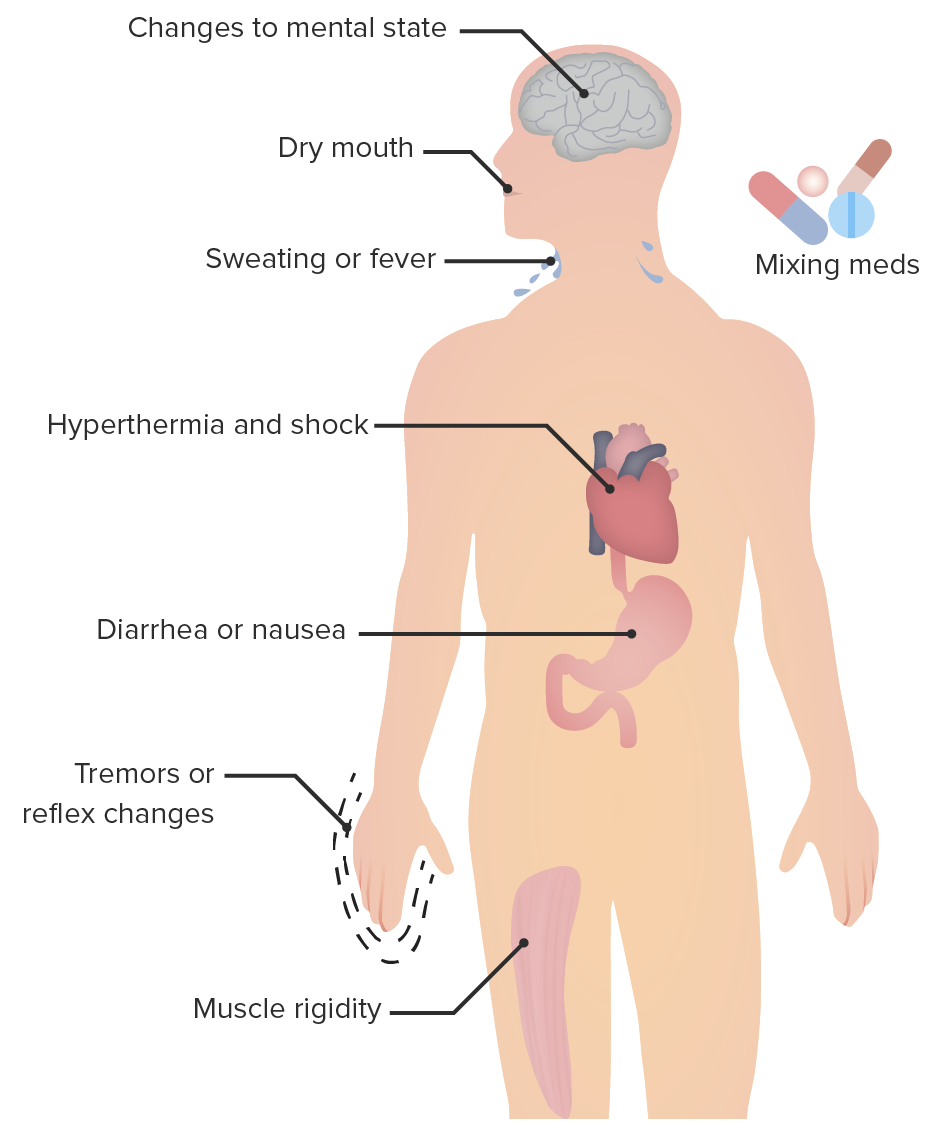
Overview Definition Serotonin syndrome is a potentially life-threatening condition caused by large increases in serotonergic activity due to exposure to serotonin agonists. Defining symptoms include altered mental status, autonomic instability, and neuromuscular abnormalities (tremors, myoclonus). Epidemiology Etiology Serotonin syndrome occurs secondary to use of therapeutic medication, drug interactions, or overdose. Pathophysiology Serotonin syndrome occurs from […]
Malignant Hyperthermia

Overview Definition Malignant hyperthermia (MH) is a hypermetabolic response in a patient exposed to a volatile anesthetic or succinylcholine resulting in fever, muscle rigidity, rhabdomyolysis, and pulmonary and cerebral edema. Epidemiology Etiology Triggering substances: “Safe” anesthetics for patients with previously diagnosed malignant hyperthermia: Pathophysiology Diagnosis Clinical features Symptoms may appear at any point during anesthesia […]
Mesenteric Ischemia
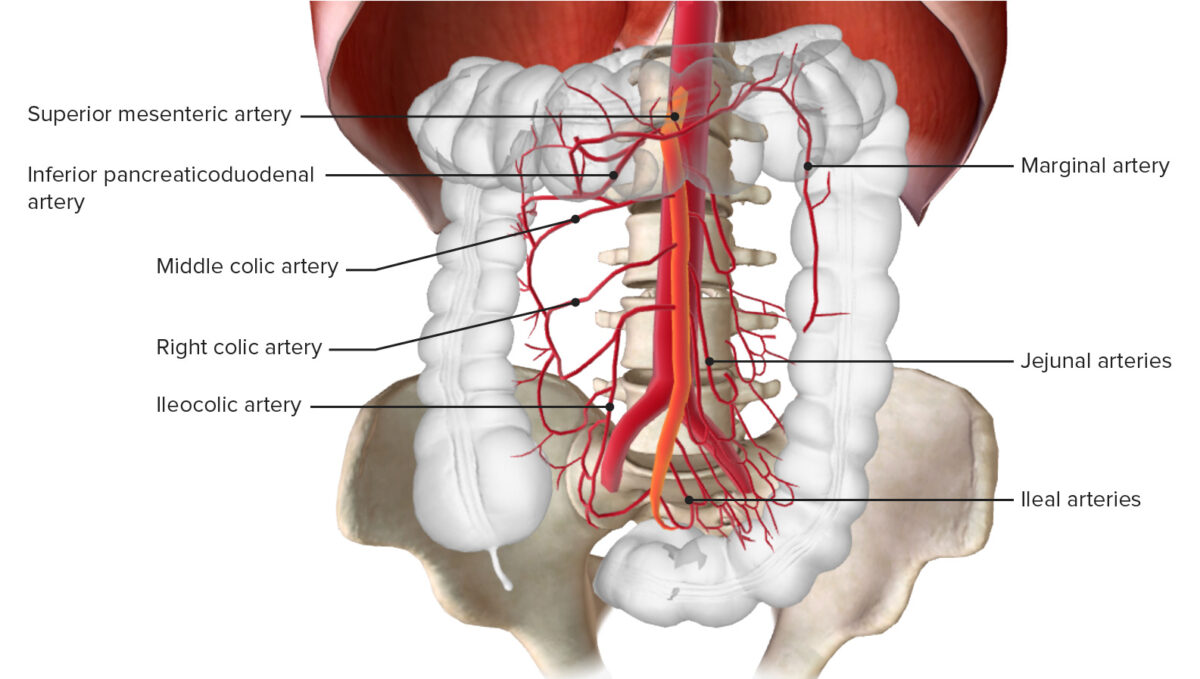
Overview Definition Mesenteric ischemia is a condition caused by hypoperfusion of the intestine, resulting in ischemia and necrosis. Mesenteric ischemia is categorized based on the time course: Anatomy The main vessels affected in mesenteric ischemia include: Pathophysiology Acute Mesenteric Ischemia Epidemiology Etiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Acute mesenteric ischemia requires a high index of suspicion to […]