Chest Pain

Overview Anatomy The anatomy of the chest and thorax includes: heart, lungs, breasts, and chest wall. History Description of chest pain: Typical chest pain descriptions and their clinical significance: Risk factors: Physical examination Vital sign abnormalities and their possible diseases: Examples of important findings in the physical exam: Diagnostic workup Differential Diagnosis Cardiovascular causes Gastrointestinal […]
Acetaminophen Overdose
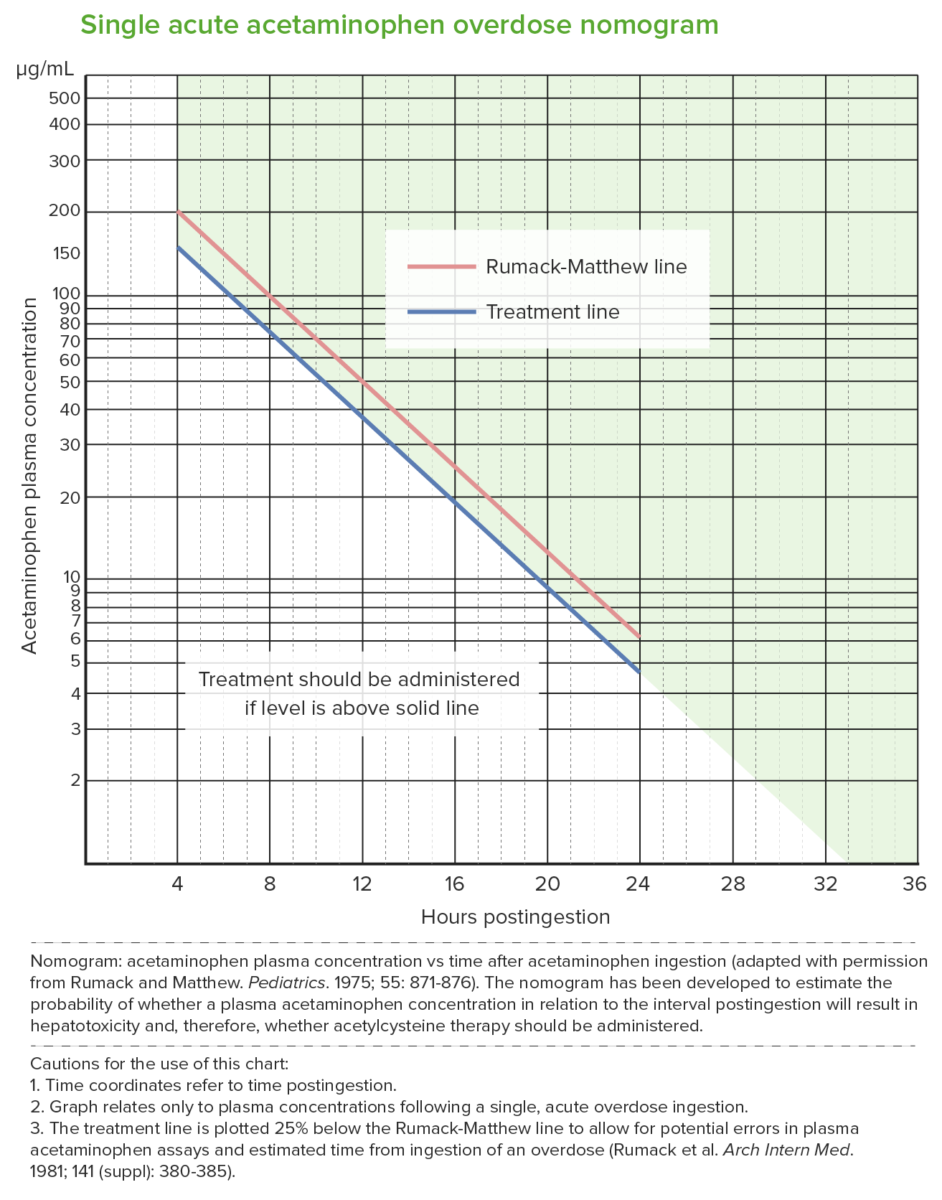
Epidemiology Pathophysiology Pharmacokinetics Normal metabolism Pathogenesis Clinical Presentation The clinical course of APAP poisoning is often divided into 4 stages that are classified according to duration since time of ingestion. Diagnosis Evaluation Rumack-Matthew nomogram Management Treatment approach Entails supportive care, limiting drug absorption, and treatment of toxic effects: N-acetylcysteine (NAC) References
Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma (FAST)
Introduction Definition Focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST) is a point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) examination protocol of the abdominal and thoracic cavities performed with the goal of identifying free intraperitoneal fluid and/or pericardial effusion. Background Table: Advantages and disadvantages of the FAST exam Advantages Disadvantages Can be performed on any individual Early operative determination ↓ […]
Insecticide Poisoning
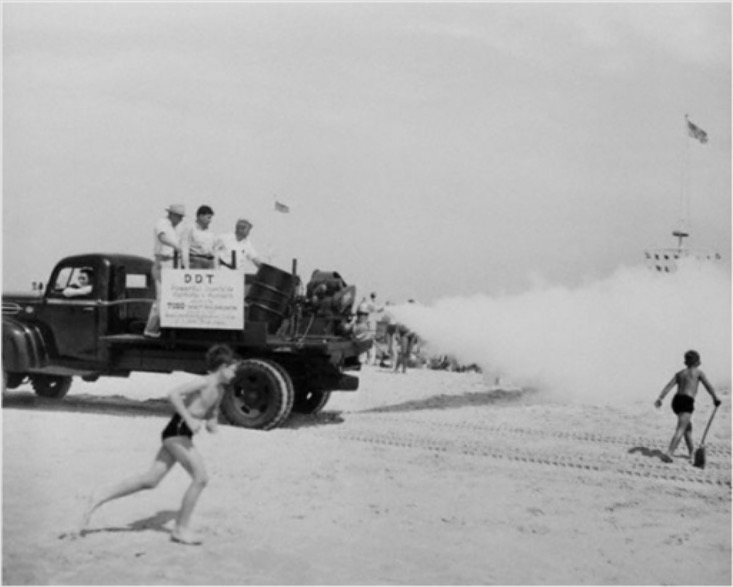

Definition Insecticides are substances used to kill insects or prevent them from destructive behaviors. Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) Etiology Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane: Pathogenesis Clinical presentation Diagnosis and management Organophosphate Toxicity Etiology Organophosphates: Pathophysiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Management Mnemonics SLUDGE BBB (muscarinic effects): DUMBELS (muscarinic effects): Carbamate Toxicity Etiology Carbamates: Pathophysiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis and management Clinical Relevance References
Antidotes of Common Poisonings

Heavy Metal Poisoning Copper Iron Lead Mercury Medication Overdose Acetaminophen Anticholinergic toxicity (e.g., atropine, diphenhydramine) Benzodiazepines Beta-blockers Digitalis (digoxin) Heparin Opioids Salicylates Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) Warfarin Toxic Alcohol Poisoning Methanol and ethylene glycol are found in automotive coolants (antifreeze) and deicing solutions, fuel, cleaners, windshield wiper fluids, solvents, and other industrial products. Methanol Ethylene glycol […]
Acute Limb Ischemia
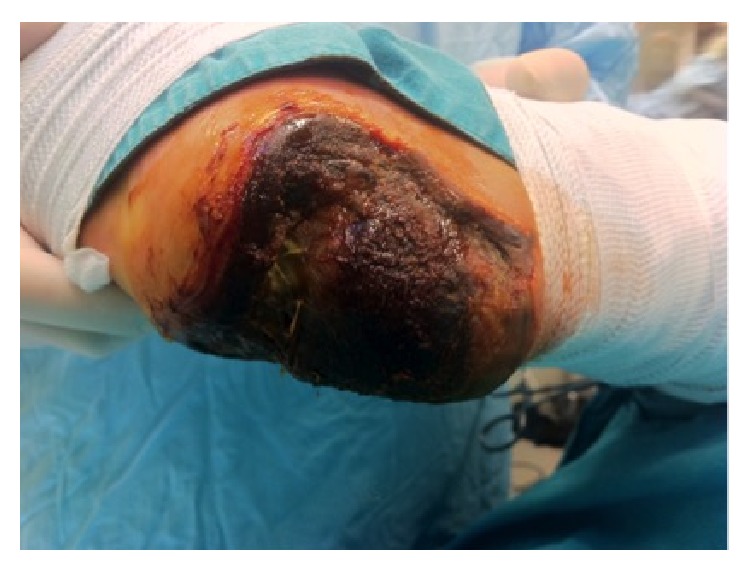
Overview Definition Acute limb ischemia (ALI) is a vascular emergency caused by a rapid decrease in limb perfusion. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Acute limb ischemia is diagnosed on the basis of medical history, clinical presentation, physical examination, and vascular imaging. History Physical exam Assess for the 6 Ps: Diagnostic testing Management The treatment […]
Herbicide Poisoning

Overview Herbicides are substances that are used to kill or control the growth of unwanted plants. Paraquat Poisoning Etiology Paraquat: Rules in the United States: Pathophysiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Management Agent Orange Exposure Etiology Agent Orange: Pathophysiology Clinical presentation Acute: Chronic: Diagnosis and management Glyphosate Toxicity Etiology Glyphosate: Pathophysiology Clinical presentation Mild to moderate toxicity: […]
General Principles of Toxidromes

Overview Definition A toxidrome describes a group of signs, symptoms, and/or characteristic effects associated with exposure to a particular substance or class of substances. Epidemiology Approach to the poisoned patient Testing Tests depend on the clinical situation and should not delay initiation of supportive care. These include but are not limited to: Anticholinergic Toxicity Etiology […]
Hypoglycemia
Overview Definition Hypoglycemia is an emergency condition defined as a serum glucose level ≤ 70 mg/dL (≤ 3.9 mmol/L). Classification Etiology Pathophysiology Glucose homeostasis Serum glucose levels are maintained within the normal range of 71–99 mg/dL owing to a coordinated balance between insulin, glucagon, and the sympathetic nervous system. As the serum glucose level falls, […]
Neutropenic Fever
Overview Definition Neutropenic fever is defined as a single oral temperature > 38.3℃ (100.9℉) or a temperature > 38.0℃ (100.4℉) for at least 1 hour with an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) of < 1,500 cells/µL or an ANC that is expected to decrease to < 500 cells/µL during the next 48 hours. Epidemiology Etiology In […]