I-cell Disease
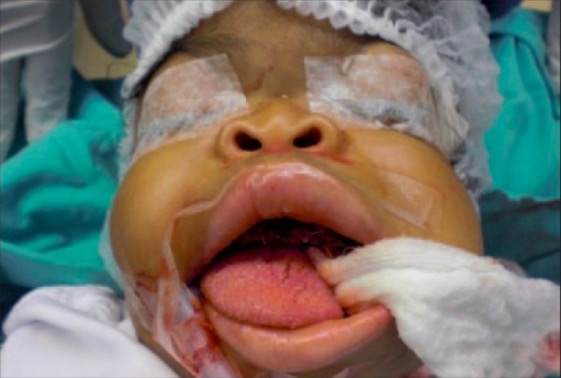
Overview Definition I-cell disease is a rare lysosomal storage disorder that presents in early childhood with severe skeletal abnormalities and failure to thrive. A mutation in the GNPTA gene causes a deficiency in the enzyme uridine diphosphate (UDP)-N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferase. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Clinical features evident by 6 months of age: Patients present in 1st […]
DNA Repair Mechanisms
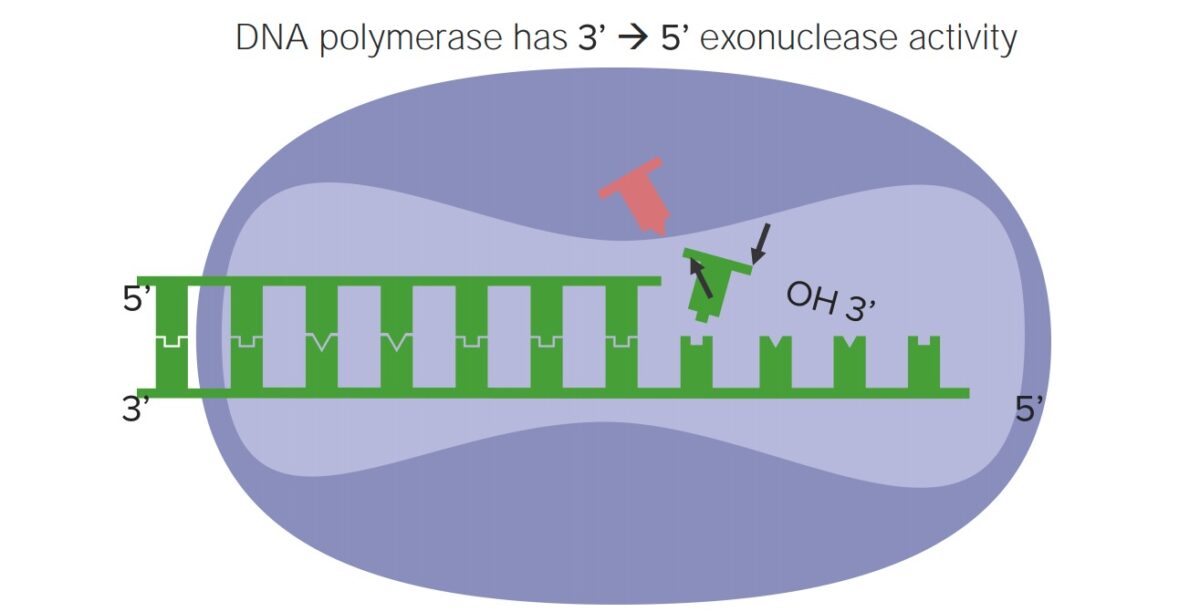
Overview of DNA Damage and Repair Etiology DNA damage can be caused by: Types of DNA damage DNA repair mechanisms Proofreading and Photorepair Proofreading Proofreading occurs during DNA replication. DNA polymerase (the enzyme complex that replicates DNA): Photorepair UV light radiation causes pyrimidine (T or C) dimers to form via covalent linkages between adjacent bases, […]
Regulation of Transcription
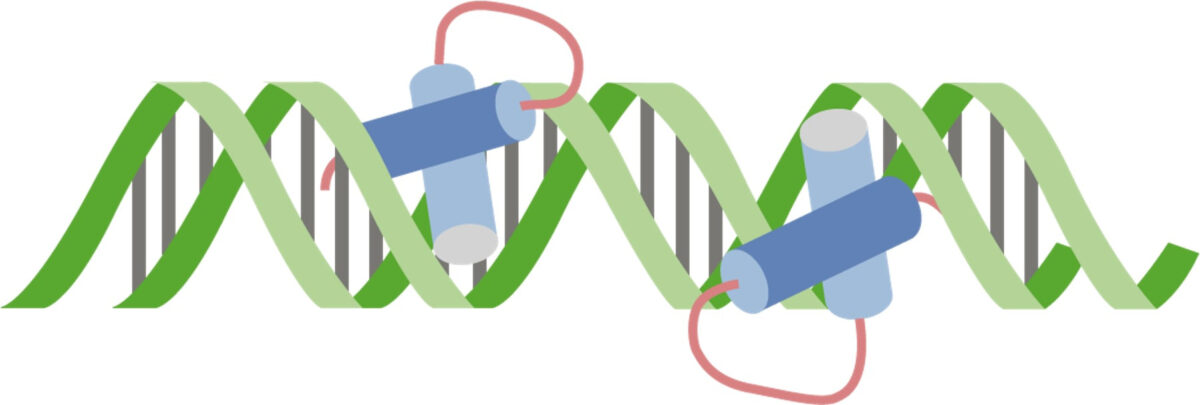
Overview Review of transcription Definition: DNA: DNA is a double-helix molecule made up of 2 antiparallel strands. DNA has a structure that looks like a twisted ladder. RNA: Overview of transcription regulation Regulatory Proteins Transcription regulation is mediated in part by regulatory proteins that can bind to the DNA in its helical form (unwinding is […]
Galactosemia
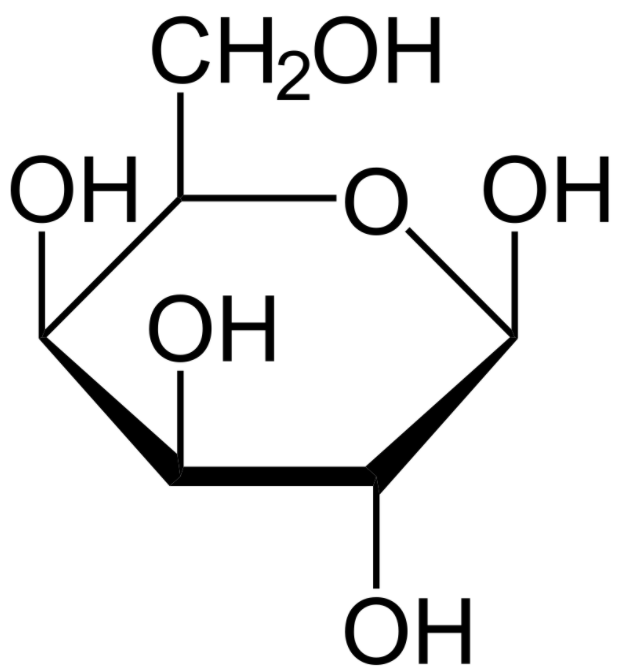
Overview Definition Galactosemia is an autosomal recessive, inborn error of carbohydrate metabolism resulting in the inability of the body to metabolize galactose into glucose. Classification Etiology Galactosemia is an inherited disorder caused by a genetic mutation, which leads to enzyme deficiency. The condition is autosomal recessive: Each child has a 25% chance of inheriting the […]
Post-transcriptional Modifications (RNA Processing)
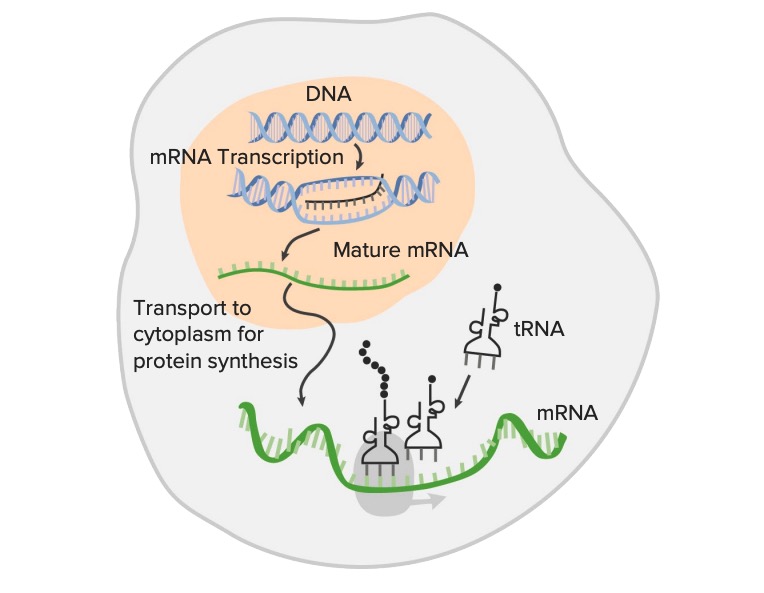
Overview Transcription Genetic information from DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA). Modifications Primary transcripts, or immediate products of transcription, undergo alterations to become biologically functional. Addition of the 5′ Cap and 3′ Poly-A Tail 5′ cap 7-Methylguanosine (methylated guanylyl residue) is added to the 5’ end of hnRNA via: Functions: 3′ Poly-A tail 50 […]
Glycolysis
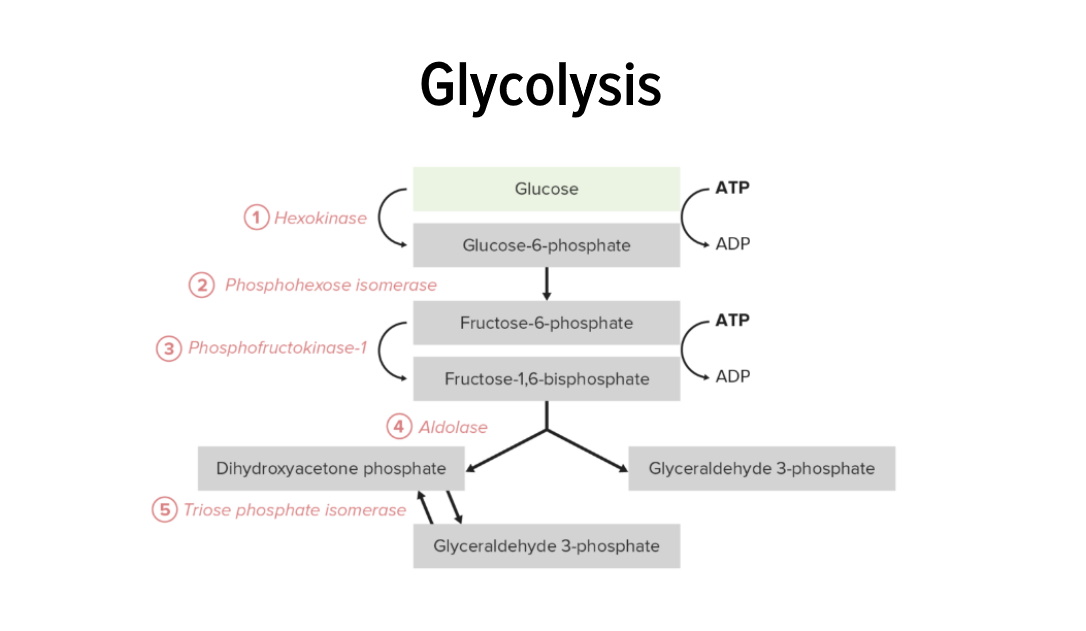
Steps 1–5: 1st Half of Glycolysis The 1st half of glycolysis requires an energy investment of 2 adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules and serves to convert the hexose glucose into 2 trioses. The process consists of 5 steps: Steps 6–10: 2nd Half of Glycolysis The 2nd half of glycolysis converts the triose GAP to pyruvate, with […]
RNA Types and Structure
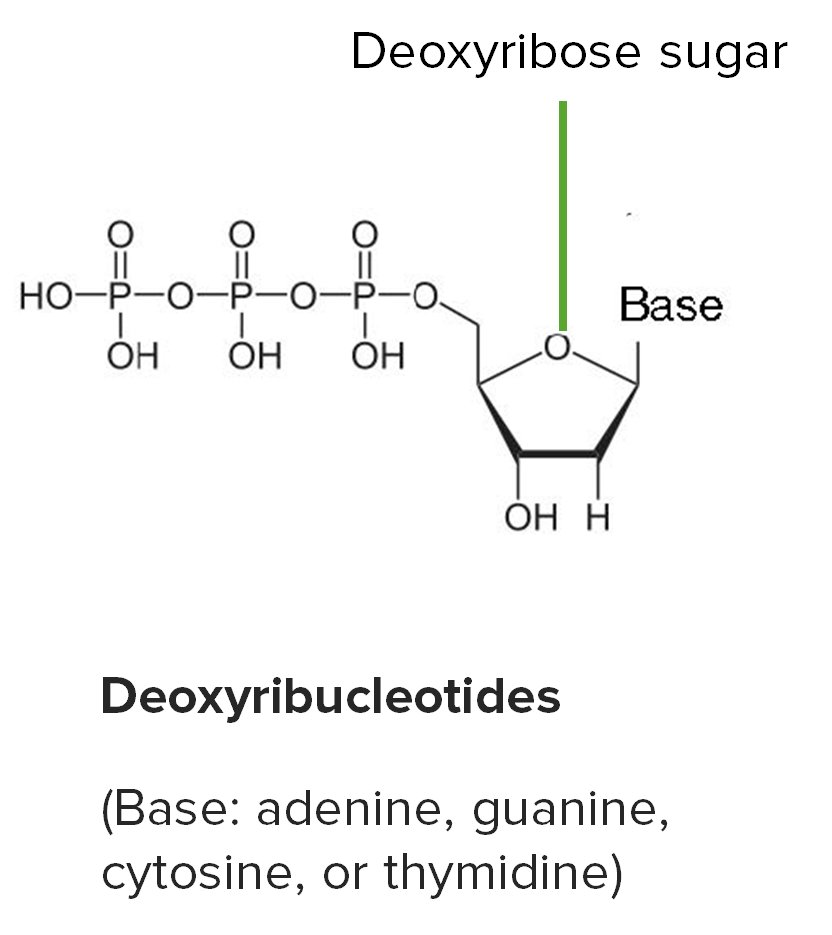
General Features of RNA Structure Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a single-stranded polymer of nucleotides that are linked through 3’–5’ phosphodiester bonds. Nucleotides are the basic unit of any nucleic acid. The nucleotides in RNA are formed by the following parts: Nucleic acid components: Table: RNA versus DNA RNA DNA Sugar moiety Ribose Deoxyribose Nitrogenous bases […]
Ethanol Metabolism
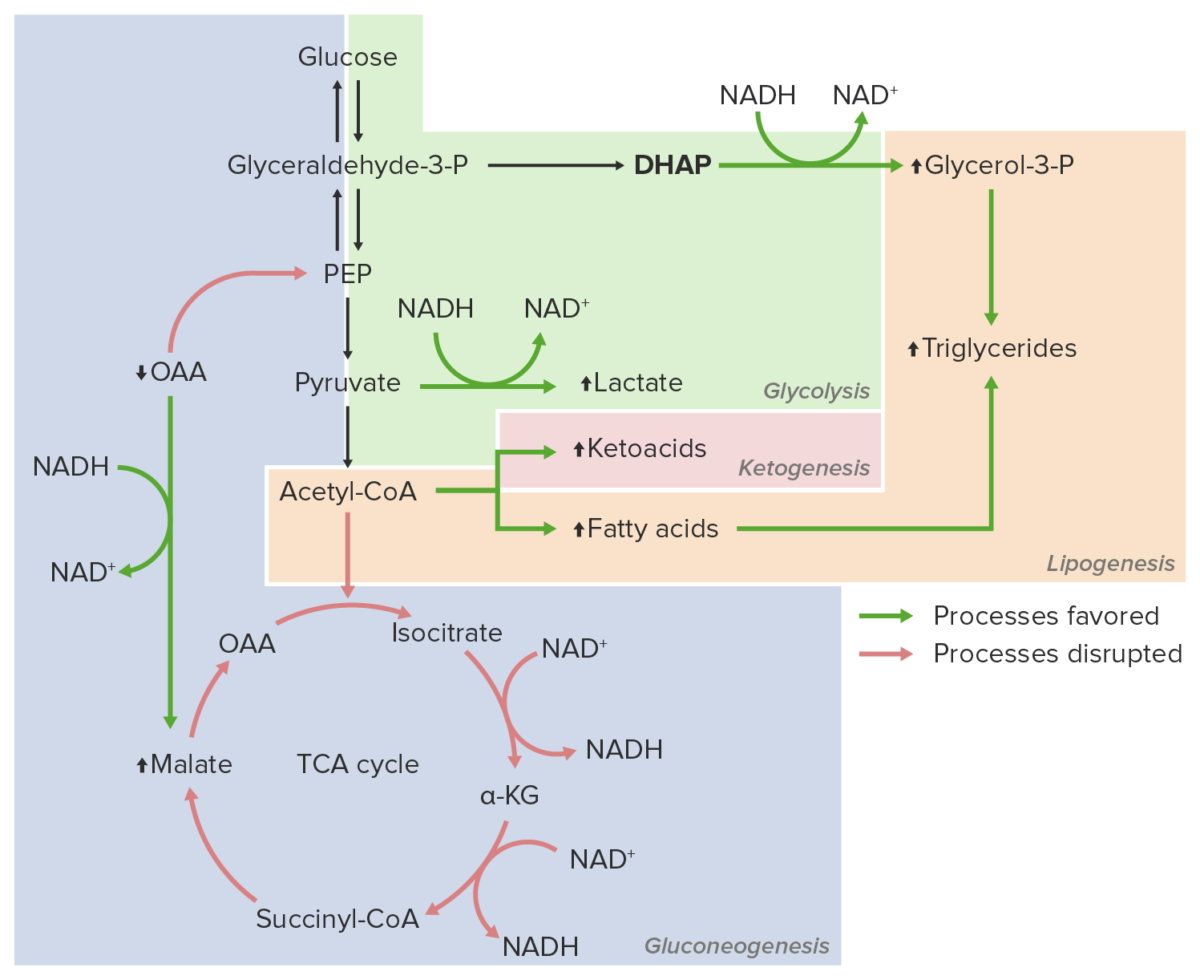
Overview Chemical characteristics Production and absorption Ethanol Metabolism The primary site of alcohol catabolism is the liver. Medications that affect ethanol metabolism Many common medications can inhibit enzymes involved in the metabolism of ethanol, leading to the accumulation of toxic products (e.g., acetaldehyde): Medication Inhibited enzyme Effects Fomepizole Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) Prevents the formation of […]
Cell Cycle
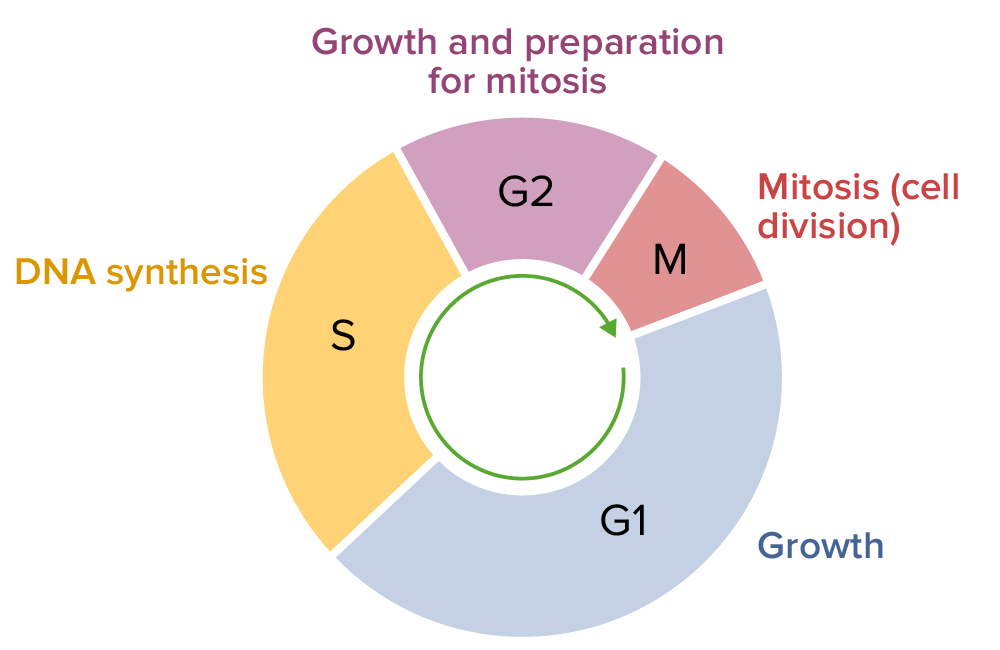
Definitions Overview The cell cycle describes the cyclic sequence of events through which a eukaryotic, proliferating parent cell splits into 2 identical daughter cells. G0 Interphase G1, S, and G2 phases are grouped together as interphase. Cell Division (Mitosis) During mitosis, the cell’s duplicated DNA is separated and distributed to 2 identical daughter cells. The […]
Basics of Amino Acids
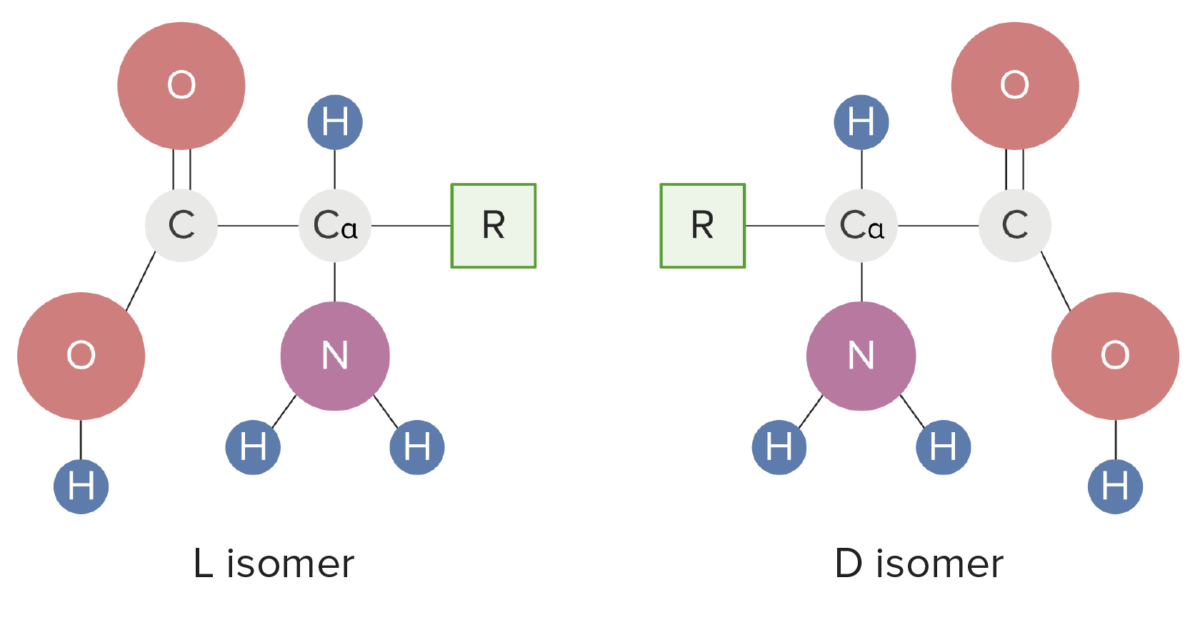
Structural Features Basic structure Each amino acid (AA) is composed of one alpha, or central, carbon bonded to: Stereochemistry R groups or side chains R groups determine the differences in structure, function, and biological interactions of AAs. R groups can be classified in 2 ways: Classifications R-group categories Non-polar or hydrophobic Polar or hydrophilic Aromatic […]