Gluconeogenesis
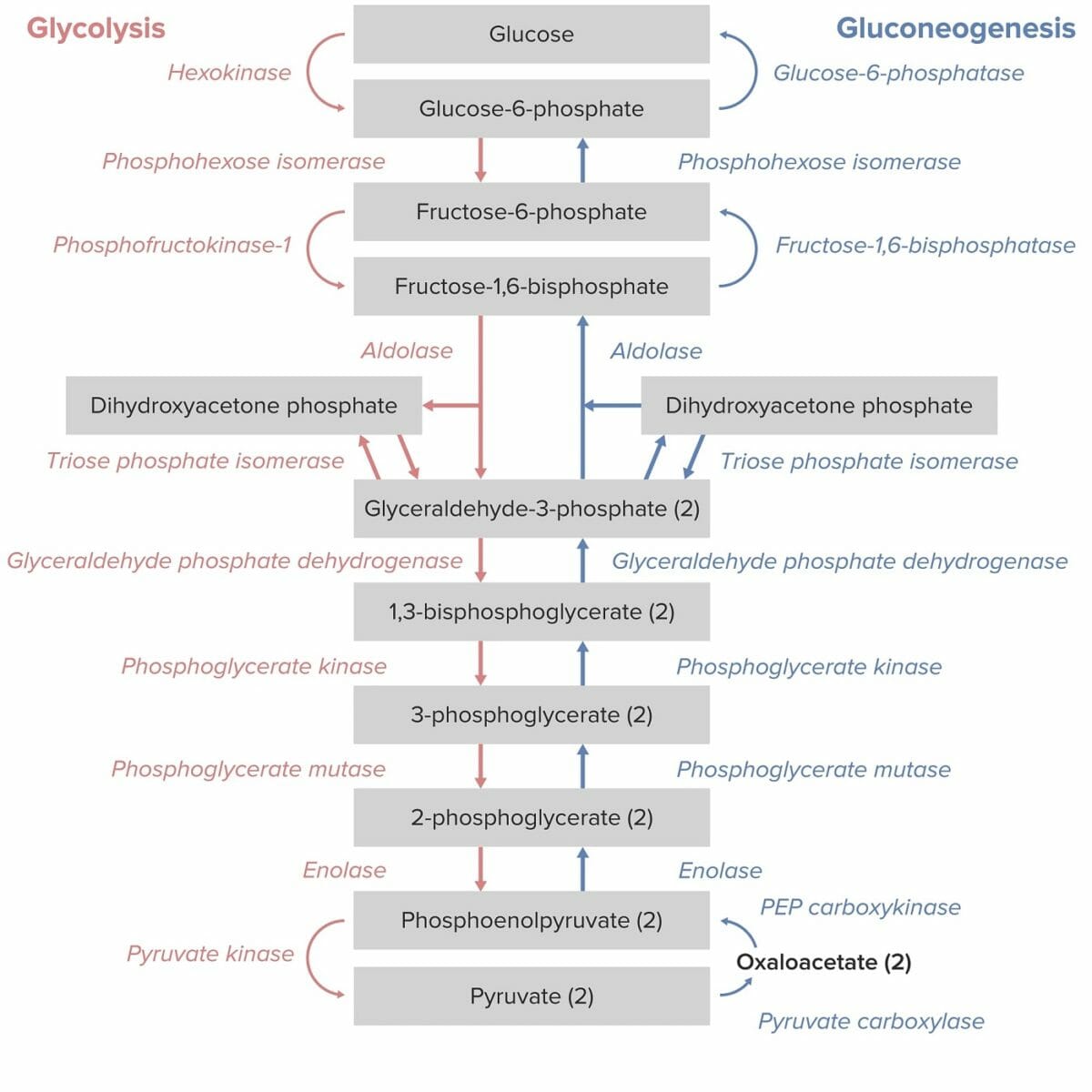
Reactions of Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis precursors include lactate, glycerol, alanine, and glutamine. This process occurs in multiple locations, beginning in the mitochondria but finishing with the shuttling of glucose into the cytoplasm via glucose transporters. Gluconeogenesis is the opposite of glycolysis. There are 11 enzymes, or steps, required for the complete process of gluconeogenesis. There are […]
Basics of Carbohydrates
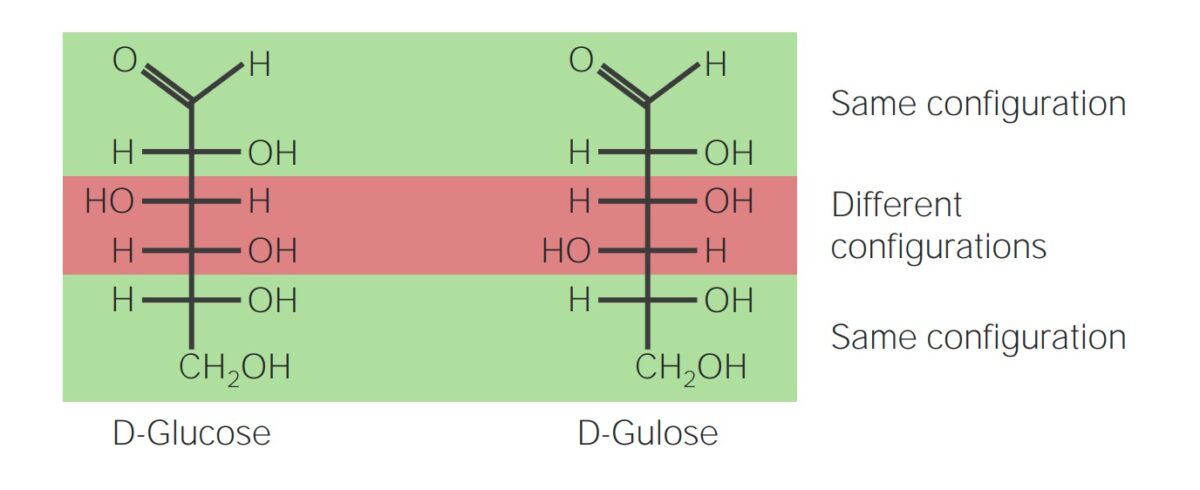
Nomenclature and Structure Nomenclature Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; they are defined as aldehydes or ketones of polyalcohols and have a general molecular formula of Cn(H2O)n. Carbohydrates are named based on the number of polymers (number of units) present in the molecule: Structure Classification Carbohydrates are classified into simple and complex carbohydrates […]
Trace Elements

Definition Trace elements (also called trace minerals) are minerals required in small amounts (1–100 mg/day for adults): Chromium General description Functions Intake and metabolism Deficiency and toxicity Copper General description Functions Intake and metabolism Deficiency and toxicity Fluoride General description Functions Provides benefits (but not necessary): Intake and metabolism Deficiency and toxicity Iodine General description […]
Tay-Sachs Disease
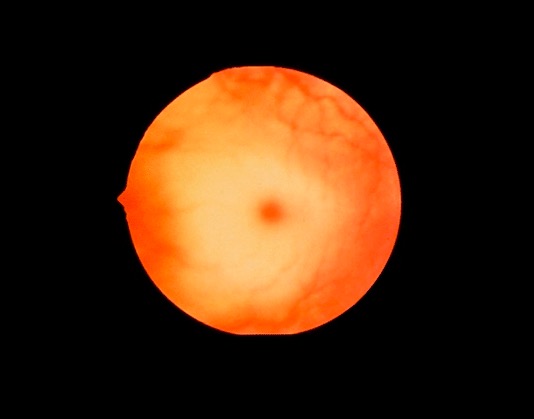
Overview Etiology Tay-Sachs disease is a lysosomal storage disorder caused by a deficiency in the hexosaminidase A (Hex-A) enzyme. Classification Tay-Sachs disease is classified into 3 variants based on age of onset and enzyme activity. Epidemiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Tay-Sachs disease is a neurodegenerative disorder with a variable clinical presentation depending on the variant. Infantile, […]
Porphyrias
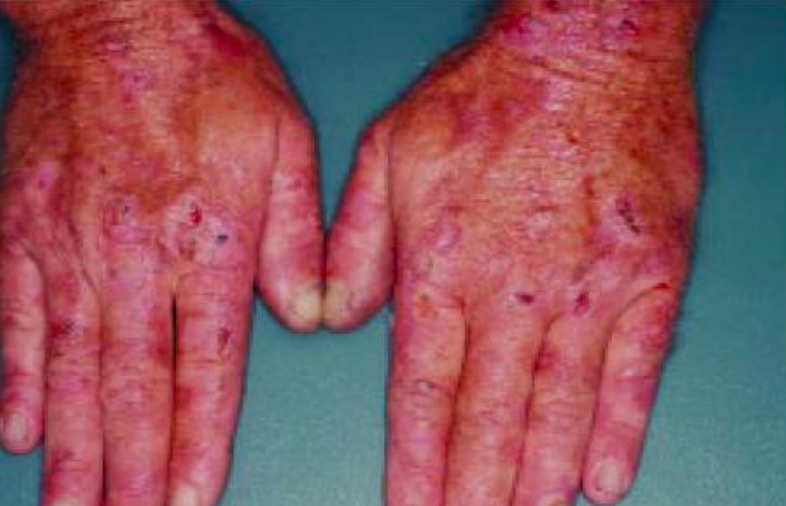
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Porphyrias are rare metabolic disorders caused by impairments in heme synthesis. Epidemiology Pathophysiology Porphyrias are due to enzymatic defects in heme biosynthesis: Table: Porphyrias and their associated defective enzyme Form of porphyria Defective enzyme Porphyria cutanea tarda Uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase Acute intermittent porphyria Porphobilinogen deaminase X-linked protoporphyria δ-Aminolevulinic acid synthase 2 […]
Mitochondrial Myopathies
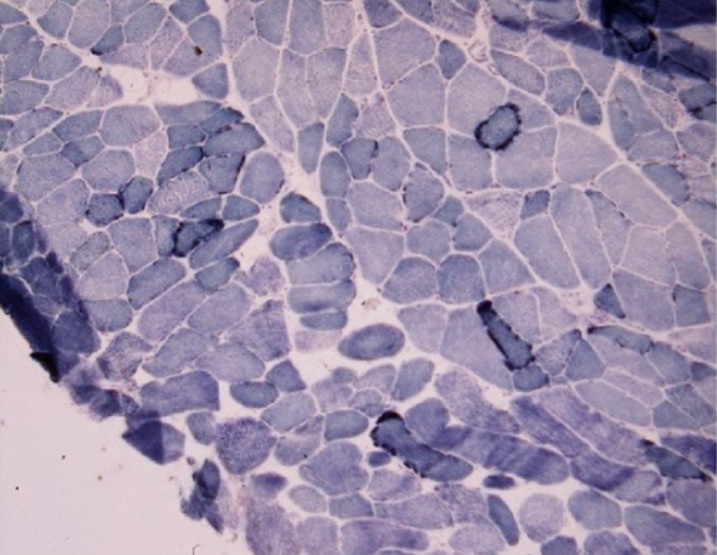
Overview Definition Mitochondrial myopathies are diseases that arise from dysfunction of the mitochondria (the energy-producing structures). These diseases are characterized by prominent muscular symptoms (such as muscle weakness) and accompanied by various symptoms from organs with high energy requirements. Etiology Epidemiology Pathophysiology Mitochondria Mitochondrial disease Clinical Presentation General findings Signs and symptoms correlate to organs […]
Fat-soluble Vitamins and their Deficiencies
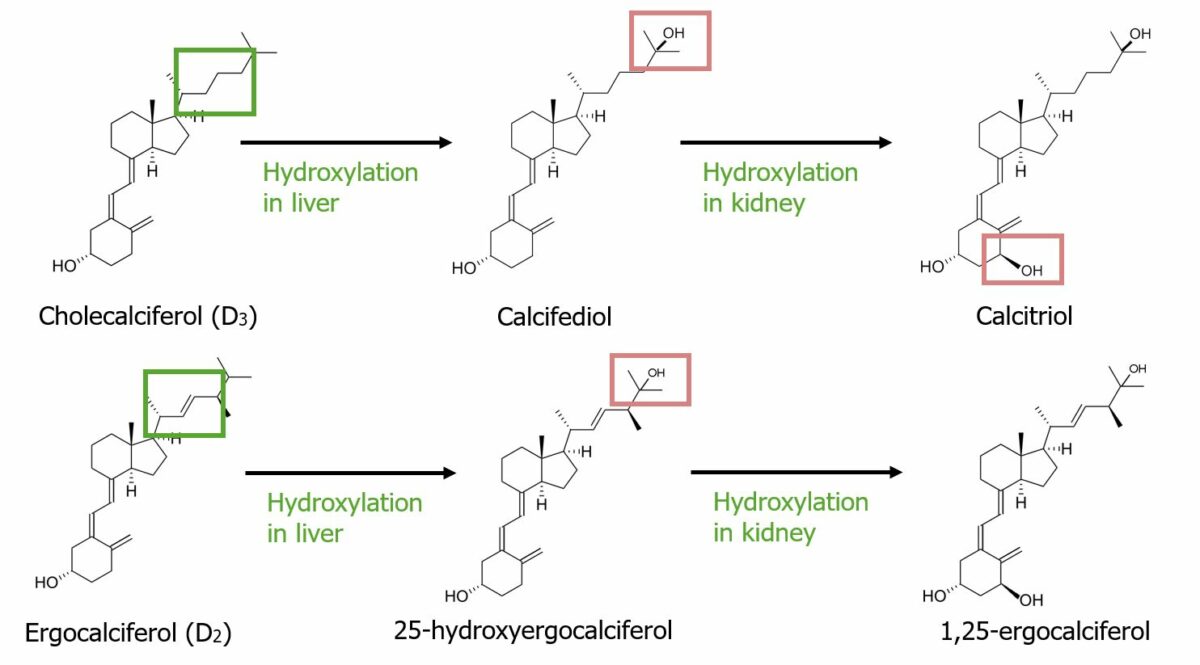
Overview Definition Vitamins are important organic substances that are required for normal metabolic functions. These substances cannot be synthesized by the body; they must be ingested in the diet. They are divided into water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins. Absorption and storage Fat-soluble vitamins are absorbed from the intestines with fat. In general, this process requires: Groups […]
Water-soluble Vitamins and their Deficiencies
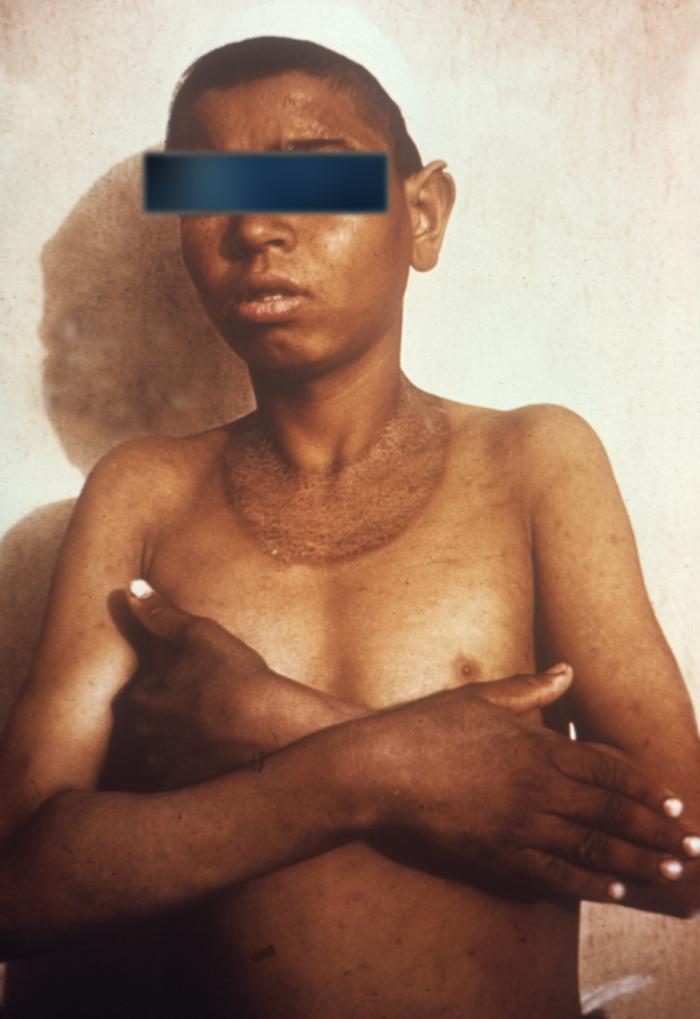
Overview Definition Vitamins are important organic substances that are required for normal metabolic functions These substances cannot be synthesized by the body; they must be ingested in the diet. The vitamins are divided into water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins. Summary of clinically important water-soluble vitamin deficiencies Table: Summary of clinically important water-soluble vitamin deficiencies Vitamin Clinical […]
Folate and Vitamin B12
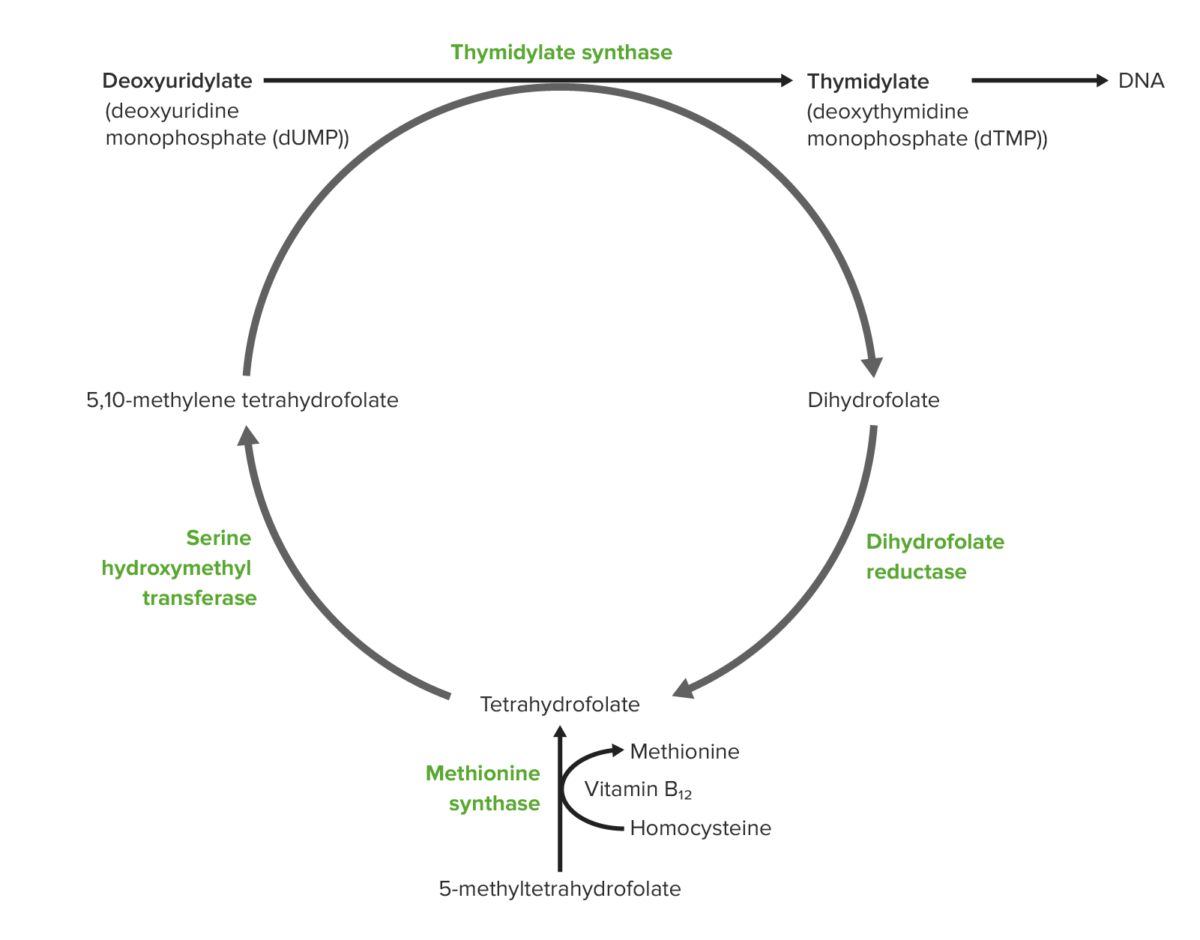
Folate Folate refers to the group of compounds occurring naturally in foods as well as folic acid, which is commonly used in supplements. Folate deficiency can result in megaloblastic anemia and, if the deficiency occurs in pregnant women, neural tube defects in their infants. Functions Absorption, metabolism, transport, and storage Daily requirement Vitamin B12: Cobalamin […]
Mucopolysaccharidoses
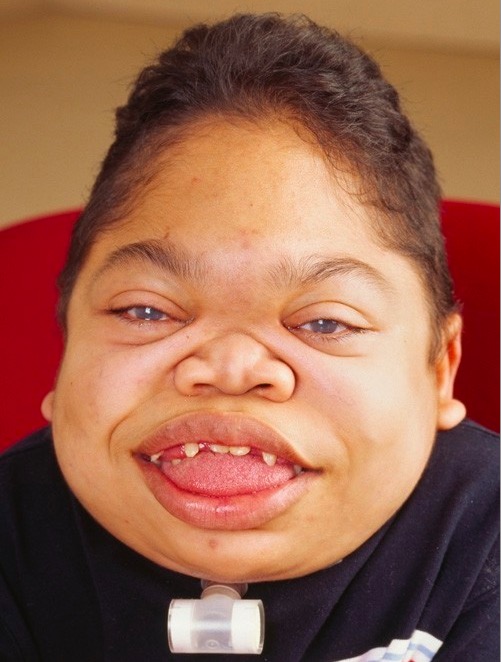
Overview Definition Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPSs) are a group of genetic metabolic diseases due to absent or defective enzymes needed to break down carbohydrate chains called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). Etiology and classification The MPSs are all inherited and classified on the basis of the enzyme deficiency. Epidemiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Affected individuals are usually not affected at birth, […]