Cholesterol Metabolism
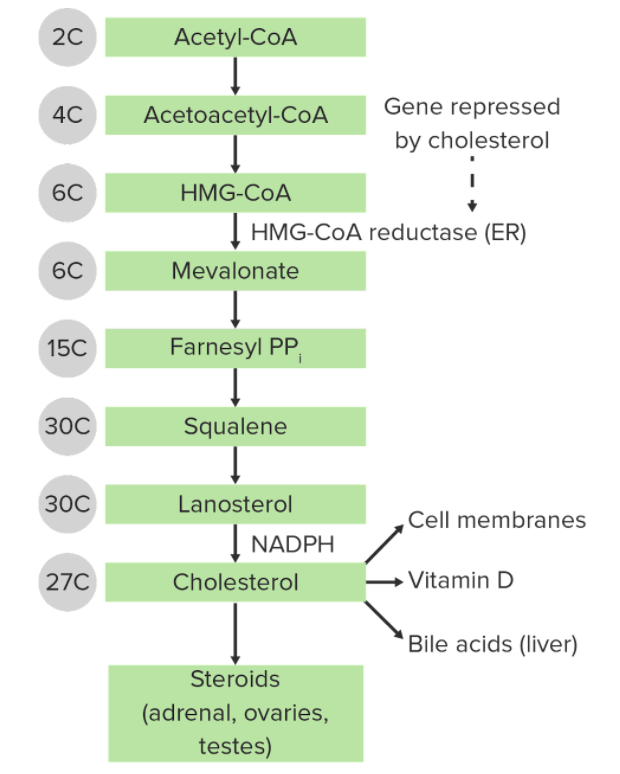
Synthesis Mevalonate pathway Cholesterol’s synthesis pathway overlaps with the synthesis of ketone bodies. The steps of this process include: Importance Cholesterol is a: Transport and Uptake Basics of lipoproteins Composition of lipoproteins Table: Composition of lipoproteins Lipoprotein Cholesterol/cholesterol ester Triglyceride Protein Phospholipid Chylomicrons 1%/3% 85% 2% 8% VLDL 7%/10% 55% 9% 20% IDL 8%/30% 26% […]
Glycogen Metabolism
Overview Structure Functions Storage Metabolic pathways There are 2 main metabolic pathways of glycogen: Glycogenesis Definition Step 1 Isomerization of glucose-6-phosphate to glucose-1-phosphate Step 2 Reaction of glucose-1-phosphate with uridine triphosphate (UTP) to form an activated form of glucose: Step 3 Formation of glycosidic bond Step 4 Branching of glycogen: Glycogenolysis Definition Breakdown of glycogen […]
Glyoxylate Cycle
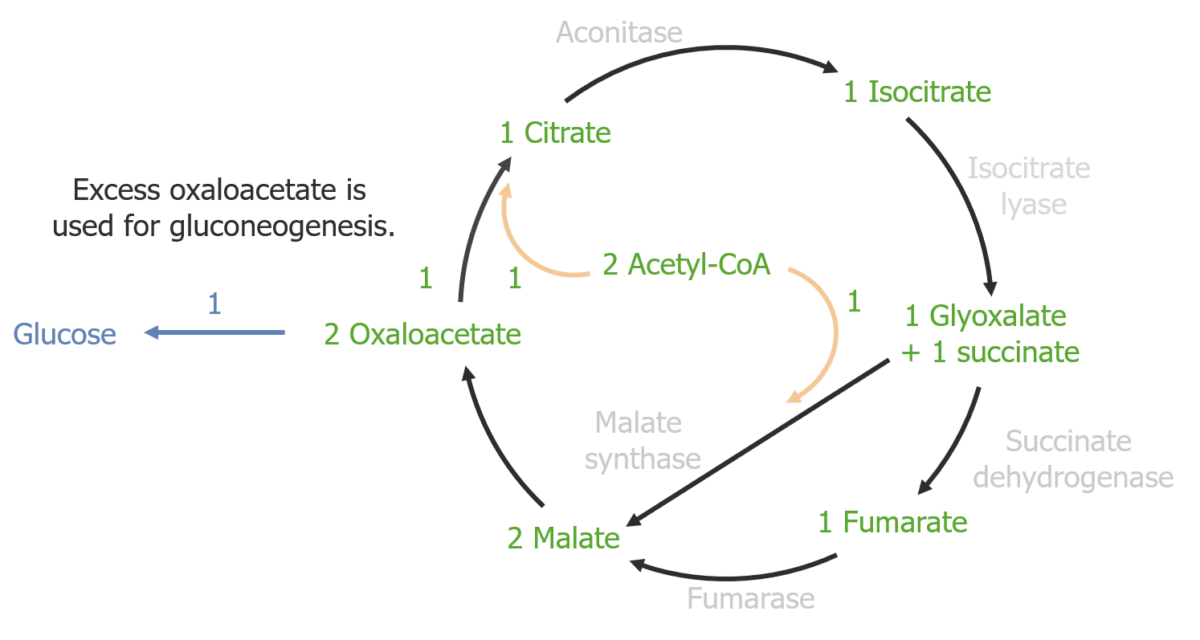
Function Vertebrates Plants Fungi Reactions, Yield, and Energy Balance Plants, fungi, and bacteria require carbohydrates for energy and cell wall synthesis (e.g., cellulose, chitin, and glycans). The glyoxylate cycle enables organisms to produce carbohydrates using acetyl-CoA from the β-oxidation of fatty acids. Reactions Key enzymes in the glyoxylate cycle The 2 key enzymes involved in […]
Heme Metabolism
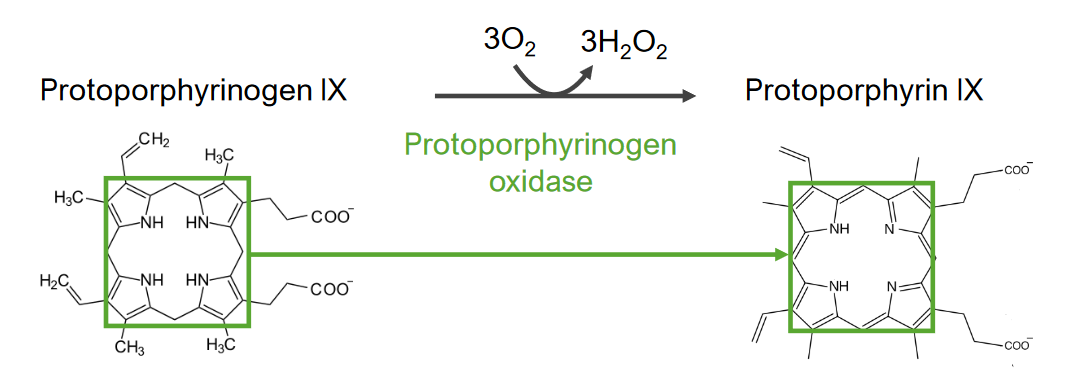
Structure and Function of Heme Structure Function Biosynthesis of Heme Heme is synthesized in the normoblasts, but not in the mature erythrocytes. The biosynthesis of heme takes place in 8 steps. Step 1 Step 1 is the synthesis of aminolevulinic acid. Step 2 Step 2 is the formation of porphobilinogen (PBG). Step 3 Step 3 […]
Disorders of Fatty Acid Metabolism
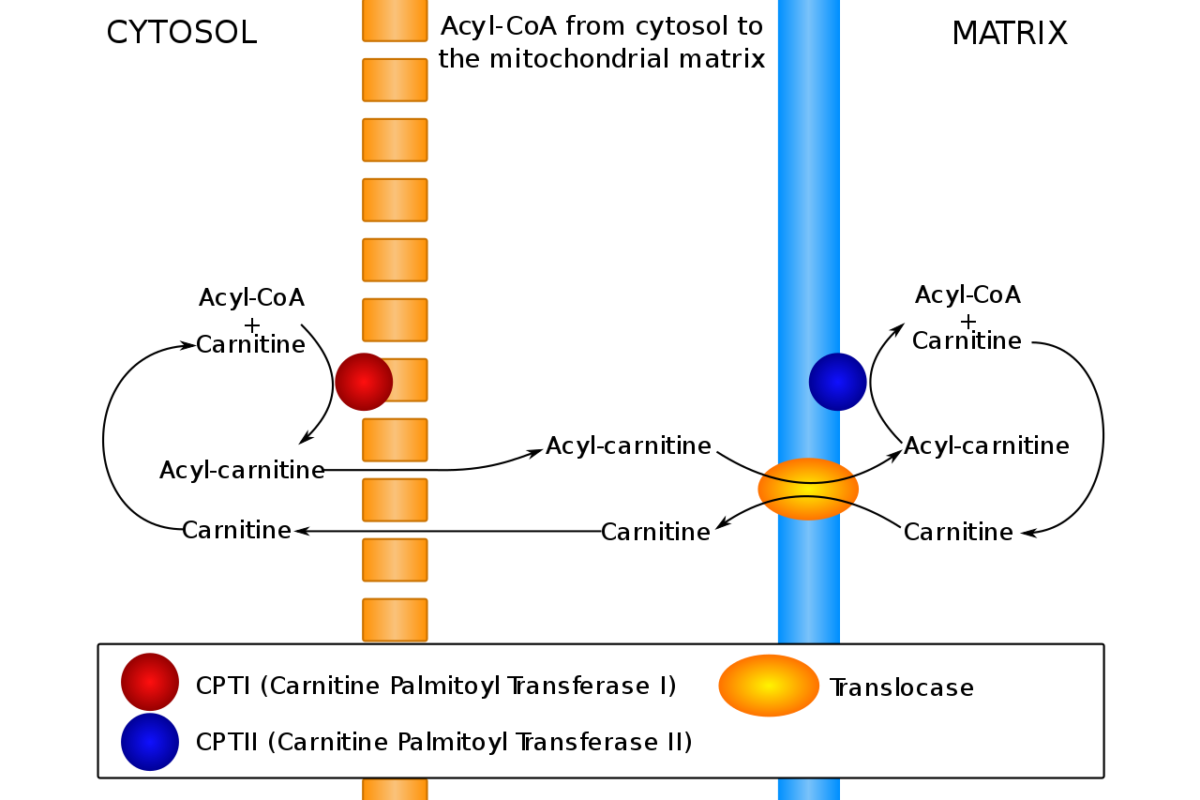
Overview Definition Disorders of fatty acid oxidation are inborn errors of metabolism that disrupt mitochondrial beta-oxidation or fatty acid transportation via the carnitine transport pathway. Types and classification Epidemiology Pathophysiology The exact pathophysiology varies depending on the deficiency, but there are a couple of overall consequences of disrupting the fatty acid oxidation process: Clinical Presentation […]
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
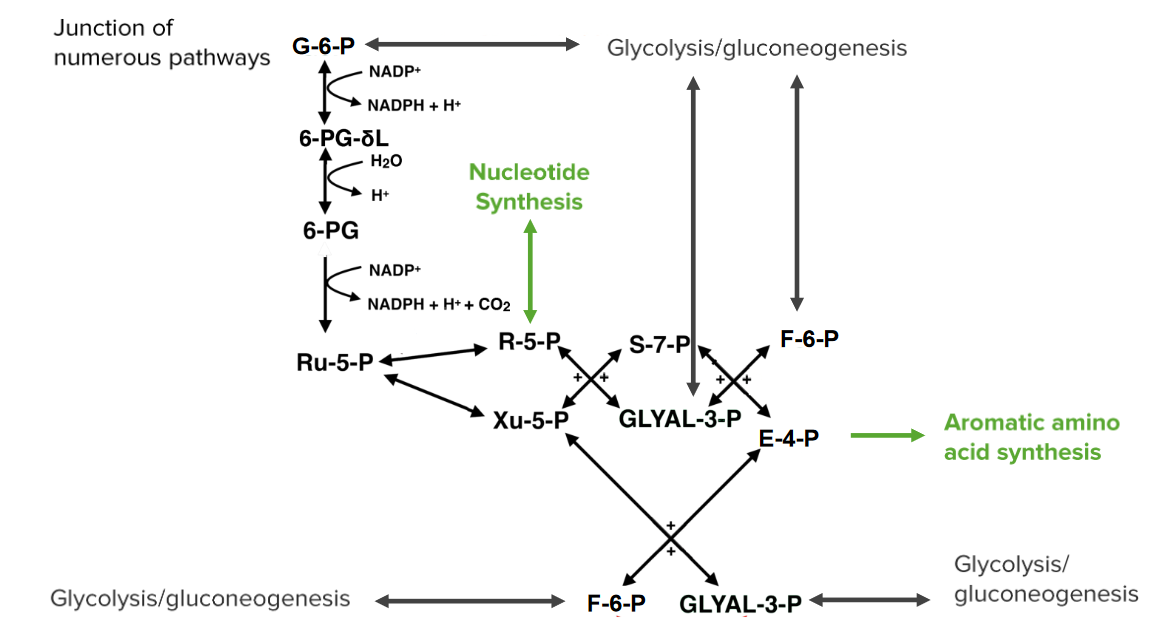
Definition and Function Definition The pentose phosphate pathway generates nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and ribose-5-phosphate through a series of reactions and occurs parallel to glycolysis. Location The pentose phosphate pathway occurs in the cytoplasm of cells. Function The pentose phosphate pathway generates intermediates that are utilized for multiple purposes: Oxidative and Nonoxidative Phases There […]
Overview of Lysosomal Storage Diseases
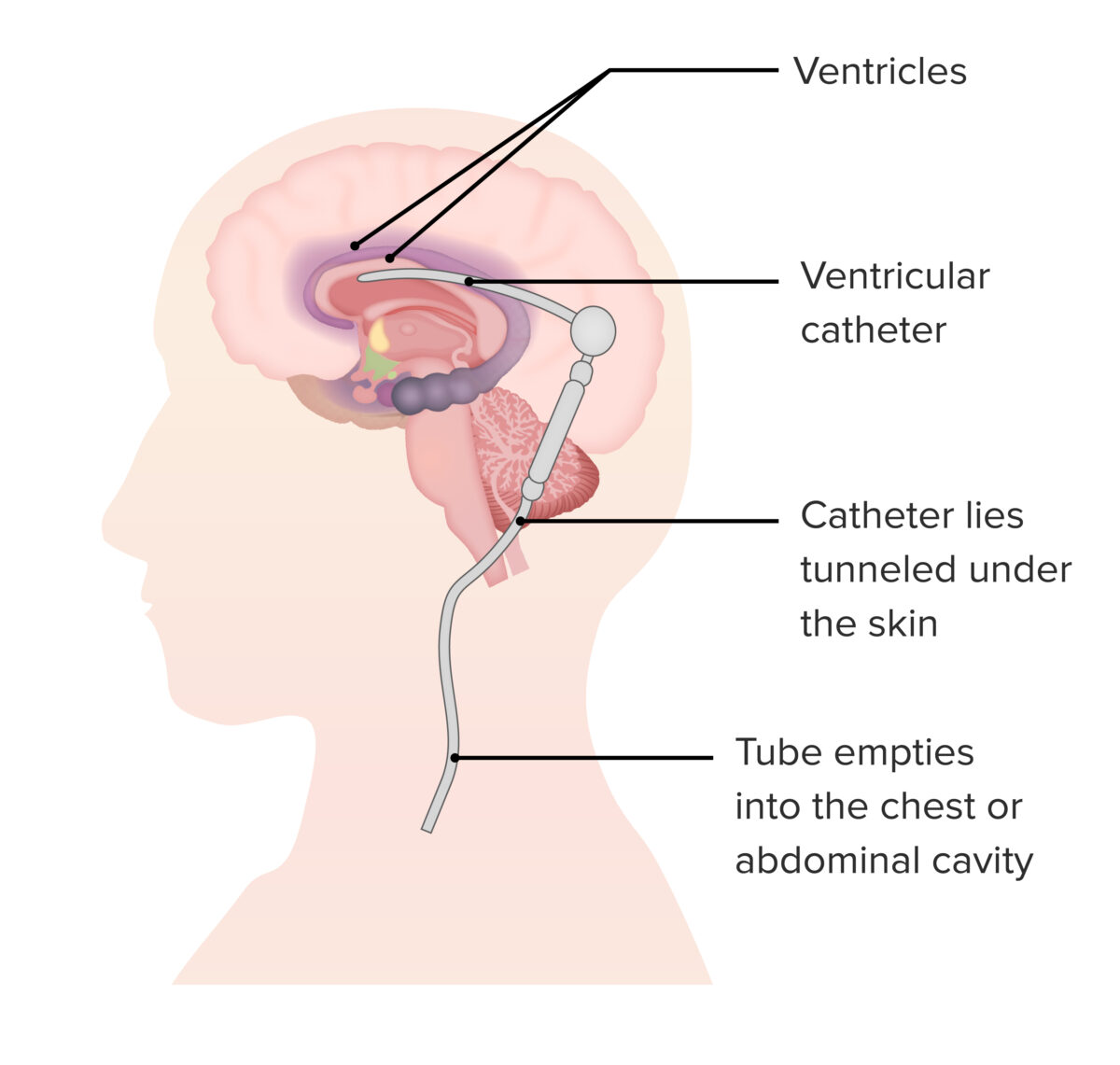
Overview Definition Lysosomal storage diseases are rare metabolic conditions caused by genetic mutations of lysosomal enzymes, which lead to dysfunctional metabolism and the accumulation of glycosaminoglycans, glycoproteins, or glycolipids. Epidemiology Etiology Disorders are due to a deficiency in a specific lysosomal hydrolase or the enzymes required for lysosomal function: Classification The disorders are considered as […]
Urea Cycle Disorders
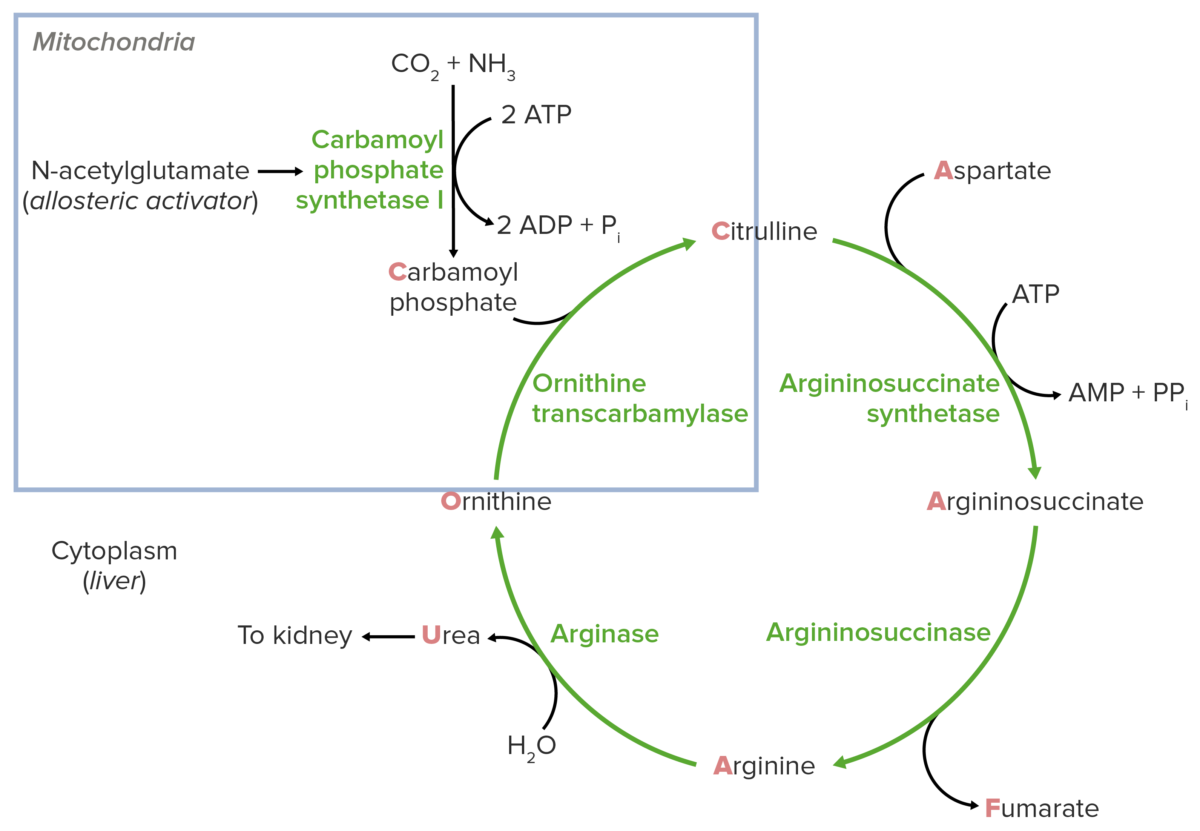
Overview Definition Urea cycle disorders (UCDs) are a group of syndromes resulting from genetic mutations, which cause deficiencies in enzymes and amino acid transporters of the urea cycle, resulting in the accumulation of nitrogenous waste products. Epidemiology Etiology All UCDs stem from genetic abnormalities, which cause deficiencies in enzymes important to the urea cycle: All […]
DNA Types and Structure
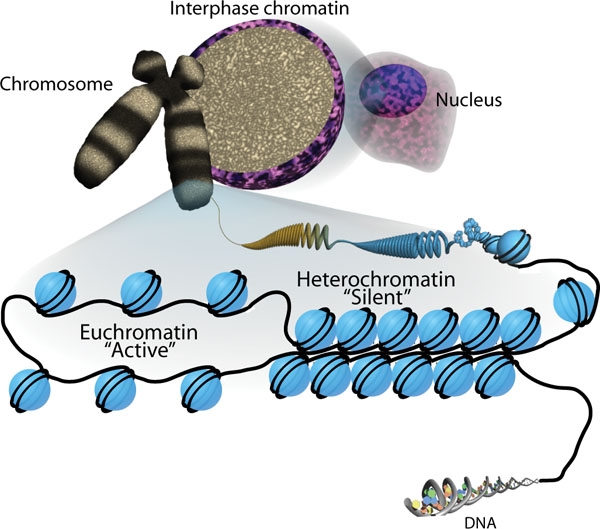
Structure of DNA The hereditary material DNA is a double-stranded nucleotide polymer: Organization and Packing of DNA in the Cell Nucleus Mitochondrial DNA Clinical Relevance References
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
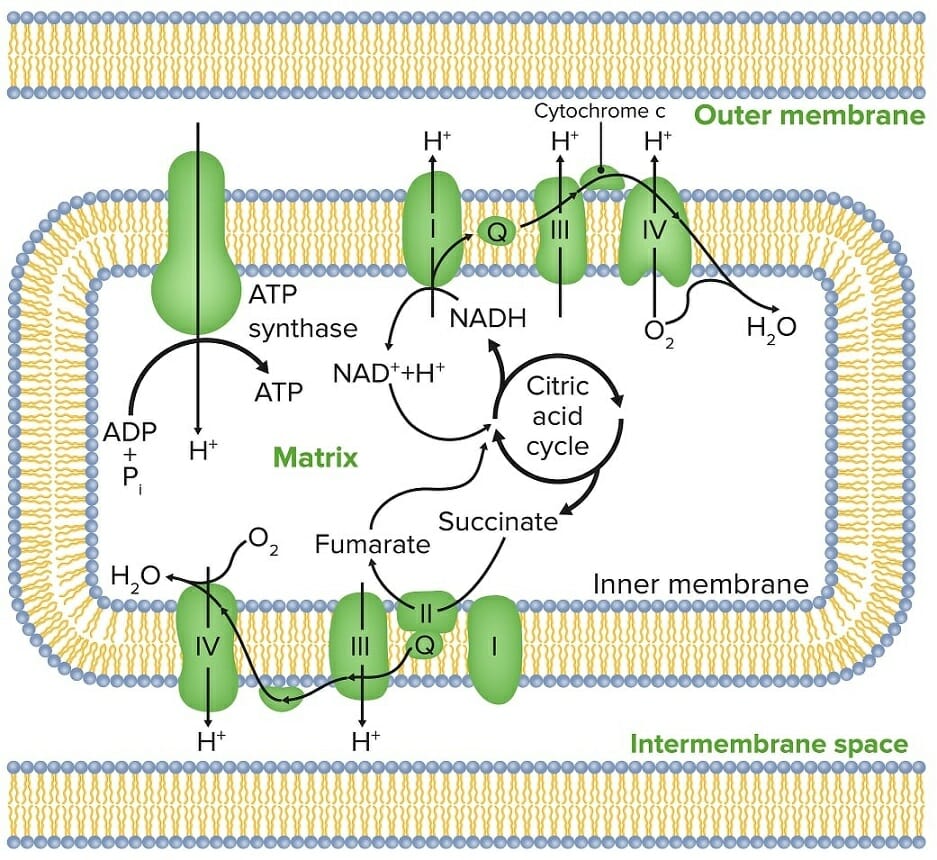
Structure of Mitochondria Complexes of the ETC Complex I Complex II Complex III Complex IV Electron Transport Oxidative Phosphorylation Table: Protons conveyed into the intermembrane space as a result of oxidation of 1 molecule of palmitoyl-CoA to CO2 and H2 Enzyme catalyzing oxidation step Number of NADH or FADH2 formed Number of protons ultimately translocated […]