Receptors
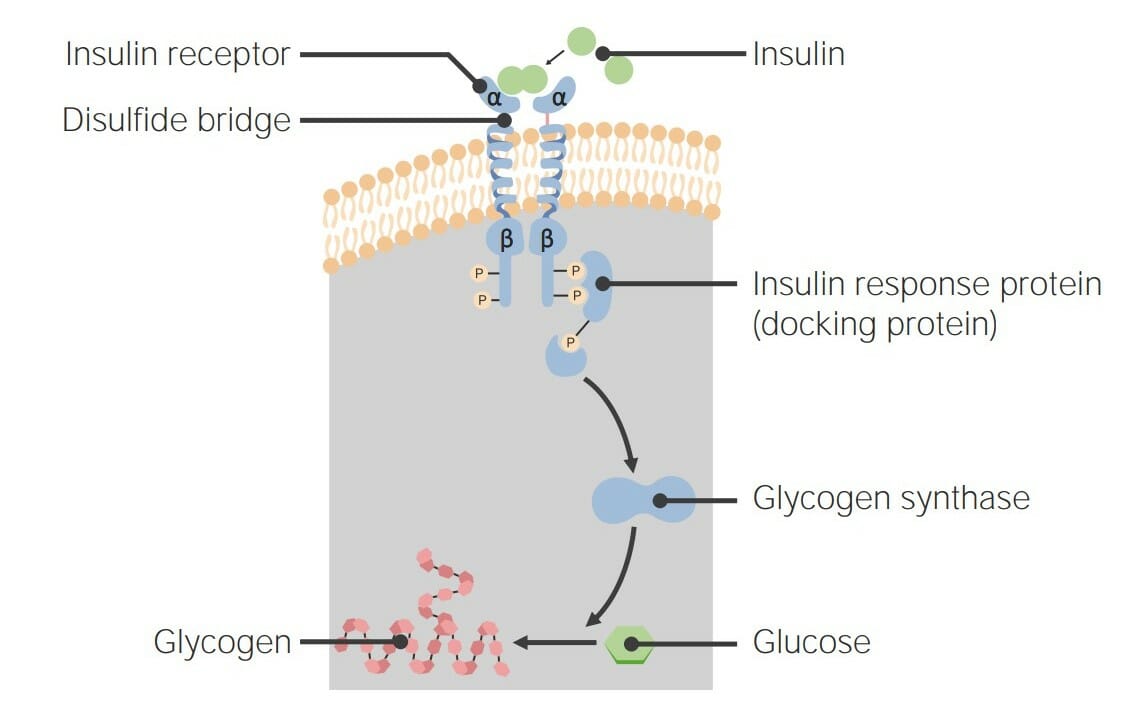
Overview Definition Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. General physiology Classification: Cell Surface vs. Intracellular Receptors Receptors can be broken down into 2 main categories: cell surface (transmembrane) […]
Energy Homeostasis
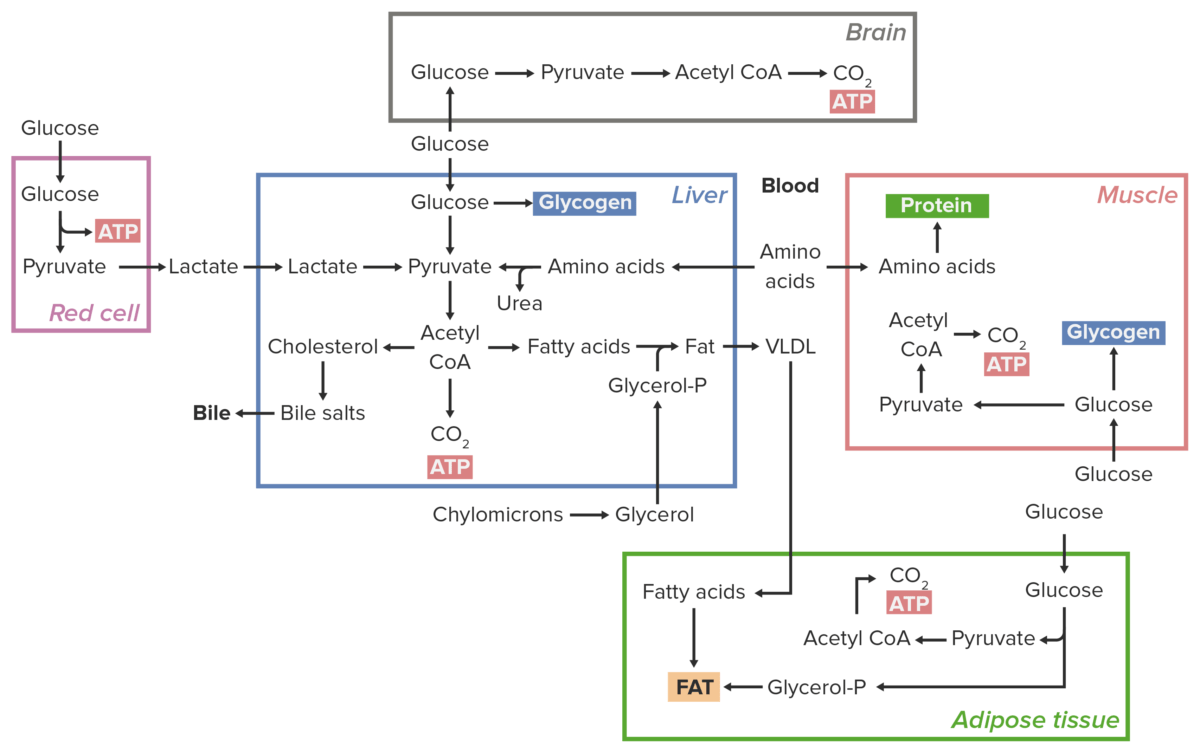
Overview Important terms Theories and models Sources of Energy General Carbohydrates Proteins Fats Metabolism Metabolism in an absorptive state Metabolism in the postabsorptive state Regulation of metabolism Metabolism in Individual Tissues Liver Table: Energy utilization of the liver during the fed and fasting states Fed state Fasting state Glucose levels ↑ after a meal Liver […]
Lipid Disorders
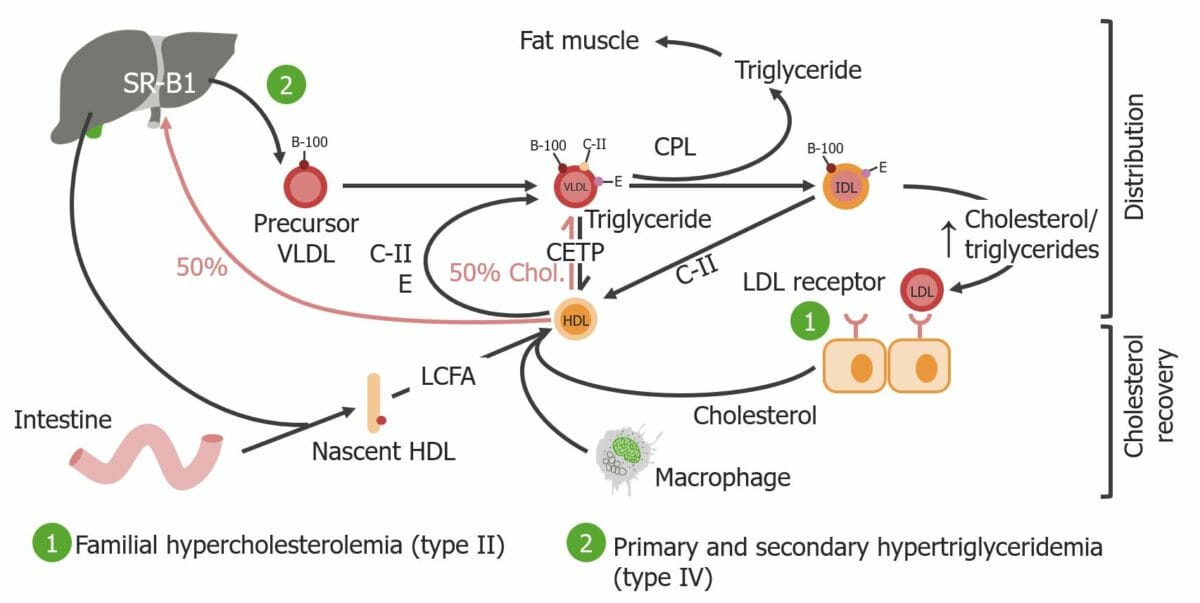
Overview Definition Dyslipidemia: abnormal amounts of lipid in the blood Epidemiology Pathophysiology Etiology and Classification Etiology Causes of dyslipidemia can be divided into primary (familial) and secondary (acquired) causes. Primary causes: Secondary (acquired) causes: Fredrickson classification for inherited dyslipoproteinemia Table: Fredrickson classification for inherited dyslipoproteinemia (DLP Type Condition, mode of inheritance (autosomal dominant (AD), autosomal […]
Overview of Protein Functions
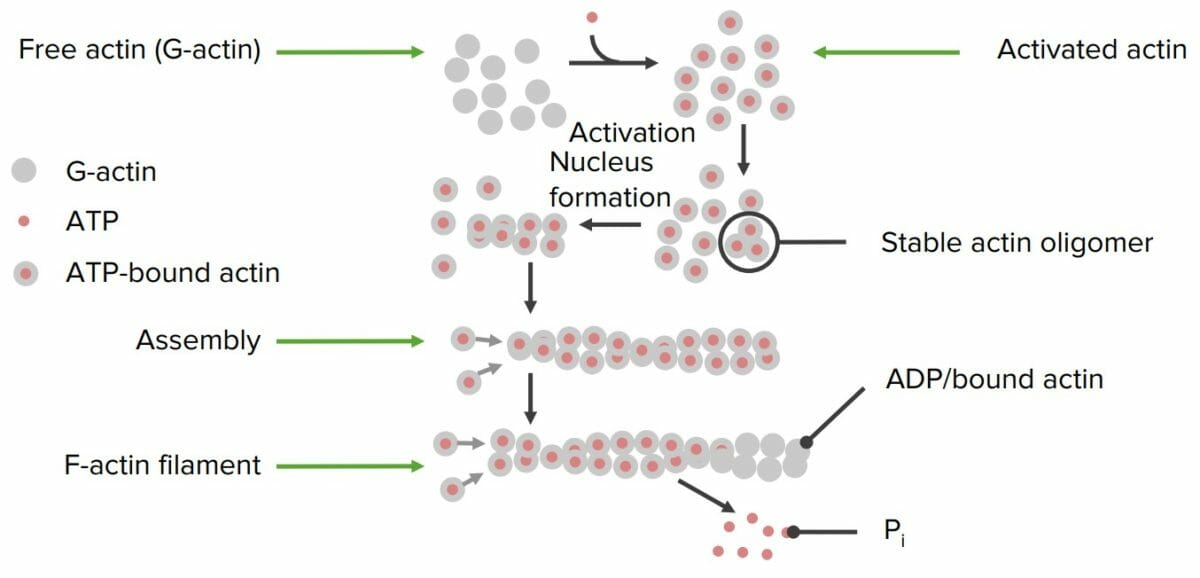
Overview Proteins are 1 of the 3 major macronutrients used in the body. Proteins are made up of amino acids (AAs) and have an extensive range of functions in the body, including: Structural Proteins Structural proteins are important in maintaining cellular shape and physical integrity. Proteins Involved in Movement Communication, Signaling, and Regulatory Proteins Functions […]
Proteins and Peptides

Structure Amino acids, peptides, and proteins Formation of peptide bonds Rotational movement within polypeptide chains Protein folding: 4 levels of protein structure There are 4 levels of protein structure; this is often referred to as protein folding. The levels are primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures. Proper folding requires the assistance of chaperone proteins Primary […]
Glycogen Storage Disorders
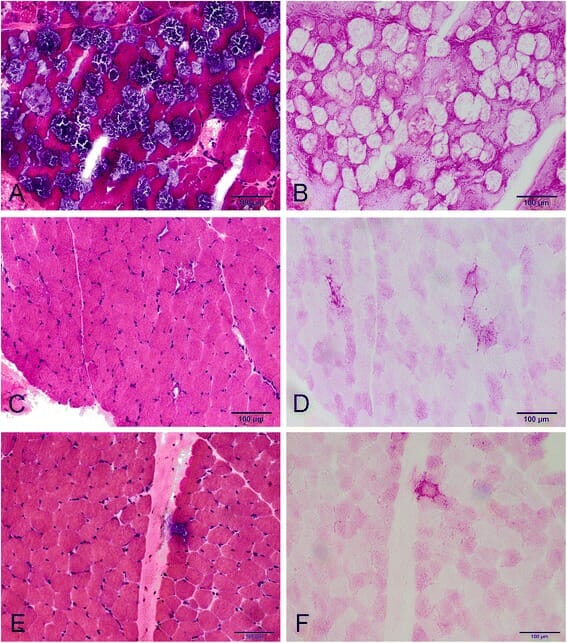
Overview Definition Glycogen storage disorders (GSDs) are genetic defects causing enzyme deficiencies that result in liver, muscle, or heart disease from abnormal glycogen deposition in tissues and episodic hypoglycemia (in most disorders), as the body cannot use glycogen as a source of energy. Epidemiology Classification Von Gierke Disease Glycogen storage disorder I (von Gierke disease) […]
Fatty Acid Metabolism
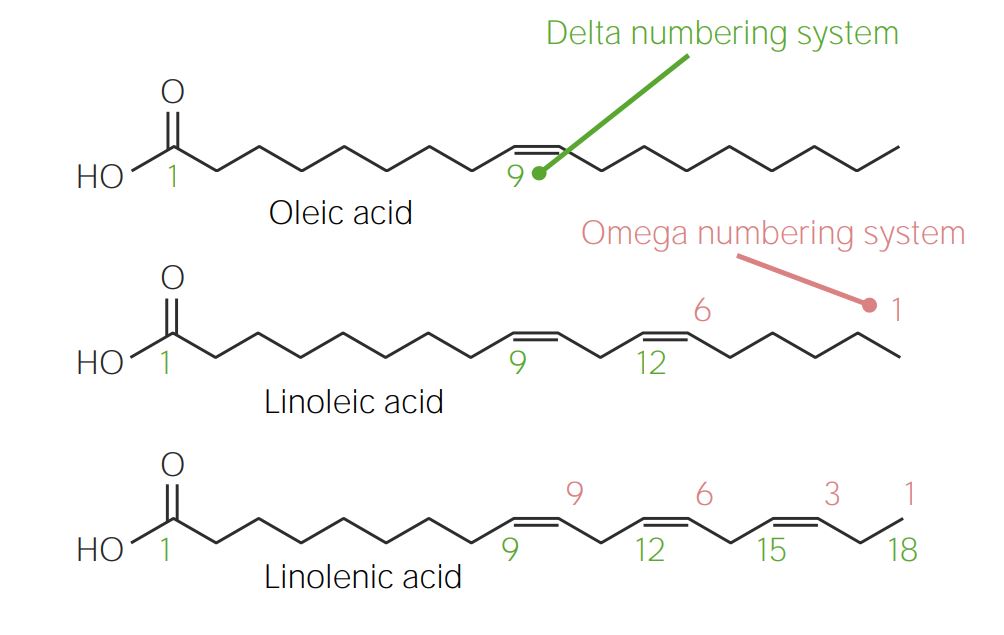
Overview Classification Fatty acids (FAs) are classified based on their carbon chain saturation and length. Saturation: Length: Numbering system Utility FAs are utilized for: Fatty Acid Synthesis Conversion of glucose Glucose is needed to produce acetyl CoA, which is required for FA synthesis. Synthesis of palmitic acid The process of FA synthesis continues in the […]
Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism
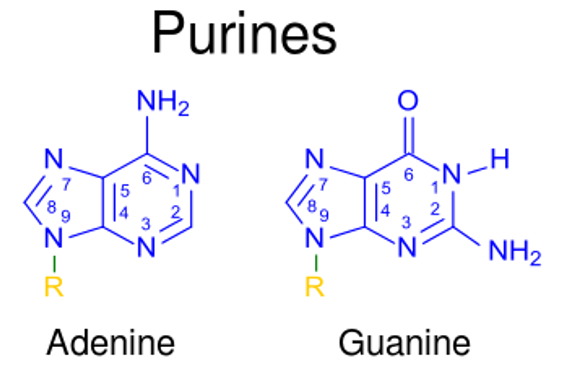
Overview Basic terms Nitrogenous base: Nucleosides: 2 components: A beta-N-glycosidic bond links the 1st carbon of the pentose sugar and N9 of a purine or N1 of a pyrimidine (e.g., adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, thymidine, uridine, inosine). Nucleotides: 3 main components: These molecules form the DNA backbone (e.g., adenosine monophosphate, guanosine monophosphate, cytidine monophosphate) > 1 […]
Fatty Acids and Lipids
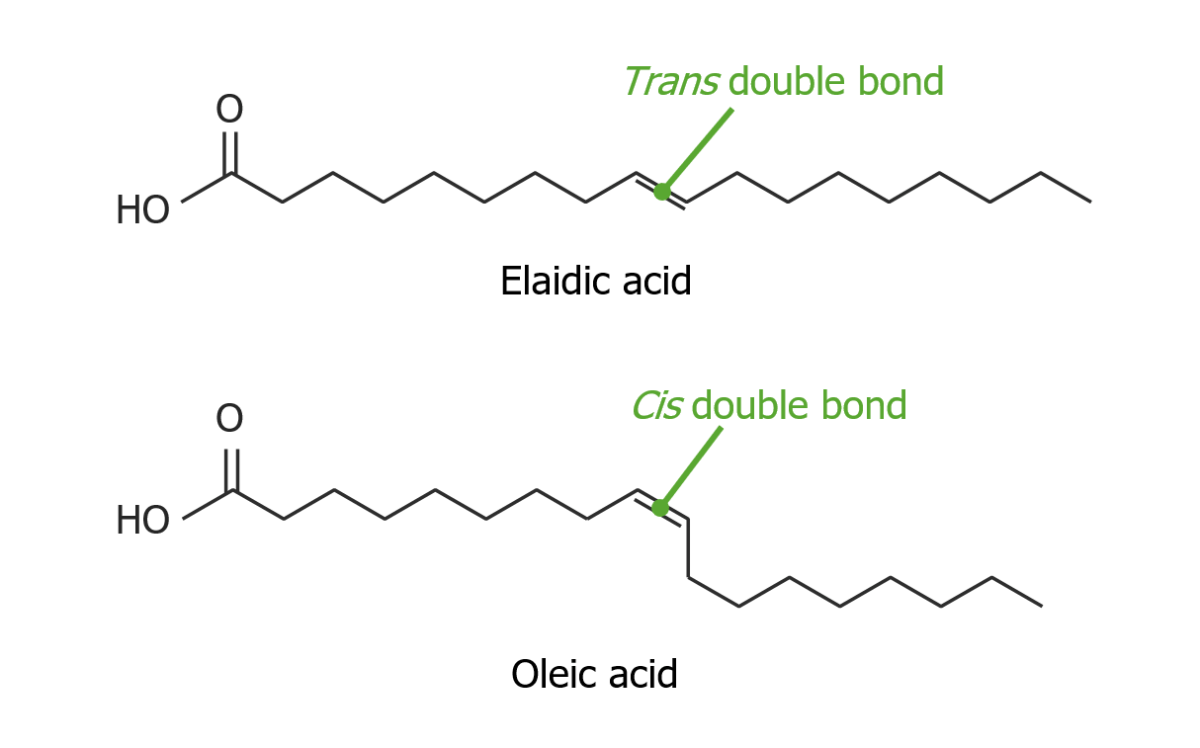
Fatty Acids Structure Nomenclature of fatty acids Table: Examples of saturated fatty acids Name Number of carbon atoms Sources Lauric acid 12 Palm kernel oil, coconut oil, laurels, and butter Myristic acid 14 Nutmeg, palm kernel, coconut oil, and butter Palmitic acid 16 Found in many animal and plant fats Stearic acid 18 Animal fats, […]
Second Messengers
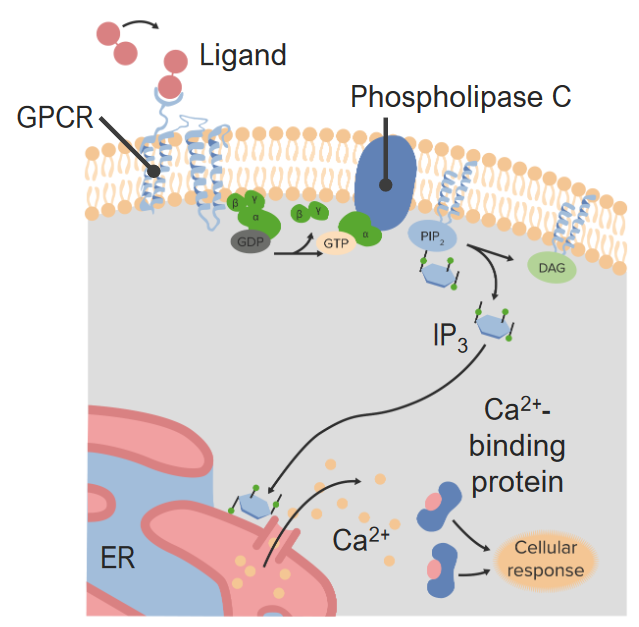
Overview of Second Messengers Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to first messengers, which are extracellular signaling molecules. Cyclic Nucleotides Cyclic adenosine monophosphate Cyclic guanosine monophosphate Lipids Lipids present in the plasma membrane, such as phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), are often modified and utilized as second messengers. Binding of first […]