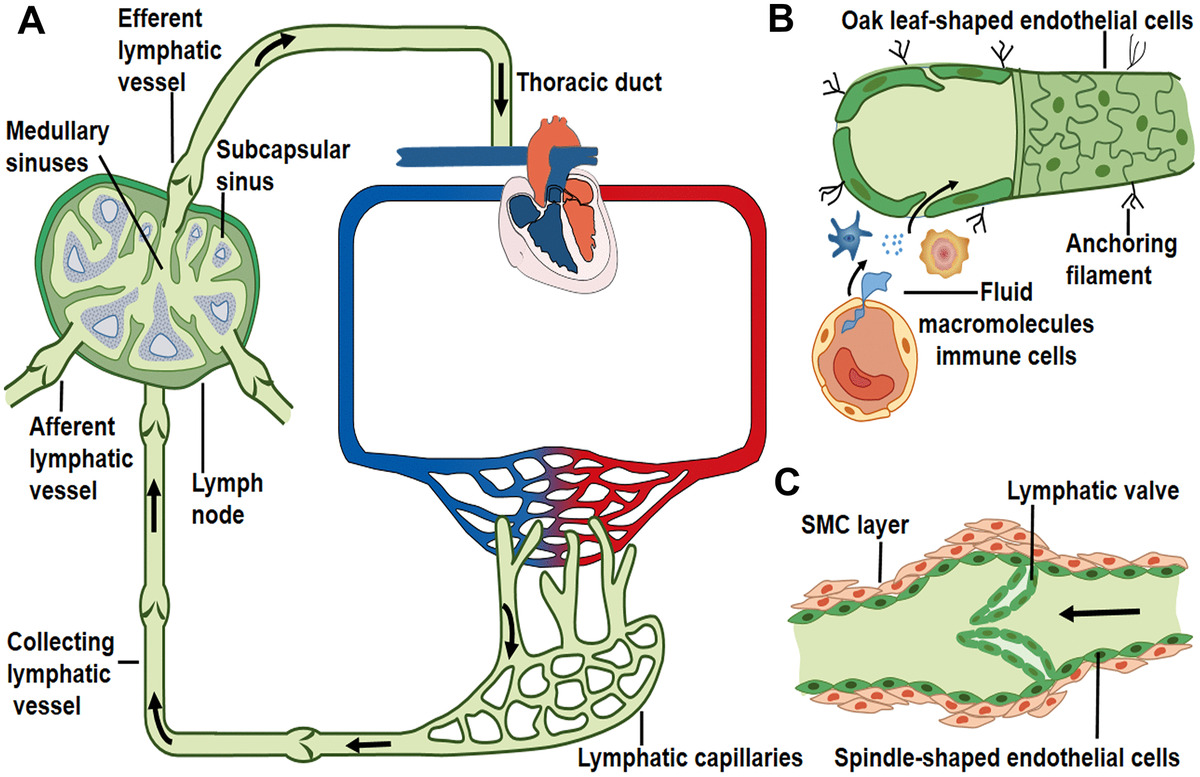
Lymphatic Drainage System: Anatomy
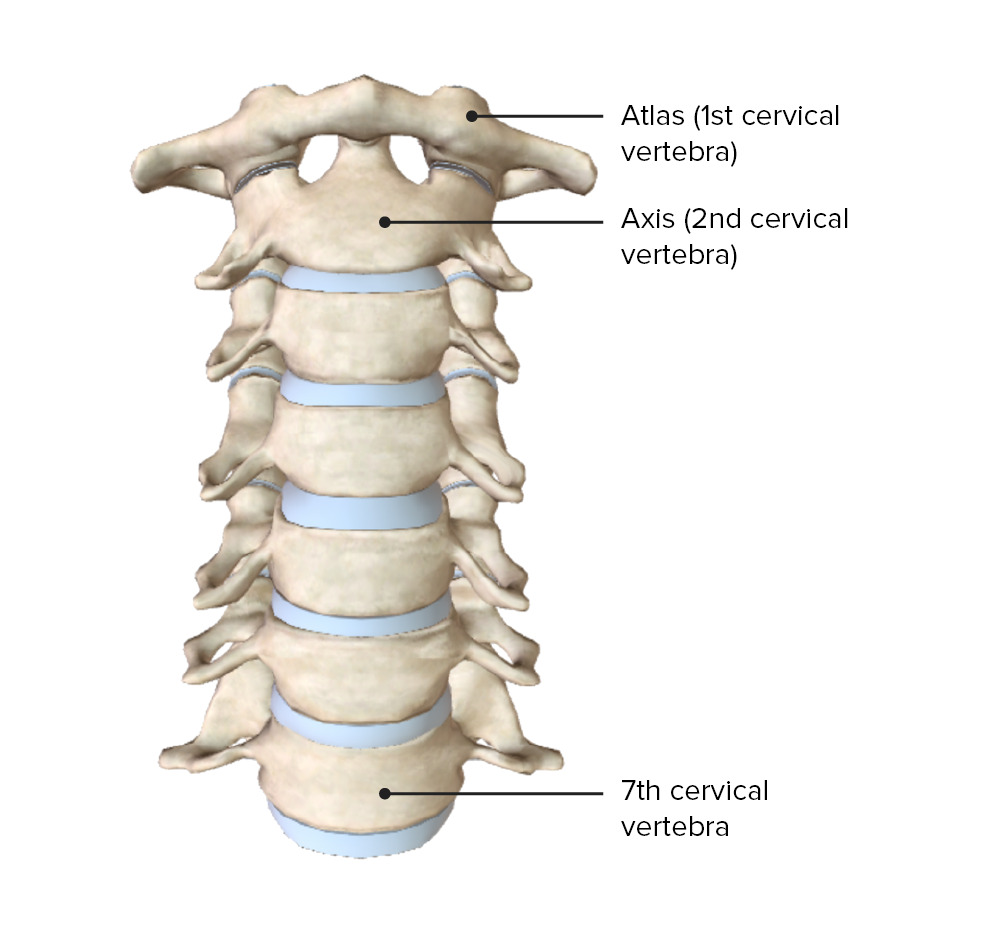
Vertebral Column: Anatomy
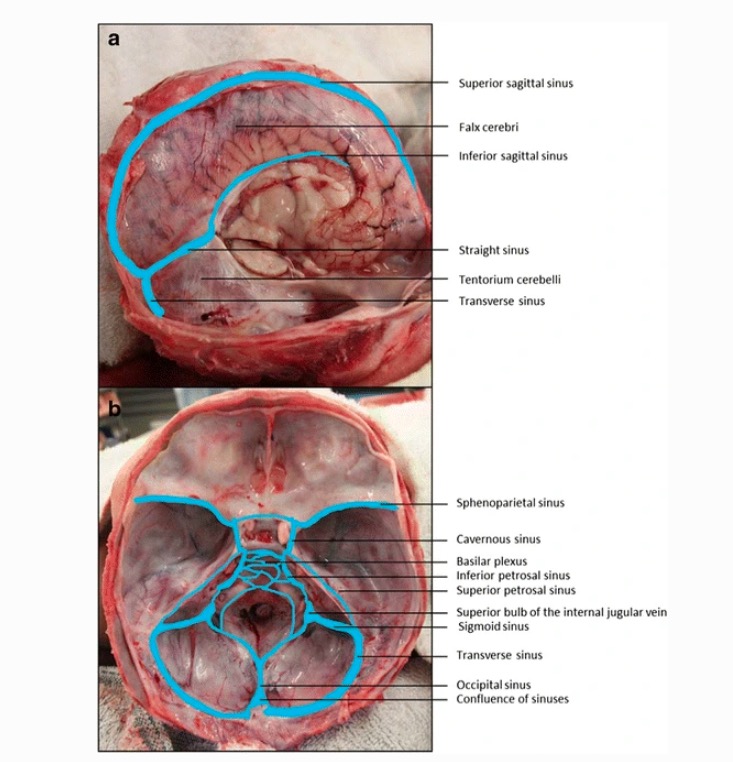
Meninges: Anatomy
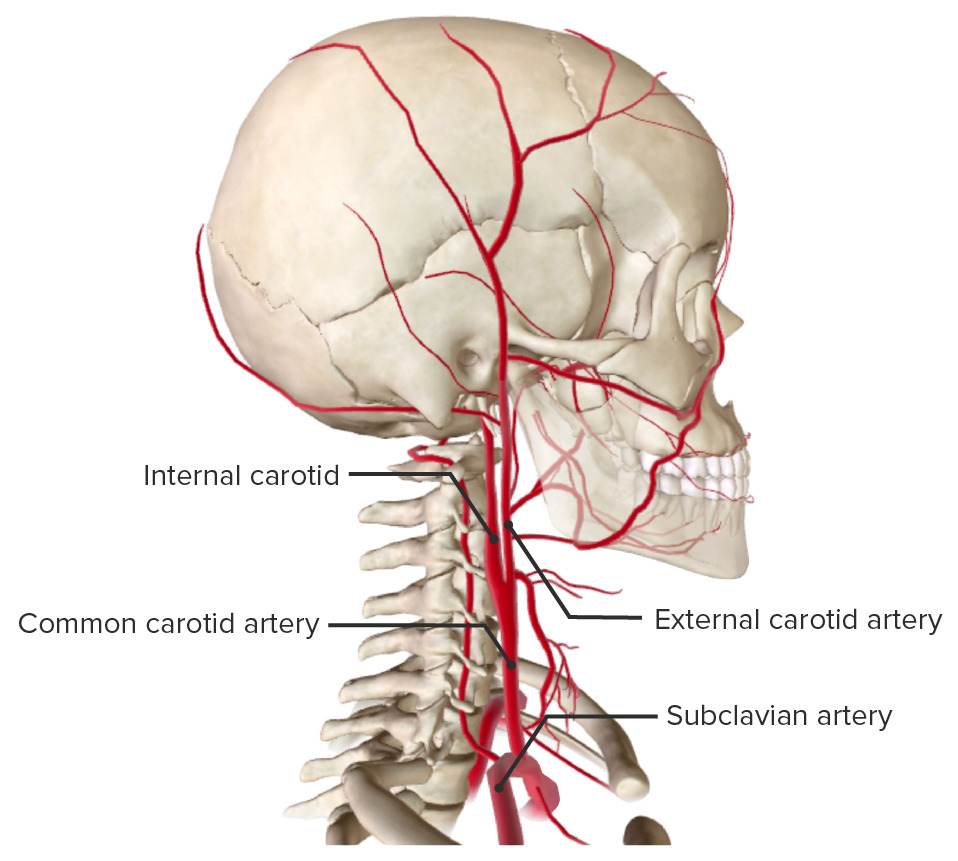
Carotid Arterial System: Anatomy
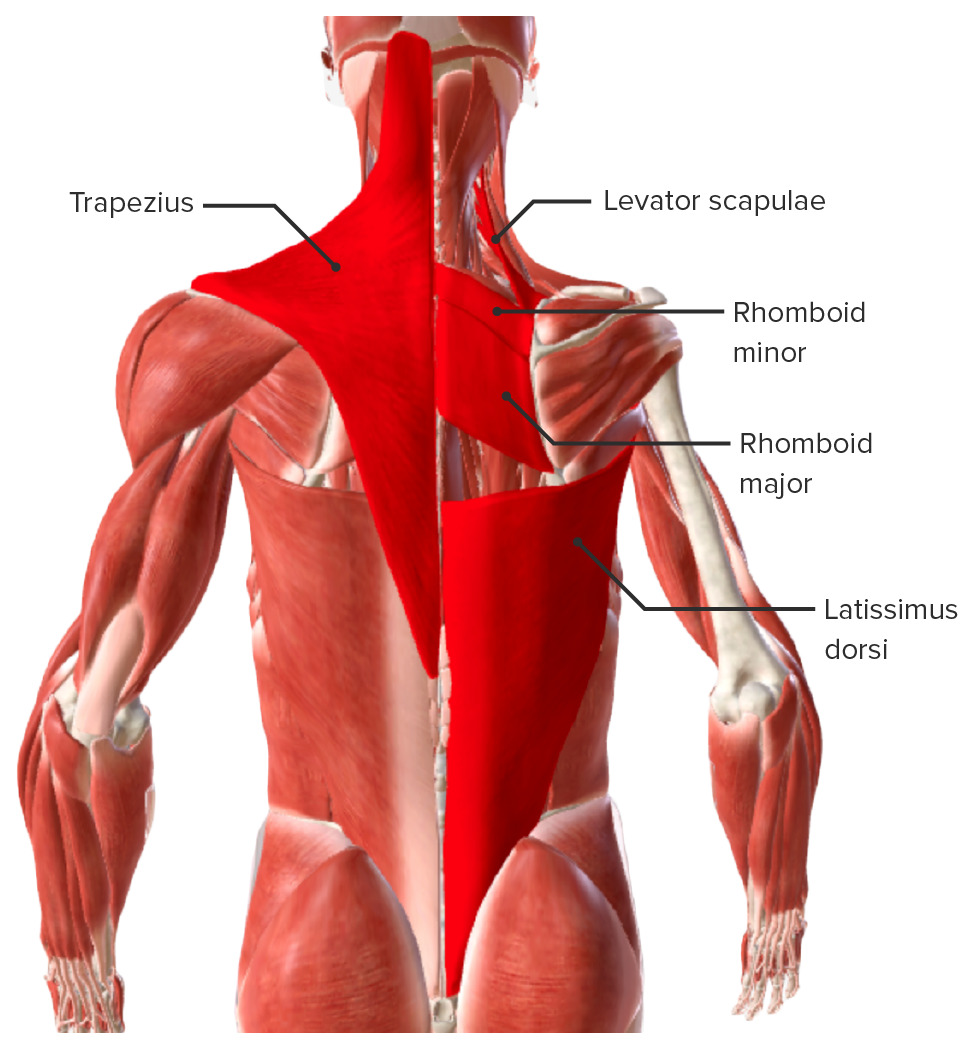
Muscles of the Back: Anatomy
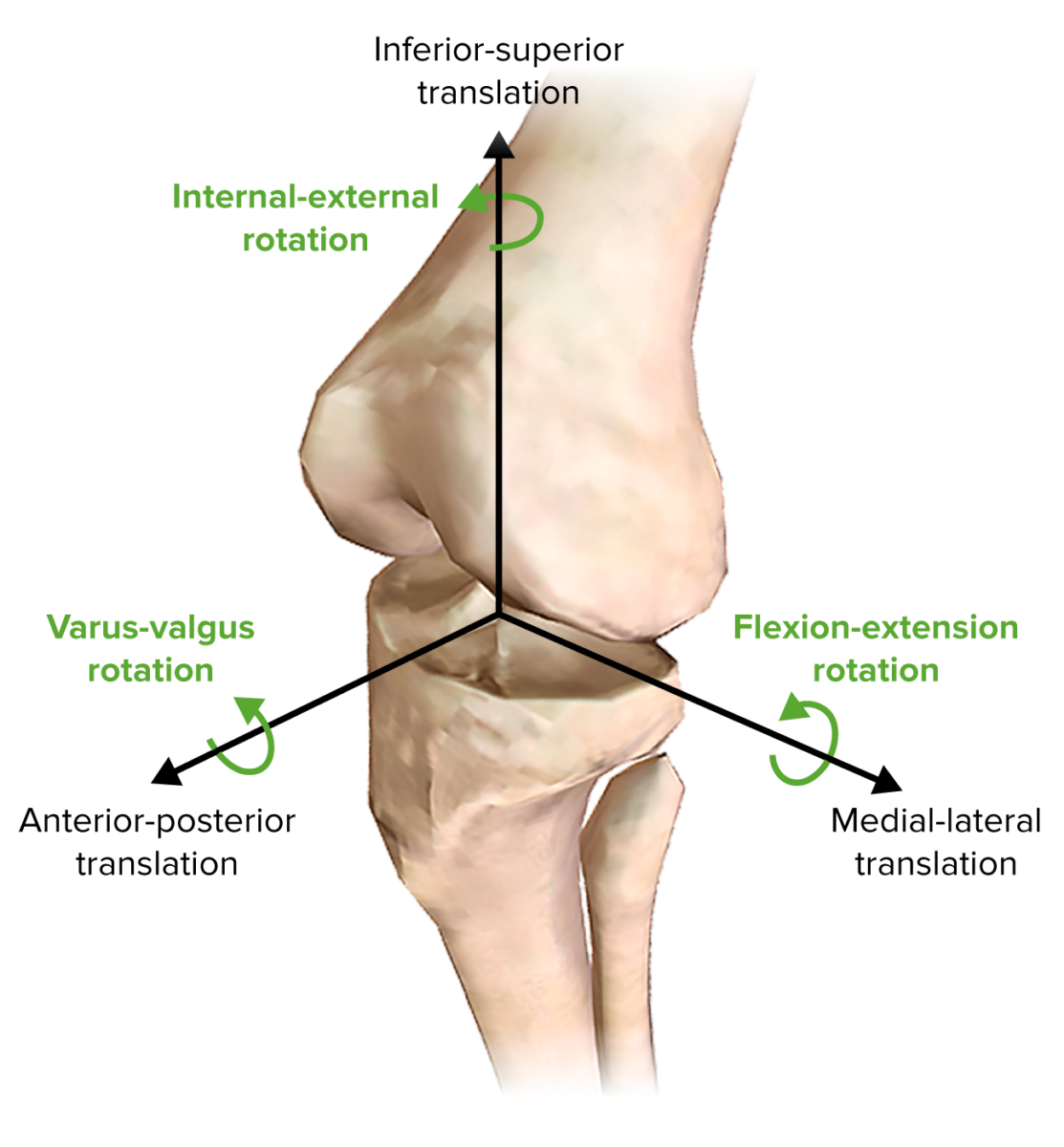
Knee Joint: Anatomy
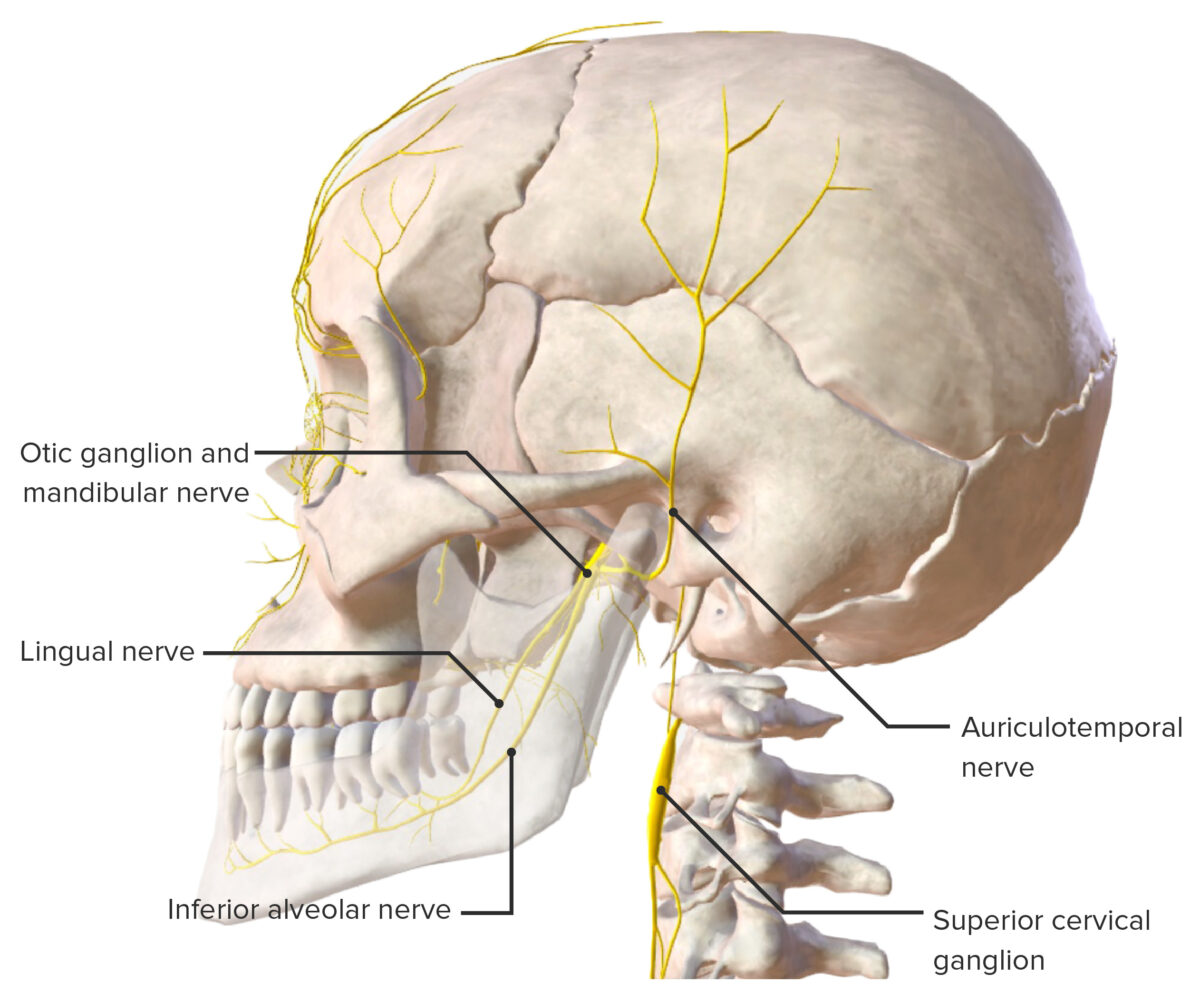
Jaw and Temporomandibular Joint: Anatomy
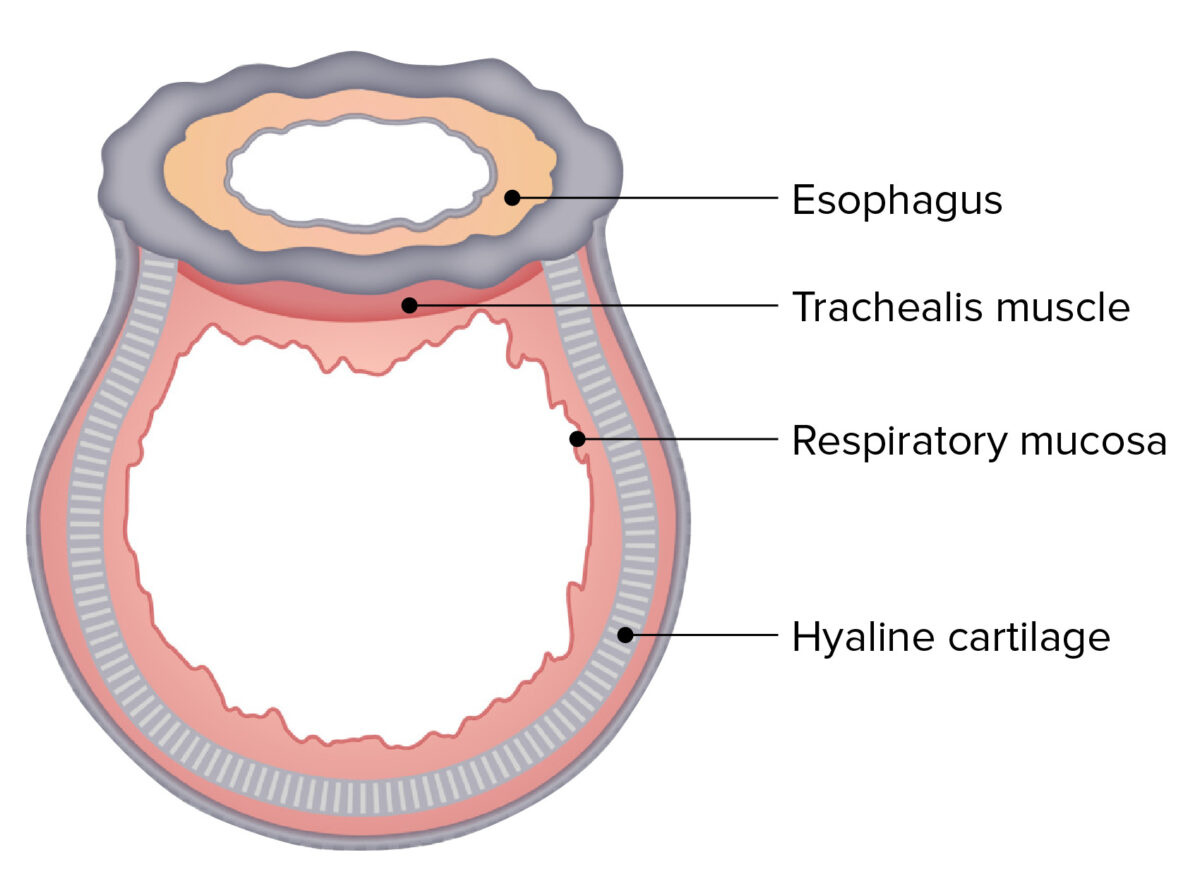
Trachea: Anatomy
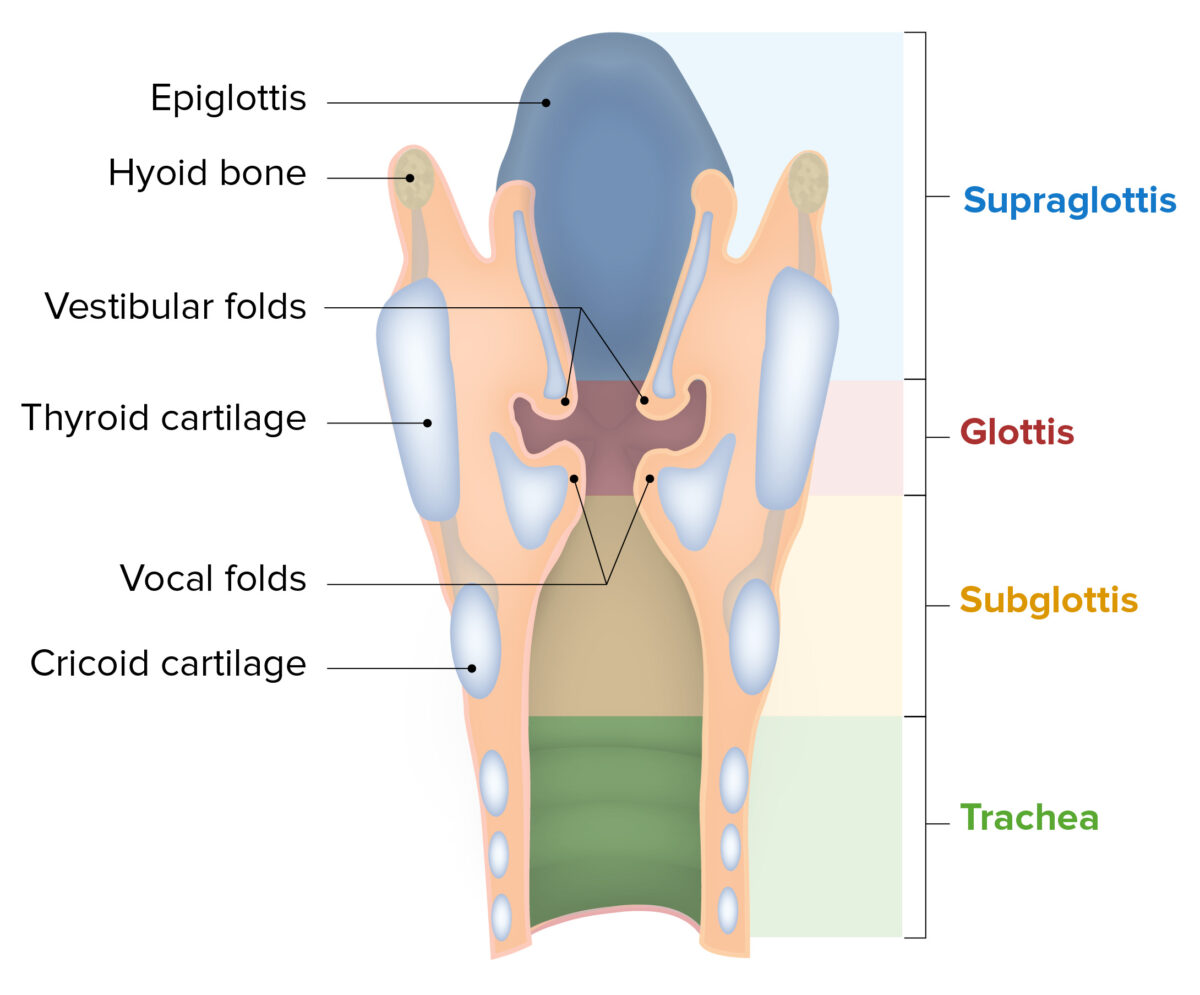
Larynx: Anatomy
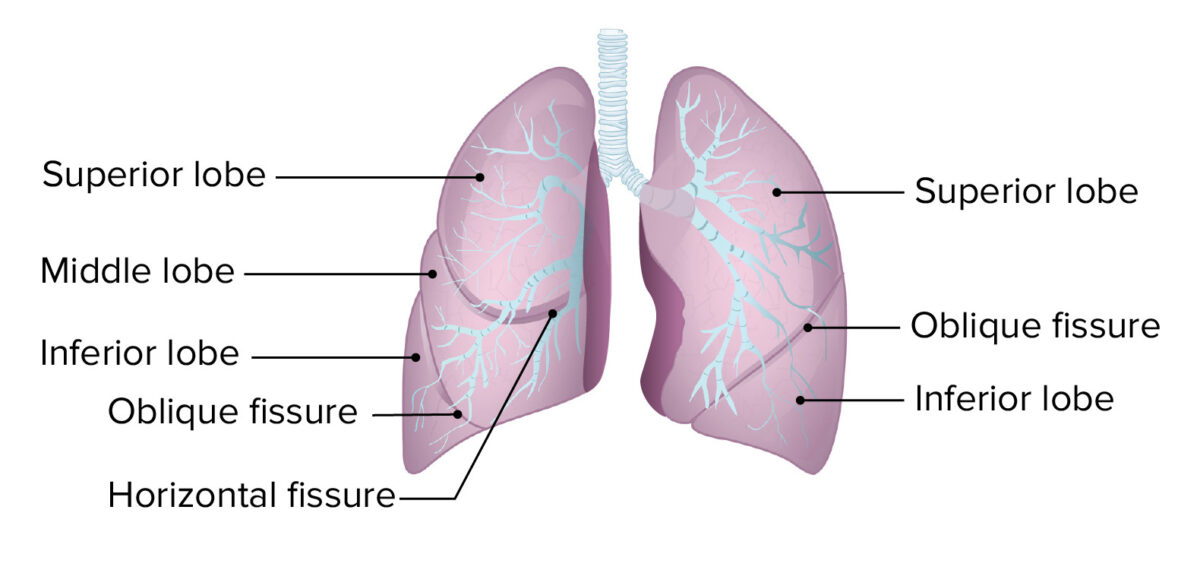
Lungs: Anatomy