Auditory and Vestibular Pathways: Anatomy
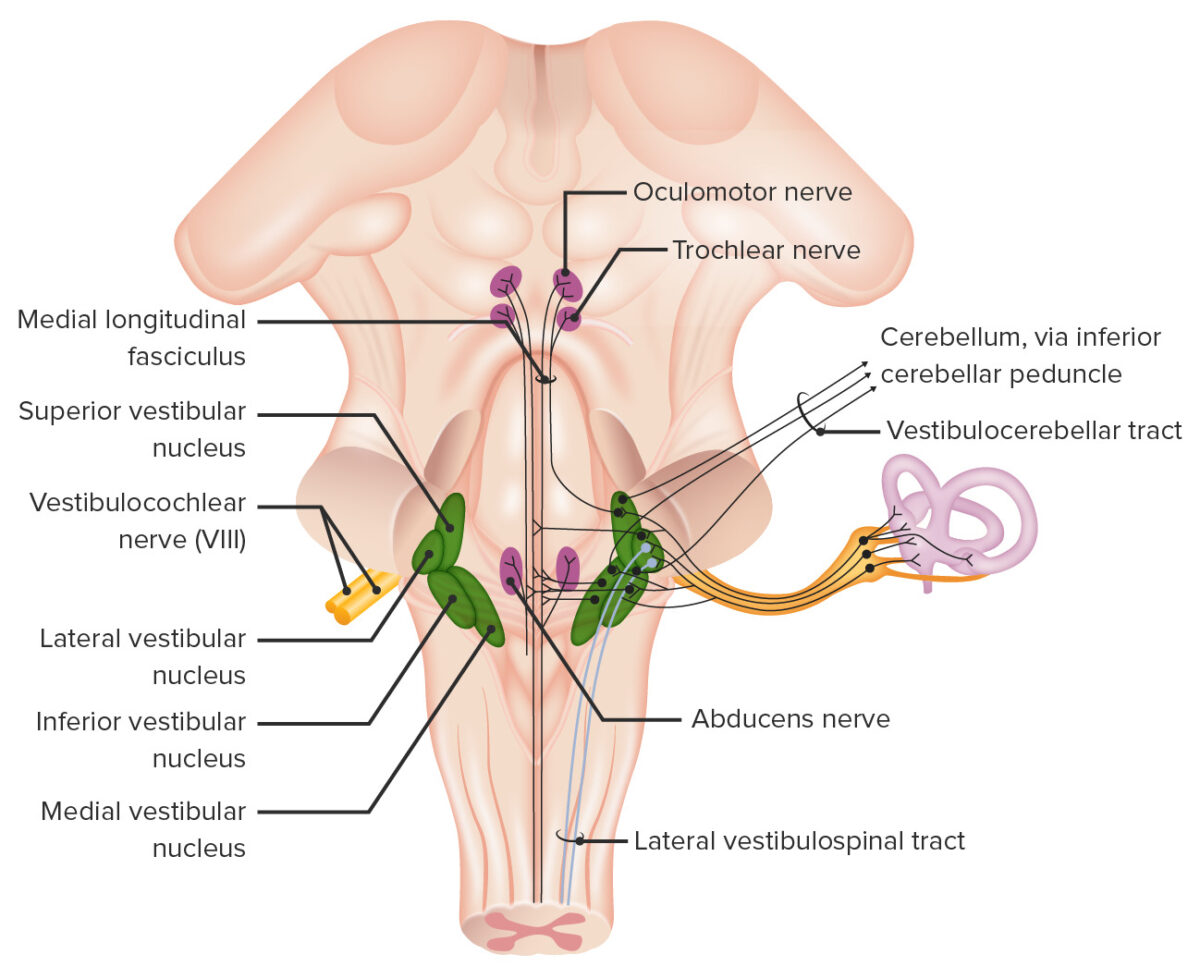
Auditory Pathway The auditory pathway of the brain begins with the external auditory canal and includes the middle/inner ear and eventually the brainstem nuclei before sending final signals to the primary auditory cortex in the temporal lobe. Peripheral components Central components Afferent fibers in CN VIII convey information from the organ of Corti → auditory […]
Pharynx: Anatomy
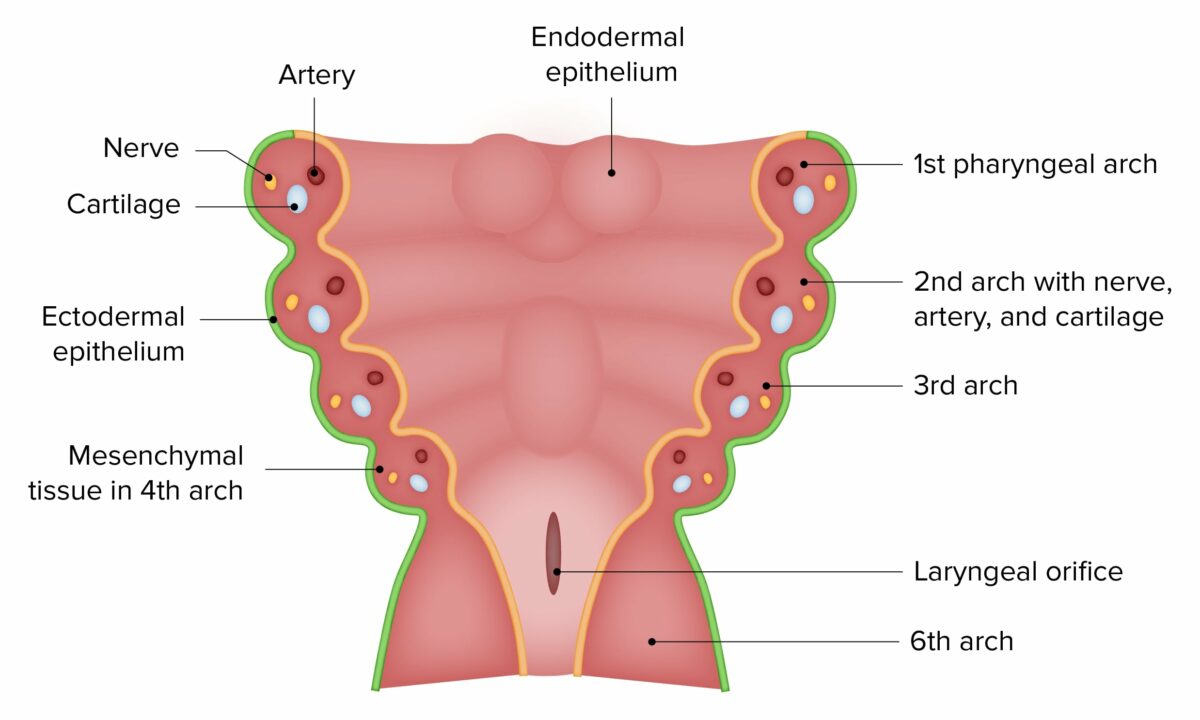
Development Formation of the pharyngeal (branchial) apparatus is during the 4th and 5th weeks of development. The pharyngeal apparatus consists of: Pharyngeal musculature develops from the 3rd, 4th, and 6th arches: Gross Anatomy Characteristics Divisions Muscles of the pharynx Constrictor muscles constitute the outer circular layer of muscle. During swallowing, constrictor muscles constrict to propel […]
Spleen: Anatomy
Development The spleen is the largest lymphatic organ in the body. Embryology Congenital variations Gross Anatomy Location Anatomic relationships Size Average measurements in normal healthy adults: Ligaments The spleen is connected to adjacent organs via several important ligaments. Surface anatomy Microscopic Anatomy The spleen consists of a capsule and inner tissue known as parenchyma. The […]
Olfaction: Anatomy
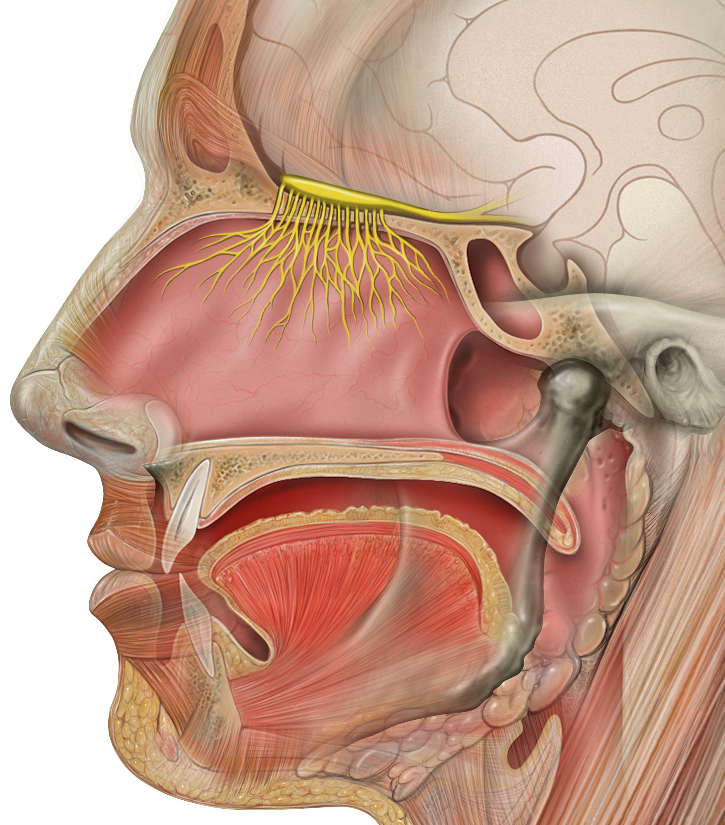
Introduction Structure of the nose Location of the olfactory epithelium Detection of smell Olfactory Epithelium and Nerve Olfactory epithelium The olfactory epithelium is a pseudostratified columnar epithelium overlying a lamina propria and consists of the following cell types: Olfactory nerve Olfactory Pathway Overview Odors are first detected at the olfactory bulb, where the information is […]
Limbic System: Anatomy
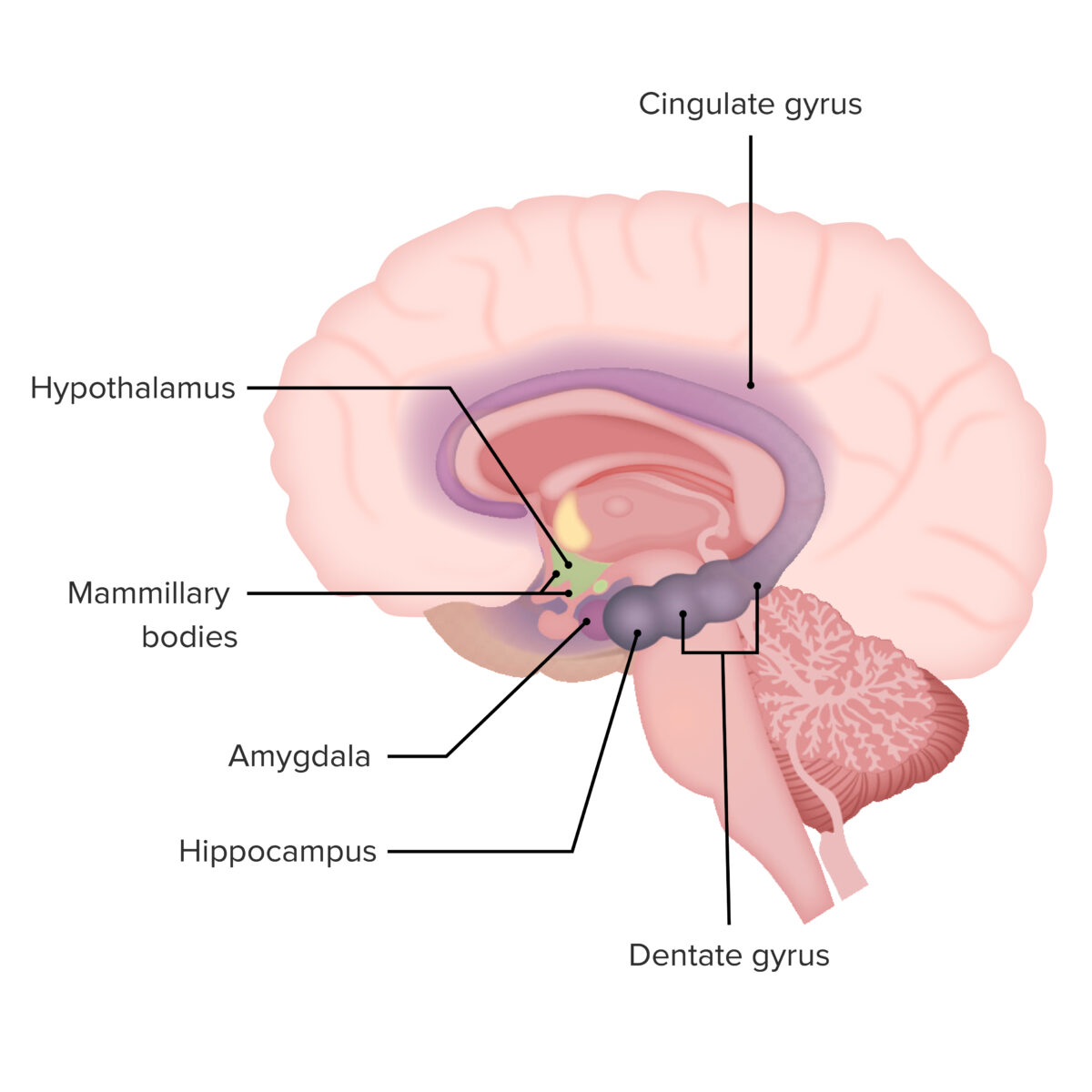
Structure and Function The limbic system is a highly integrated system of structures with feedback mechanisms to appropriately balance the continuous stream of information that is received. Structure The limbic system is composed of several structures that produce subconscious responses to stimuli: Functions Papez Circuit The Papez circuit is an interconnected network within the brain […]
Nose Anatomy (External & Internal)

Functions of the Nose The nose assists with numerous body functions, ranging from the vital process of respiration to the augmentation of taste. Respiration Olfaction Purification and moisturizing of inhaled air Sense of taste Speech The External Nose (+ Diagram) Structure (skin, bony components, nasal cartilage) The external nose is pyramidal in shape. The nose […]
Palate: Anatomy
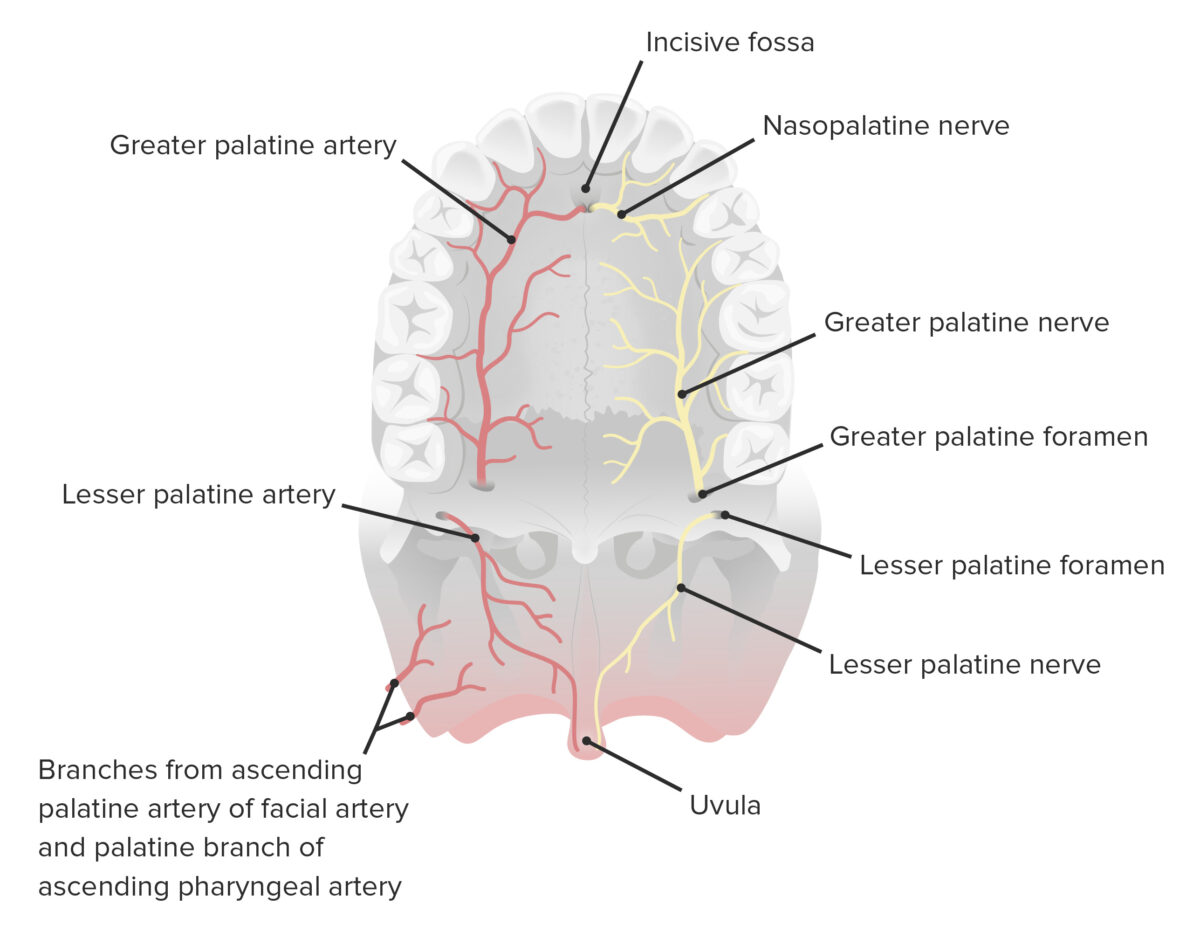
Embryology The embryology of the palate is complex, with a critical stepwise process to midline fusion. Interruption of this process can result in cleft disorders. Process: Medial nasal prominences fuse and descend. Primary palate moves posteriorly. Palatine shelves fuse with each other and with the nasal septum. Secondary palate is formed. Primary palate fuses with […]
Peritoneum: Anatomy
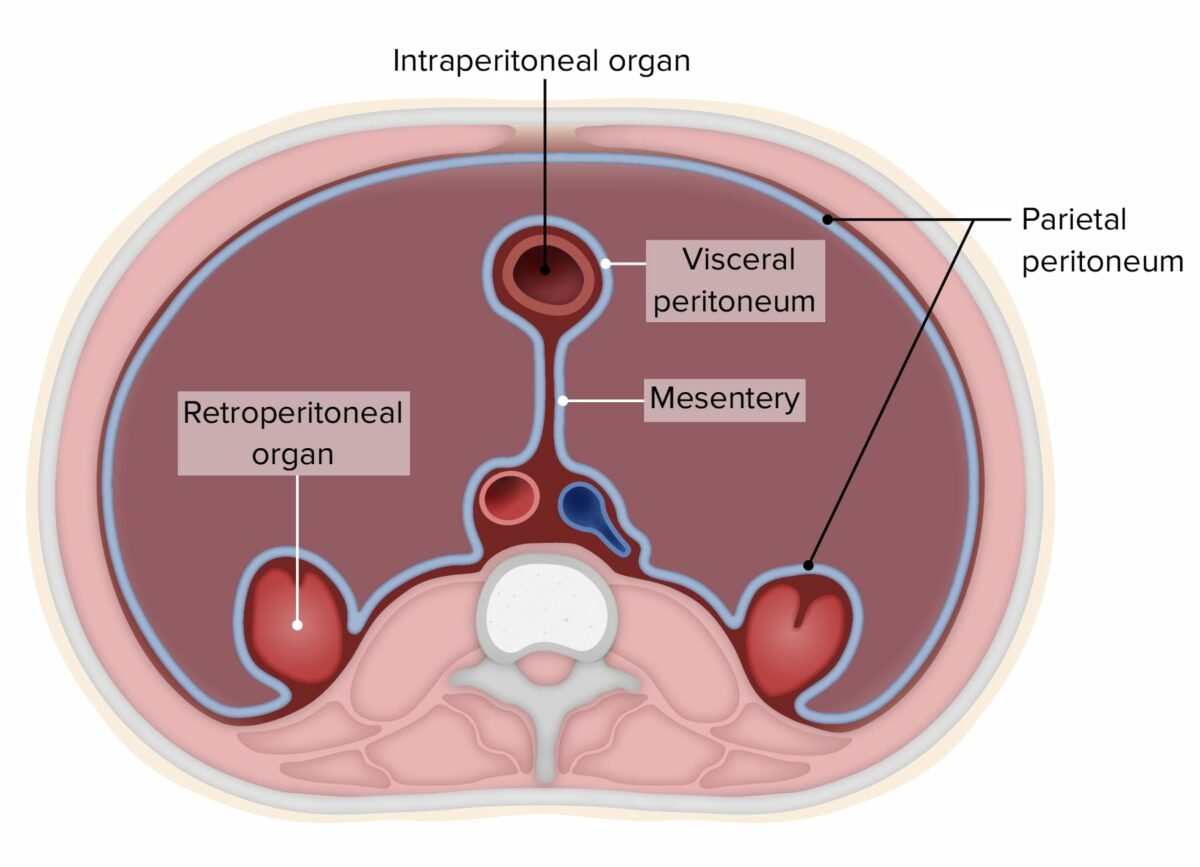
Overview Definition The peritoneum is a serous membrane lining the abdominopelvic cavity and covering its organs. Development The peritoneum develops from the mesoderm of the trilaminar embryo: Peritoneum and the Peritoneal Cavity Anatomy of the peritoneum Visualizing the peritoneal cavity Boundaries of the peritoneal cavity Intraperitoneal versus retroperitoneal organs Organs can be classified according to […]
Rectum and Anal Canal: Anatomy
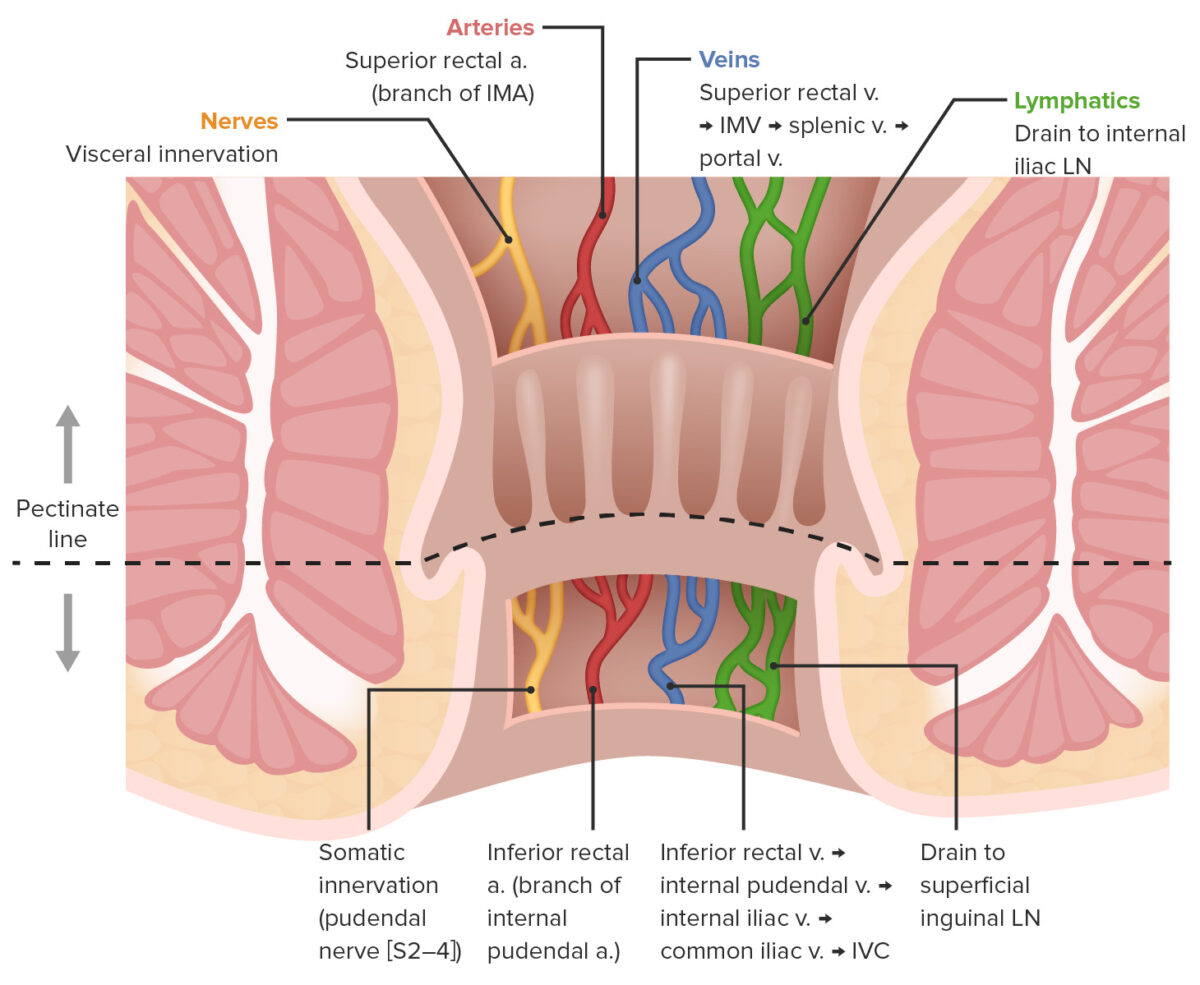
Development Gross anatomy Rectum Anal canal Anatomic relations The rectum is the most posterior visceral organ in the pelvic cavity. Microscopic Anatomy Similar to other segments of the GI tract, the layers of the anorectal wall (from the inner lumen outward) are mucosa → submucosa → muscular layer → serosa. There are no villi or […]
Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy
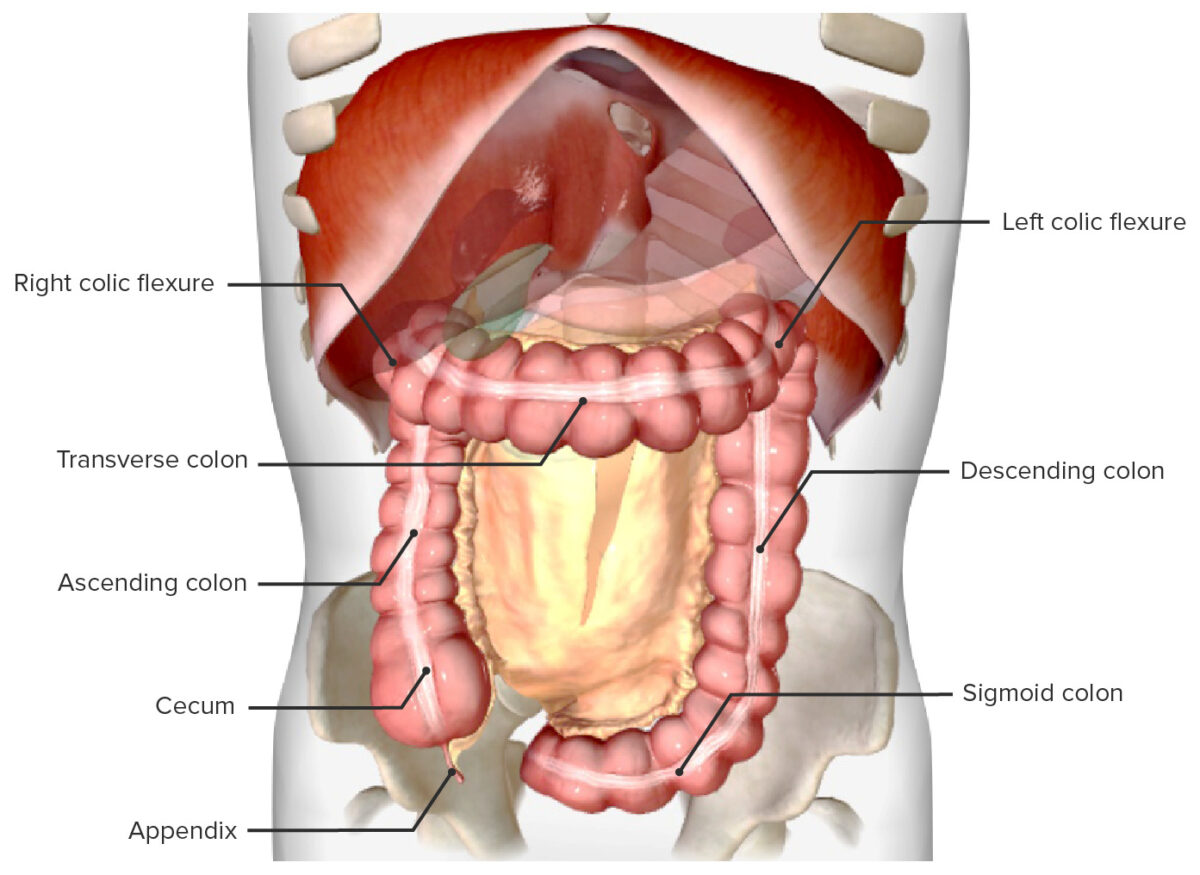
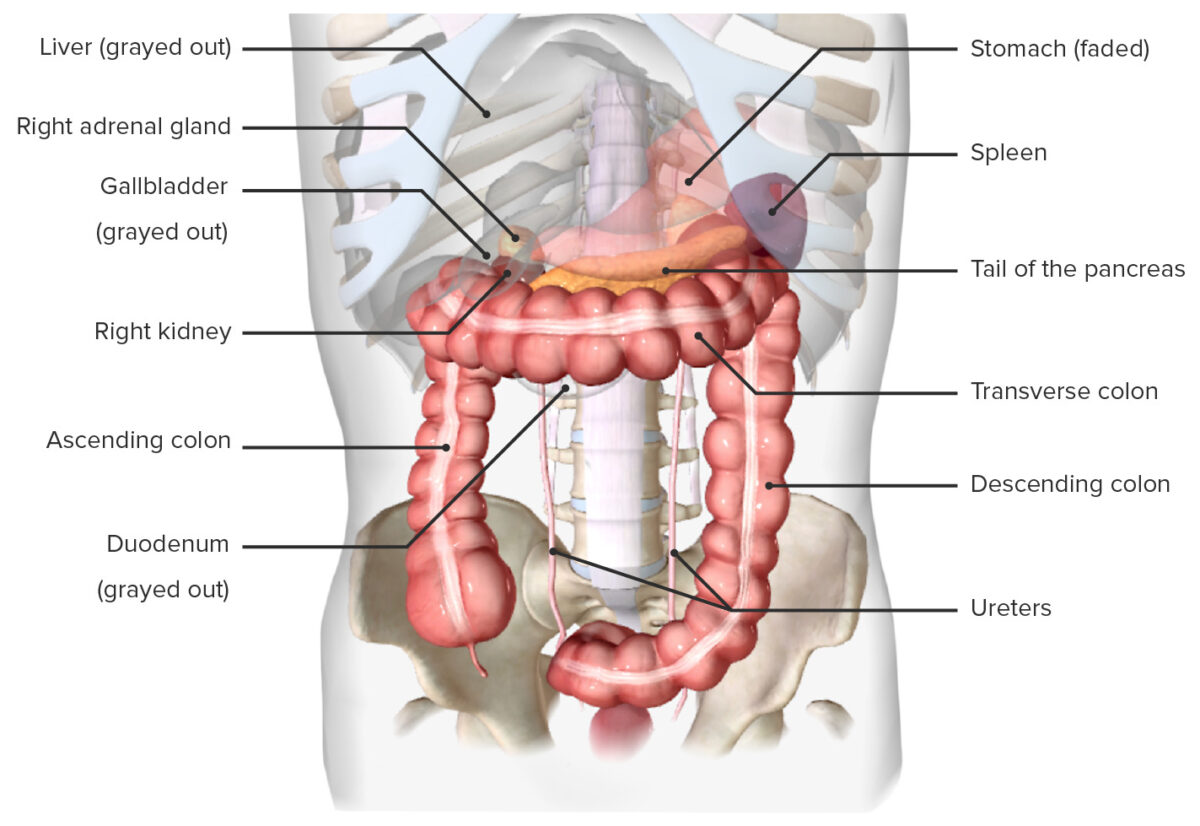
Development The large intestines develop from the primitive midgut and hindgut: Gross Anatomy Parts of the large intestine Mesenteries and intraperitoneal versus retroperitoneal location General characteristics of the colon Cecum Appendix Ascending colon Transverse colon Descending colon Sigmoid colon Gross anatomic features unique to the colon Several anatomic features distinguish the large intestine from the […]