Heart: Anatomy
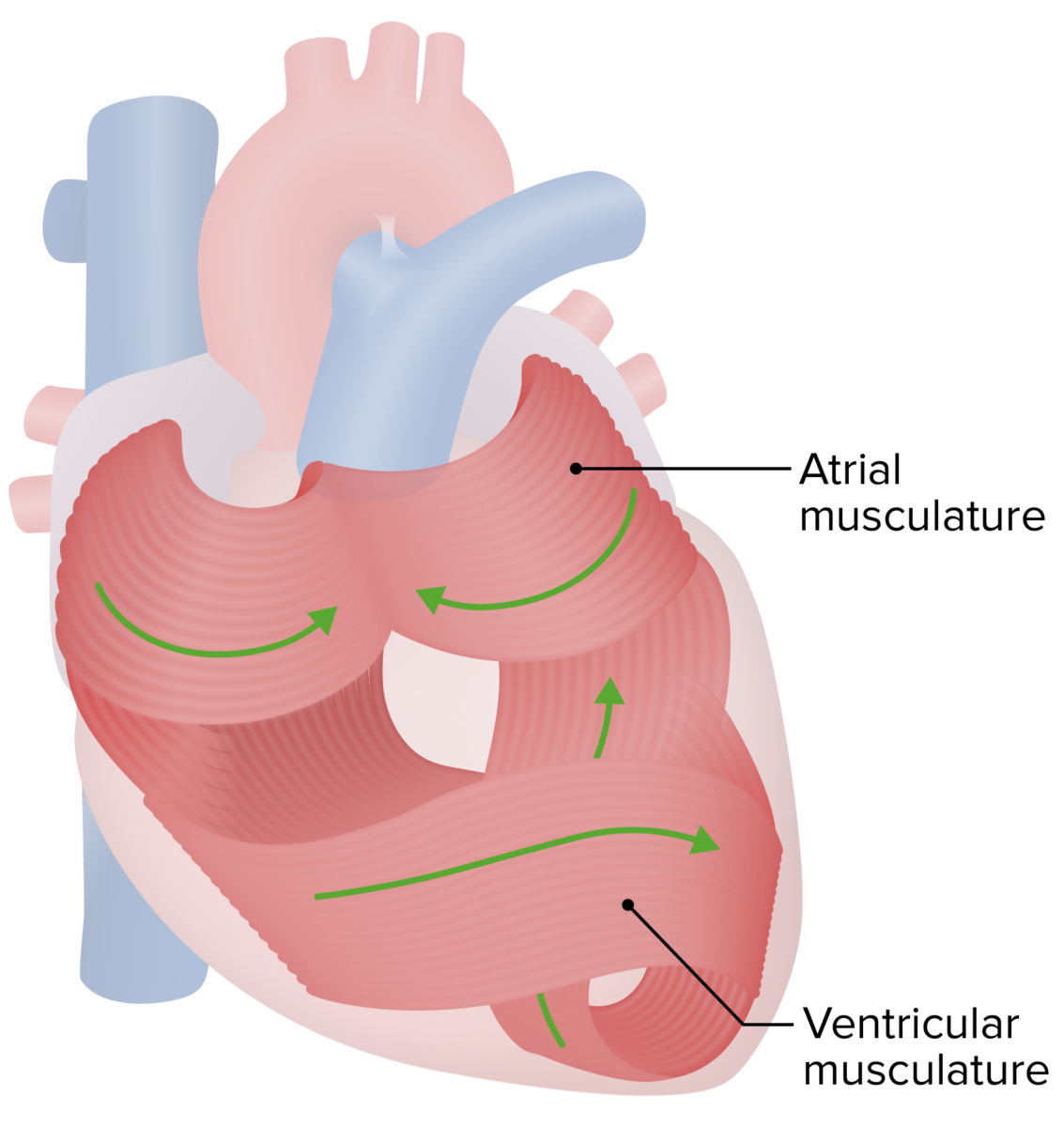
General Structure and Location of the Heart Overview of the heart structure The heart is a 4-chambered muscular pump made of cardiac muscle tissue. Size and shape Location and orientation Anatomic relationships The Pericardium Like the pleural cavity around the lungs and the peritoneal cavity inside the abdomen, the pericardial cavity around the heart is […]
Basal Ganglia: Anatomy
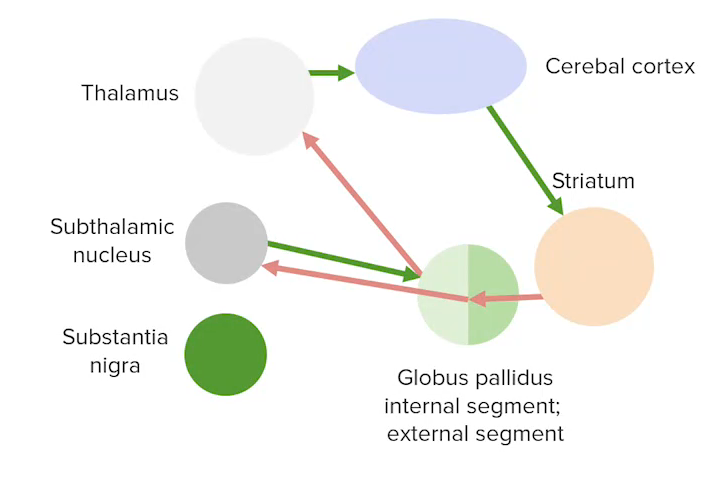
Development General Features Definition The basal ganglia are a cluster of subcortical nuclei deep to cerebral hemispheres and are involved in the initiation, maintenance, and inhibition of movement. Major structures The striatum (neostriatum) is composed of: The lenticular nucleus is made up of: Substantia nigra: Subthalamic nucleus: Functions Vasculature Neural Pathways and Intrinsic Relations Pathways […]
Spinal Cord: Anatomy
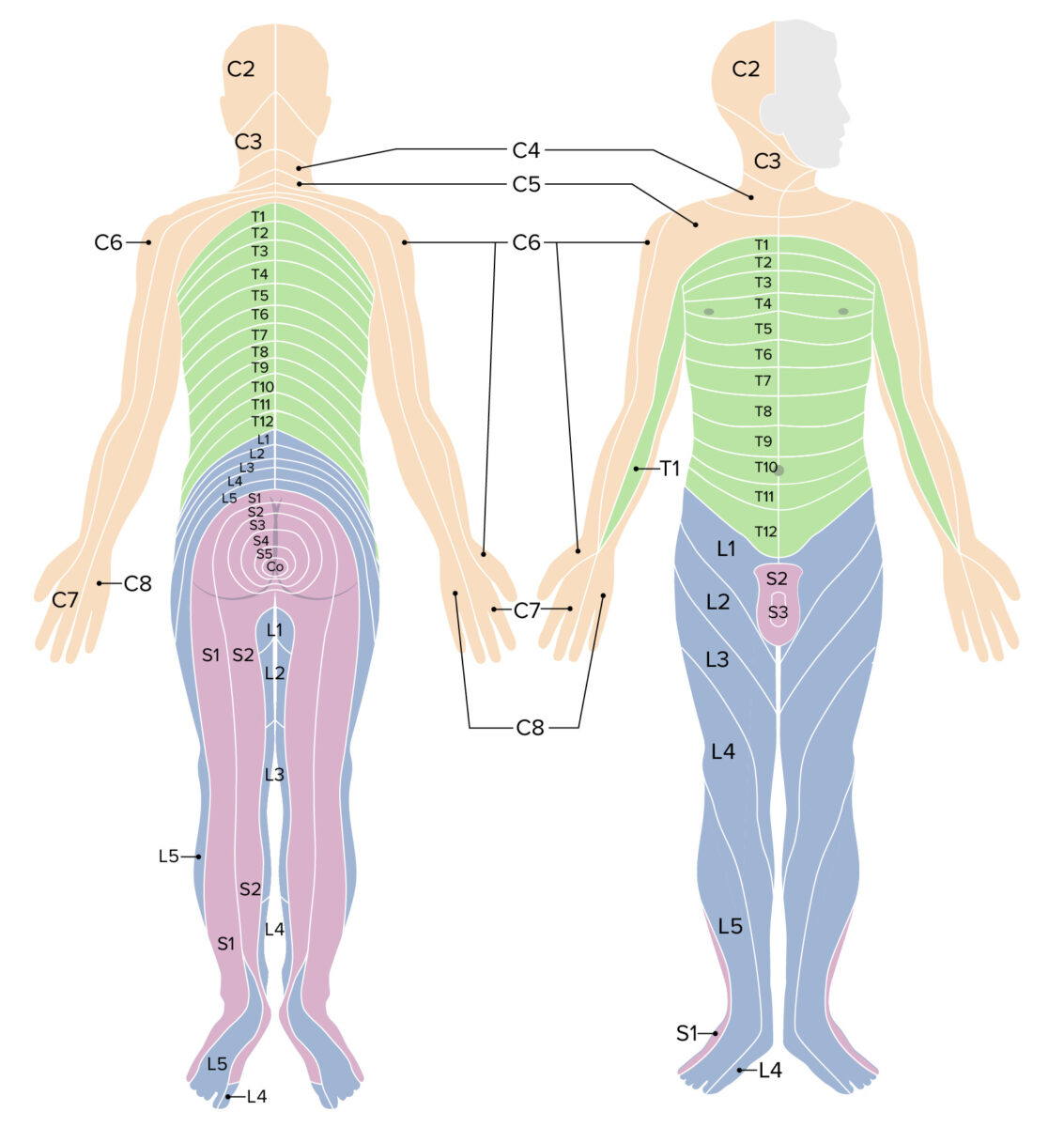
Development Summary of neurulation Neurulation is the process by which ectoderm in the trilaminar embryo develops into the neural tube. This process occurs as the cells destined to become the spinal cord progress through the following structures: Differentiation of the spinal cord The neural tube differentiates into 3 layers. Gross Anatomy General structure Cross-sectional anatomy […]
Autonomic Nervous System: Anatomy
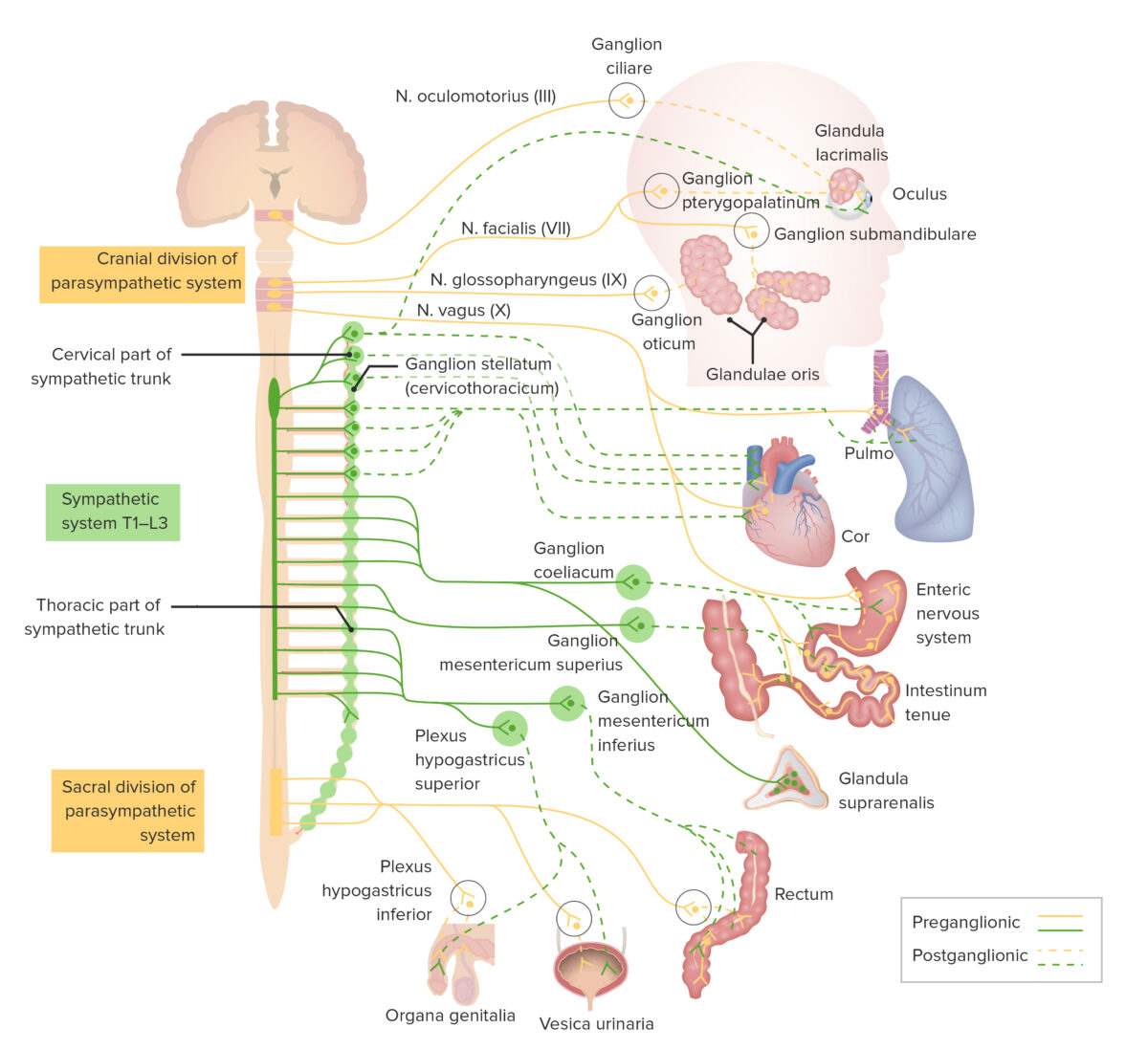
Overview Definition The ANS is responsible for controlling functions that do not require conscious thought. Components Divisions of the ANS Sympathetic Nervous System The SNS is involved with many of the functions associated with the “fight-or-flight” response. Although this response is at the extreme end of the sympathetic physiology spectrum, it serves as a model […]
Triangles of the Neck: Anatomy
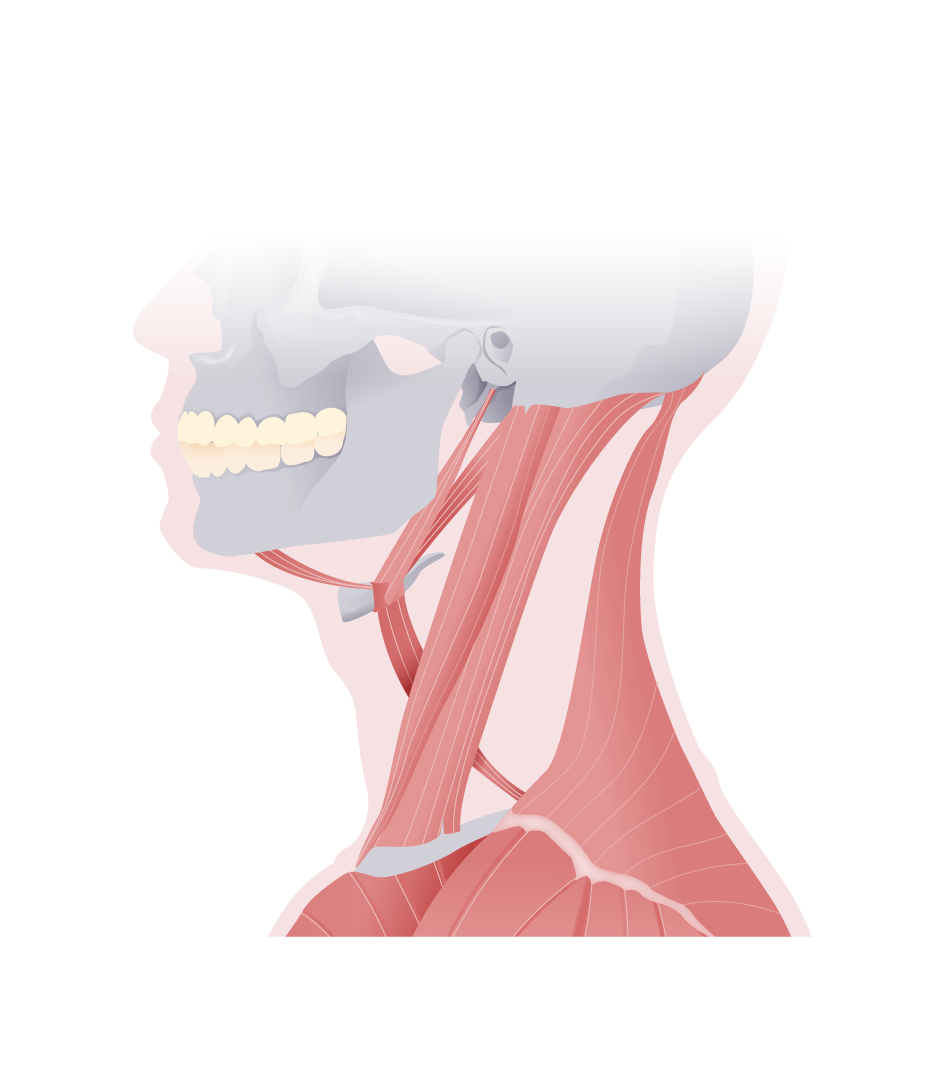
Overview Anterior Triangle Overview Muscular triangle Boundaries: Contents: Carotid triangle Boundaries: Contents: Submandibular triangle Boundaries: Contents: Submental triangle Boundaries: Contents: Posterior Triangle Overview Occipital triangle Boundaries: Contents: Supraclavicular triangle The supraclavicular triangle is also called the omoclavicular or subclavian triangle, and it is smaller with the arm raised and bigger with the arm/clavicle depressed. Boundaries: […]
Kidneys: Anatomy
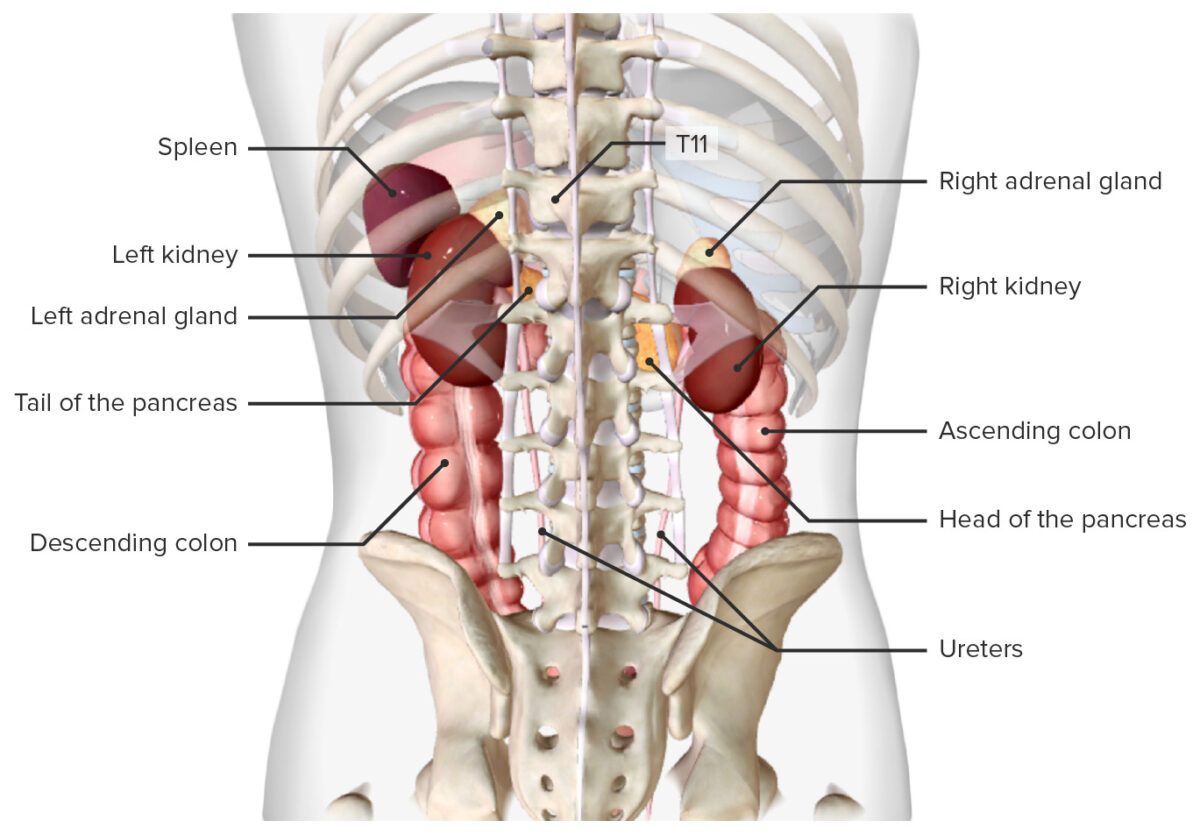
Embryology The kidney develops from embryonic mesoderm in 3 successive forms from the nephrogenic cords as they elongate in a cranial-to-caudal direction. Pronephros Mesonephros Metanephros The permanent kidney is formed from the metanephros. Position of the kidney and changes in vascularization Gross Anatomy Location Anatomical relations Table: Anatomic relations of the kidneys Direction (in relation […]
Diaphragm: Anatomy
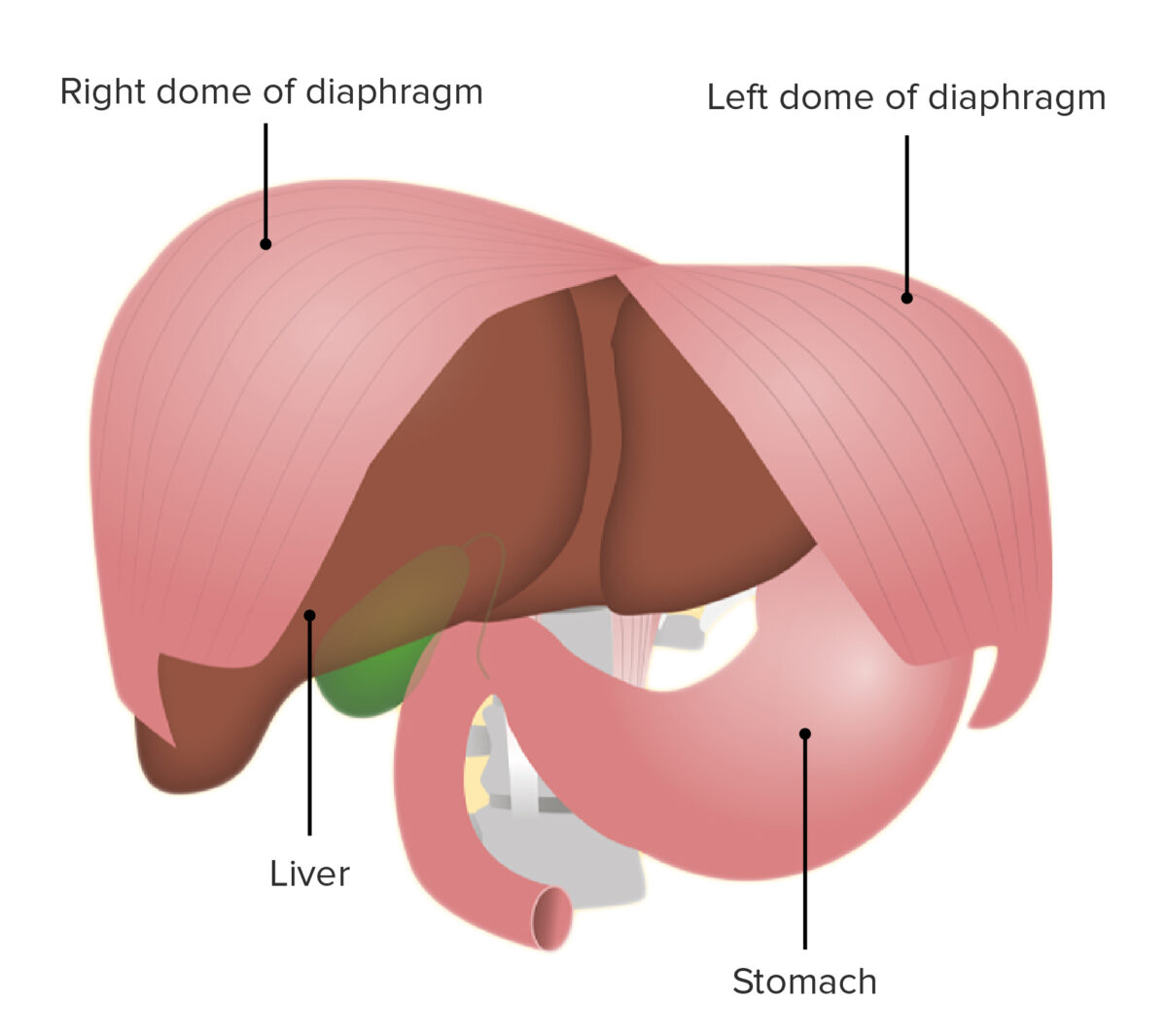
Embryology Anatomy Parts The diaphragm consists of 3 parts, all of which insert into the central tendon. Domes Surfaces Openings Table: Openings in the diaphragm through which the chest communicates with the abdomen Opening Location Passage for Vena caval foramen At level of T8–T9 Inferior vena cava Right phrenic nerve Esophageal hiatus At level of […]
Testicles: Anatomy
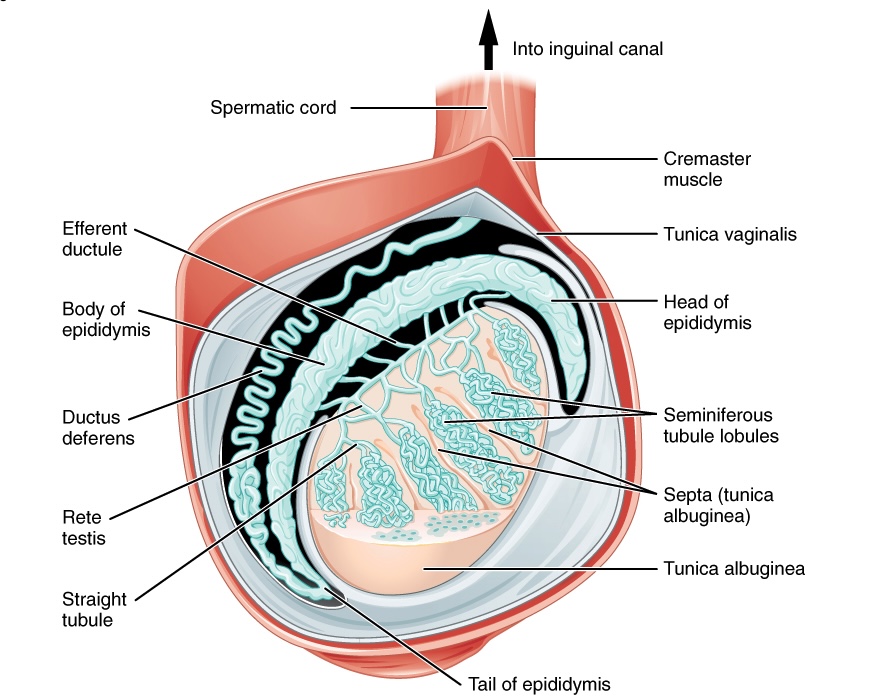
Embryology Male development Testicular development Gross Anatomy Testes (the male gonads) are responsible for the production of sperm and testosterone: Microscopic Anatomy Blood vessels, lymphatics, and the genital ducts enter the mediastinum of the testis and give rise to numerous lobules composed of seminiferous tubules and interstitial tissue: Seminiferous tubules Interstitial tissue Epididymis The epididymis […]
Breasts: Anatomy
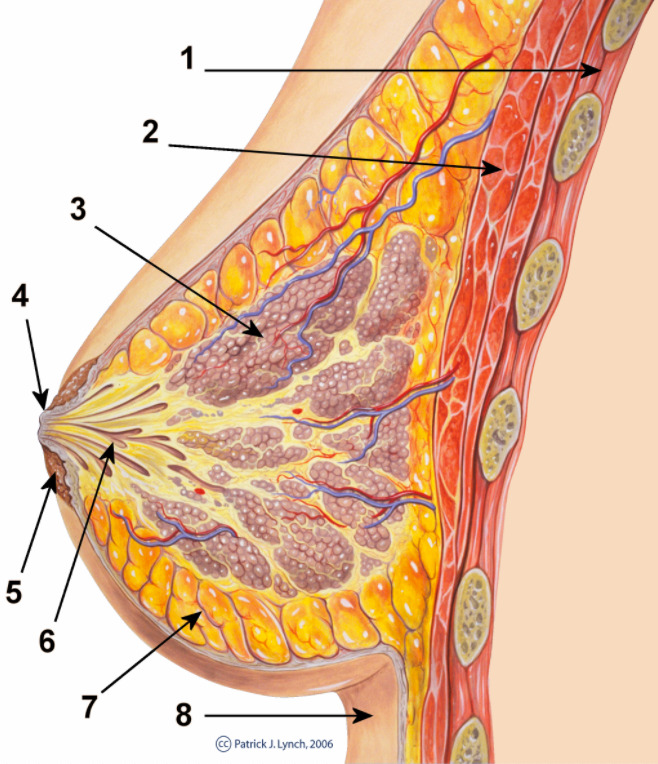
Gross Anatomy of the Breast The breasts are paired organs on the anterior chest wall and are composed of modified apocrine sweat glands arranged into lobules and ducts. Location and structure Location: Structure: Development Microscopic Anatomy of the Mammary Gland The mammary gland is composed of modified apocrine sweat glands divided into lobules, which reach […]
Ear: Anatomy
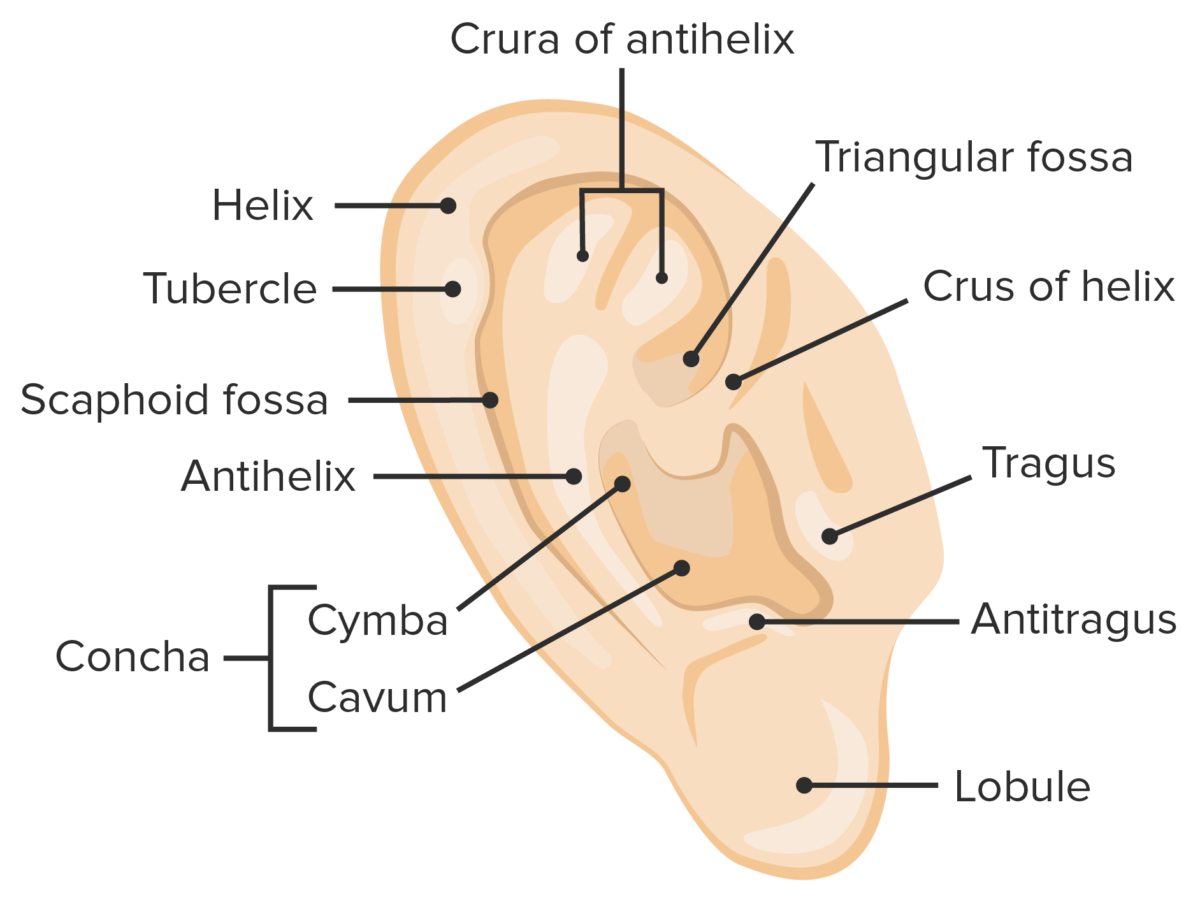
Embryology of the Ear Development of the ear begins at 3 weeks of gestation and is usually complete by 20 weeks of gestation. Inner ear Middle ear Outer ear Outer Ear Anatomy Auricle The auricle is composed of musculocutaneous tissue and elastic cartilage covered by skin. This structure is responsible for collecting and redirecting sound […]