Prostate, Seminal, and Bulbourethral Glands: Anatomy
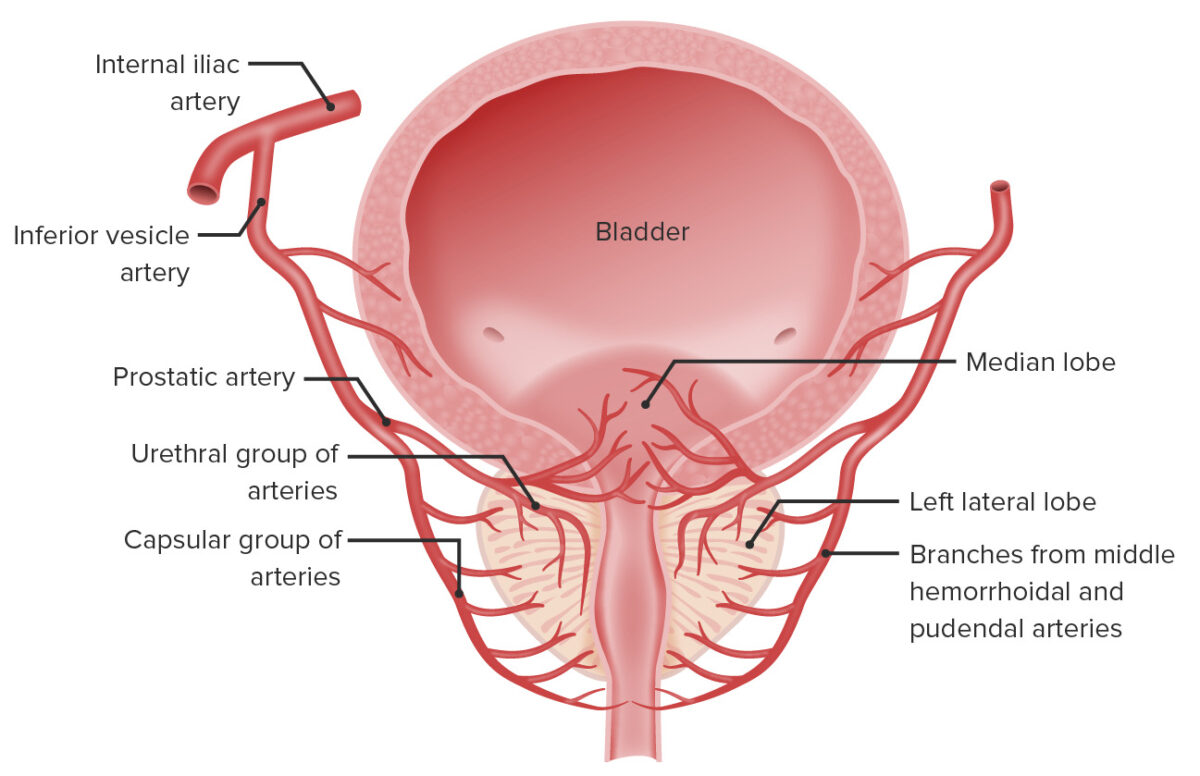
Development Gross Anatomy Structure of the prostate Accessory glandular structures Neurovasculature and Lymphatics Arterial supply Blood vessels supplying the prostate arise from the internal iliac artery and enter the gland from the posterolateral region. Venous drainage Lymphatic drainage Innervation Microstructure The prostate consists of glandular tissue and fibromuscular tissue. Clinical Relevance References
Ankle Joint: Anatomy
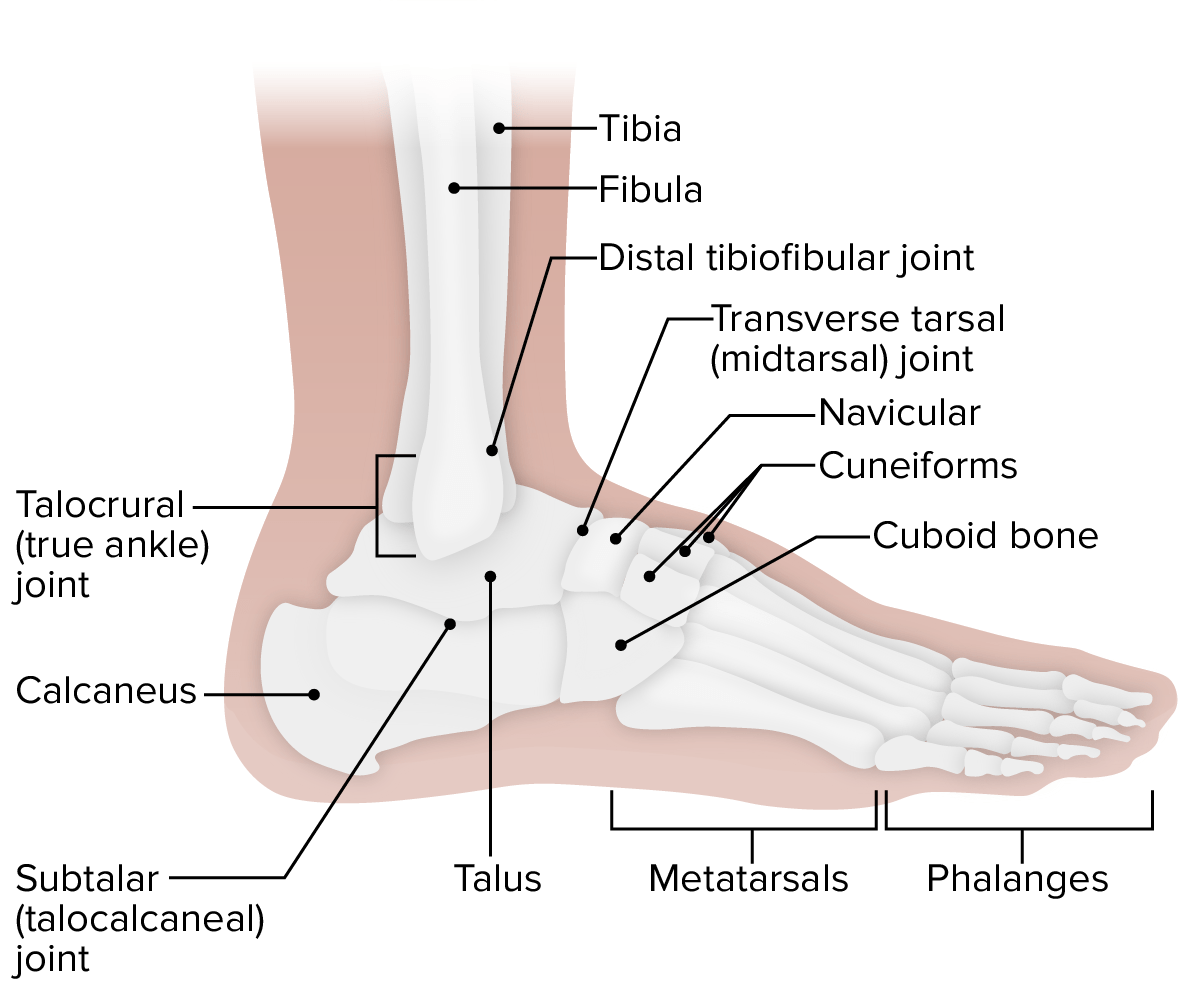
Bones of the Ankle The ankle is a synovial joint that consists of articulations between the tibia, fibula, and talus, which are reinforced by the medial, lateral, and syndesmotic ligament. Generally, the ankle joint has a shape that is wider superiorly and anteriorly to accommodate the wedge-shaped talus, which contributes to joint stability. Joints of […]
Foot: Anatomy
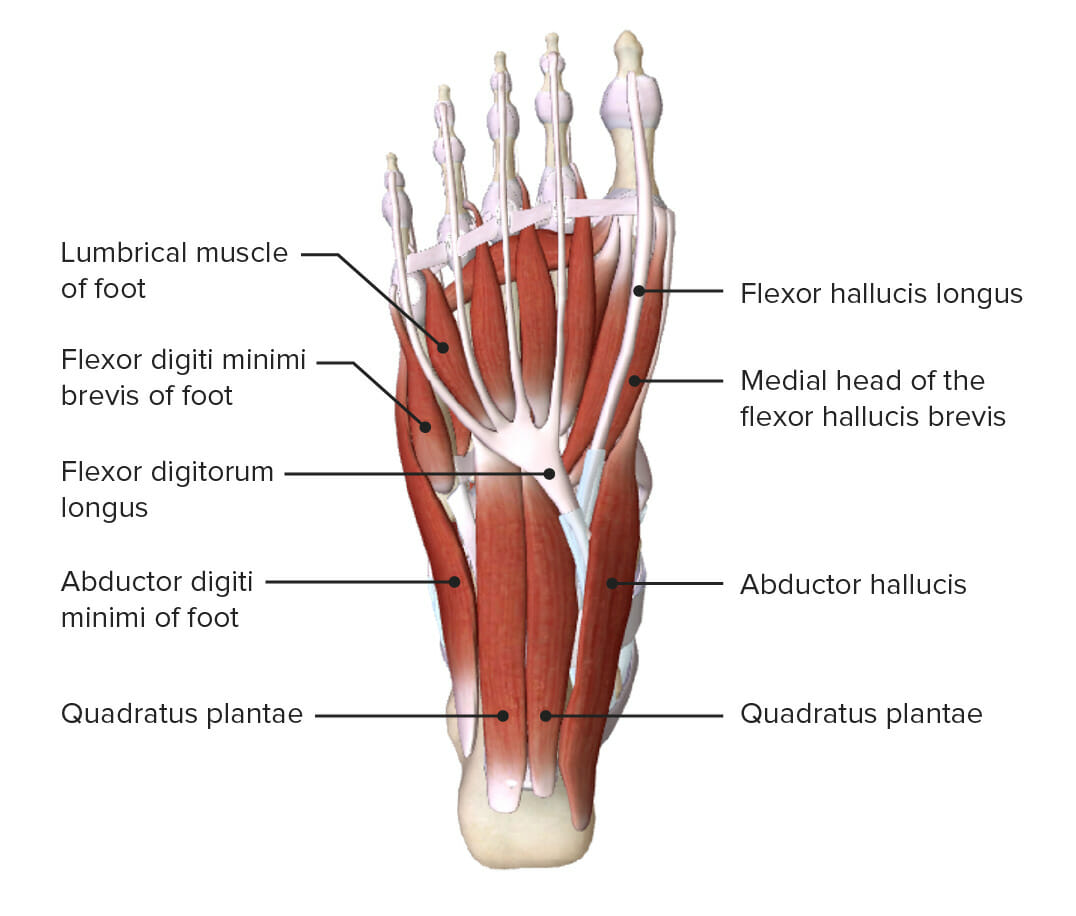
Bones and Joints Bones of the foot The 26 bones of the foot are divided into 3 groups: tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges. Mnemonic From superior to inferior and from medial to lateral in a right foot: Talus, Calcaneus, Navicular, Medial cuneiform, Intermediate or middle cuneiform, Lateral cuneiform, Cuboid Joints of the foot The joints of […]
Posterior Abdominal Wall: Anatomy
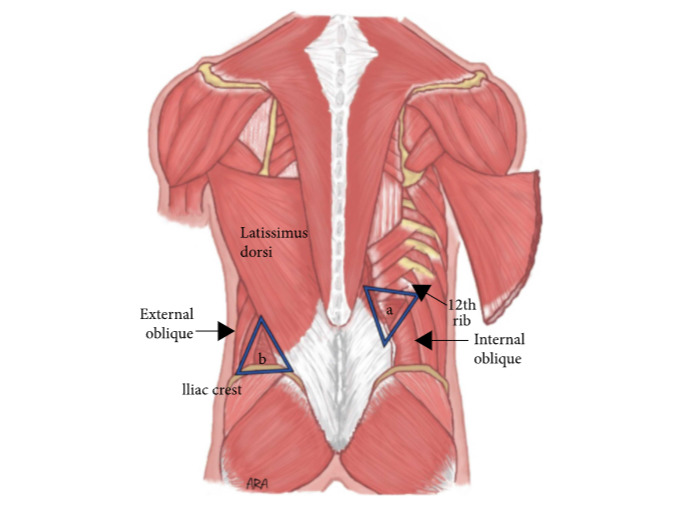
Introduction Posterior abdominal wall Structures Fascia and Related Structures of the Posterior Abdominal Wall Thoracolumbar fascia Large area of connective tissue that is made up of 3 layers: Psoas fascia Lumbar triangles Similarly to the anterior abdominal wall, herniation can occur in weakened areas in the posterior abdominal wall. These herniations occur in the Grynfeltt-Lesshaft […]
Uterus, Cervix, and Fallopian Tubes: Anatomy
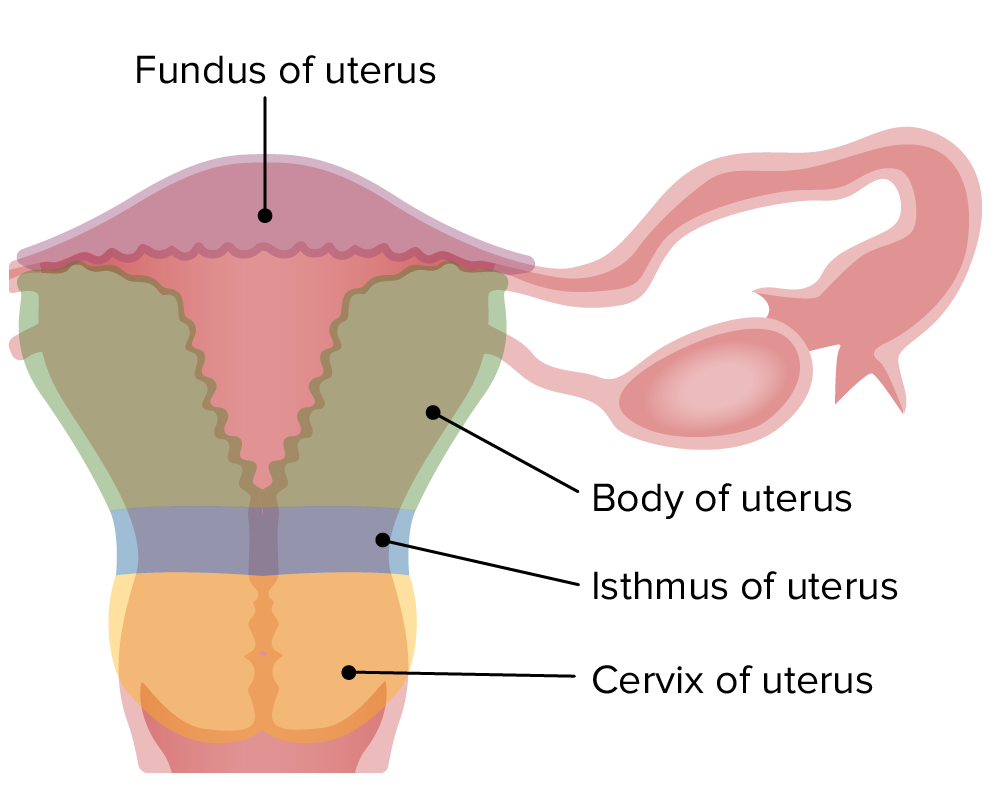
Overview and Development Overview The uterus, cervix, and fallopian tubes are all important organs in the female reproductive tract. Location The uterus and fallopian tubes are pelvic organs. Function Embryologic development Gross Anatomy Structure and size of the uterus Parts of the uterus Uterine orientations The uterus is often tilted or bent forward or backward. […]
Eye: Anatomy
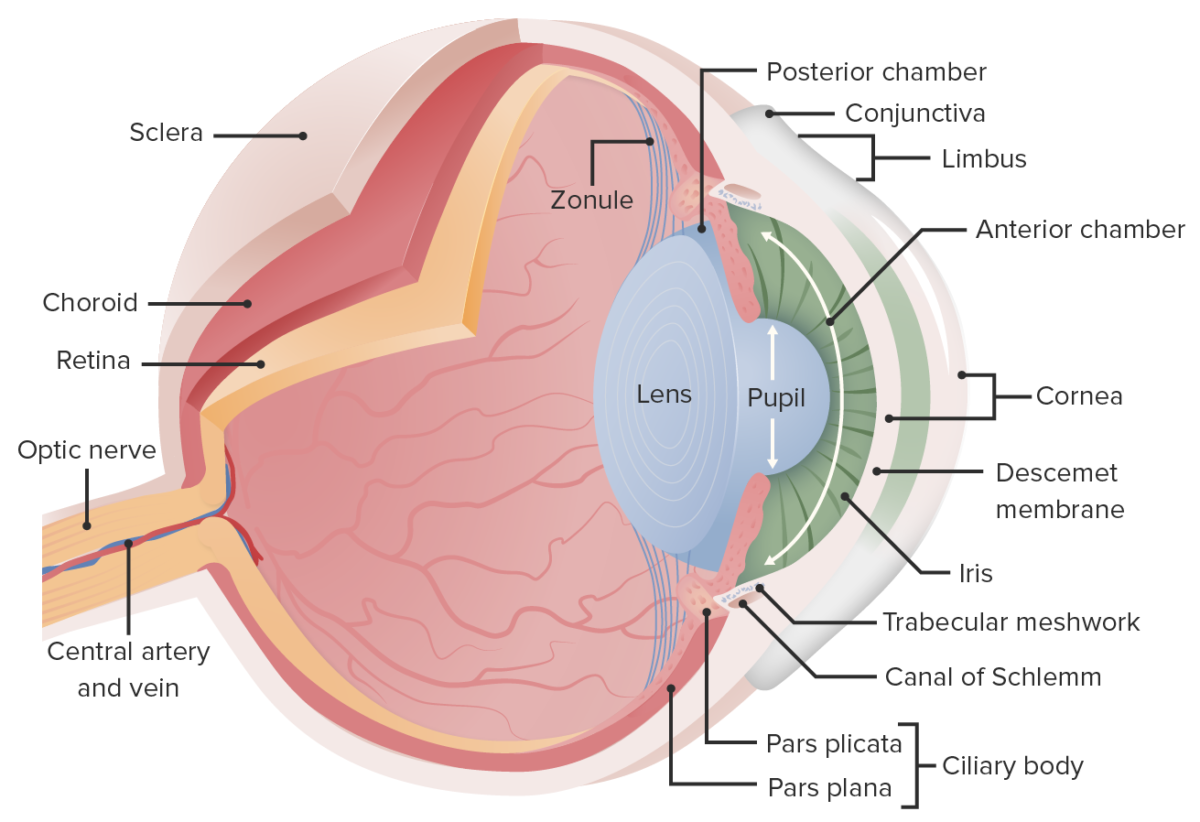
Development General Timeline Gross Anatomy General characteristics The adult eye is a complex organ contained within the orbital cavity (composed of 7 bones). Each eye has multiple layers and chambers and is surrounded by 6 extraocular muscles. Layers of the eye The eye is composed of 3 layers (fibrous, vascular, neural) and a transparent connective […]
Pelvis: Anatomy
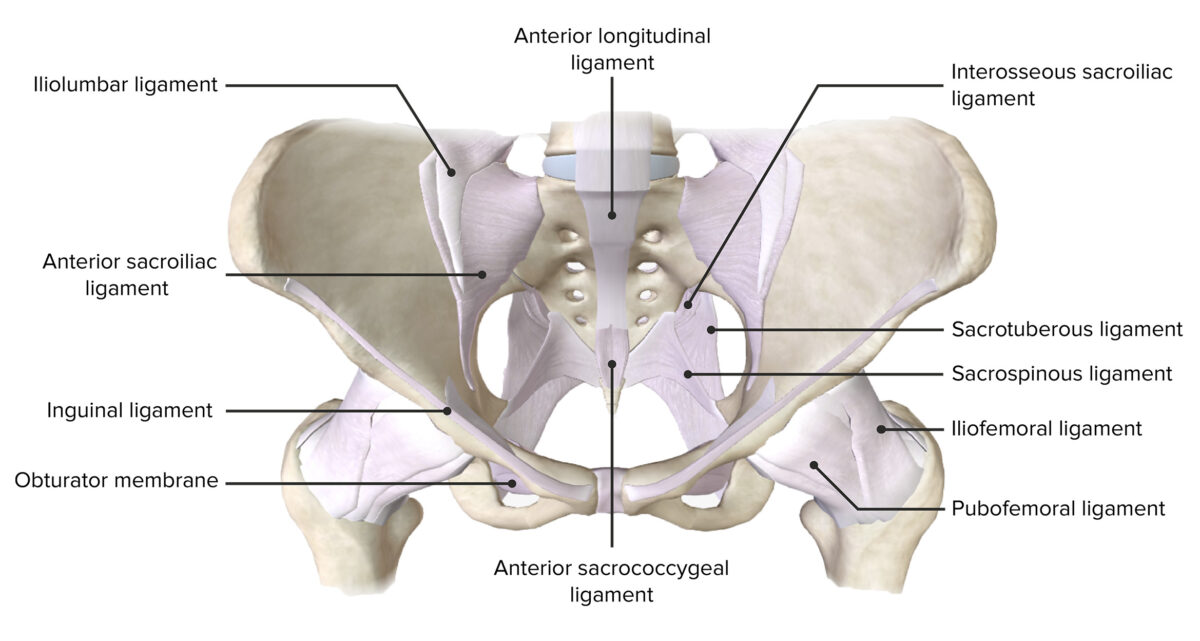
Structure of the Bony Pelvis Bones The pelvis is a ring-like structure that surrounds and protects the pelvic cavity. The pelvis is composed of the following bones: Joints There are 4 primary joints within the pelvis: Ligaments The bony pelvis is primarily stabilized by the following ligaments: Pelvic Cavity The pelvic cavity is bound by […]
Anterior Abdominal Wall: Anatomy
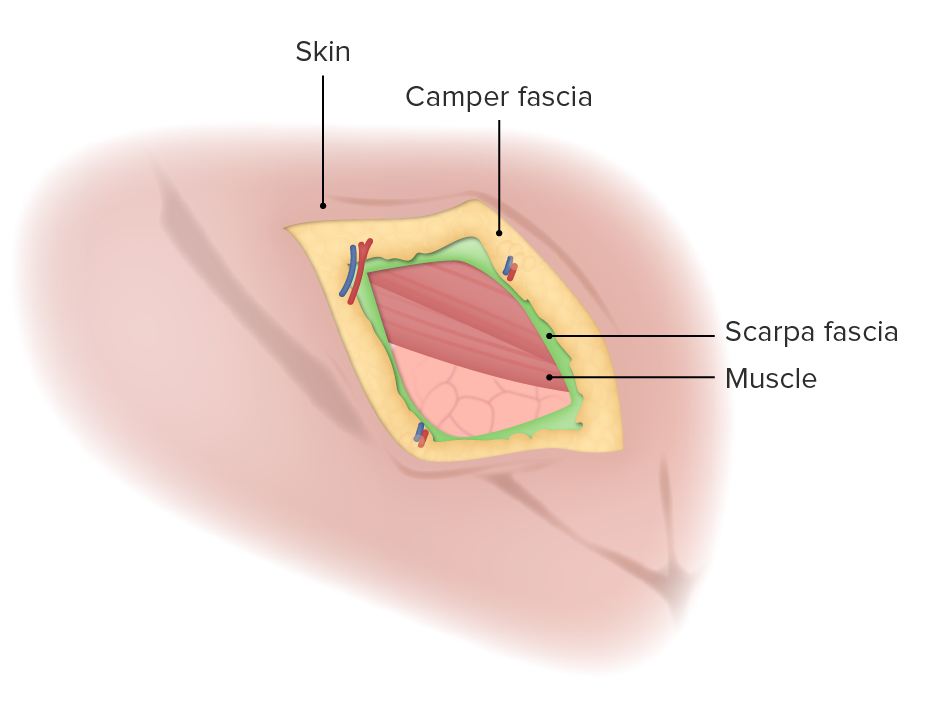
Introduction Surface landmarks Abdominal planes The abdomen can be divided into 4 quadrants with the transverse and sagittal planes. The abdomen can also be divided into 9 regions using the following planes: Abdominal Wall Muscles Layers of the abdominal wall The layers of the anterior abdominal wall from superficial to deep are: Lateral abdominal muscles […]
Urinary Tract: Anatomy
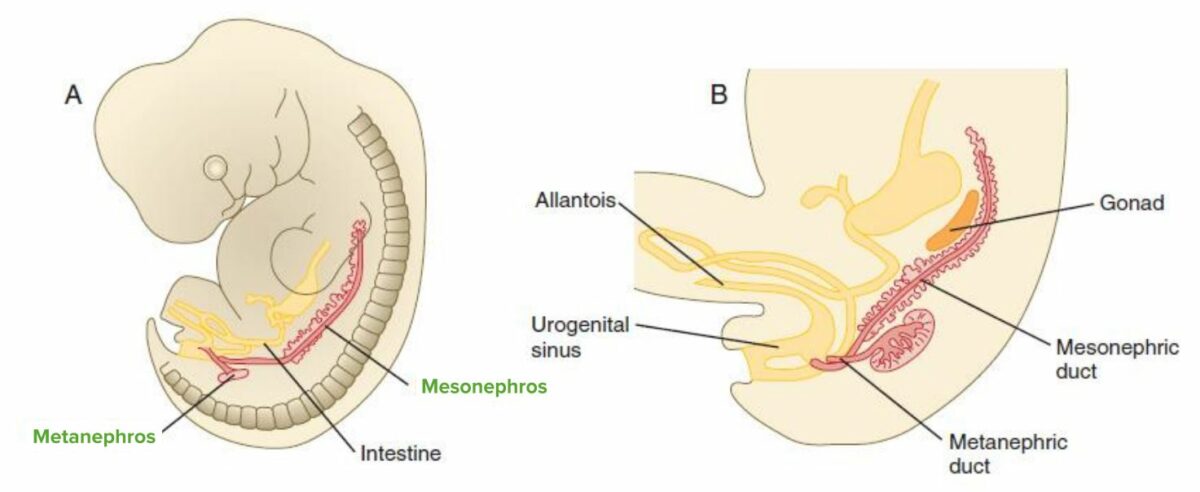
Embryology Kidneys and ureters Kidneys go through 3 embryologic stages: Bladder and urethra Ureters Anatomy Description: Function: The function of the ureters is to transport urine from the renal pelvis to the urinary bladder. Route of ureters: 3 sites of narrowing: Vasculature and lymphatic drainage: Innervation: Histology Ureteral wall structure from the lumen toward the […]
Salivary Glands: Anatomy
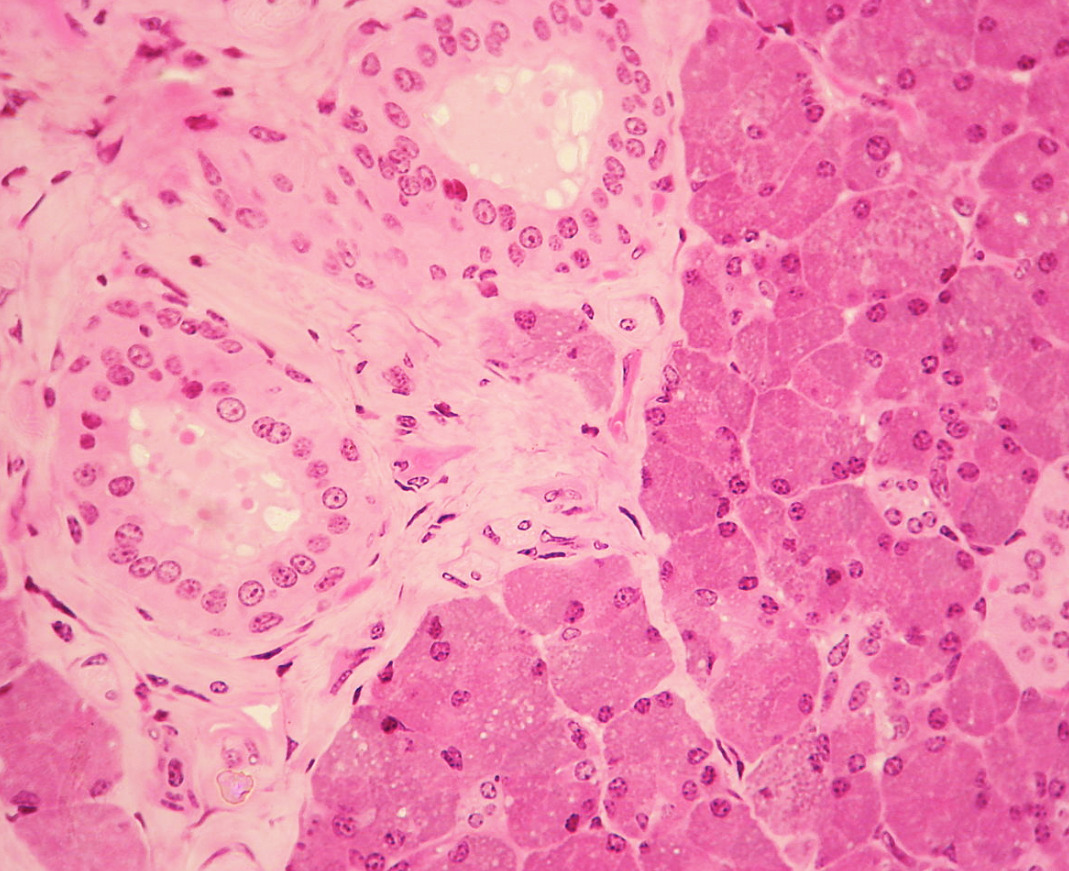
Introduction The 3 pairs of major salivary glands are the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. Embryonic development The parotid gland arises in weeks 5–6 from the ectoderm. The submandibular gland arises in weeks 6–7 from the endoderm. The sublingual gland arises in weeks 7–8 from the endoderm. Intraoral minor salivary glands develop during the 3rd […]