What is an ischemic stroke?
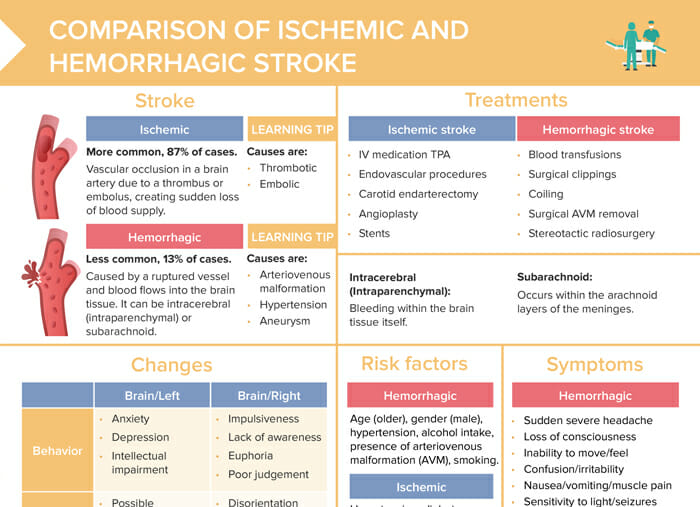
An ischemic stroke is a vascular occlusion in a brain artery due to a thrombus or embolus, creating sudden loss of blood supply. Ischemic strokes are the more common type with about 87% of stroke cases being ischemic strokes.
Click here for a written step-by-step walkthrough of a stroke-related NCLEX practice question ➜
What is a hemorrhagic stroke?
A hemorrhagic stroke (13% of stroke cases) is caused by a ruptured vessel through which blood flows into the brain tissue. It can be intracerebral (intraparenchymal, bleeding within the brain tissue itself) or subarachnoid (within the arachnoid layers of the meninges).
Hemorrhagic stroke risk factors vs ischemic stroke risk factors and causes
What causes ischemic stroke?
Risk factors for ischemic stroke include:
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Older age
- Male gender
- Race (African American)
What is the most common cause of ischemic stroke?
The most common cause of ischemic stroke is atherosclerosis, where fatty deposits (plaques) build up on the inner walls of arteries, leading to reduced blood flow or blockages.
What type of ischemic stroke has no single determined cause?
A type of ischemic stroke that has no single determined cause is called a cryptogenic stroke. In these cases, despite thorough evaluation, the specific cause of the stroke remains unidentified.
What causes hemorrhagic stroke?
Risk factors for hemorrhagic stroke include:
- Older age
- Male gender
- Hypertension
- Alcohol intake
- Presence of arteriovenous malformation
- Smoking
Ischemic stroke symptoms vs hemorrhagic stroke symptoms
What are the symptoms of ischemic stroke?
The symptoms of ischemic strokes will have a sudden onset and include:
- Blindness/double vision
- Weakness/paralysis
- Dizziness/vertigo
- Loss of coordination
- Face drooping one sided
- Arm drifting
- Slurred speech
What are the symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke?
The symptoms of hemorrhagic strokes include:
- Sudden severe headache
- Loss of consciousness
- Inability to move/feel
- Confusion/irritability
- Nausea/vomiting/muscle pain
- Sensitivity to light/seizures
- Unequal size pupils
- Drooping eyelid/vision problems
Hemorrhagic stroke treatment vs ischemic stroke treatment
How is ischemic stroke treated?
The following are treatment measures for ischemic stroke:
- IV medication TPA
- Endovascular procedures
- Carotid endarterectomy
- Angioplasty
- Stents
How is hemorrhagic stroke treated?
The following are treatment measures for hemorrhagic stroke:
- Blood transfusions
- Surgical clippings
- Coiling
- Surgical AVM removal
- Stereotactic radiosurgery
Neuro checks for stroke diagnosis
- Asymmetric smile, drooping side of the face?
- Arm drifting down?
- Speech slurred?
- Alert and oriented x3?
- Pupils, equal, round, reactive to light, and accommodation (PERRLA)
A very common tool to assess for stroke are the FAST warning signs:
- F: Face drooping
- A: Arm weakness
- S: Speech difficulty
- T: Time to call 911
Possible long-term effects of stroke
Long-term changes after a stroke can include:
- Behavior changes (anxiety/depression, intellectual impairment, impulsiveness, lack of awareness, euphoria, poor judgment)
- Memory impairment (disorientation, inability to recognize faces, possible memory deficit)
- Language difficulties (aphasia, agraphia, alexia, impaired sense of humor)
- Vision problems (reading problems, visual field impairment, loss of depth perception)
Stroke nursing diagnosis
Potential nursing diagnoses for stroke can include:
- Anxiety
- Impaired verbal communication
- Confusion (chronic)
- Constipation
- Interrupted family processes
- Ineffective coping (related to disability)
- Impaired memory
- Impaired physical mobility
- Unilateral neglect
- Self-care deficit
- Impaired social interaction