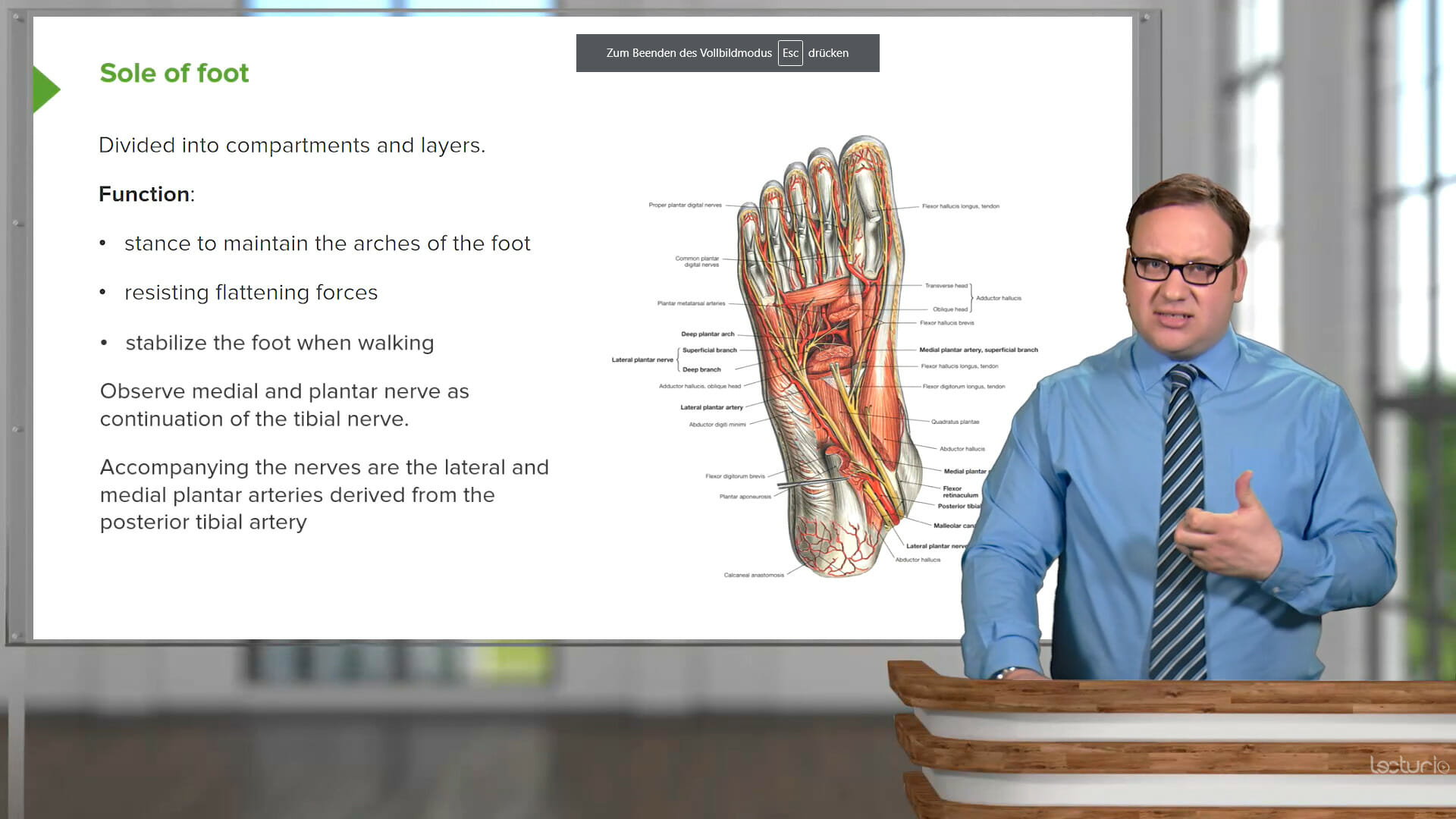
This short summary has been prepared to help students better understand the similarities and differences between these two degrees, as well as some recommendations on what to do if they wish to study abroad.
What Does MD Stand For, and What Is It?
The acronym “MD” stands for the Latin term “Medicinae Doctor,” which translates to “Doctor of Medicine” in English.
It refers to the title that students from the United States of America obtain after finishing medical school. Some countries consider the “MD” title a postgraduate doctoral degree that MBBS graduates can obtain with additional years of training.
How To Become an MD
In order for a student to graduate from medical school in the United States, they must first obtain an undergraduate degree called a “bachelor’s degree” from an American University. This title can be earned in various subjects, such as the following: Bachelor of Arts (BA), Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA), Bachelor of Music (BM), and Bachelor of Science (BS).
Most American students obtain a BS before applying to medical school. This process involves taking the MCAT examination and preparing a dedicated CV showcasing their experiences.
Upon completing medical school, students obtain their MD degree and can apply for a medical residency. It’s important to remember that, unlike other countries, the United States requires physicians to complete at least one year of residency training before practicing medicine.
Other Medical Degrees in the United States
A different type of medical degree that some American medical schools offer is MD/MPH, which provides students with both a master’s degree in public health and a medical degree.
Also, a type of medical degree unique to the United States is worth mentioning because many international students can become confused by these health professionals when they do rotations abroad: The Physician Assistant degree (PA). PAs follow a distinct career path that takes an average of 2 years and is available to students with bachelor’s degrees. As the name suggests, PAs assist physicians with patient duties such as:
- Taking histories
- Performing physical examinations
- Giving consultation in some settings
- Performing certain procedures
Finally, it’s worth highlighting that some American students obtain a degree known as “Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine” (DO) from certain medical schools in the United States. This degree has the same validity as an MD; the only difference is that DOs follow a curriculum that emphasizes a more holistic approach to medicine, including how lifestyle and environmental modification can affect health.
What Does MBBS Stand For, and What Is It??
The full form of the acronym “MBBS” is the Latin term “Medicinae Baccalaureus, Baccalaureus Chirurgiae,” which translates to “Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery.”
This degree is awarded by many European and Asian nations to medical students upon completing their training.
How to Obtain an MBSS
Unlike the American MD degree, MBBS degrees can be obtained without a prior undergraduate college “bachelor experience.” Although each country’s medical schools have their own admission criteria, most of them require students to study specific life science subjects in high schools, such as Biology and Chemistry, and achieve a certain final grade in them.
Other Differences between MBBS and the MD Degree
Another difference between American degrees and those awarded by other countries is the absence of a widely-known equivalent to osteopathic medicine in these nations.
Finally, most countries allow medical graduates with MBBS titles and no residency training to practice as primary care physicians. However, it’s worth mentioning that in some of these countries, physicians can practice outside of their professional scope due to the degree’s ambiguity. For example, medical graduates have been known to perform surgeries without a specialization degree in Surgery due to the name “Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery.”
What to Do to Train Abroad
The most important thing is to thoroughly research the specifics of each health system before making a decision to travel to another country for specialization studies. If you wish to work as a physician in the United States, it’s important to know that you need to undergo residency training in this country before obtaining a license, even if you have legally practiced medicine in your own country. It’s important to mention that you do not need to obtain an undergraduate college degree in the United States to do residency training if you already have an MBBS degree (or an equivalent title) from another country. However, you must undergo several steps to qualify for residency training and further medical practice.
Conclusions
The names and abbreviations of different medical degrees worldwide can confuse students, especially if they have only trained in their home country. However, most of them are equivalent and only have some variations regarding how they are obtained. Some degrees, such as MD/MPH do entail additional training.
Students from the United States must undergo undergraduate bachelor’s degree training before entering medical school, which must not be confused with other countries’ “Bachelor in Medicine, Bachelor in Surgery” degrees.